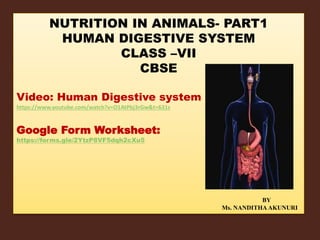
HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
- 1. NUTRITION IN ANIMALS- PART1 HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS –VII CBSE Video: Human Digestive system https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O1AtPbj3rGw&t=631s Google Form Worksheet: https://forms.gle/2YtzP8VF5dqh2cXu5 BY Ms. NANDITHAAKUNURI
- 2. Human digestive system starts from Mouth, buccal cavity, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum and anus are the parts in the human digestive system.
- 3. Mouth, salivary glands and their functions Mouth is only an opening of the digestive system. Taking in of food digestive system. Taking in of food through mouth is called ingestion. The cavity or space in the mouth is called oral cavity or buccal cavity.
- 4. Digestion starts in buccal cavity. Teeth, tongue and openings of three pairs of salivary gland are present in buccal cavity. Physical and chemical nature of the food changes when it is masticated with the help of teeth and mixed with saliva.
- 5. There are four types of teeth in man- incisors, canines, premolars and molars- each for a specific functions. The arrangement of teeth is same on the upper and lower jaws. An adult human has thirty two teeth – 8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 premolars, and 12 molars.
- 6. Tongue is muscular and pushes the food on to the teeth during mastication. Taste buds on the tongue sense the taste of food.
- 7. Three pairs of salivary glands are present in the buccal cavity. They are parotid, sub-lingual and sub-maxillary glands. Parotid glands are present near the ear. Secretion from these glands is sent into buccal cavity through ducts.
- 8. Other two pairs of glands open below the tongue through ducts. Saliva is released when food is present in buccal cavity. It is also released at the sight, smell and even thought of food. Saliva contains large amount of waste small amounts of salts and mucous.
- 9. Saliva is slightly alkaline in nature. It contains an enzymes called salivary. Amylase converts starch into dextrin and maltose sugar. As the food stays only for short time in the buccal cavity, starch is partly digested here.
- 10. Mucous present in the saliva makes the food sticky and helps its passage easy through pharynx. The food in buccal cavity undergoes mainly physical changes. Saliva is also useful as a solvent for dissolving the chemical substance present in food.
- 11. Oesophagus is a narrow tube and connects pharynx and stomach. It has both volume and involuntary muscles. These muscles are arranged circularly and longitudinally. Internally, the wall of oesophagus is lined with a mucous membrane which secretes mucous. Mucous acts as a lubricant and helps in the easy and smooth passage of food.
- 12. Swallowing means pushing food into oesophagus, is a voluntary act. Once food enters oesophagus, swallowing becomes an involuntary act. When food enters into oesophagus, the muscles present in its wall contract and relax alternately producing wave like movements. These are called peristaltic movements.
- 13. They help in pushing the food down the oesophagus into the stomach. Peristaltic movements of oesophagus are involuntary. There are no digestive enzymes in oesophagus. Oesophagus is only a passage through which food enters into stomach.
- 14. Hence, food does not undergo any change in pharynx and oesophagus. However, amylase present in the saliva continues to act on the starch present in the food. Stomach as a muscular bag it is present on the left side in the abdominal cavity, below the diaphragm. Part of the stomach into which oesophagus opens is called cardiac stomach.
- 15. Part of the stomach that opens into duodenum is called pyloric stomach. Opening of the pyloric stomach into duodenum is protected by pyloric sphincter. Muscles in the walls of the stomach are involuntary muscles. These are arranged longitudinally, diagonally and circularly. These muscles, contract in different directions. As a result food is churned in the stomach.
- 16. Stomach has three important roles: 1. It stores the food temporarily. 2. Mixing of various components in the food thoroughly – this occurs due to contraction and relaxation of muscles. 3. It brings about physical and chemical changes in the food.
- 17. Internally stomach wall is lined by mucous membrane. A number of glands called gastric glands are present in this membrane. Each gastric gland opens by a small pore into the lumen of stomach. Gastric glands secrete gastric juice and mucin.
- 18. Gastric juice is a thick, clear and straw coloured fluid. Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid and enzymes. The food gets mixed with hydrochloric acid present in the gastric juice. Hydrochloric acid kills bacteria present in food. It also destroys the structure of proteins, so that enzymes can digest them easily. Mucous membrane protects stomach wall from the action of acid present in the gastric juice.
- 19. Pepsin and lipase are the enzymes present in the gastric juice. When pepsin is secreted, it is inactive and is called as pepsinogen. Acids converts inactive pepsinogen to pepsin which is the active form of the enzyme. Pepsin breaks down proteins into peptones and proteases. Lipase converts fats into fatty acids and glycerol. In children, another enzyme called rennin is secreted into the stomach. It curdling of milk. This enzyme disappears as the child grows.
- 21. Food is retained in the stomach for two to four hours and is partially digested in the stomach. As the food is undergoing changes in stomach, the pyloric sphincter closes the opening of stomach into duodenum. The pyloric sphincter allows only small quantities of food into duodenum at a time. The food that enters the duodenum is called chyme. This is acidic and very soft.
- 22. Duodenum, pyloric sphincter, liver, gall bladder, pancreas Duodenum is ‘U’ shaped and connects stomach with ileum. Bile from the live and pancreatic juice from pancreas reach duodenum through separate ducts. The pyloric sphincter remains closed until digestion of food in the stomach is completed.
- 23. It opens and allows small amounts of acidic chime to enter into duodenum, so that entire duodenum is not filled with chyme. Pyloric sphincter closes immediately after the chyme enters duodenum and this prevents the back flow of chyme into stomach. Opening and closing of pyloric sphincter is involuntary.
- 24. Liver Liver is present on the right side of duodenum, below the diaphragm. It is brown in color there are four lobes in the liver. Cells present in the liver are called hepatocytes. Liver produce bile duct through cystic duct.
- 25. Gall bladder: Gall bladder is a pear shaped dark colored sack. Bile is stored temporarily and also concentrated – by the removal of water in the gall- bladder. Bile from the gall-bladder is sent to bile reaches duodenum through a duct called bile duct.
- 26. Bile : in human beings bile has a mixed colour of yellow and golden brown. Bile is thick and sticky fluid it has about 86% of water, bile salts and bile pigments. Sodium cholate and sodium deoxycholate are the bile salts. Bilirubin and biliverdin are the bile pigments. Bile pigments are products during the degradation of haemoglobin. Color of bile depends on the amount of bile pigments.
- 27. When the bile duct is blocked, bile gets mixed with blood and circulates in the body. Because of this, the eyes and skin become yellow. This is called jaundice.
- 28. Pancreas : Pancreas is an yellow grey gland and is present on the left side of duodenum, below the stomach. There are two parts in pancreas. One of them is called exocrine pancreas. Cells of exocrine pancreas open into ducts and secrete a juice called pancreatic juice.
- 29. Small intestine – structure and functions of enzymes. Small intestine is a tube of 6 meters length and 3cm width. The anterior part is called duodenum. The middle part is called jejunum and posterior part is called ileum. Ileum joins large intestine. The middle part of intestine is coiled.
- 30. Cells present in the intestinal wall secrete mucous and enzymes in the form of intestinal juice. This is called succusentericus. Enter kinesis, peptidase, lipase, sucrose, nucleotides, nucleosides are some of the enzymes present in the intestinal juice. Partially digested food entering the intestine mixes with the intestinal juice. Enzymes present in the intestine completely digested the partially digested food.
- 31. Absorption: Transport of the products of digestion from the intestine into blood is called absorption. Internally, intestinal wall has a number of finger like process called villi. The villi increase the surface area for absorption. Blood vessels are present in the form a network in the villi. Products of digestion are absorbed first into the villi and from there into the blood vessels and lymph vessels.
- 32. Colon The diameter of large intestine is greater than the diameter of the small intestine. Large intestine is present between small intestine and rectum. The wall of colon is made of involuntary muscles. Movement of these muscles pushes the food large intestine.
- 33. Water and minerals salts present in the chime are absorbed in the colon and soft, solid faeces is formed. Faeces consists of undigested food material, dead material, bile salts and bile pigments. By the peristaltic movements of large intestine, faeces is pushed towards rectum. It is expelled out through the anus. This happens when the sphincter muscles that guard anus expand. This activity is called defecation.
- 34. Video : Human Digestive System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O1AtPbj3rGw&t=631s Google form worksheet: Thank you By Ms.Nanditha Akunuri
