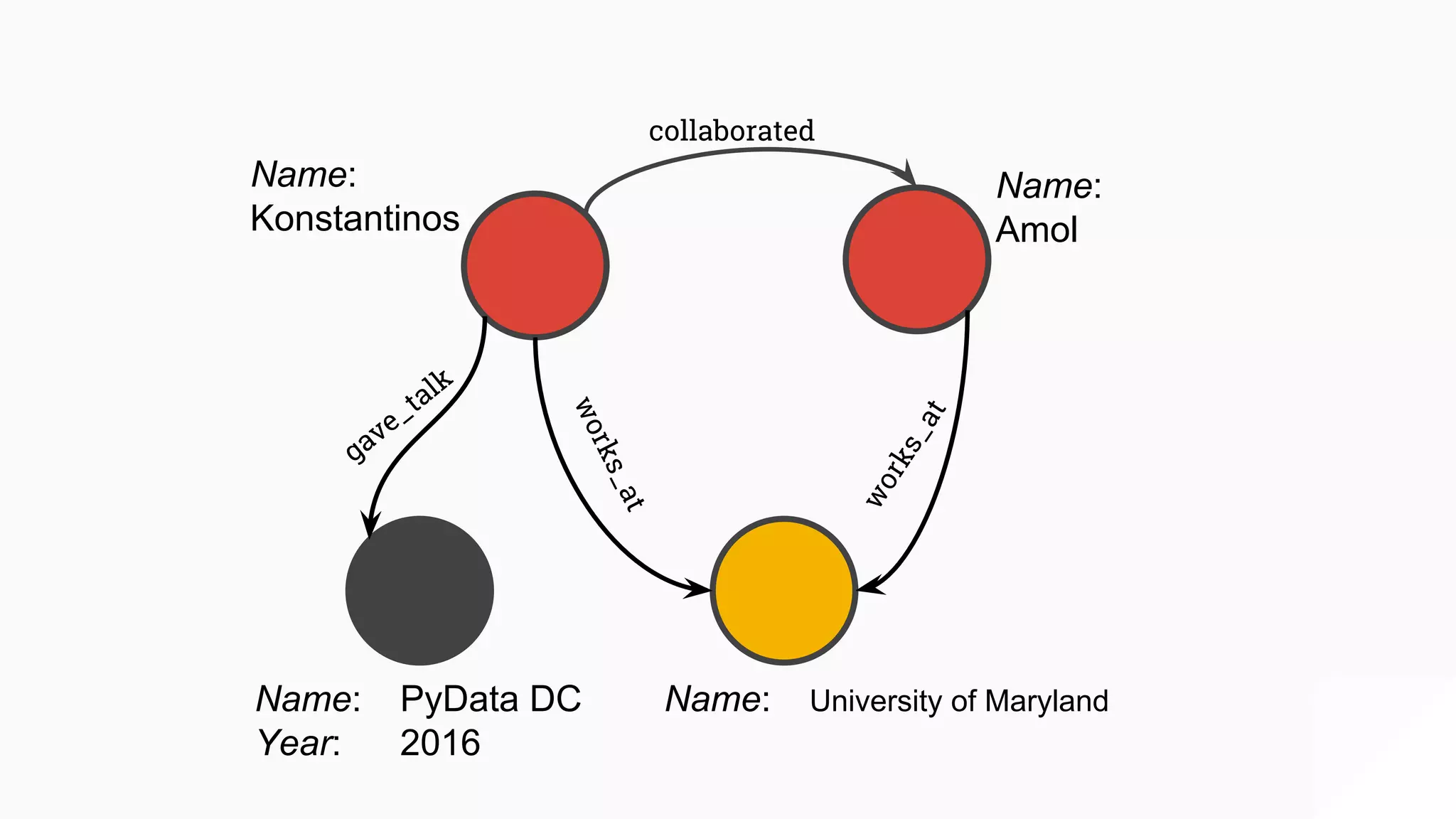
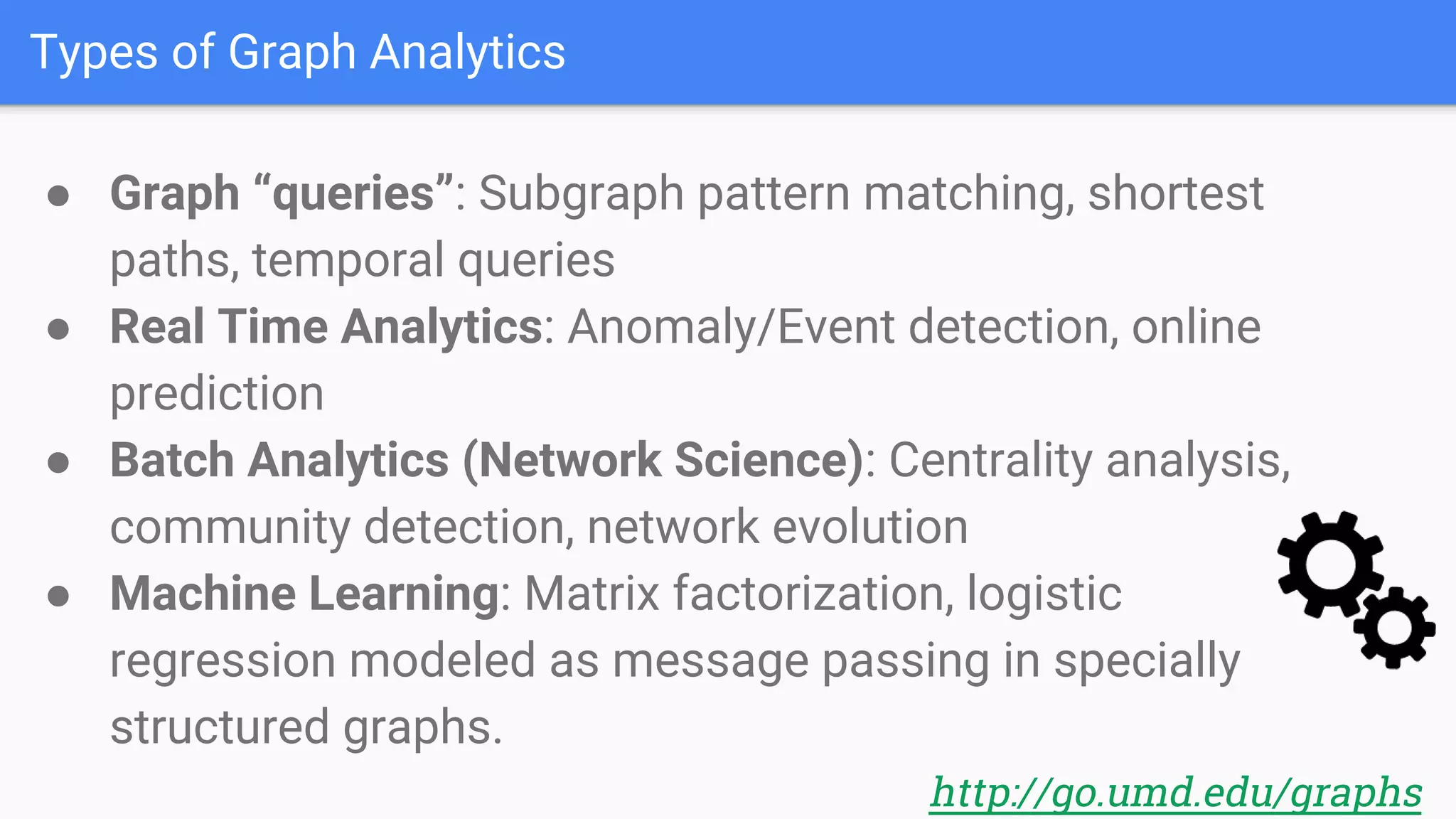
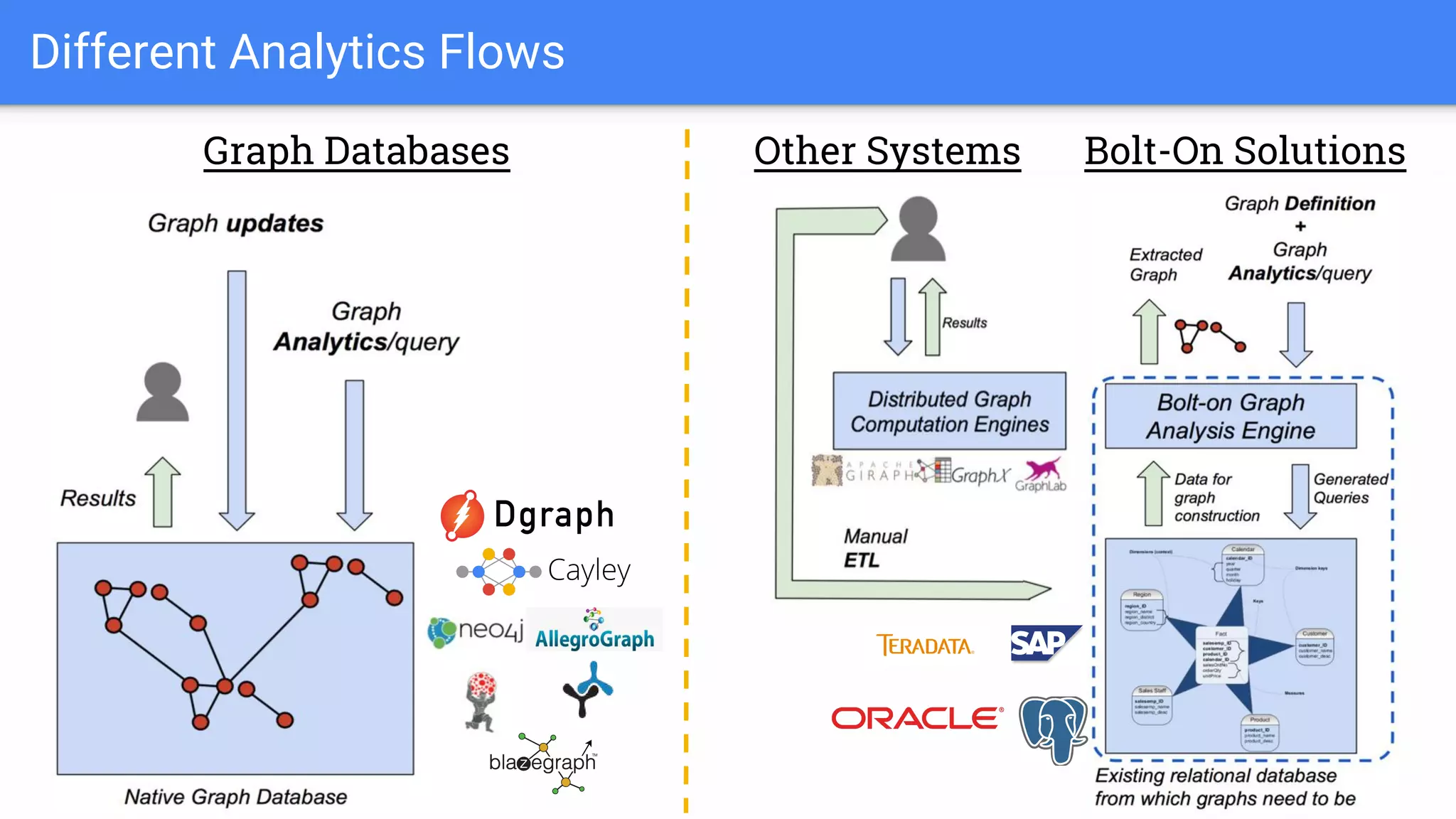
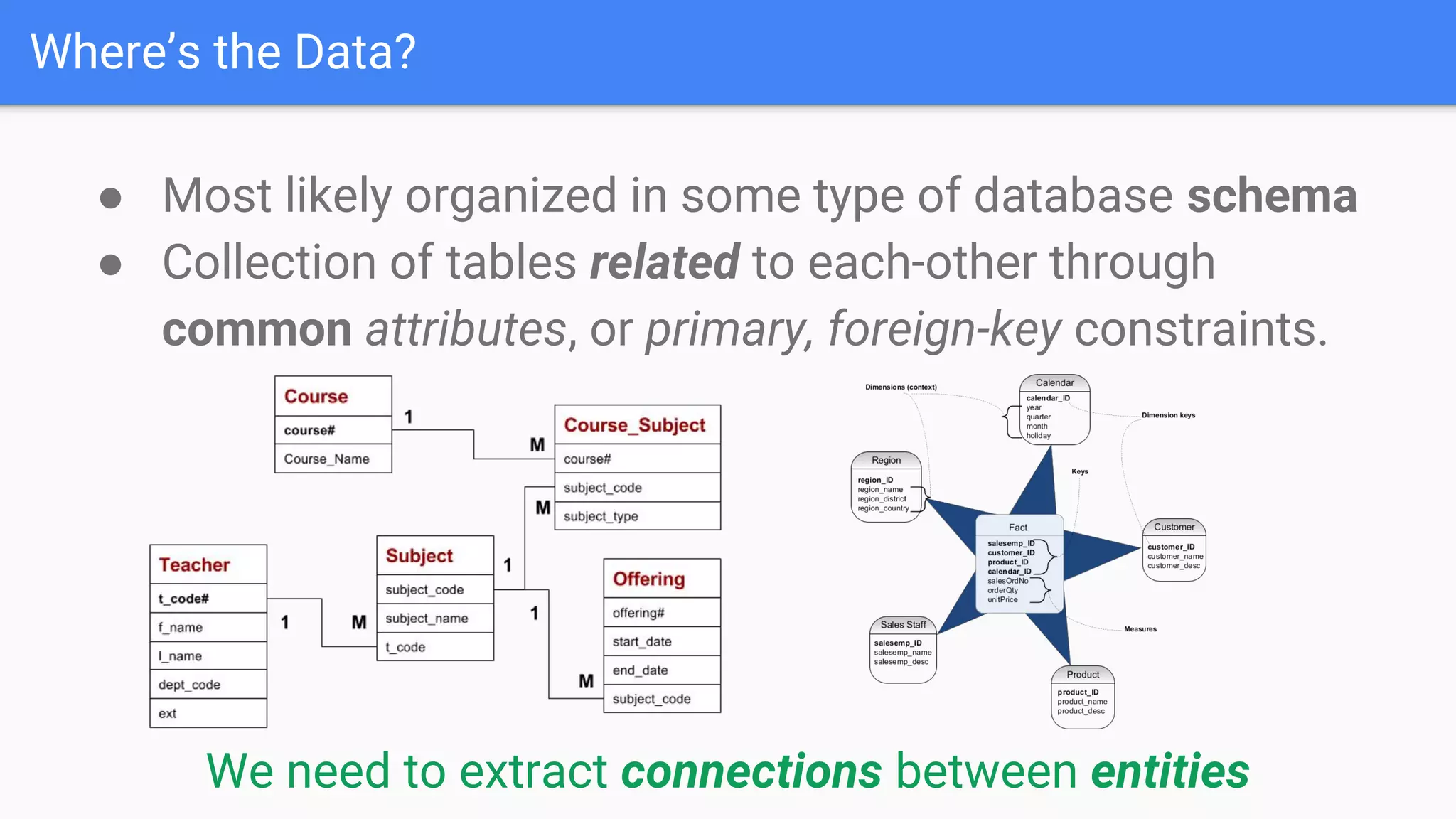
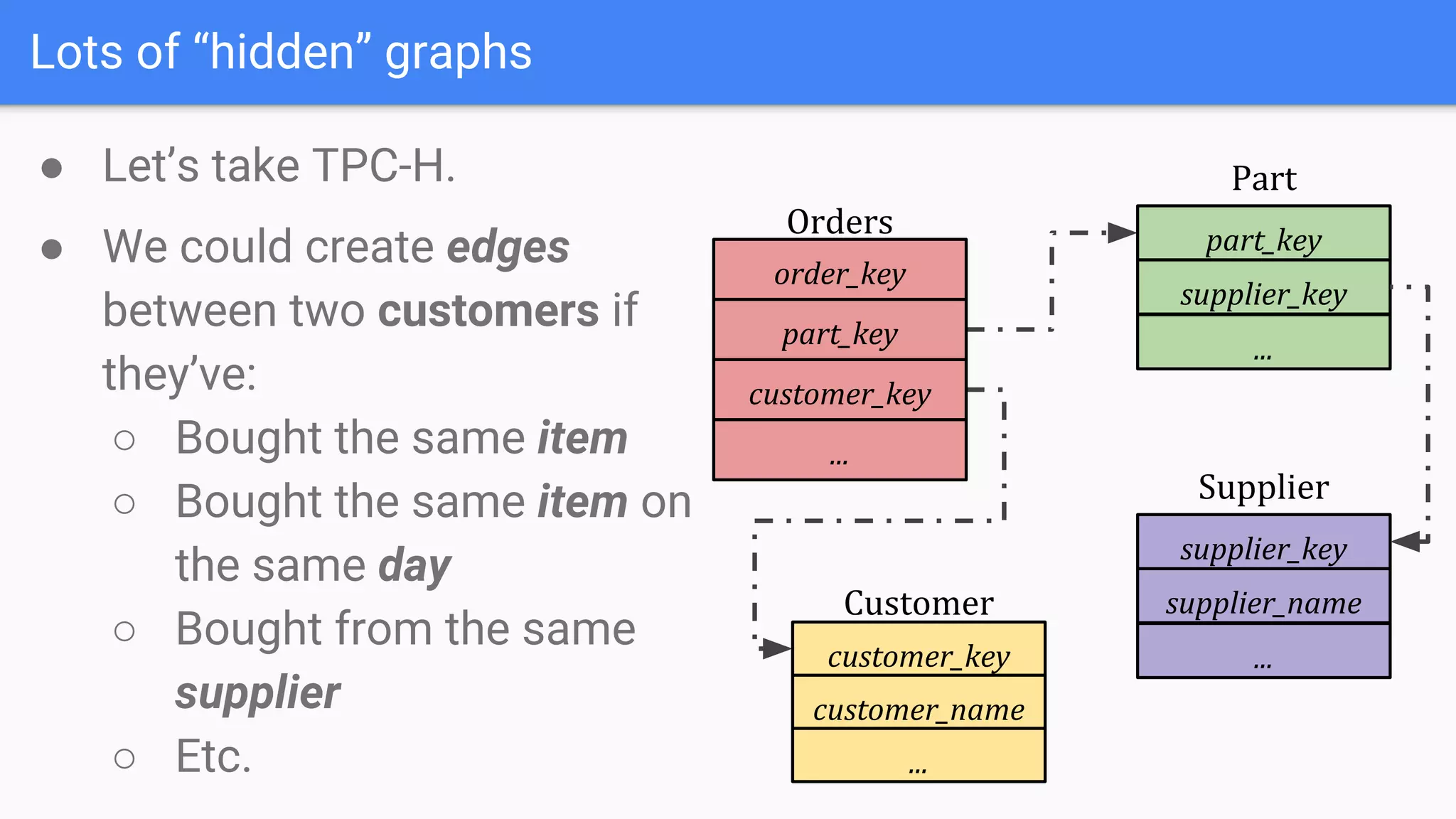
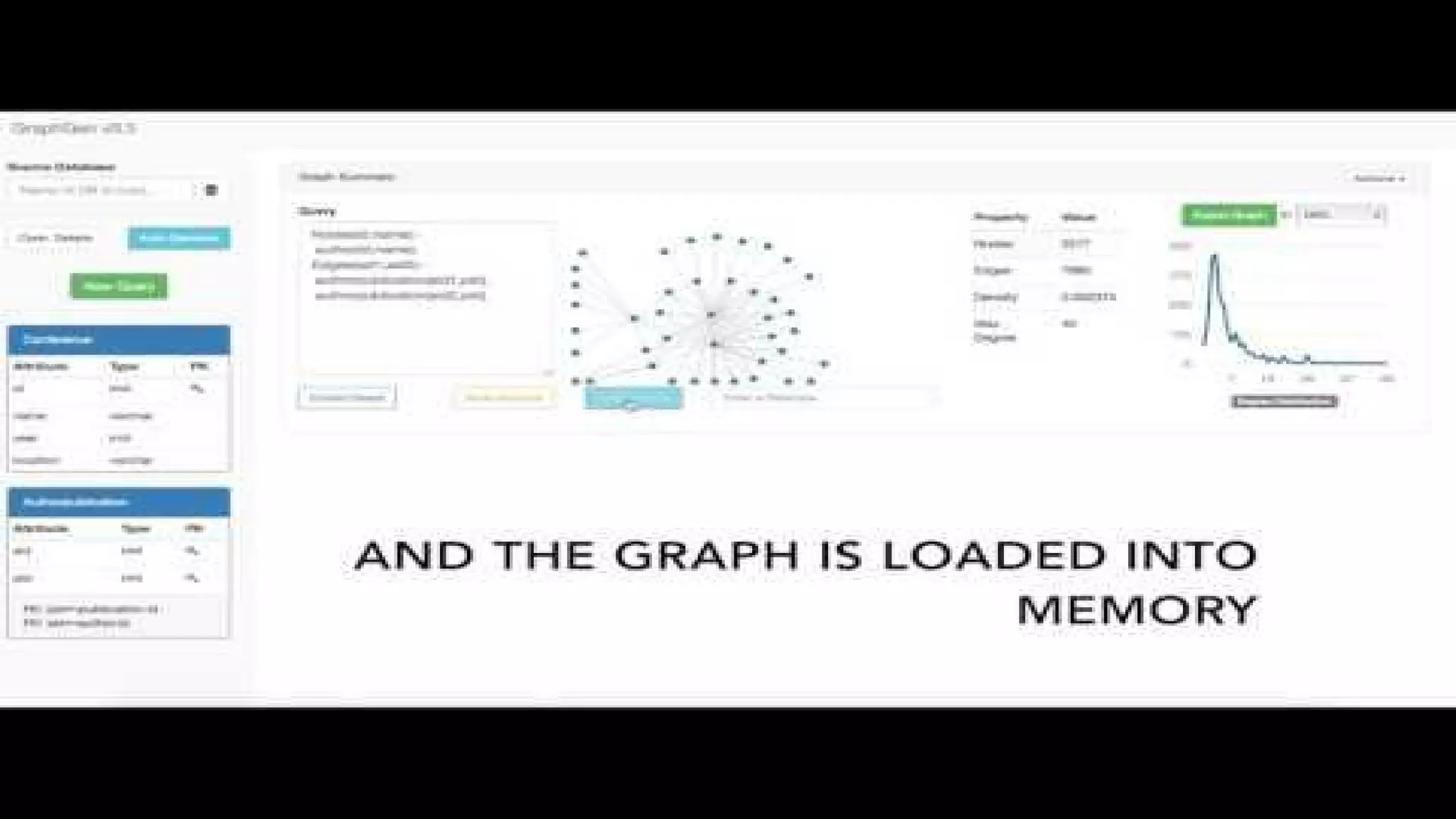
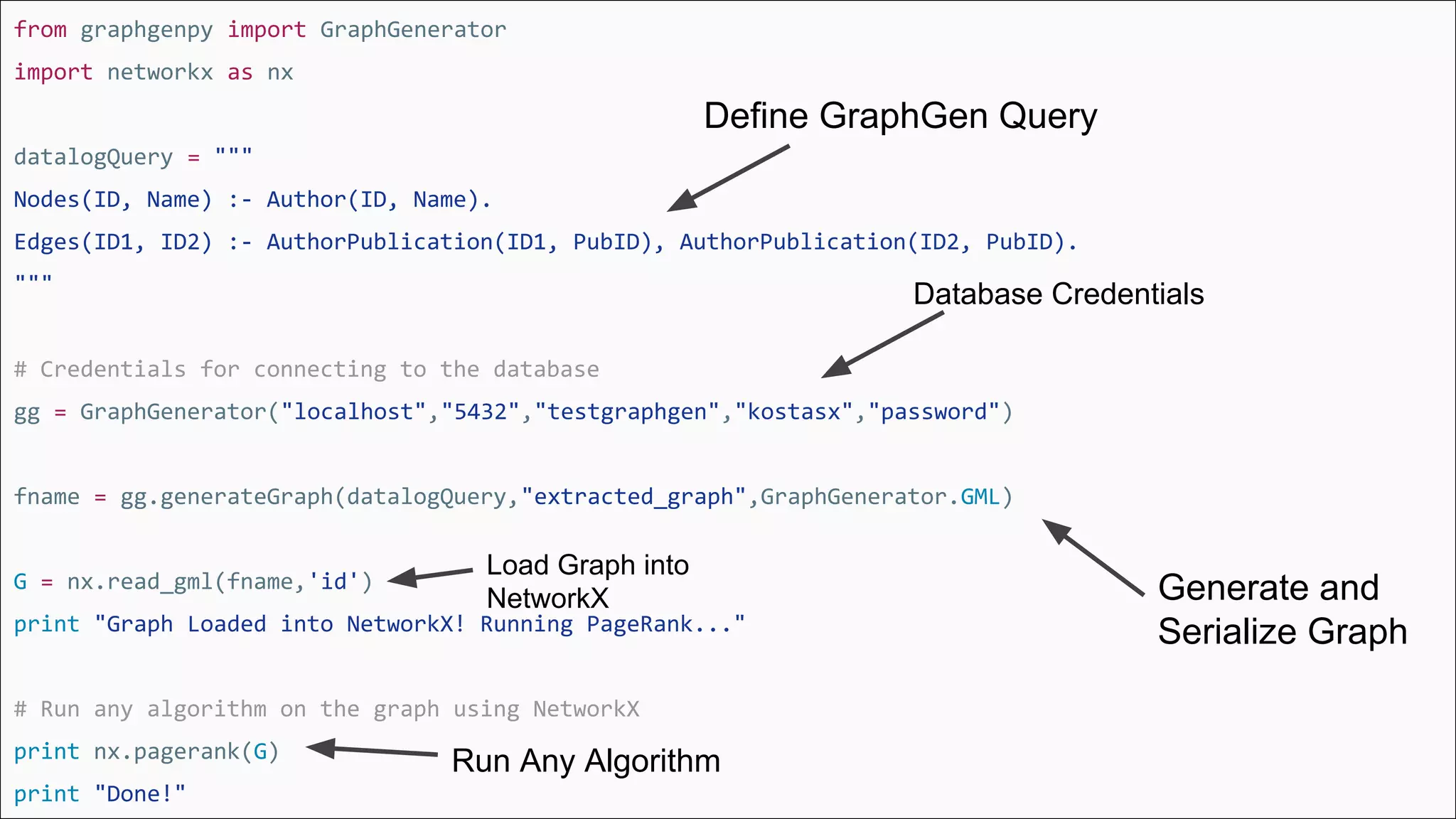
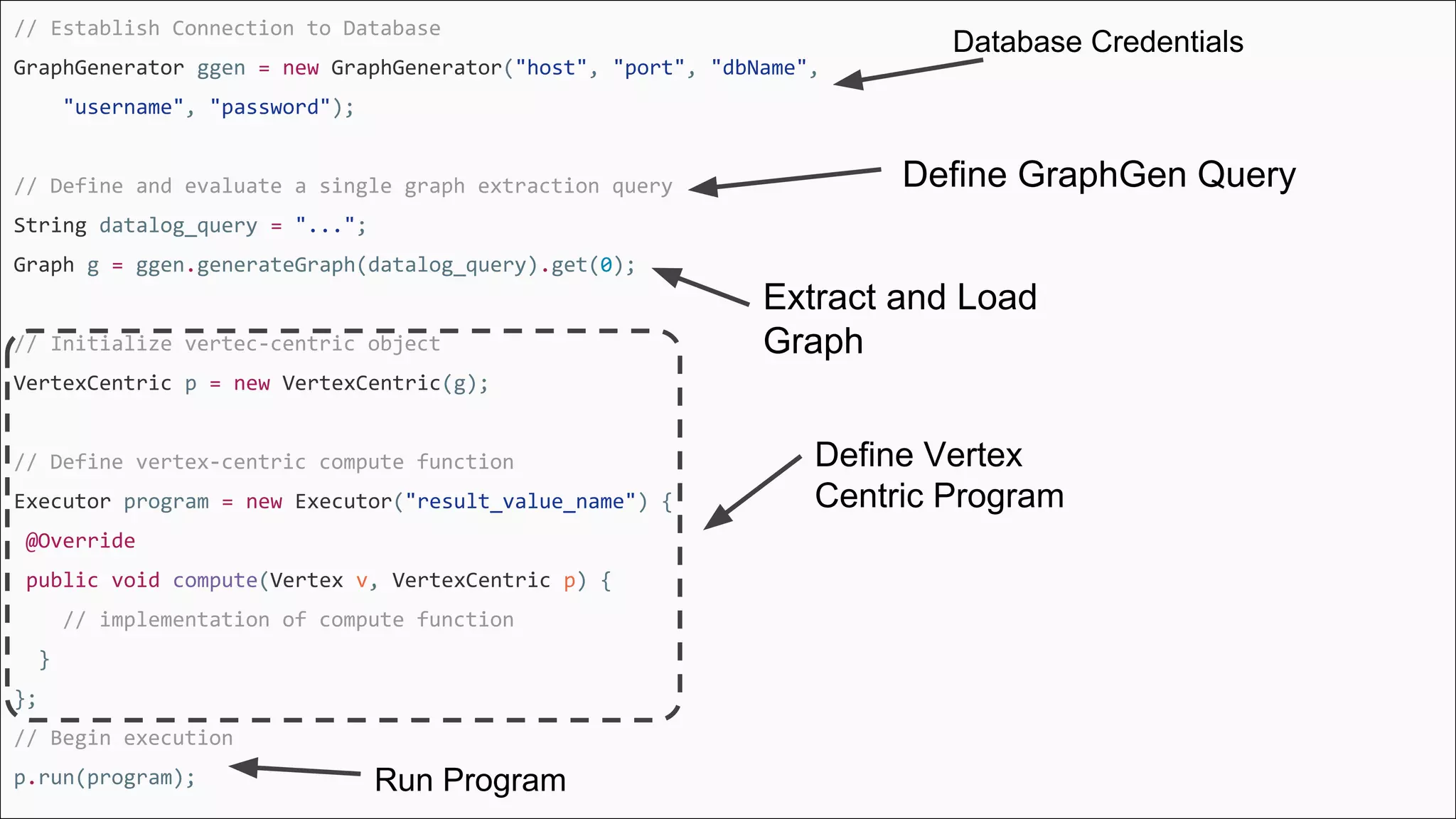
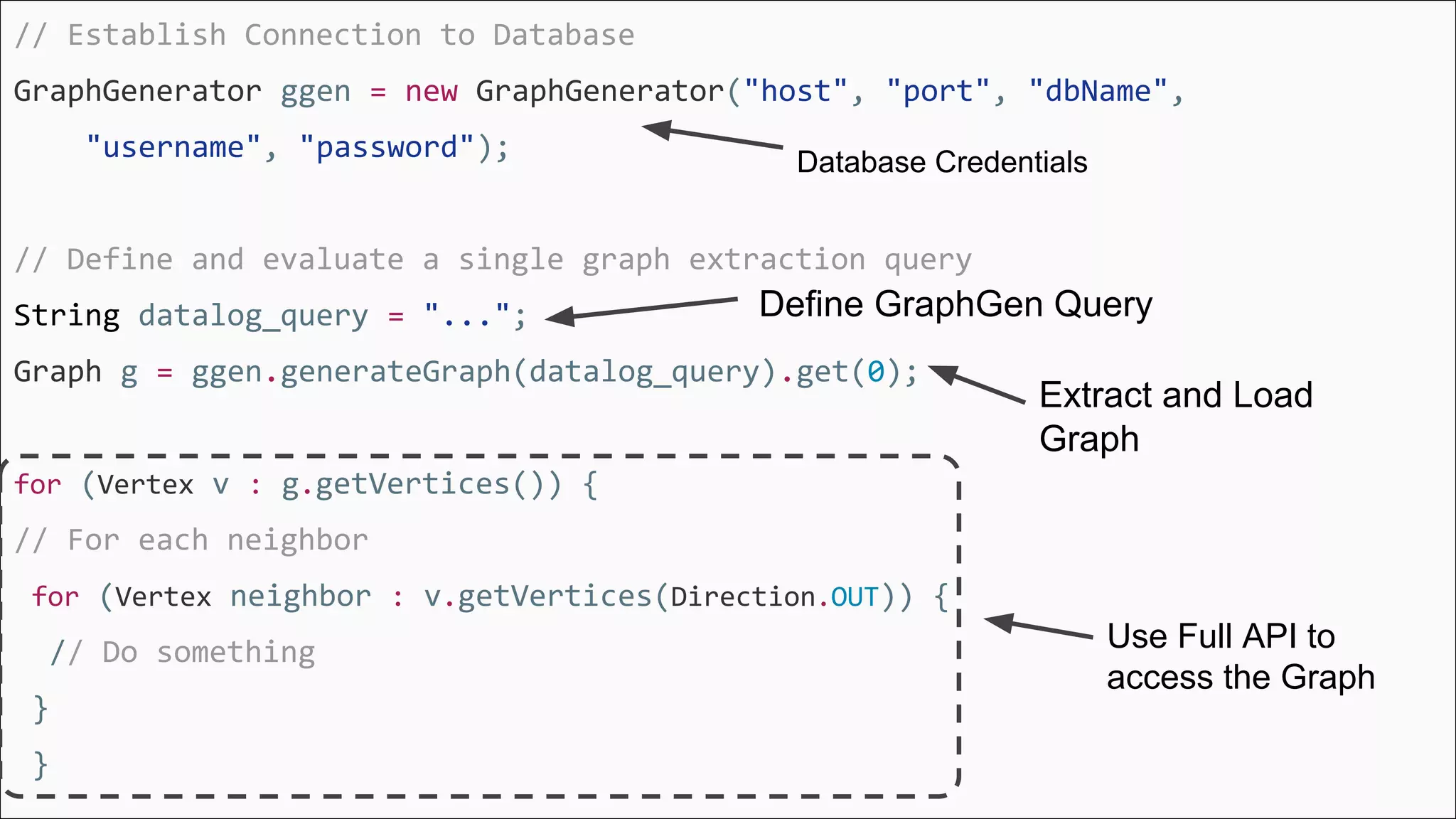
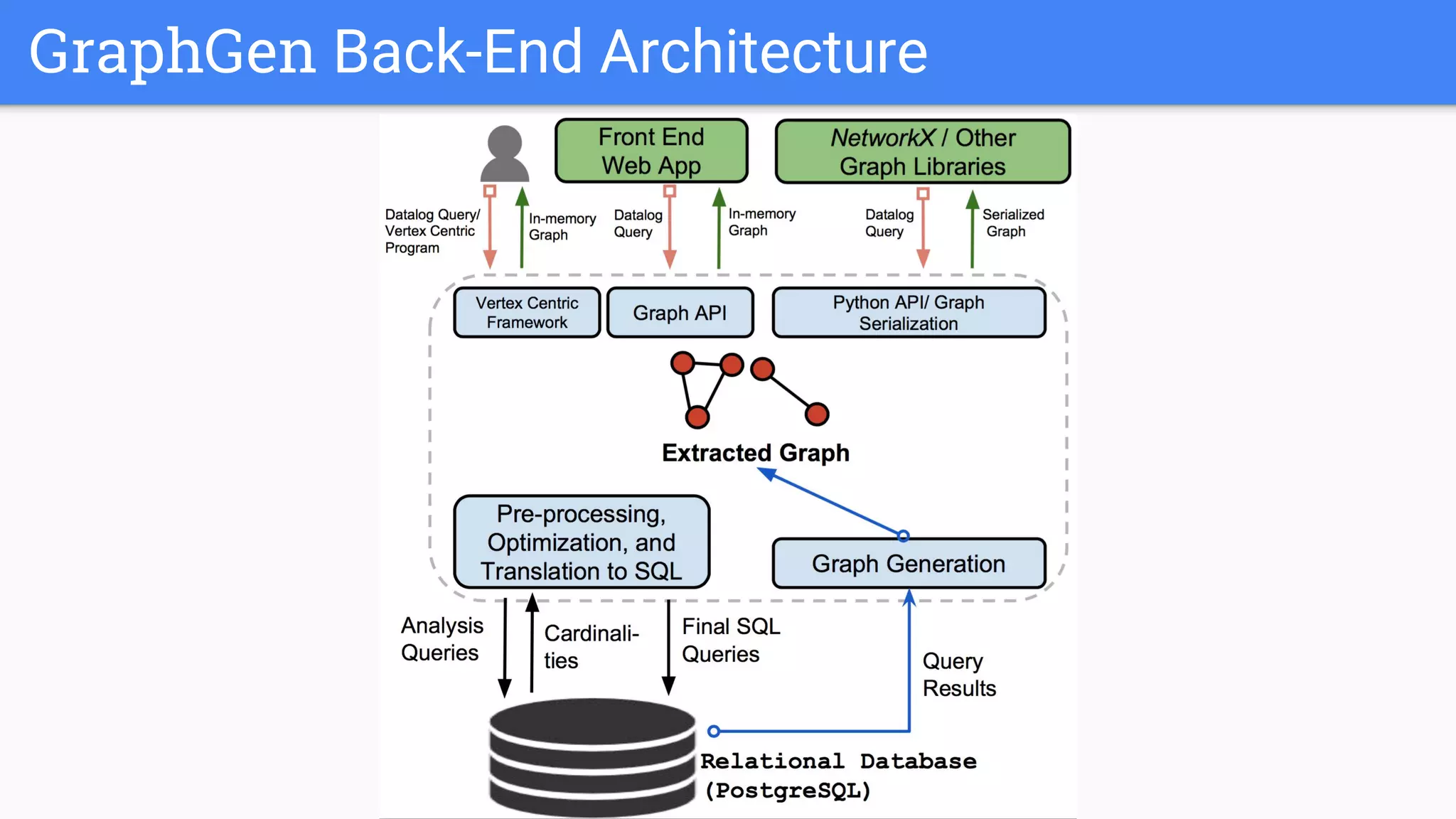
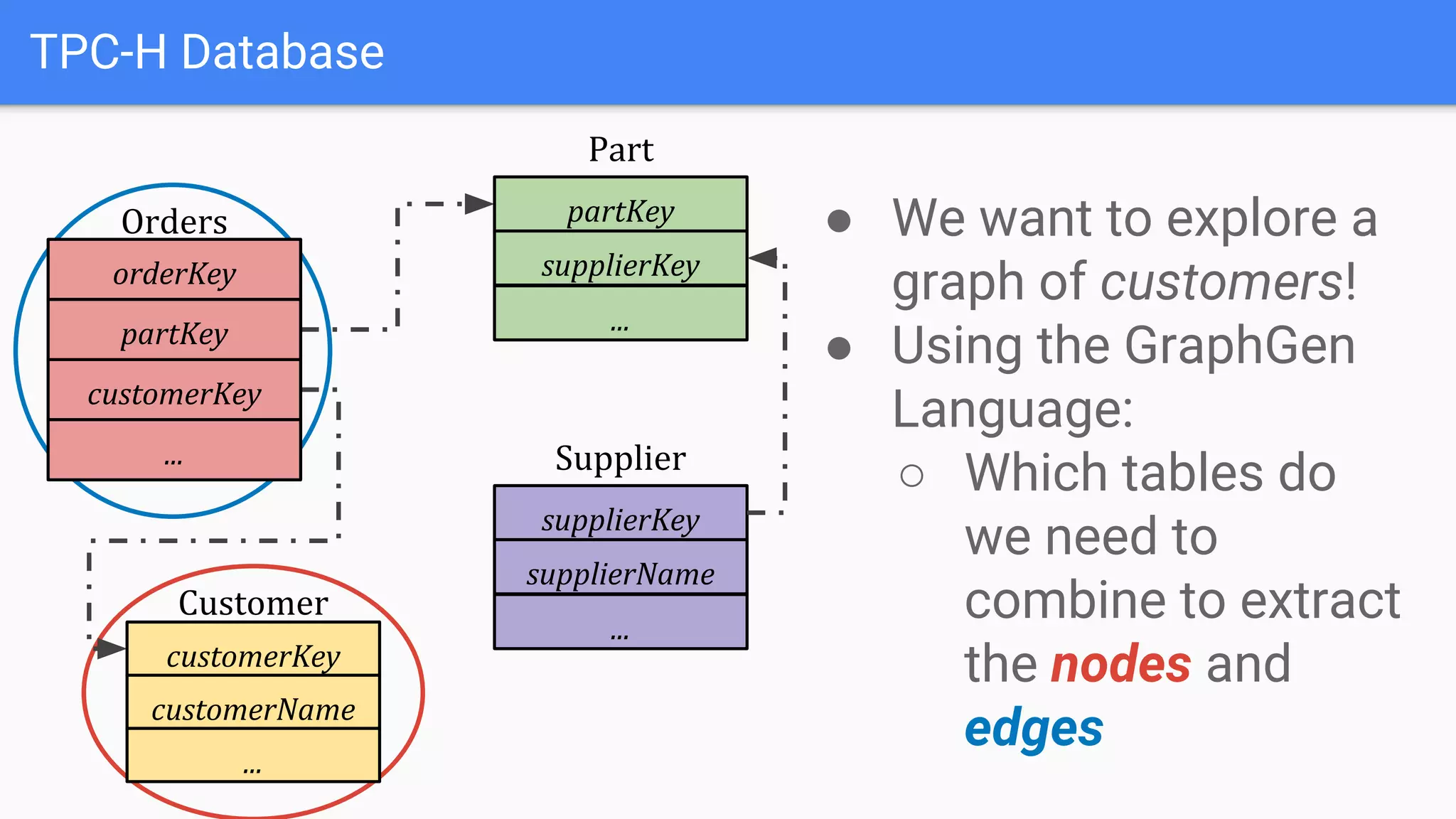
The document discusses GraphGen, a tool for conducting graph analytics over relational databases, emphasizing the importance of graph analytics for understanding connections between entities across various domains. It highlights the current challenges in graph analytics, including the lack of a one-size-fits-all solution and the necessity for specialized databases and frameworks. GraphGen offers a user-friendly, domain-specific language for extracting and analyzing different types of graphs without the need for complex ETL processes.