NUCLEIC ACIDS: THE RNA DOCUMENT
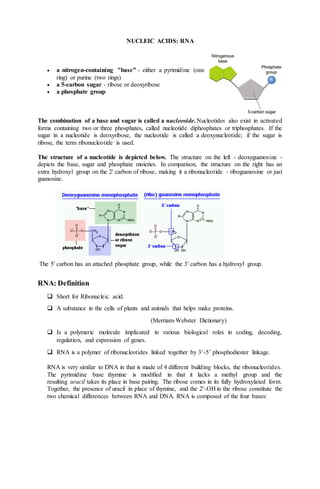
- 1. NUCLEIC ACIDS: RNA a nitrogen-containing "base” - either a pyrimidine (one ring) or purine (two rings) a 5-carbon sugar - ribose or deoxyribose a phosphate group The combination of a base and sugar is called a nucleoside. Nucleotides also exist in activated forms containing two or three phosphates, called nucleotide diphosphates or triphosphates. If the sugar in a nucleotide is deoxyribose, the nucleotide is called a deoxynucleotide; if the sugar is ribose, the term ribonucleotide is used. The structure of a nucleotide is depicted below. The structure on the left - deoxyguanosine - depicts the base, sugar and phosphate moieties. In comparison, the structure on the right has an extra hydroxyl group on the 2' carbon of ribose, making it a ribonucleotide - riboguanosine or just guanosine. The 5' carbon has an attached phosphate group, while the 3' carbon has a hydroxyl group. RNA: Definition Short for Ribonucleic acid. A substance in the cells of plants and animals that helps make proteins. (Merriam-Webster Dictionary) Is a polymeric molecule implicated in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes. RNA is a polymer of ribonucleotides linked together by 3’-5’ phosphodiester linkage. RNA is very similar to DNA in that is made of 4 different building blocks, the ribonucleotides. The pyrimidine base thymine is modified in that it lacks a methyl group and the resulting uracil takes its place in base pairing. The ribose comes in its fully hydroxylated form. Together, the presence of uracil in place of thymine, and the 2'-OH in the ribose constitute the two chemical differences between RNA and DNA. RNA is composed of the four bases:
- 2. Purines: Adenine A Guanine G Pyrimidines: Uracil U Cytosine C Structure of RNA RNA differs, however, from DNA because it does not form an analogous double helical structure. RNA does, however, form base pairs with DNA resulting in a heteromeric double helix consisting of one DNA and one RNA strand. This annealing of an RNA strand to its complementary DNA strand is called hybridization and plays a crucial role in the transcription and translation of genetic sequences into protein sequences. RNA does, in contrast to DNA, form short double strand structures on itself, thereby forming so called stem and loop structures. Many RNA molecules have secondary structure in which intramolecular loops are formed by complementary base pairing. Base pairing in RNA follows exactly the same principles as with DNA: the two regions involved in duplex formation are antiparallel to one another, and the base pairs that form are A-U and G-C. Both DNA/RNA double helices and RNA/RNA double strands have an A-DNA like conformation, also called A-RNA or RNA-II. RNA-DNA hybrids are more stable than the corresponding DNA-DNA and RNA-RNA duplexes. Types of RNA Messenger RNA is used as template to make proteins. All members of the class function as messengers carrying instructions for polypeptide synthesis from nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm. The 5’ terminal end is capped by 7- methyl guanosine triphosphate cap. The cap is involved in the recognition of mRNA by the translating machinery. It stabilizes m RNA by protecting it from 5’ exonuclease. Ribosomal RNA makes up the ribosomes. Forms an important part of both subunits of the ribosomes. The functions of the ribosomal RNA molecules in the ribosomal particle are not fully understood, but they are necessary for ribosomal assembly and seem to play key roles in the binding of mRNA to ribosomes and its translation. Recent studies suggest that an rRNA component performs the peptidyl transferase activity and thus is an enzyme (a ribozyme).
- 3. Transfer RNA transfers the amino acids from cytoplasm to the protein synthesizing machinery, hence the name tRNA. Transfer RNA matches amino acids to mRNA to help make proteins. They are the key to the translation process of mRNA sequence into the amino acids sequence of proteins. To be precise, the amino-acyl-tRNA-synthase proteins are the ‘true’ translator of the genetic code into the amino acid sequence. A failure of properly acetylating the tRNA with the right amino acid results in a amino acid mutation even though the DNA sequence has not been changed. They are easily soluble , hence called “Soluble RNA or s RNA. They are also called Adapter molecules, since they act as adapters for the translation of the sequence of nucleotides of the mRNA in to specific amino acids. There are at least 20 species of t RNA one corresponding to each of the 20 amino acids required for protein synthesis. Structure of tRNA • Primary structure- The nucleotide sequence of all the tRNA molecules allows extensive intrastand complimentarity that generates a secondary structure. • It contains about 73 to 93 nucleotides. • Three of the nucleotides make up the anticodon. • It has a CCA at the end of the structure which helps enzymes identify the tRNA molecule. • All 4 bases are methylated. • Secondary structure- Each single tRNA shows extensive internal base pairing and acquires a clover leaf like structure. The structure is stabilized by hydrogen bonding between the bases and is a consistent feature. • All t-RNA contain 5 main arms or loops which are as follows- • Acceptor arm • Anticodon arm • D HU arm • TΨ C arm ((pseudouridine)) • Extra arm • Tertiary structure-The L shaped tertiary structure is formed by further folding of the clover leaf due to hydrogen bonds between T and D arms. The base paired double helical stems get arranged in to two double helical columns, continuous and perpendicular to one another. Other Types of RNA’s Small Nuclear RNAs- play a critical role in gene regulation by way of RNA splicing. The splicing of pre-mRNA give rise to mature mRNA. snRNAs are found in the nucleus and are typically tightly bound to proteins in complexes called snRNPs (small nuclear ribonucleoproteins, sometimes pronounced "snurps"). The most abundant of these molecules are the U1, U2, U5, and U4/U6 particles, which are involved in splicing pre-mRNA to give rise to mature mRNA MicroRNAs- have been shown to inhibit gene expression by repressing translation. also play significant roles in cancer and other diseases
- 4. Small Interfering RNAs- they also work to inhibit gene expression. They may have evolved as a defense mechanism against double-stranded RNA viruses. Small Nucleolar RNAs- These molecules function to process rRNA molecules, often resulting in the methylation and pseudouridylation of specific nucleosides Riboswitches- are RNA sensors that detect and respond to environmental or metabolic cues and affect gene expression accordingly. Functions of RNA Its principal role is to act as a messenger carrying instructions from DNA for controlling the synthesis of proteins, In some viruses RNA rather than DNA carries the genetic information. PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Protein synthesis is defined as the process by which individual amino acids are connected to each other in a specific order dictated by the nucleotide sequence in DNA. It is the production of proteins by an individual cell. The genetic information stored in DNA is used as a blueprint for making proteins. Why Proteins? Because these macromolecules have diverse primary, secondary and tertiary structures that equip them to carry out the numerous functions necessary to maintain a living organism. These functions include: • Structural integrity (hair, horn, eye lenses etc.). • Molecular recognition and signaling (antibodies and hormones). • Catalysis of reactions (enzymes)..
- 5. • Molecular transport (hemoglobin transports oxygen). • Movement (pumps and motors). Process of Protein Synthesis Transcription The first step in transcription is the partial unwinding of the DNA molecule so that the portion of DNA that codes for the needed protein can be transcribed. Once the DNA molecule is unwound at the correct location, an enzyme called RNA polymerase helps line up nucleotides to create a complementary strand of mRNA. Since mRNA is a single-stranded molecule, only one of the two strands of DNA is used as a template for the new RNA strand. The new strand of RNA is made according to the rules of base pairing: DNA cytosine pairs with RNA guanine DNA guanine pairs with RNA cytosine DNA thymine pairs with RNA adenine DNA adenine pairs with RNA uracil For example, the mRNA complement to the DNA sequence TTGCAC is AACGUG. The SAT II Biology frequently asks about the sequence of mRNA that will be produced from a given sequence of DNA. For these questions, don’t forget that RNA uses uracil in place of thymine. After transcription, the new RNA strand is released and the two unzipped DNA strands bind together again to form the double helix. Because the DNA template remains unchanged after transcription, it is possible to transcribe another identical molecule of RNA immediately after the first one is complete. A single gene on a DNA strand can produce enough RNA to make thousands of copies of the same protein in a very short time. Adding an Amino Acid to tRNA An enzyme called aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase adds the correct amino acid to its tRNA. The correct amino acid is added to its tRNA by a specific enzyme called an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. The process is called aminoacylation, or charging. Since there are 20 amino acids, there are 20 aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. All tRNAs with the same amino acid are charged by the same enzyme, even though the tRNA sequences, including anticodons, differ. Translation In translation, mRNA is sent to the cytoplasm, where it bonds with ribosomes, the sites of protein synthesis. Ribosomes have three important binding sites: one for mRNA and two for tRNA. The two tRNA sites are labeled the A site and P site.
- 6. Once the mRNA is in place, tRNA molecules, each associated with specific amino acids, bind to the ribosome in a sequence defined by the mRNA code. tRNA molecules can perform this function because of their special structure. tRNA is made up of many nucleotides that bend into the shape of a cloverleaf. At its tail end, tRNA has an acceptor stem that attaches to a specific amino acid. At its head, tRNA has three nucleotides that make up an anticodon. An anticodon pairs complementary nitrogenous bases with mRNA. For example if mRNA has a codon AUC, it will pair with tRNA’s anticodon sequence UAG. tRNA molecules with the same anticodon sequence will always carry the same amino acids, ensuring the consistency of the proteins coded for in DNA. The Process of Translation Translation begins with the binding of the mRNA chain to the ribosome. The first codon, which is always the start codon methionine, fills the P site and the second codon fills the A site. The tRNA molecule whose anticodon is complementary to the mRNA forms a temporary base pair with the mRNA in the A site. A peptide bond is formed between the amino acid attached to the tRNA in the A site and the methionine in the P site. The ribosome now slides down the mRNA, so that the tRNA in the A site moves over to the P site, and a new codon fills the A site. (One way to remember this is that the A site brings new amino acids to the growing polypeptide at the P site.) The appropriate tRNA carrying the appropriate
- 7. amino acid pairs bases with this new codon in the A site. A peptide bond is formed between the two adjacent amino acids held by tRNA molecules, forming the first two links of a chain. The ribosome slides again. The tRNA that was in the P site is let go into the cytoplasm, where it will eventually bind with another amino acid. Another tRNA comes to bind with the new codon in the A site, and a peptide bond is formed between the new amino acid to the growing peptide chain. The process continues until one of the three stop codons enters the A site. At that point, the protein chain connected to the tRNA in the P site is released. Translation is complete. Prepared By: LILY ROSEMARY L. MASILANG REFERENCES: • http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/genetics/biotech/basics/nastruct.html • http://www.whatislife.com/reader/dna-rna/dna-rna.html • https://www2.chemistry.msu.edu/faculty/reusch/virttxtjml/nucacids.htm • http://www.nature.com/scitable/definition/ribonucleic-acid-rna-45 • http://www.nature.com/scitable/definition/ribonucleic-acid-rna-45 • http://www.slideshare.net/namarta28/rna • http://chemistry.tutorvista.com/biochemistry/nucleic-acid-function.html • http://slideplayer.com/slide/4640877/ • http://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/rna-functions-352 • http://chemistry.elmhurst.edu/vchembook/584proteinsyn.html • www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/translation/init.html
