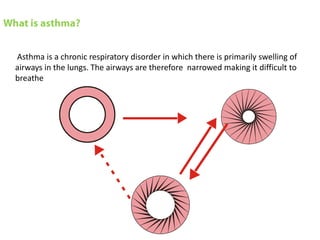
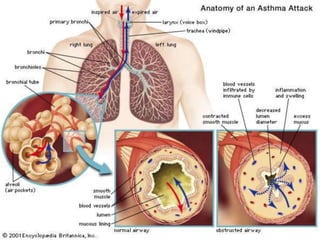
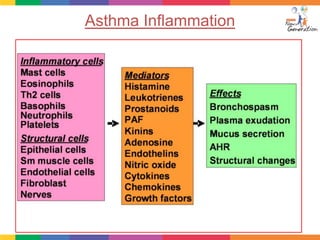
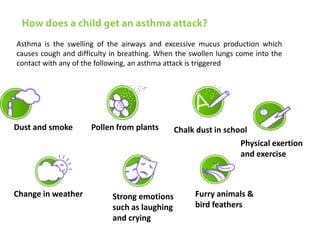
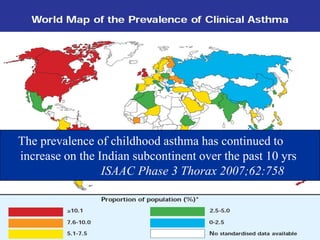
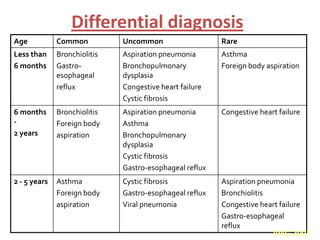
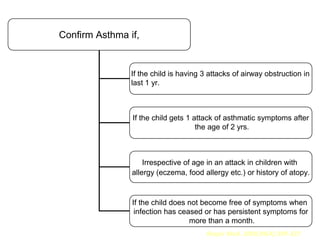
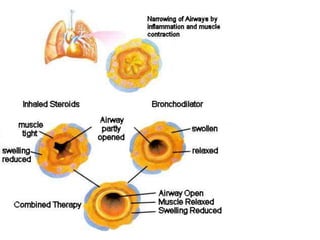
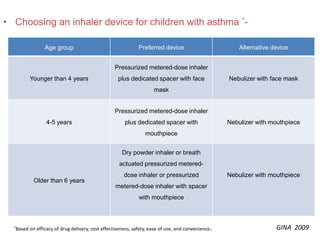
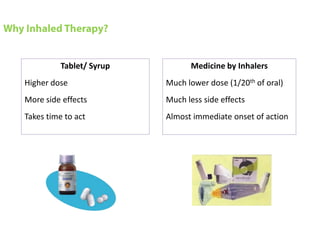
This document is a paper presentation on pediatric asthma by Mr. Namdeo Shinde of Satara College of Pharmacy in India. The presentation defines asthma, discusses its increasing prevalence in children worldwide and in India specifically, and outlines the challenges of diagnosing and treating asthma in younger children. It also covers asthma symptoms, triggers, risk factors, investigations, differential diagnosis, long-term management including medications, and concludes by emphasizing the importance of patient education.