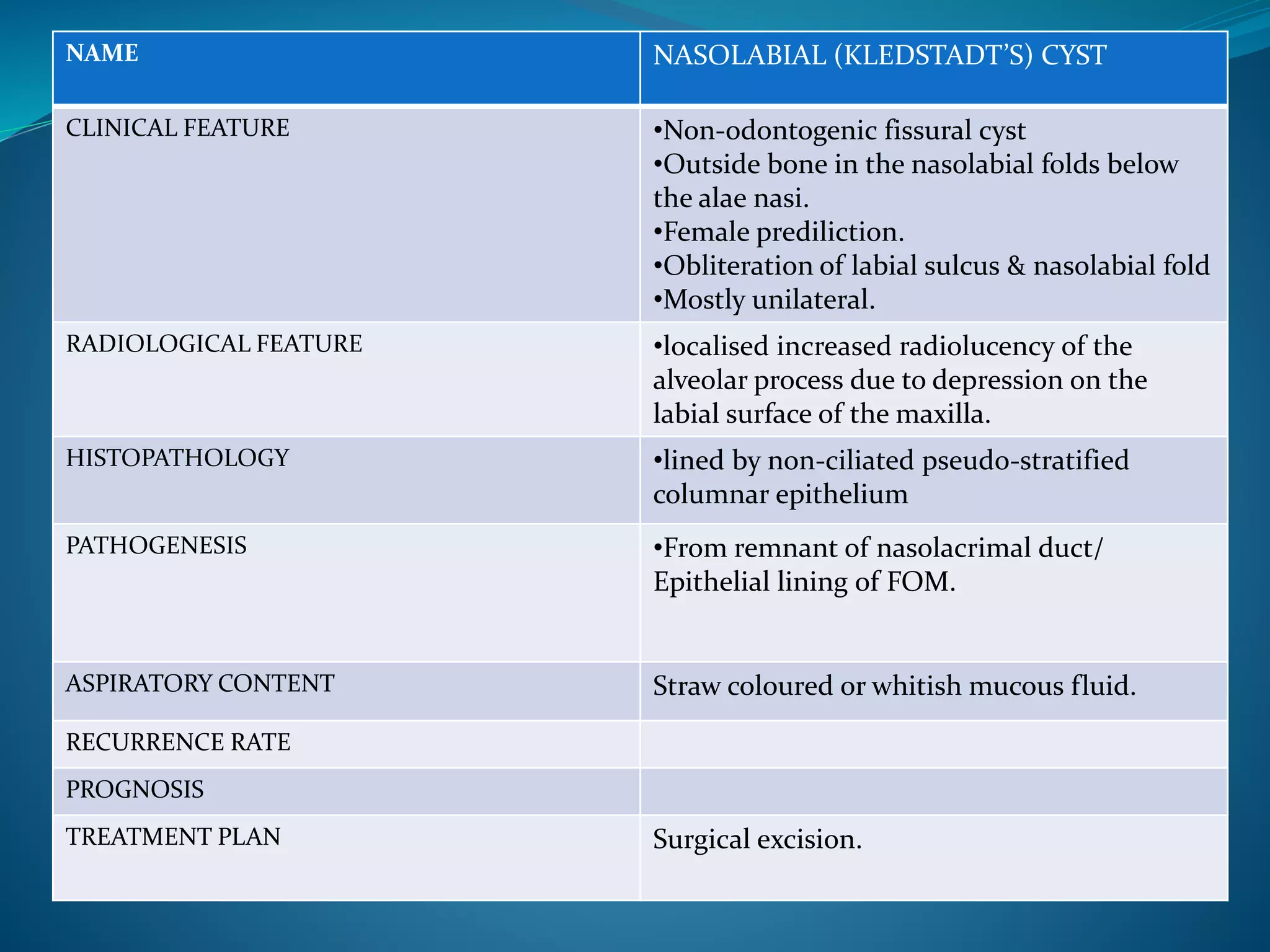
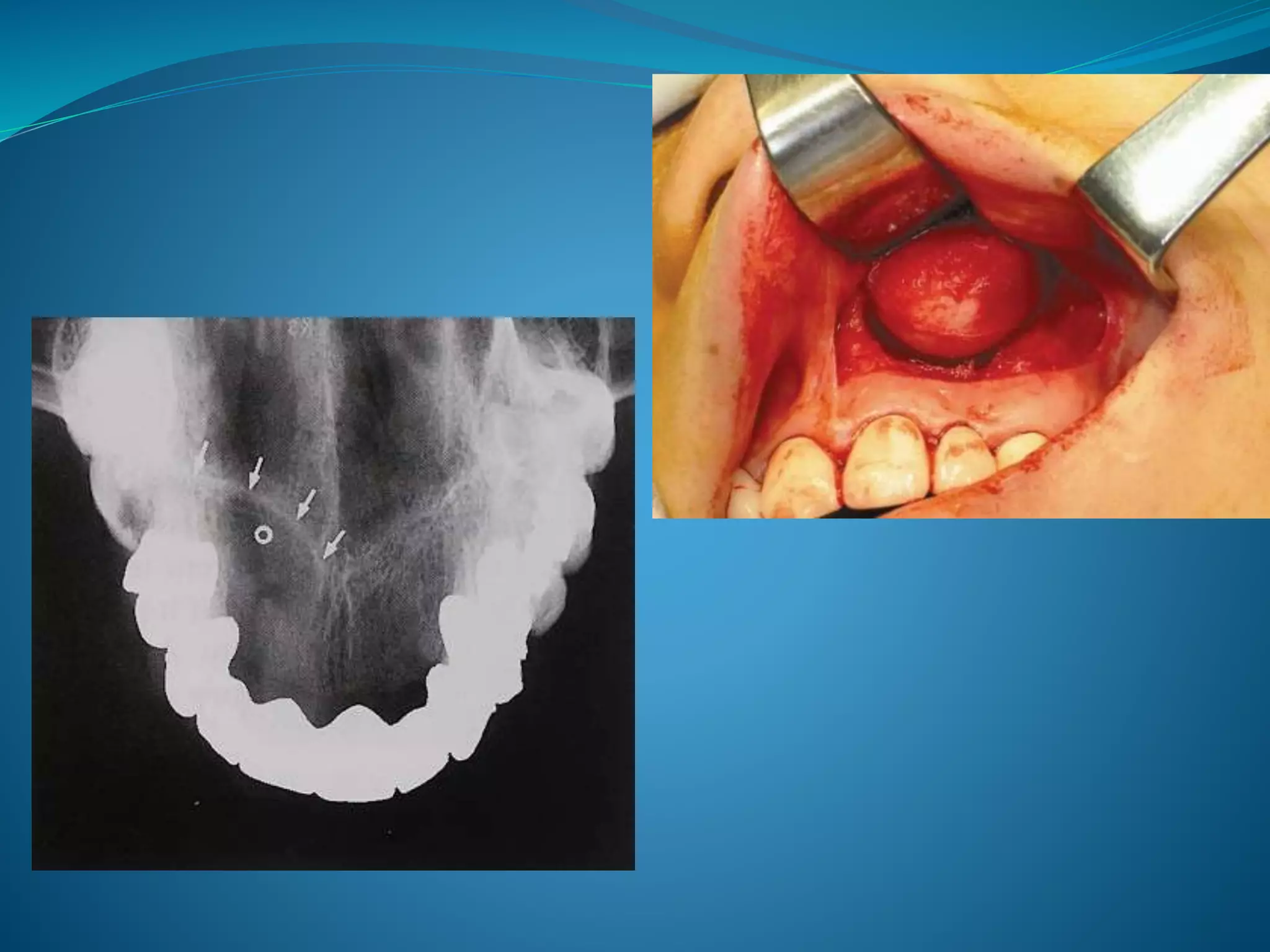
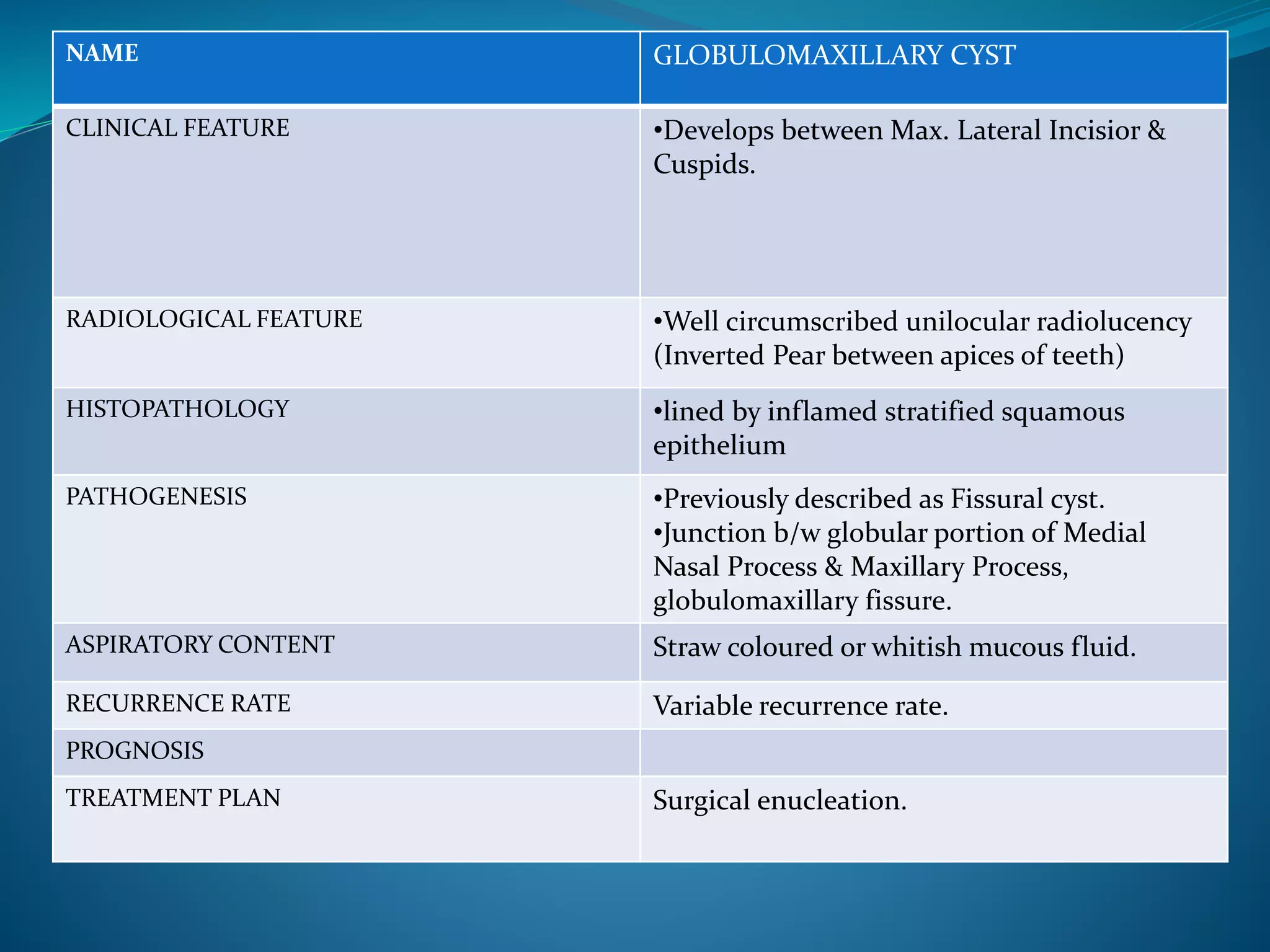
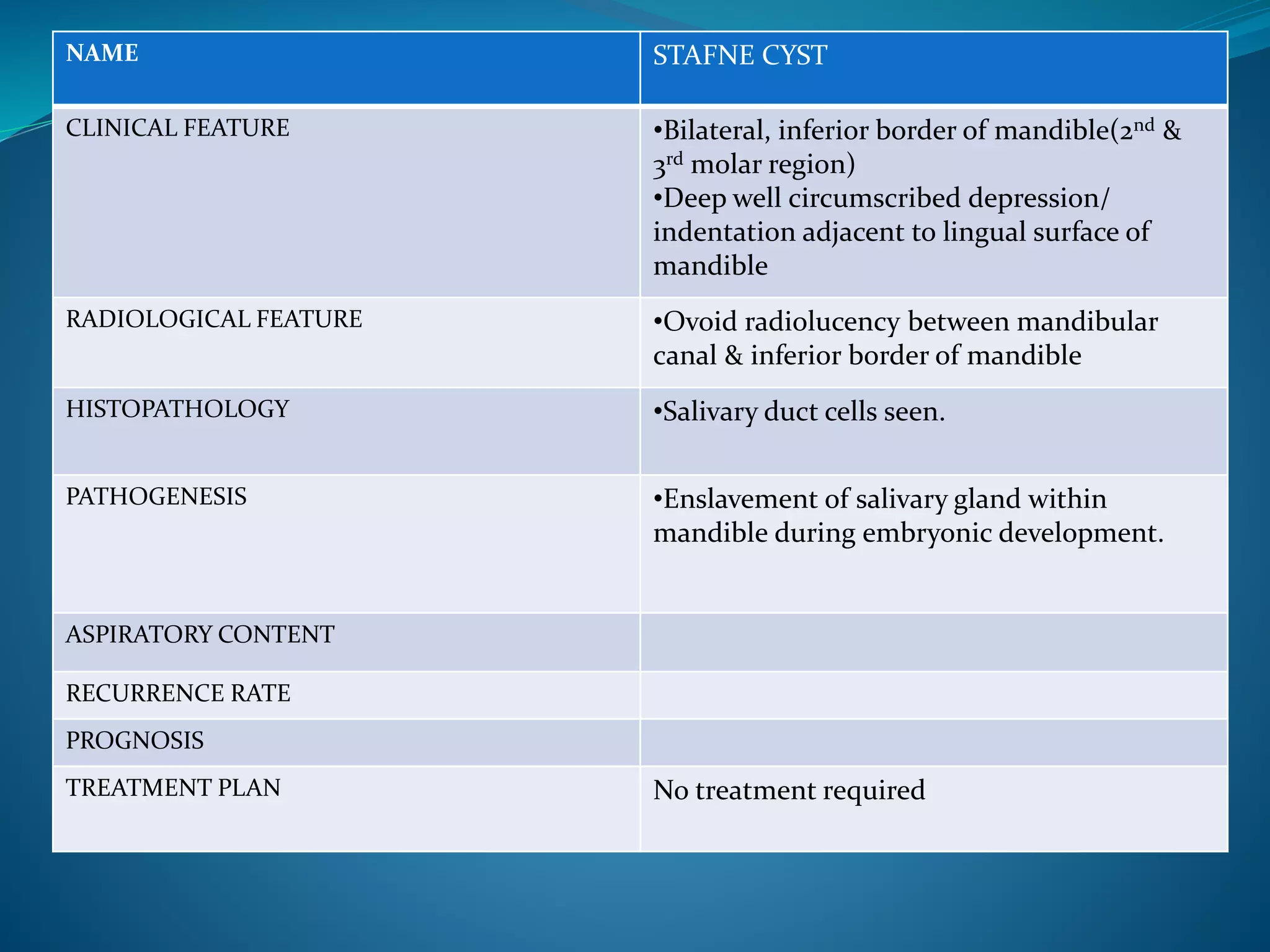
The document provides an extensive overview of cysts in the jaws, including their classifications, clinical features, radiological characteristics, histopathology, pathogenesis, management options, and recurrence rates. It covers multiple classifications such as Kruger’s, Lucas’, Gorlin’s, and WHO’s, detailing various odontogenic and non-odontogenic cyst types. Treatment approaches primarily favor surgical enucleation or marsupialization, with emphasis on the importance of accurate diagnosis and management to prevent complications.











![NAME DENTIGEROUS CYST
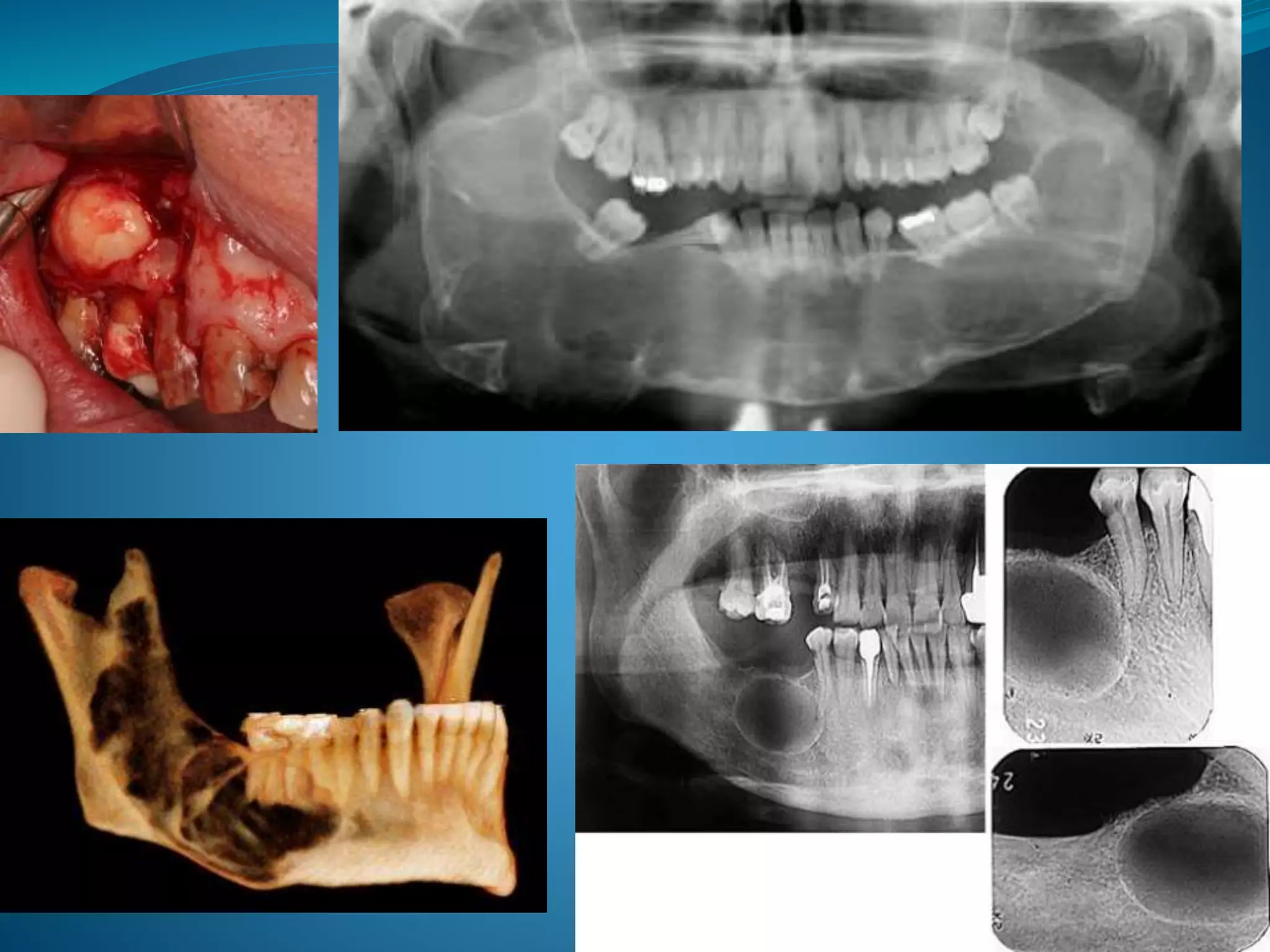
CLINICAL FEATURE •Associated with
Impacted/Embedded/Unerupted teeth.
•Most common in mandibular third molars.
•Cleidocranial Dysplasia & Maroteaux-Lamy
syndrome.
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURE •Radiolucency of at least >5 mm(enlarged
follicle). [Normal 3-4mm]
•Variations:- Central, Lateral, Circumferential.
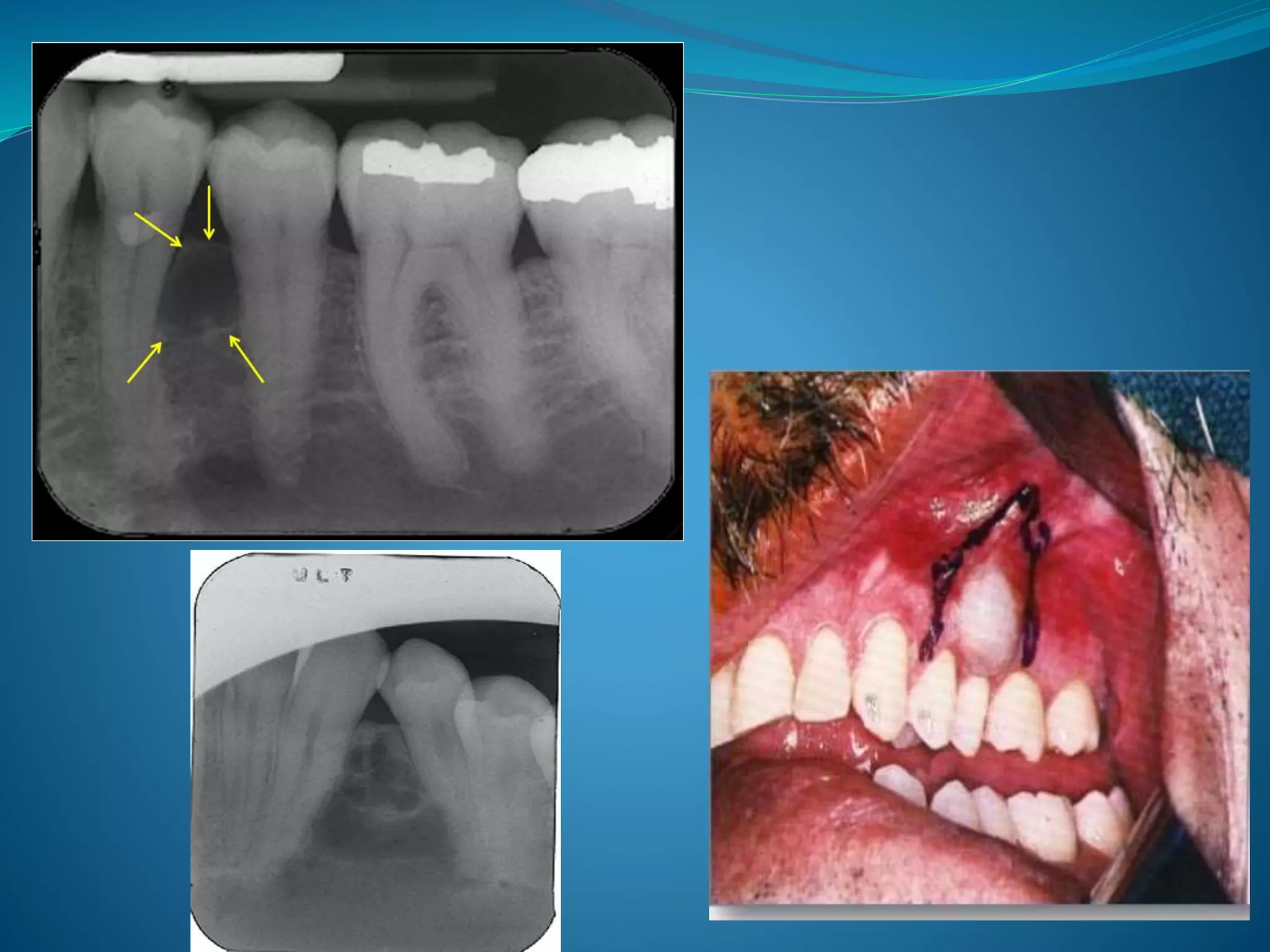
HISTOPATHOLOGY •Lining epithelium-2-4 layers
thick(flat/cuboidal) & no rete pegs
•Rushton bodies within lining epithelium.
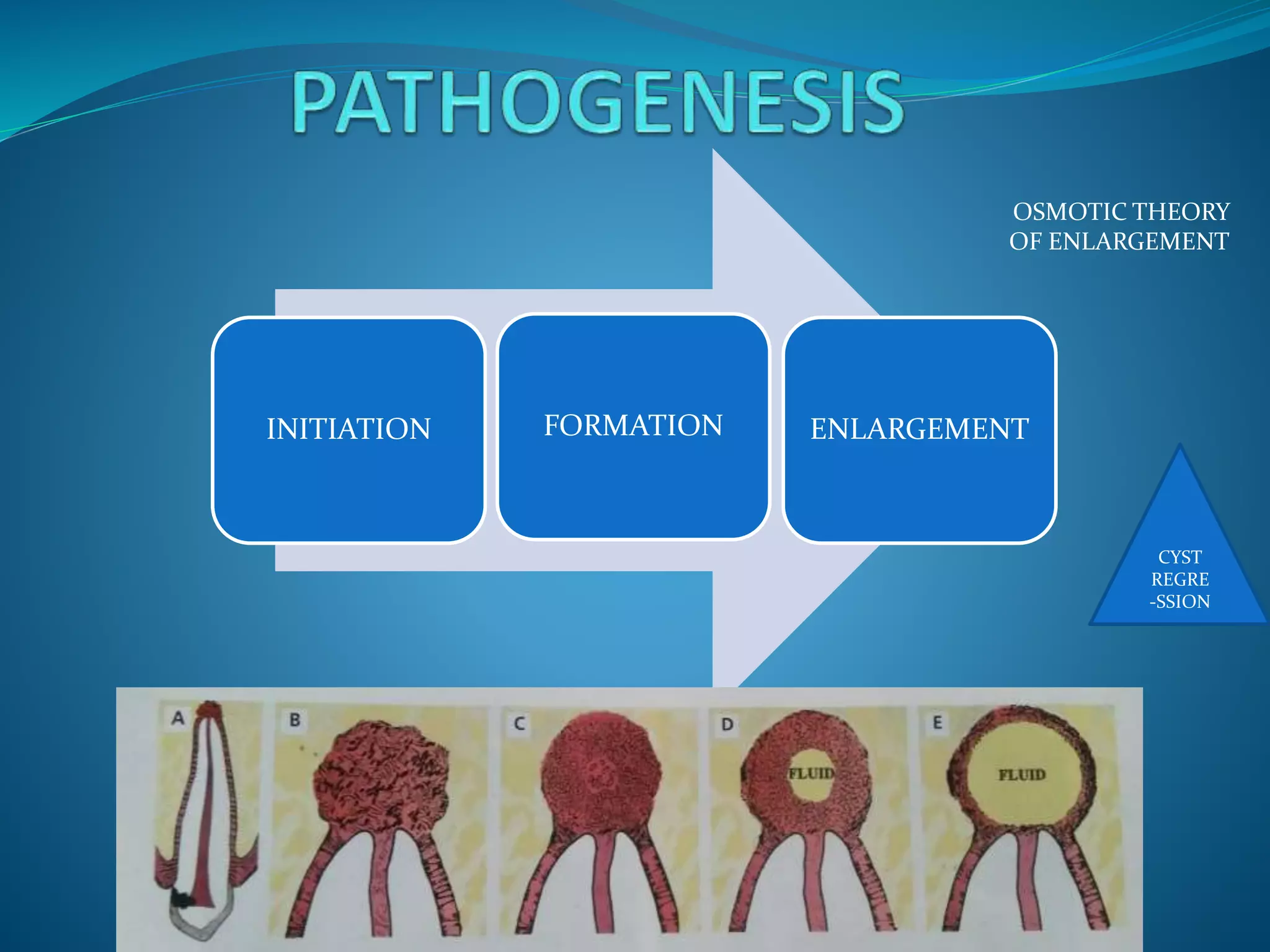
PATHOGENESIS Fluid accumulation between the REE &
enamel surface>>crown within the lumen
ASPIRATORY CONTENT Aspiration-thin watery, yellow straw-coloured
fluid.
RECURRENCE RATE uncommon
PROGNOSIS Untreated can transform into
Ameloblasrtoma or Mucoepidermoid
Carcinoma
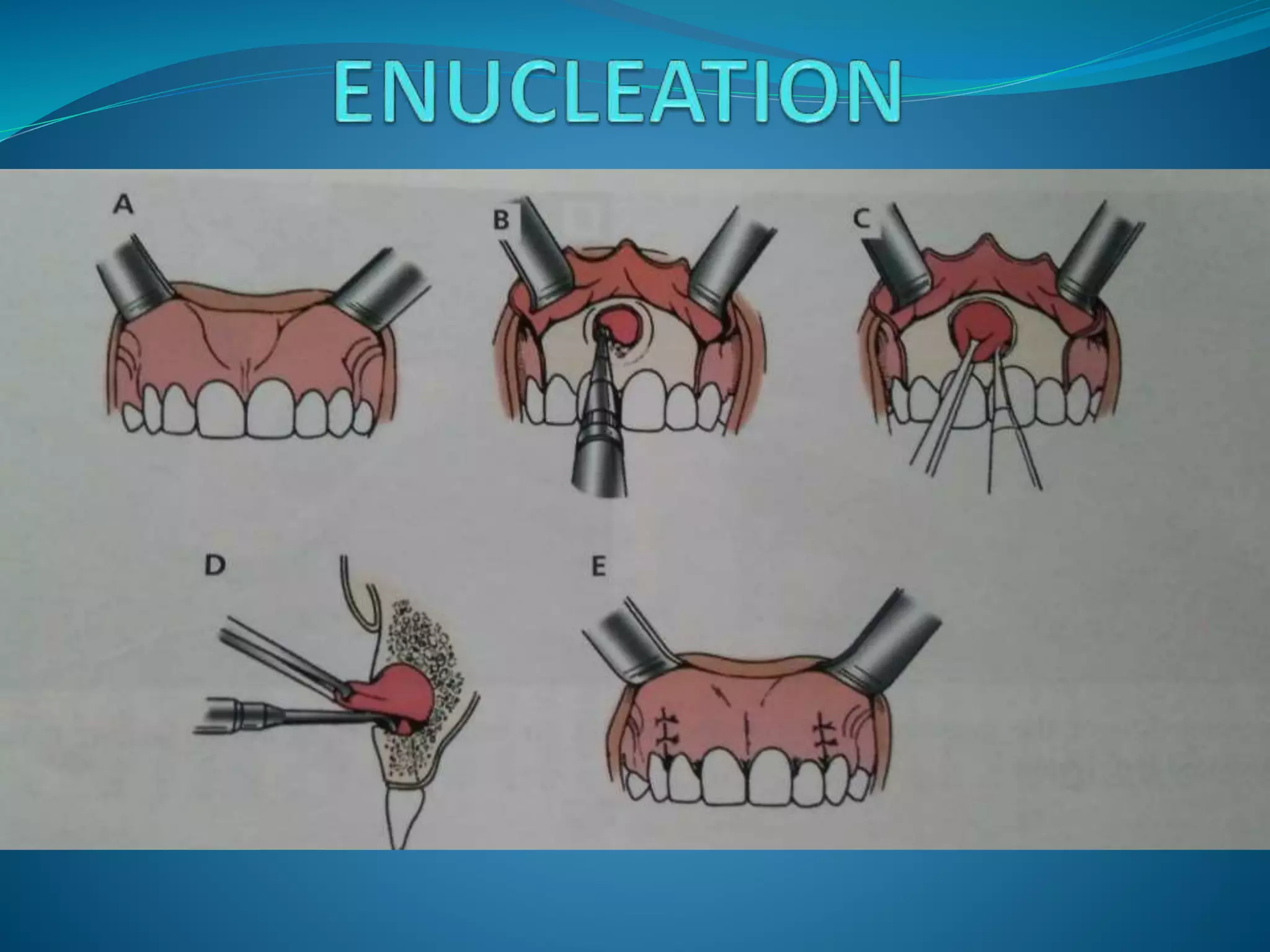
TREATMENT PLAN Smaller lesions- surgical removal in toto.
Large lesions- surgical
drain/Marsupialization.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cystsofthejaws-170429030902/75/Cysts-of-the-jaws-13-2048.jpg)



























![• Shafer’s Textbook of Oral Pathology(seventh edition)~ Shafer, Hine, Levy.
Editors- R Rajendran, B Sivapathasundharam.
• Textbook of ORAL & MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY(Second edition)~ S.M.
Balaji.
• Cysts Of Jaws (Posted on 15/05/2016). Available at
https://maxfactutorial.wordpress.com/2016/05/15/cysts-of-jaws/
• Jaws: Cysts and Odontogenic Neoplasms(Topic 10). PTHL 312b: Oral and
Maxillofacial Pathology. Available at
http://www.patologiabucal.com/index_htm_files/QyTO.pdf
• Cysts of the jaws [Kompatibilis mód]. Available at
http://semmelweis.hu/oralis-diagnosztika/files/2012/11/Cysts-of-the-jaws.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cystsofthejaws-170429030902/75/Cysts-of-the-jaws-50-2048.jpg)
