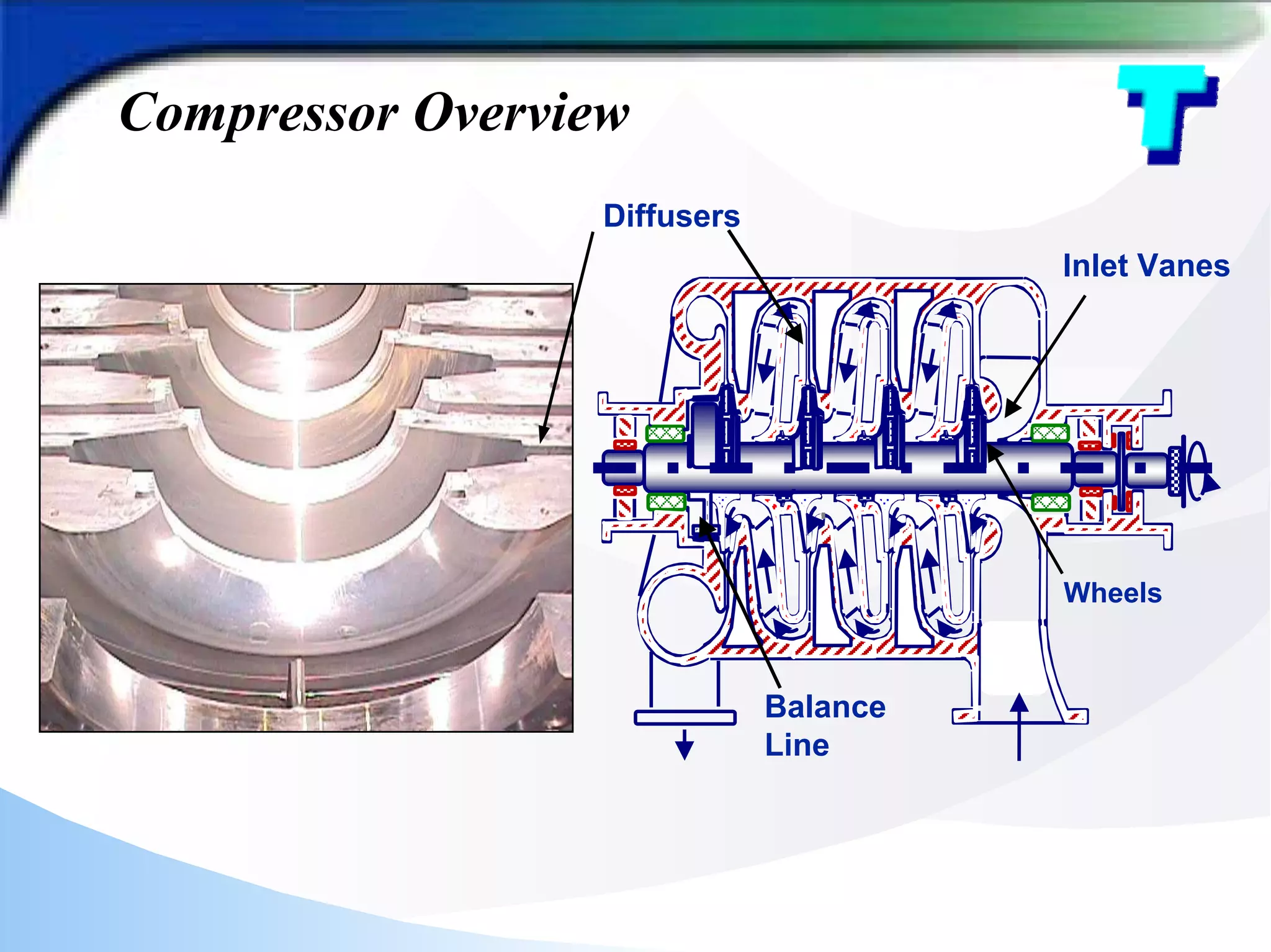
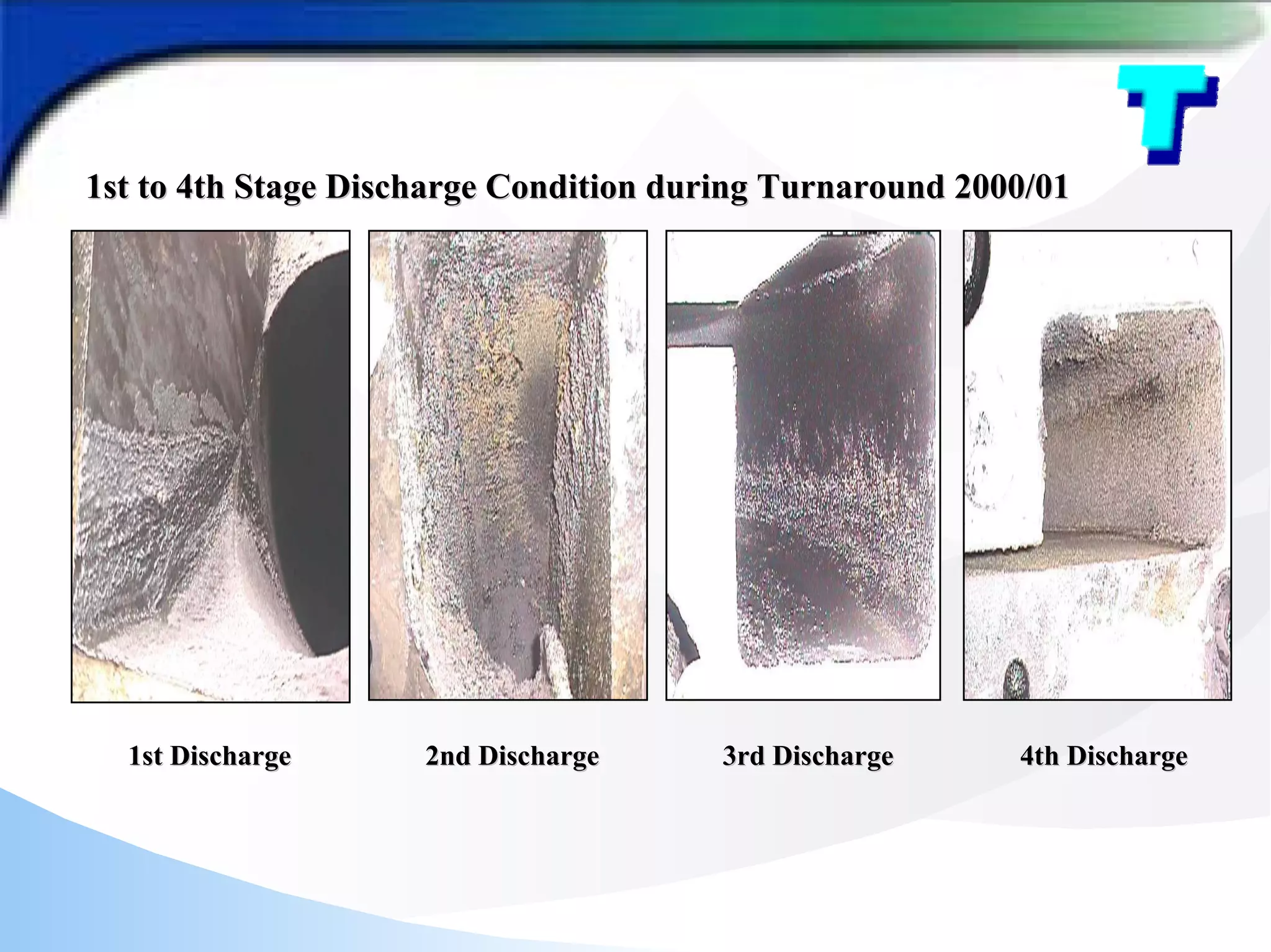
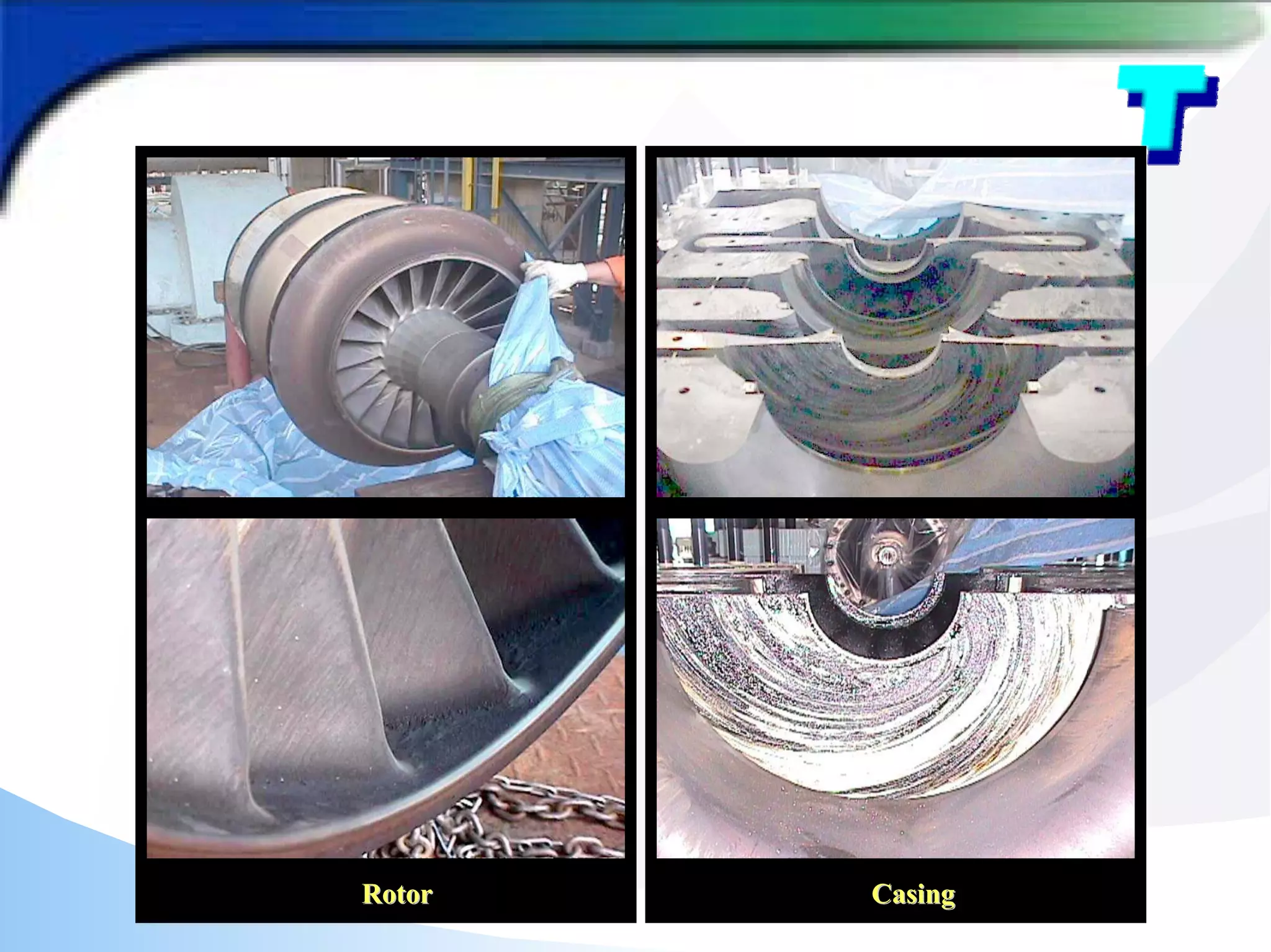
The document provides a detailed analysis of fouling in a cracked gas compressor unit, discussing equipment setup, fouling experiences, identification of turbine fouling, and countermeasures for fouling control. Key findings from turnaround inspections and trials indicate the efficacy of antifoulant injection in improving compressor efficiency and reducing polymer fouling. Future improvements are suggested, including better wash oil quality, antifoulant injection strategies, and enhanced equipment design for optimal performance.