Life sciences ebook
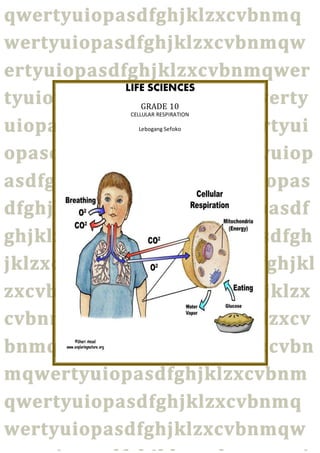
- 1. LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 10 CELLULAR RESPIRATION Lebogang Sefoko
- 2. 1 LIFE SCIENCES GRADE 10 CONTENT CHAPTER ONE Introduction to cellular respiration page 2 What is cellular respiration? What is the law of conservation of energy? Raw materials of cellular respiration. Products of cellular respiration. *End of chapter activity. CHAPTER TWO Anaerobic respiration page 3 Anaerobic respiration in muscles during exercise. Anaerobic respiration in plants *End of chapter activity RUBRIC page 4 CHAPTER THREE The role of anaerobic respiration in the industry page 5 Baking of bread *End of chapter activity CHAPTER FOUR Aerobic respiration page 6 *End of chapter activity and RUBRIC page 7
- 3. 2 CHAPTER ONE Cellular respiration – is the breaking down of organic compounds (glucose) with the gradual release of energy that is stored in ATP molecules. Oxygen is required and Carbon dioxide and water are released as waste products. Law of Conservation of Energy – energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another. The sun is the primary source of energy for life. During photosynthesis, radiant energy from the sun is converted into chemical potential energy and built into organic carbohydrate molecules (glucose). During cellular respiration, these organic compounds (glucose) are broken down, releasing the stored chemical potential energy. This energy is carried to all parts of the cell/body by ATP (energy carrier). Raw material needed for cellular respiration are: Glucose Oxygen Products of cellular respiration are: Carbon Dioxide Water ATP Photosynthesis is an anabolic process, because energy-rich glucose is built up. Cellular respiration is a catabolic process, because energy-rich glucose is broken down. The following activity to be done out of 10: https://testmoz.com/899227
- 4. 3 CHAPTERTWO When respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen, it is known as anaerobic respiration. Glucose is only partially broken down and therefore less energy is released. Anaerobic respiration in animals (humans) During vigorous exercise, the muscles do not receive enough oxygen.The muscle cells must therefore respire anaerobically. Only glycolysis takes place. Glucose is broken down. Pyruvic acid is formed. Only a small amount of energy is released. Pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid, which is released in the muscle cells. This process is known as lactic acid fermentation. Lactic acid is a toxin that leads to muscle stiffness and muscle pain. Oxygen is needed to convert the lactic acid back to pyruvic acid. Moderate exercise with deep breathing is needed to get rid of muscle stiffness. If there is sufficient oxygen, aerobic respiration takes place and pyruvic acid enters the Krebs cycle. The oxygen needed to get rid of the lactic acid which accumulates in the cells is called oxygen debt. Anaerobic respiration in plants Only glycolysis occurs. Glucose is broken down. Pyruvic acid is formed. Only a small amount of energy is released. Pyruvic acid is broken down further. Carbon dioxide is released. Alcohol is formed. This process is known as alcoholic fermentation. Do the following activity out of 20: https://todaysmeet.com/respiration10
- 5. 4 Scoring level Structure Content Coherence Application 4 - Accomplished Developsand defendsan informedposition, integratingvalues and science. Integratesand appliesbasic scientificconcepts and principles. Demonstrates scientificreasoning across multiple disciplines. Demonstrates comprehensionof the scientific approach; illustrateswith examples 3 - Competent Correctlydescribes perspectives concerningthe scientificaspectsof a societal issue. Showsclear comprehensionof basicscientific conceptsand principles. Accurately expressesconcepts relatingtothe scientificapproach Interpretsand relatesscientific resultsina way that showsa clear recognitionof the nature of science. 2 - Developing Product does not reflect the assignment, does not distinguish what information is needed, restates the question without making an attempt at a solution. Able tostate basic scientificconcepts and principles. Uses vocabulary relatedtoscientific methods ina rote manneror showing simple conceptualization Providessimplistic or incomplete explanationsof the nature of science. 1 - Beginning Doesnot visualize a role or needfor science inhuman affairs. Lacks understandingof basicscientific conceptsand principles. Showsminimal understandingof scientificmethods Doesnot distinguish betweenscientific, political,religious, or ethical statements.
- 6. 5 CHAPTER THREE The role of anaerobic respiration in the industry Yeast cells and other fungi respire anaerobically and are used to produce alcoholic beverages, such as beer and wine. Yeast cells are also used to causebread to rise during the baking process. Certain bacteria can be used to produce cheese, yoghurtand sour milk under anaerobic conditions in the presenceof sugar (lactose). The use of these living organisms in industrial processes such as food processing is known as biotechnology. Baking bread To bake bread, flour, water, yeast and a little sugar aremixed together to form a dough. The yeastferments the sugar into alcohol and CO2. The CO2 that is released causes the dough to rise. The dough rises faster if it is kept warm. The alcohol that is formed evapourates during the baking process and the yeast cells are destroyed by the high temperature. Watch the introduction video and read the discussion description box where it states: You are required to bake a loaf of bread, write down the step by step process, take a video recording for evidence that you havebaked the bread. This can be done in pairs. Answer the question after watching the introduction video to know whatto expect. https://create.kahoot.it/#/preview/abbda511-6a38-4be2-b1aa-3fff6943dfa7
- 7. 6 CHAPTER FOUR Aerobic respiration Three stages can be distinguished: Glycolysis Krebs cycle Oxidative phosphorylation GLYCOLYSIS Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol just outside the mitochondrion. This phase requires no oxygen and is therefore an anaerobic phase. Glucose is broken down step by step. Two molecules of pyruvic acid, with 3 carbon atoms each are formed. Energy-rich H- atoms as well as a small amount of energy, is released and stored in ATP. Coenzymes carry the energy- rich hydrogen atoms to the third phase. KREBS CYCLE The Krebs cycle takes place inside the mitochondrion, this phase is an aerobic phase as it requires oxygen. Pyruvic acid enters the mitochondrion, a series of cyclic reactions take place. Energy–rich H- atoms and CO2 is released. Coenzymes act as hydrogen carriers that transmit the energy – rich H – atoms to the next phase. OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION Oxidative phosphorylation takes place on the inner folded membrane (cristae) of the mitochondrion. This phase requires oxygen and is therefore aerobic phase. Energy – rich H-atoms from the Krebs cycle are carried to a hydrogen transfer system by coenzymes. H-atoms are transferred from one hydrogen acceptor to the next. Every time an H-atom is transferred from one acceptor to the next, energy is released. This energy binds a phosphate molecule with ADP to form ATP, which is the energy carrier in the cell. Oxygen is the final hydrogen acceptor. Two hydrogen atoms combine with one oxygen atom to form a molecule of water. Summarise the aerobic respiration process in a form of a mind map. The skeleton of the mind map is done for you already just fill in where neccessary:
- 8. 7 https://bubbl.us/#7317498 COMMENT CRITERIA RATING COMPETENT Clarity of thought, shows understanding of major processes, includes good draws of acceptable inferences and conclusions, may have graphic representations shown. 0-20 MINORFLAWS Completes the activity, but explanations may be slightly ambiguous or unclear, may contain some incompleteness, inappropriateness, or unclearness in representation, understanding of processes, or conclusions. 0-16 SATISFACTORY Begins successfully, but omits significant parts or fails to complete, may misuse scientific terms, representations may be incorrect or omitted, incorrect or incomplete in analysis, inferences and conclusions. 0-12 FAILS TO COMPLETEFULLY Work shows concept mastery but incorrect use of scientific terms and inappropriate. 0-6 UNABLE TO BEGIN EFFECTIVELY Product does not reflect the activity, does not distinguish what information is needed, restates the question without making an attempt at a solution. 0- 3
- 9. 8 NO ATTEMPT No evidence of planning or research. 0-1 https://b.socrative.com/teacher/#reports The above link is a continuation activity on Aerobic respiration.
- 10. 9