Seafood supply chain use case by Sarkopagus.pdf
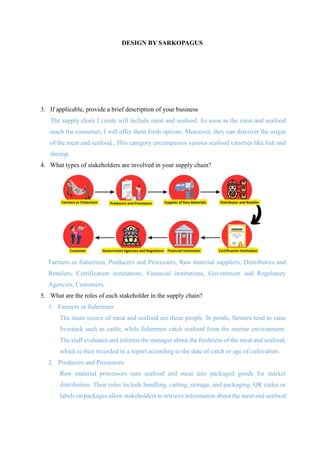
- 1. DESIGN BY SARKOPAGUS 3. If applicable, provide a brief description of your business The supply chain I create will include meat and seafood. As soon as the meat and seafood reach the consumer, I will offer them fresh options. Moreover, they can discover the origin of the meat and seafood., This category encompasses various seafood varieties like fish and shrimp. 4. What types of stakeholders are involved in your supply chain? Farmers or fishermen, Producers and Processors, Raw material suppliers, Distributors and Retailers, Certification institutions, Financial institutions, Government and Regulatory Agencies, Customers. 5. What are the roles of each stakeholder in the supply chain? 1. Farmers or fishermen The main source of meat and seafood are these people. In ponds, farmers tend to raise livestock such as cattle, while fishermen catch seafood from the marine environment. The staff evaluates and informs the manager about the freshness of the meat and seafood, which is then recorded in a report according to the date of catch or age of cultivation. 2. Producers and Processors Raw material processors turn seafood and meat into packaged goods for market distribution. Their roles include handling, cutting, storage, and packaging. QR codes or labels on packages allow stakeholders to retrieve information about the meat and seafood
- 2. contents. Managers provide important guidance for keeping meat and seafood fresh by setting proper temperature thresholds. 3. Supplier of raw materials Raw material sellers are those who sell raw resources such as beef feed, fish feed, or chemical compounds used in the preparation of meat and seafood components. They should also provide information about the main ingredients used so that stakeholders can find out about this information later. 4. Distributors and Retailers The distribution of meat and seafood requires the cooperation of distributors and retailers. Their responsibilities may include coordinating logistics for customers. Including tracking technology in transportation in this phase ensures that customers can monitor the route taken by their goods. Meat and seafood transport requires a combination of refrigeration and temperature sensors, which ensures product quality during transit. 5. Certification institutions This organization provides credentials or symbols (including organic certification for meat and seafood, sustainable accreditation, or sustainability labels). Blockchain integration of this information can facilitate verification. Consumer trust is the goal of this certification, as well as protecting against counterfeit products. 6. Financial institutions Banking organizations investing in supply chain management can leverage blockchain innovation to enable payments between parties or offer other financial administrations. Fast payment processing and an intuitive mobile application are important components of the payment system. Transactions will be more transparent with blockchain. 7. Government Agencies and Regulators It is the duty of regulatory organizations to monitor and guarantee that meat and seafood products comply with specifications by offering documents or certificates related to these items. Blockchain technology can facilitate compliance and promote data openness. 8. Customers Consumers complete the supply chain by being the final link. Blockchain technology facilitates verification of the origin and quality of products, thus increasing consumer confidence in their purchases. A lightweight application with easy navigation can simplify the process of getting information about goods consumed.
- 3. 6. Which stages are included in the supply chain process? Raw material preparation, production, distribution, storage, transportation, transaction, consumer, marketing, customer service, and product returns. 7. What types of documents and events are exchanged at each stage? 1. Event: Materials from farmers or fishermen are obtained, materials are delivered to the manager, production, packaging, time and date of storage, required temperature information, certificate of product authenticity, loading materials into the truck, the truck begins to deliver, the truck is opened, a QR code is created 2. Documents: date of receipt of material from farmer or fisherman, production time, result of material quality test, information related to material such as material type and weight, material receipt, QR code 8. Who can submit, accept, and see the document and event in each organization? People who can deliver documents or events are people sent by the company in running the supply chain. Meanwhile, the person who receives the document or event is a person who has stakeholders in the supply chain. The people who can see documents or events are people in the supply chain. 9. What are the problems typically encountered at each stage of the supply chain? Please provide at least one example problem for each stage. 1. Farmers and Fishermen Industries dealing with meat and seafood face challenges in maintaining consistent supply due to factors such as seasonal changes in yields, overfishing problems, or reduced agricultural productivity due to extreme weather events. 2. Production Inadequate processing techniques can result in subpar products.
- 4. 3. Distribution Proper storage and transportation procedures are required to maintain the freshness and superiority of meat and seafood products. Other supply chain problems such as delayed shipments, damage during transportation, or poor temperature control can lead to reduced inventories and economic losses. 4. Storage Inventory errors or poor handling in warehouses can damage products and lead to unnecessary buildup of expired stock. 5. Transportation Perishable meat and seafood items are usually subject to strict transport and licensing regulations. Faulty tracking technology on delivery vehicles can hinder accurate monitoring. 6. Marketing and Sales Unforeseen changes in market demand can result in excess inventory or stock deficit, which adversely affects business profitability. 7. Customer Service Deficiencies in product quality or customer service can trigger upset customers and damage a company's image. 8. Product Returns Spoiled or spoiled food products can result in costly returns, putting extra pressure on businesses while jeopardizing societal well-being. 9. Information Management and Coordination Certain stakeholders in the meat and seafood value chain may not have access to key details, including product origin or manufacturing techniques, complicating cooperation and threat or adverse assessment initiatives. 10. How can these problems be effectively solved using Smart Hub? 1. Farmers and Fishermen • Using a blockchain smart hub to create a decentralized network between farmers, fishermen, and suppliers. This makes it possible to communicate with each other and share real-time information about demand, supply, and production forecasts. • Implementation of a product origin tracking system with blockchain technology that is transparent and cannot be manipulated, enabling tracking and direct
- 5. control of the origin of agricultural and fishery products. This helps solve the problem of overfishing and ensures stock sustainability. 2. Production • Smart contracts will facilitate simplified and standardized production operations using automated controls. These contracts can improve the quality of the final product by strictly enforcing production steps. • Sensors connected to IoT can track product quality during production. This sensor data can be accessed through the blockchain, which ensures data transparency and accuracy. 3. Distribution • Use of the blockchain to record temperature data and other environmental conditions during product transportation. In doing so, this information is available to all parties in the supply chain, enabling early detection of problems and rapid corrective action. • Use of blockchain technology in logistics and transportation management to increase the efficiency and transparency of meat and seafood marketing.
- 6. 4. Storage • Implementing a blockchain-based inventory management system that makes it possible to track and manage inventory more accurately and efficiently. Thus, the risk of storing obsolete stock can be reduced. 5. Transportation • Use smart contracts to automate transportation and licensing requirements. This ensures compliance with all laws and regulations when transporting the product. • Implementation of blockchain-based tracking technology on transportation vehicles to ensure accurate and real-time tracking during transportation. 6. Marketing and sales • Integrate market demand data obtained via blockchain to apply more accurate analysis and better predict customer demand. • The use of blockchain facilitates direct trading between manufacturers and retailers, reducing excess and shortage of stock. 7. User service • Implement blockchain-based customer feedback to collect and manage customer feedback more efficiently and transparently. • Use blockchain to record product quality and customer service history so that they can be tracked if there is a complaint or problem. 8. Product returns • Use a blockchain-based product tracking system to quickly identify and manage damaged or contaminated products that need to be returned. • Ensure all returned products are recycled or destroyed through the blockchain in a safe and efficient manner. 9. Information Management and Coordination • Implementation of a blockchain smart hub platform to ensure full visibility of meat and seafood supply chain. This allows all parties to access important information in real-time and improves collaboration and coordination in the supply chain. • Include smart contracts in the automation and management of supply chain risk management processes so they are handled proactively.
- 7. 11. What value will be generated at each stage after implementing Smart Hub in your supply chain? 1. Farmers and Fishermen Stage Collaboration between farmers, fishermen, and suppliers and real-time information allows for better demand and production anticipation, reducing excess and understocking, and increasing supply chain efficiency. 2. Production Stage - Automation of production processes through smart contracts improves product quality and ensures compliance with strict operational standards. - IoT sensors connected to the blockchain enable real-time monitoring of product quality risks during production, helping to detect problems earlier and reduce product defects. 3. Distribution Stage - Records of temperature and environmental conditions during transportation on the blockchain help identify and deal with problems that occur during distribution. - Logistics operations see improved efficiency thanks to blockchain adoption. 4. Storage Stage - A decentralized inventory tracking system powered by blockchain technology reduces losses. 5. Transport Stage - Automating agreements for freight management and permit obligations, guaranteeing legal adherence. - Vehicle tracking technology that employs blockchain ensures prompt and reliable information updates. 6. Marketing and Sales Stage - Blockchain integration enhances customer demand analysis through more accurate data. - Using blockchain can reduce excess and scarcity of stock while cutting exchange costs. 7. Stages of User Service - Leveraging blockchain enables optimized customer feedback handling. - Blockchain-based records of product quality and customer service enable precise tracing when disputes arise.
- 8. 8. Product Return Stage - A blockchain-powered product monitoring system enables rapid detection and management of compromised or tainted items, guaranteeing secure and seamless product handling. 9. Information Management and Coordination Stage - The smart blockchain platform offers unparalleled supply chain visibility, facilitating swift communication and amplifying collaborative efforts throughout the supply chain. - Supply chain risk management processes are actively overseen through smart contracts. On the whole, the Smart Hub will enhance the effectiveness, clarity, and trimming of meat and seafood ingredients, minimize squandering, perfect merchandise quality, and secure the long-term maintainability of normal asset supplies. The implementation of this will bring an overall increase worth for those invested in supply networks.