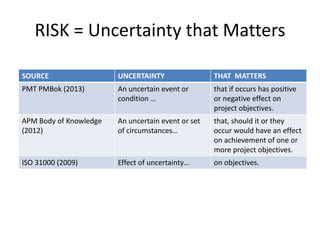
This document discusses risk management in corporate projects. It defines risk as uncertainty that matters, which can include both threats and opportunities that positively or negatively impact project objectives. Risks come in four types: event risks involving uncertain future events, variability risks where certain events have uncertain characteristics, ambiguity risks where the characteristics of certain events are unknown, and emergent risks involving unknown unknowns. The key phases of risk management are identified as risk identification, assessment, response, and monitoring/control. Response strategies should address both threats and opportunities. Managing risk is important for achieving project objectives on time and on budget while also finding potential benefits.