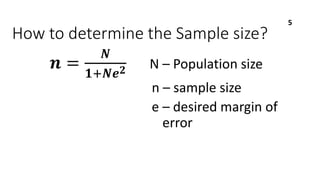
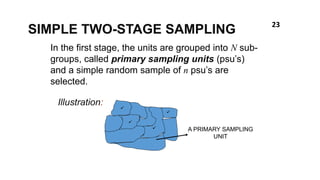
This document discusses key concepts in sampling techniques and methods. It defines sampling as selecting a subset of items from a population to make inferences about the whole population. There are two main types of samples: probability samples, which use random selection so probabilities are known; and non-probability samples, which use non-random methods so probabilities are unknown. Some common probability sampling techniques described include simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, systematic sampling, cluster sampling, and multistage sampling. The document also discusses factors to consider in determining sample size and how to compute it.