Classification of igneous rocks
- 1. Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)
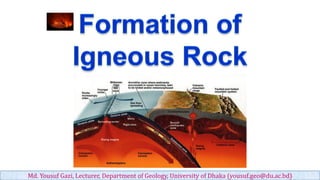
- 2. Considerable evidence indicates that most magma originates in the uppermost mantle. It is also clear that plate tectonics plays a major role in generating most magma. The greatest quantities are produced at divergent plate boundaries in association with seafloor spreading, whereas lesser amounts form at subduction zones, where oceanic lithosphere descends into the mantle. Some igneous activity occurs far from plate boundaries, indicating that not all magma is produced in these relatively narrow zones. Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd) Origin of Magma
- 3. Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd) Origin of Magma
- 4. Where do Magmas Form? ➢ Mid Oceanic Ridges at Divergent plate boundary ➢ Subduction zones at Convergence plate boundary ➢ Mantle Plume or Hot Spot Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)
- 5. Most of the magmas originate when essentially solid rock, located in the crust and upper mantle, melts. The most obvious way to generate magma from solid rock is to raise the temperature above the rock’s melting point. Keep in mind: ❑ Temperature of hottest erupting basaltic lavas between 1000°C and 1350°C. ❑ Felsic lavas are about 650-800°C. ❑ Melting point of basalt is about 1250°C ❑ Melting point of granite is about 700°C Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)
- 6. 1. Role of heat Most of the heat that contributes to the generation of magma comes from the very hot Earth’s core (where temperatures are estimated to be greater than 5,000°C). Heat is conducted toward the Earth’s surface through the mantle and crust. Heat is also brought from the lower mantle when part of the mantle flows upward, either through convection or by hot mantle plumes. Factors controlled the melting of Solid Rocks Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)
- 7. 2. Role of Pressure Melting, which is accompanied by an increase in volume, occurs at higher temperatures at depth because of greater confining pressure. Consequently, an increase in confining pressure causes an increase in the rock’s melting temperature. Conversely, reducing confining pressure lowers a rock’s melting temperature. Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)
- 8. 3. Role of Volatiles Another important factor affecting the melting temperature of rock is its water content. Water and other volatiles act as salt does to melt ice. That is, volatiles cause rock to melt at lower temperatures. Further, the effect of volatiles is magnified by increased pressure. Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)
- 9. Crystallization of Magma ➢ Formation of crystals from a melt. ➢ Liquids have lots of entropy (disorder) due to temperature → kinetic energy (movement) of atoms and molecules. ➢ Solids, especially, crystals have less entropy because of their ordered, fixed internal structures. ➢ Entropy lost as temperature is decreased. ➢ Crystallization begins when atoms, by chance, bond together to form nuclei. Other atoms will follow… Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)
- 10. ➢ Why igneous rocks are so varied in composition? ➢ On a global scale, magma composition is clearly controlled by geologic setting. But why? ➢ On a local scale, igneous bodies often show considerable variation in rock type. Why? Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)
- 11. Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd) Bowens Reaction Series
- 12. Discontinuous Reaction Series: ❑ The upper left branch of Bowen’s reaction series indicates that as a magma cools, olivine is the first mineral to crystallize. Once formed, olivine will chemically react with the remaining melt to form the mineral pyroxene. ❑ In this reaction, olivine, which is composed of individual silicon–oxygen tetrahedra, incorporates more silica into its structure, thereby linking its tetrahedra into single chain structures of the mineral pyroxene. (Note: pyroxene has a lower crystallization temperature than olivine and is more stable at lower temperatures.) Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)
- 13. ❑ As the magma body cools further, the pyroxene crystals will in turn react with the melt to generate the double- chain structure of amphibole. This reaction will continue until the last mineral in this series, biotite mica, crystallizes. ❑ This branch of Bowen’s reaction series is called a discontinuous reaction series because at each step a different silicate structure emerges. Olivine, the first mineral in the sequence, is composed of isolated tetrahedra, whereas pyroxene is composed of single chains, amphibole of double chains, and biotite of sheet structures. Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)
- 14. Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)
- 15. Continuous Reaction Series: ➢ The right branch of the reaction series is called continuous reaction series. The continuous branch contains only plagioclase feldspar. ➢ Plagioclase is a solid solution mineral in which either sodium or calcium atoms can be accommodated in its crystal structure, along with aluminum, silicon, and oxygen. Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)
- 16. ➢ The composition of plagioclase changes as magma is cooled and earlier formed crystals react with the melt. The first plagioclase crystals to form as a hot melt cools contain calcium but little or no sodium. ➢ As cooling continues, the early formed crystals grow and incorporate progressively more sodium into their crystal structures. Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)
- 17. Final Stage: ✓ Any magma left after the crystallization is completed along the two branches is richer in silicon than the original magma and also contains abundant potassium and aluminum. ✓ The potassium and aluminum combine with silicon to form potassium feldspar. (If the water pressure is high, muscovite may also form at this stage.) ✓ Finally, if the remaining melt has excess silica, the mineral quartz will form. Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)
- 18. ❖ Magmatic Differentiation ❖ Assimilation ❖ Magma Mixing ❖ Partial Melting Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)
- 19. Magmatic Differentiation: The process by which different ingredients separate from an originally homogenous mixture is differentiation. Differentiation in magmas takes place mainly through crystal settling, the downward movement of minerals that are denser (heavier) than the magma from which they crystallized. When the remaining melt solidifies—either in place or in another location if it migrates into fractures in the surrounding rocks—it will form a rock with a chemical composition much different from the parent magma. Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)
- 20. Once a magma body forms, its composition can change through the incorporation of foreign material. For example, as magma migrates upward, it may incorporate some of the surrounding host rock, a process called assimilation. This process may operate in a near-surface environment where rocks are brittle. As the magma pushes upward, stress causes numerous cracks in the overlying rock. The force of the injected magma is often sufficient to dislodge blocks of “foreign” rock and incorporate them into the magma body. In deeper environments, the magma may be hot enough to simply melt and assimilate some of the surrounding host rock, which is near its melting temperature. Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd) ❖ Assimilation
- 21. Some of our igneous rocks may be “cocktails” of different magmas. The concept is quite simple. If two magmas meet and merge within the crust, the combined magma should be compositionally intermediate. Magma Mixing: Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)
- 22. Partial Melting: Recall that the crystallization of a magma occurs over a temperature range of at least 200°C. As you might expect, melting, the reverse process, spans a similar temperature range. As rock begins to melt, those minerals with the lowest melting temperatures are the first to melt. Should melting continue, minerals with higher melting points begin to melt and the composition of the magma steadily approaches the overall composition of the rock from which it was derived. Most often, however, melting is not complete. The incomplete melting of rocks is known as partial melting, a process that produces most, if not all, magma. Md. Yousuf Gazi, Lecturer, Department of Geology, University of Dhaka (yousuf.geo@du.ac.bd)