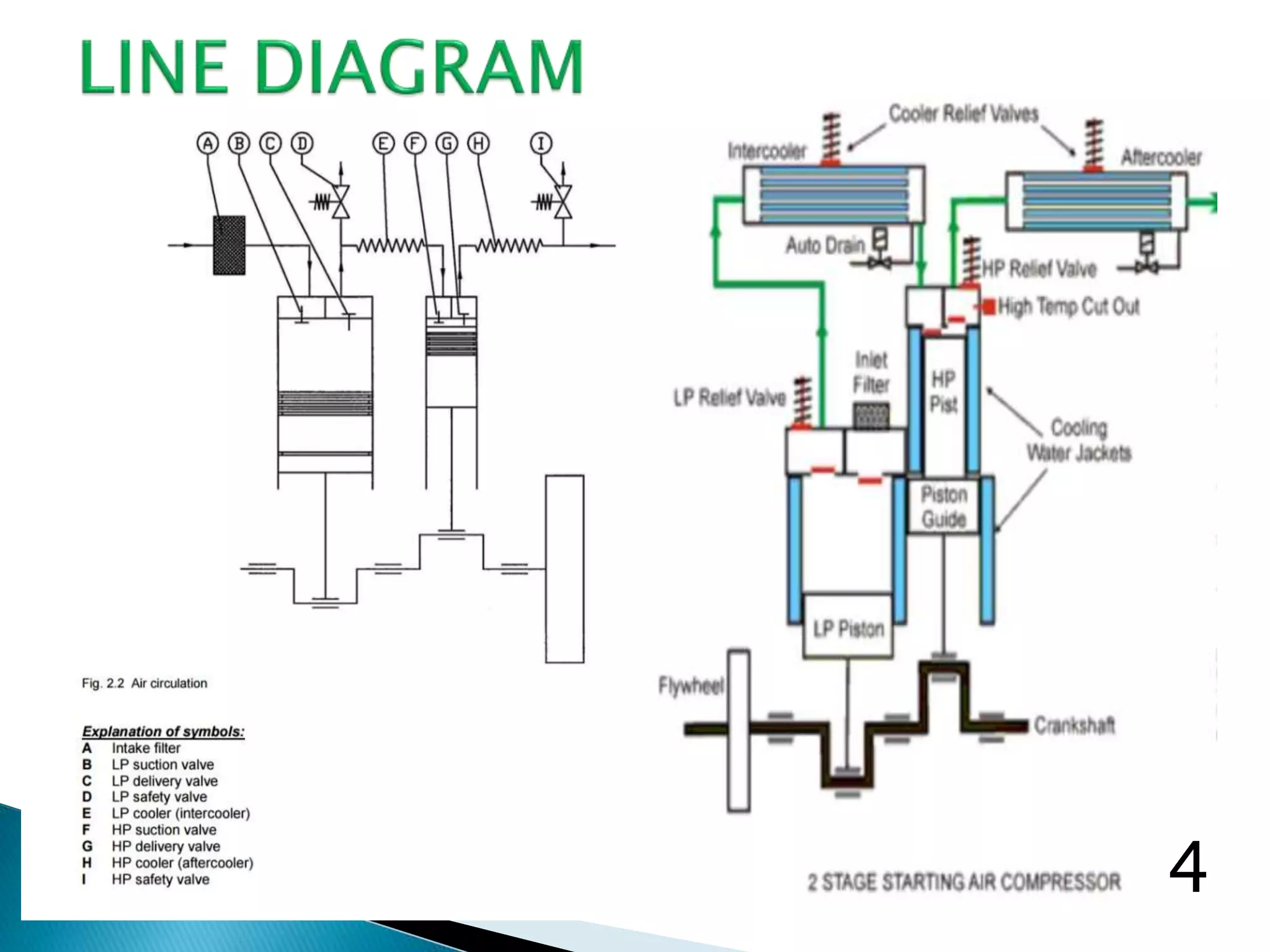
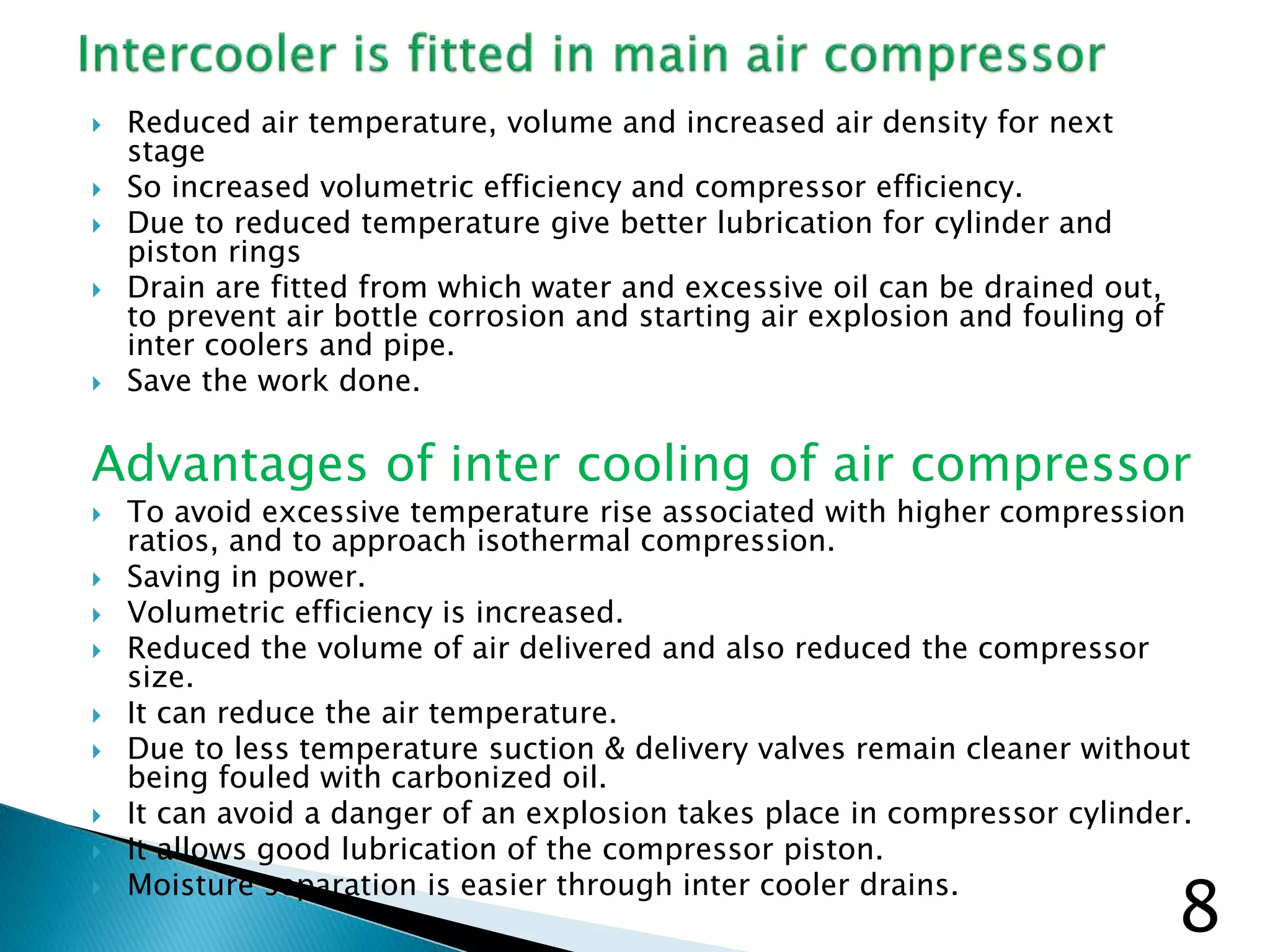
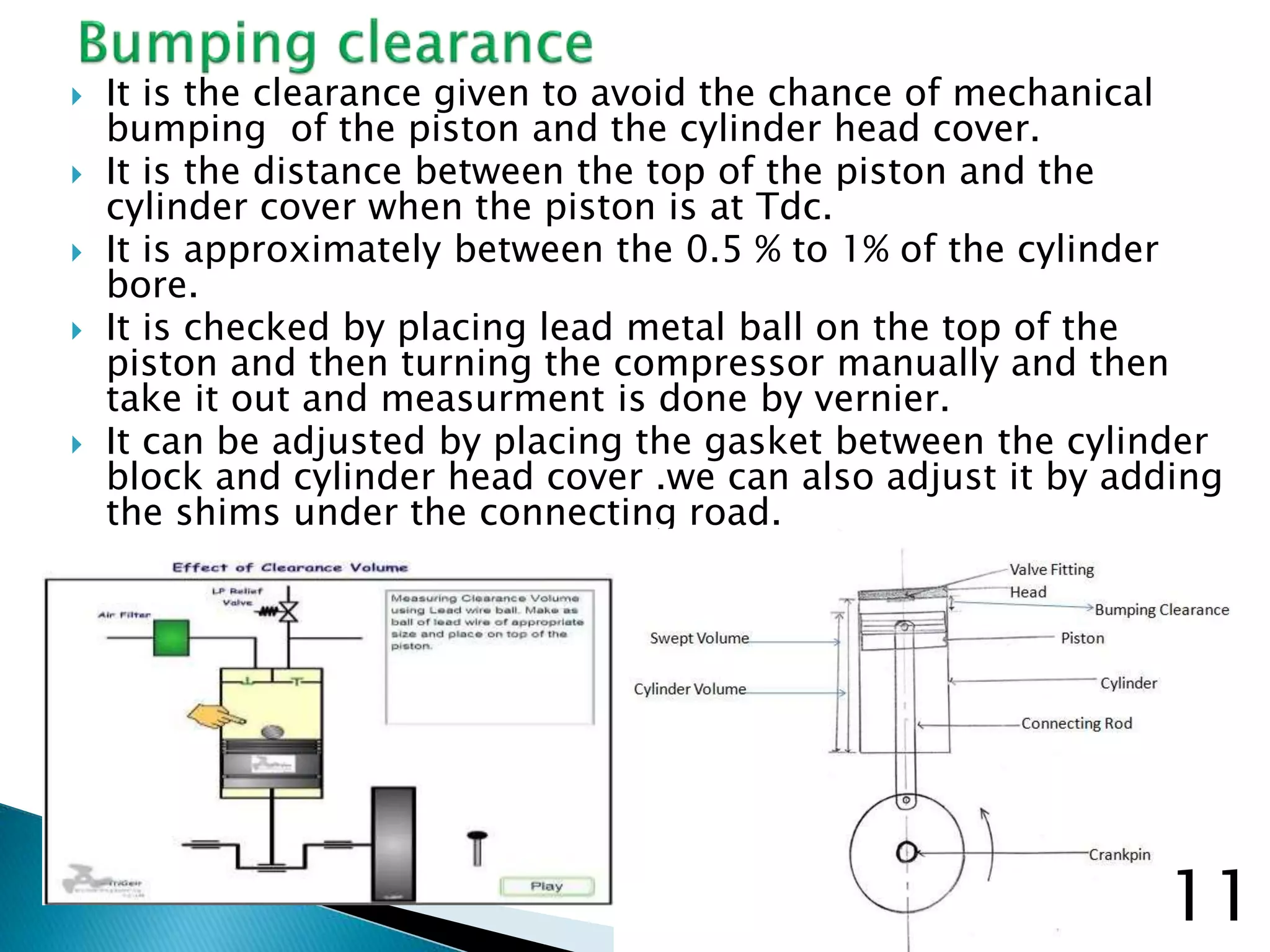
The document discusses marine air compressors used on ships. It describes the various uses of compressed air on ships, including starting main/auxiliary engines, automation/control, pneumatic tools, fog horns, and more. It provides details on compressor requirements, operating principles, intercooling benefits, maintenance procedures, and common issues like low efficiency.