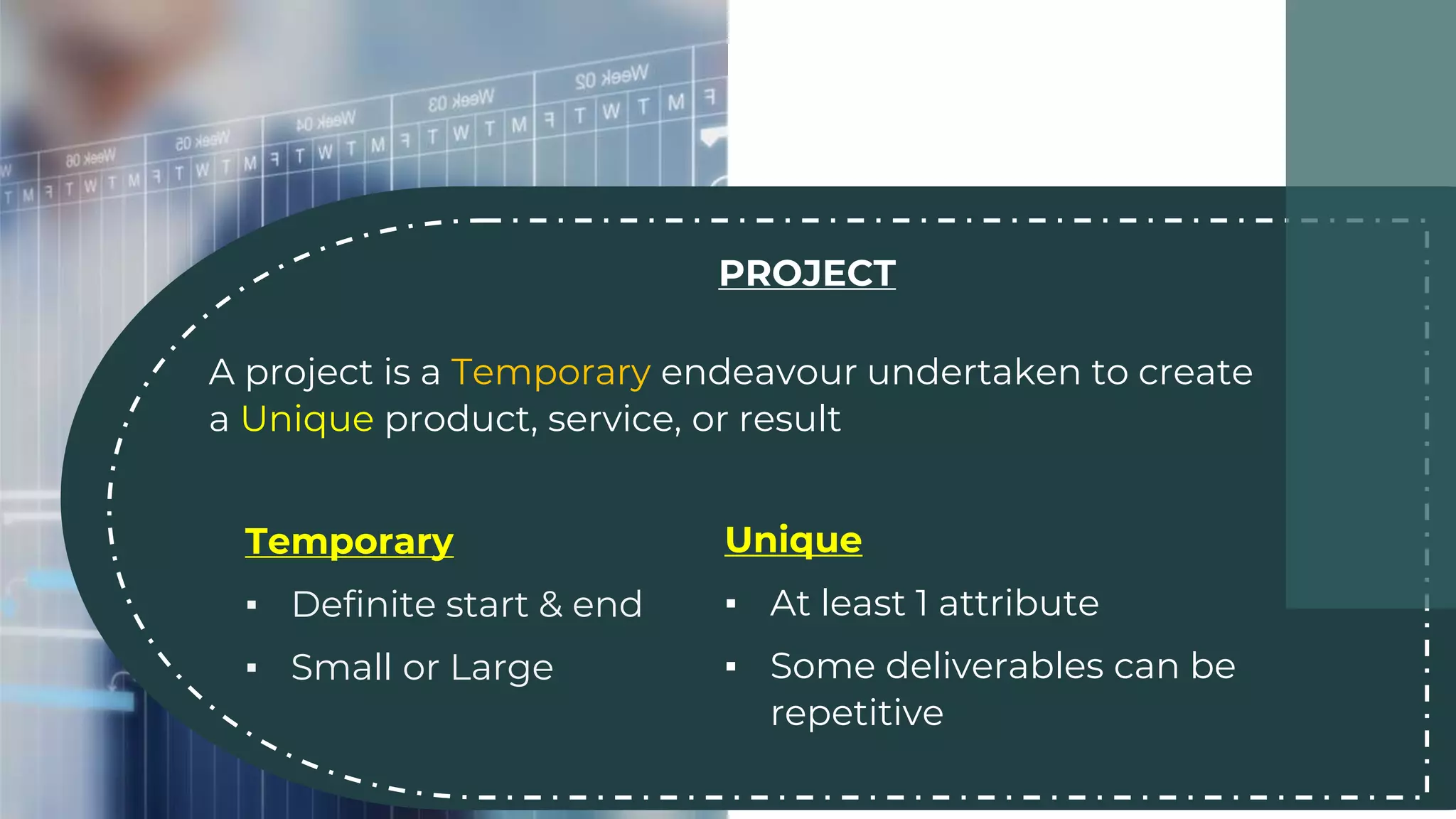
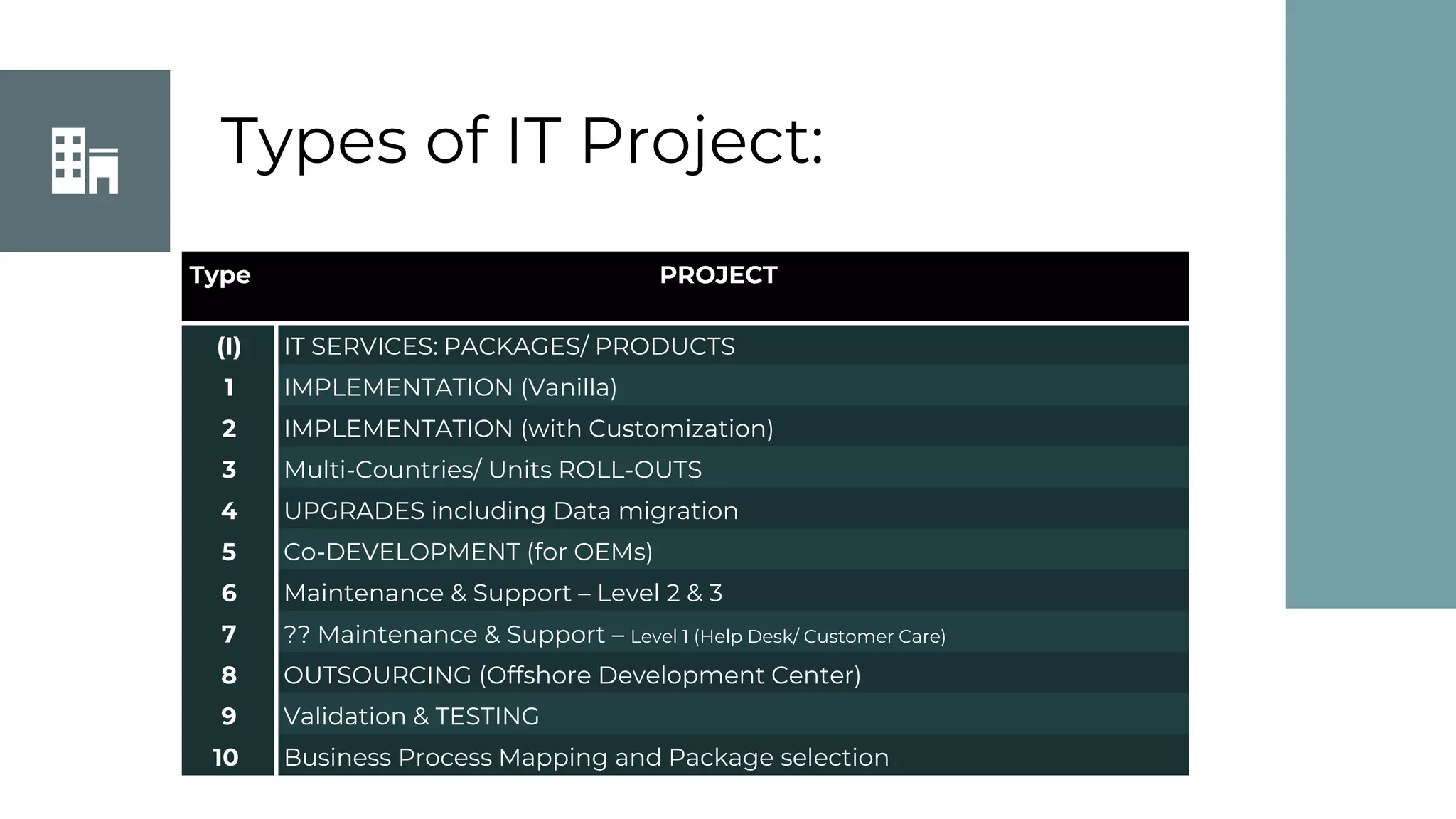
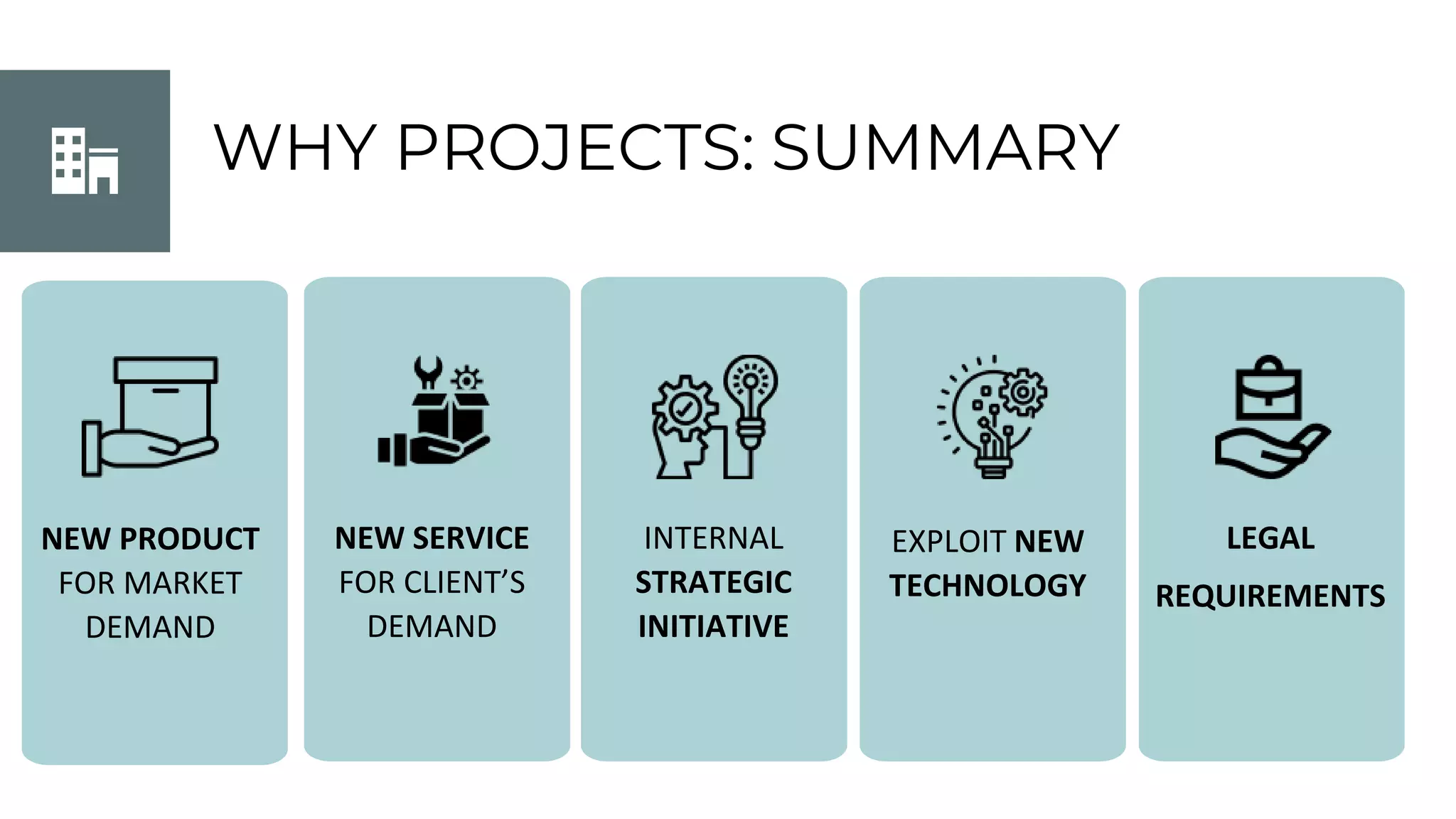
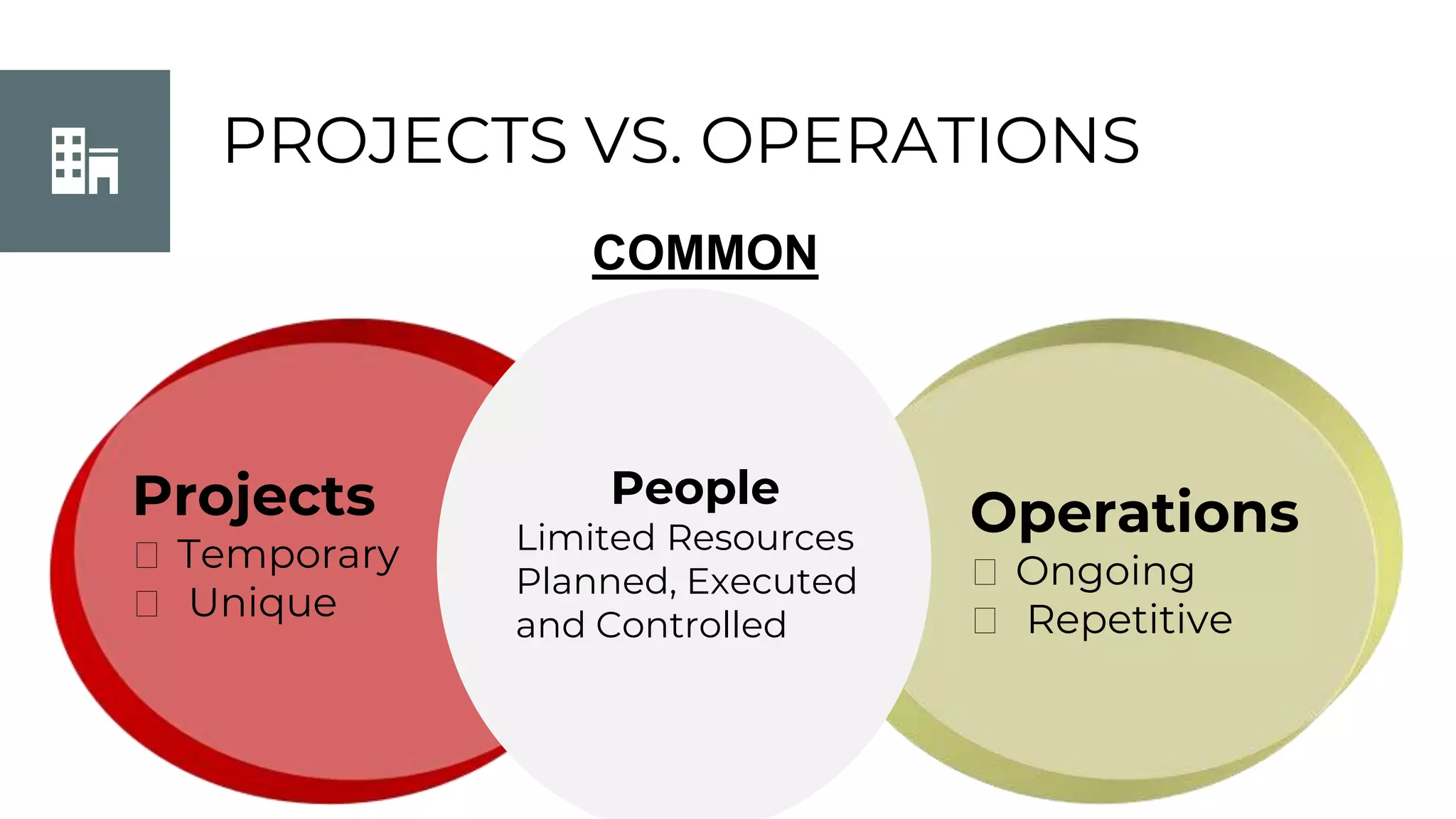
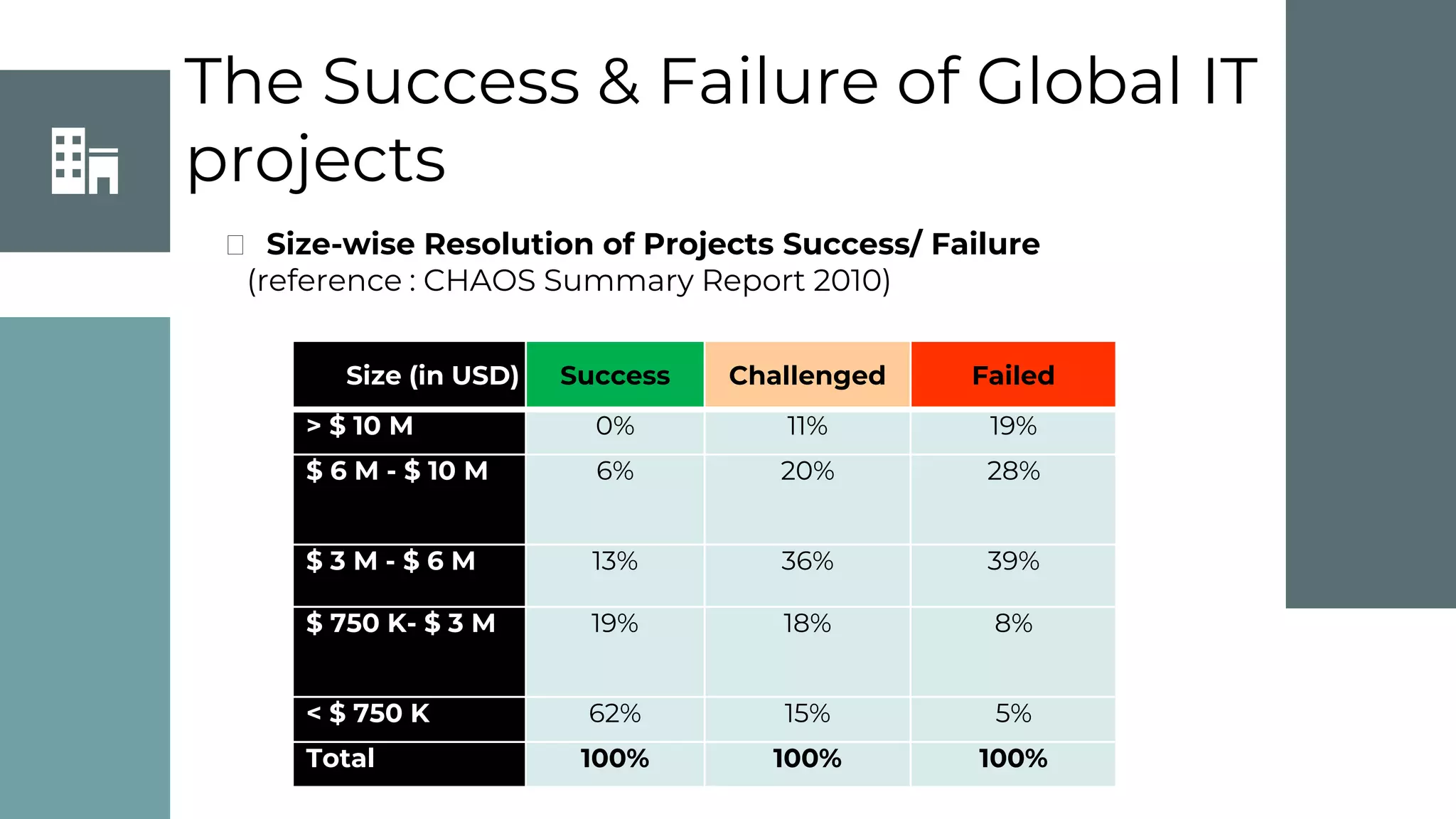
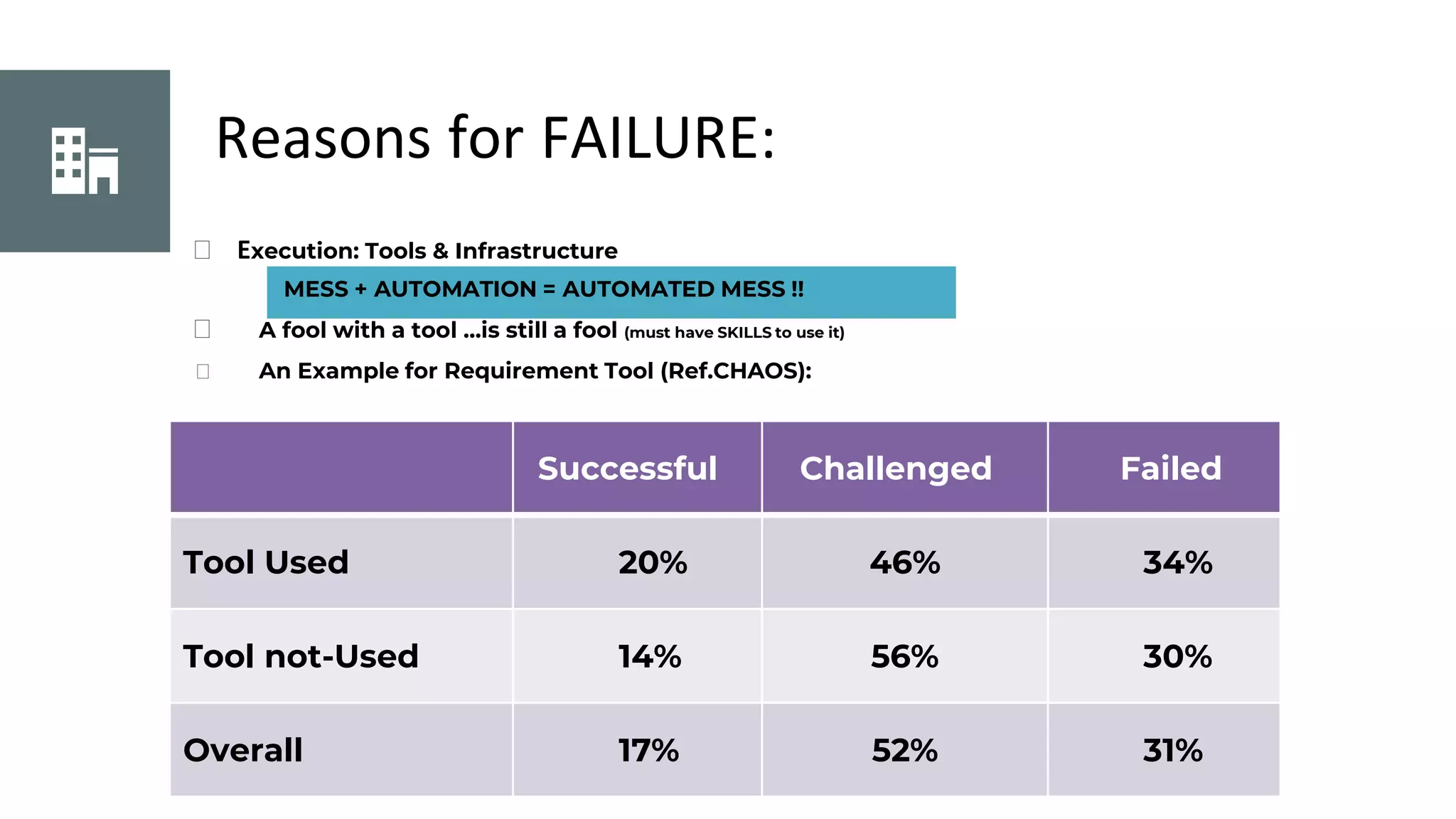
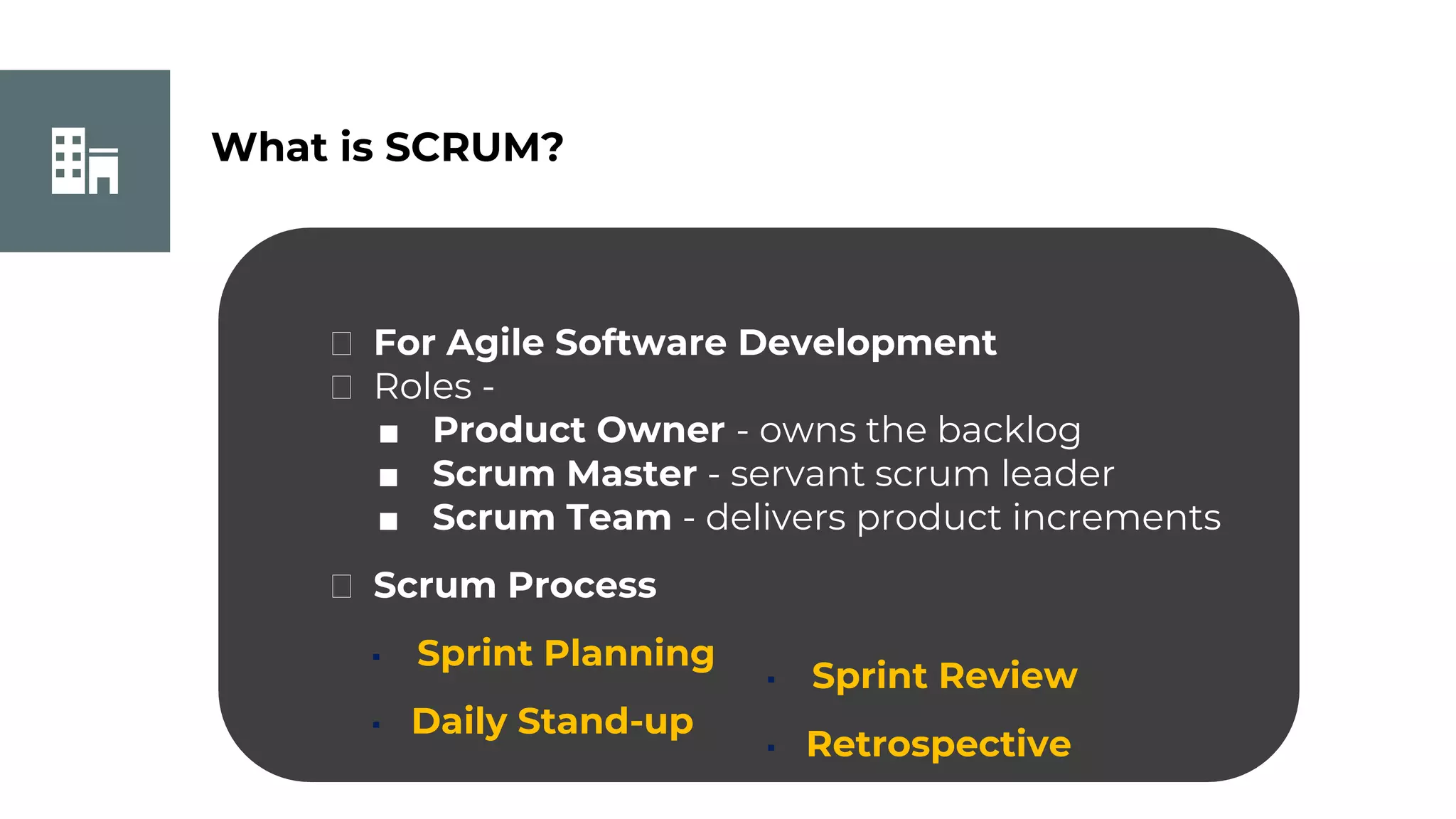
This document discusses project management basics. It defines a project as a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service or result. It outlines the 9 knowledge areas of project management: integration management, scope management, time management, cost management, quality management, human resource management, communication management, risk management, and procurement management. It discusses reasons for project success and failure, noting that lack of user involvement, poor communication and focus are common reasons for failure. The document also introduces project management standards like PMBOK and the Scrum framework for agile software development.