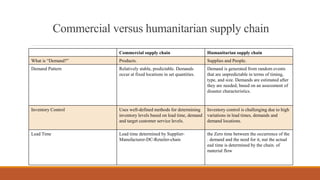
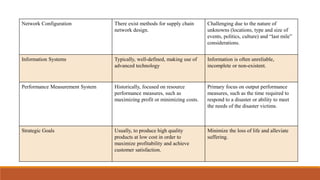
This document discusses humanitarian supply chain management. It defines a humanitarian supply chain as acquiring, storing, transporting, and distributing relief items during disasters to provide relief. Key differences between humanitarian and commercial supply chains include unpredictable demand from random events and challenges with inventory control and lead times. The document outlines elements of a humanitarian supply chain like information, inventory, and transportation. It also discusses principles, typical structures, management approaches, challenges, and the need for improved assessment, collaboration and analysis to enhance relief efforts.