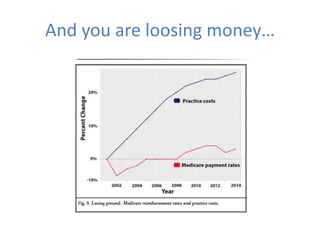
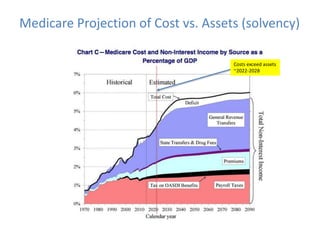
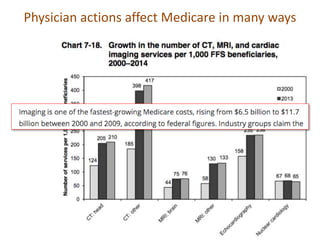
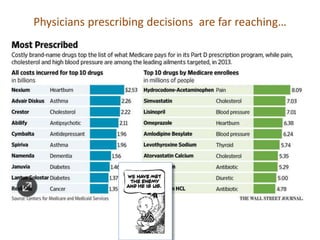
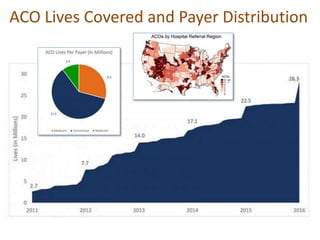
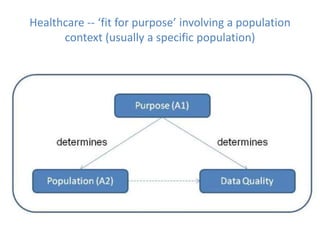
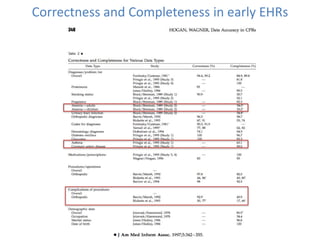
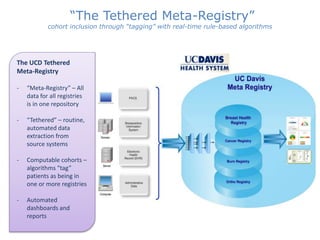
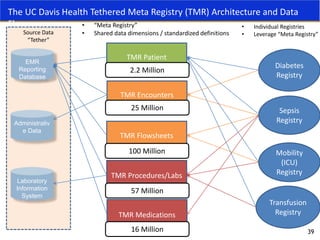
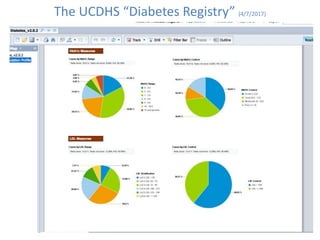
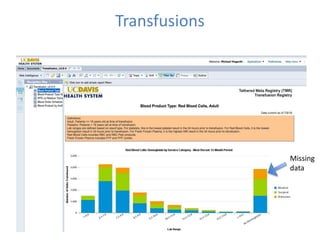
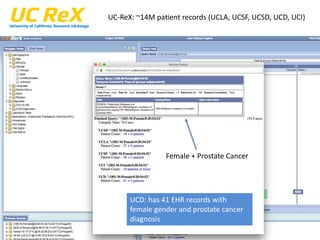
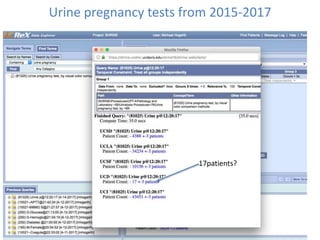
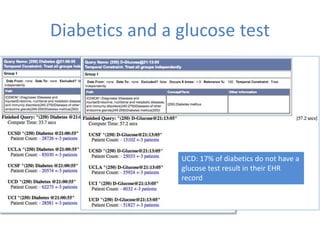
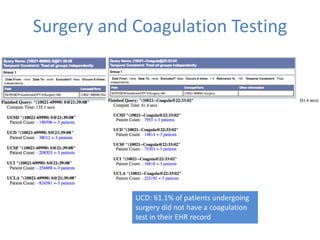
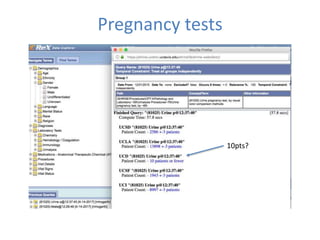
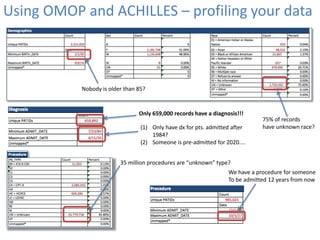
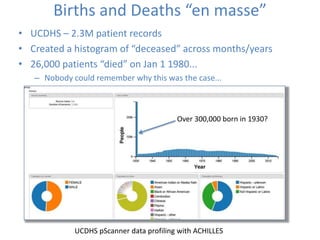
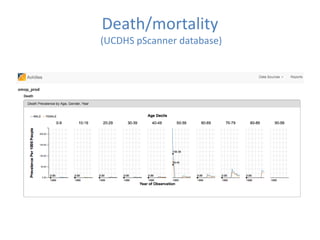
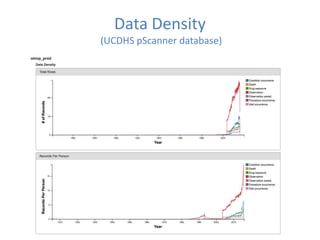
This document discusses data quality in electronic health records and its importance for Medicare programs and healthcare quality. It makes three key points:
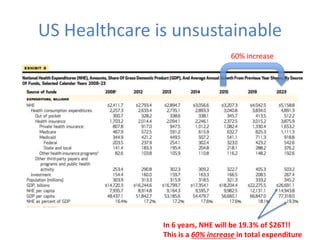
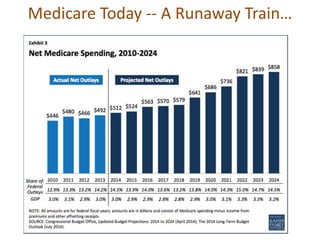
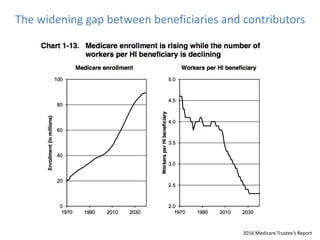
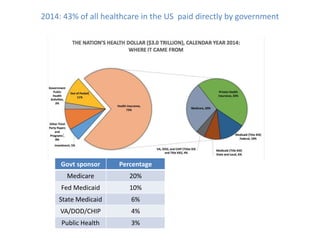
1) Medicare spending is unsustainable at current rates and data quality is important for value-based programs like MACRA that tie reimbursement to quality and cost measures.
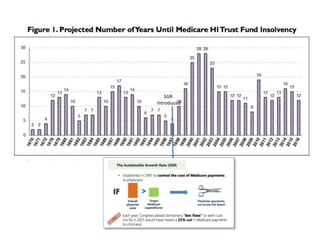
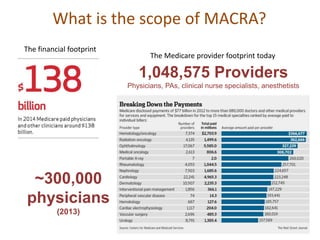
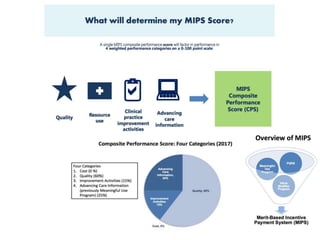
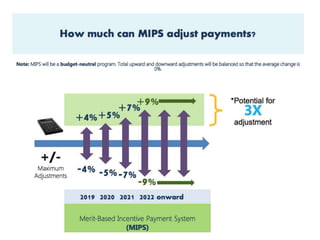
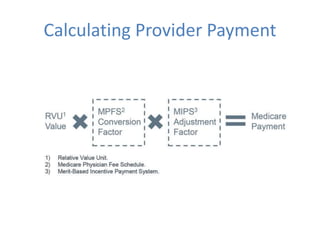
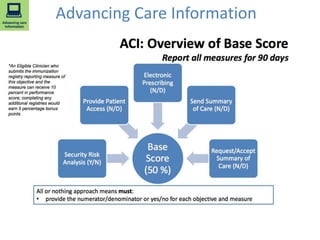
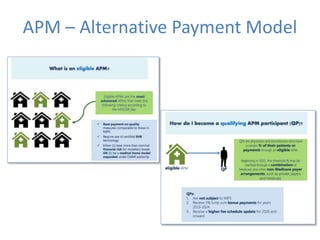
2) MACRA was introduced to replace the flawed Sustainable Growth Rate formula and moves Medicare reimbursement towards value-based payments through programs like MIPS and APMs that require accurate clinical data.
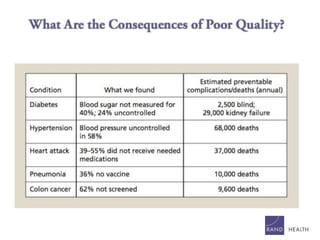
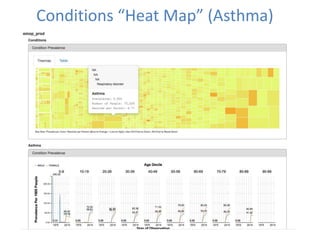
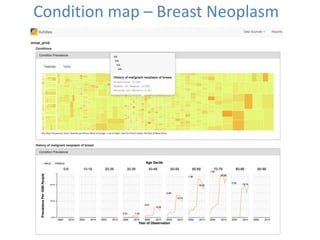
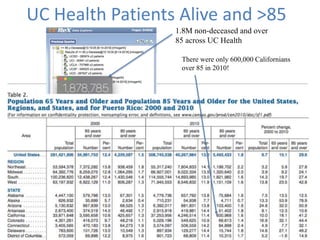
3) High quality clinical data is essential for measuring healthcare quality, costs, and outcomes required by programs like MACRA and value-based payment models. Data profiling of EHRs reveals many quality issues that can