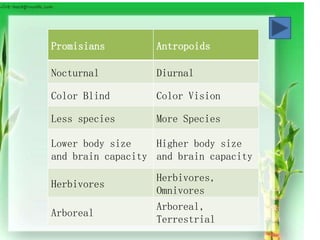
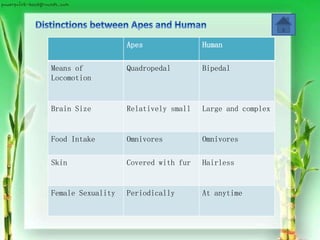
The document discusses primates and their classification. It describes the distinguishing characteristics between prosimians and anthropoids, and between apes and humans. The closest family to humans is identified as chimpanzees, with whom we share 99% of proteins and genes. The document provides details on the taxonomy of primates including their orders, suborders, and families. It outlines differences between prosimians and anthropoids, and between apes and humans in terms of locomotion, brain size, food intake, skin/hair, and female sexuality. References used are cited.



![Suborder Prosimi ‘before apes’
ex. Shrews, lemurs, lorises, bush bay, tarsiers.
Suborder Anthropoidea ex. Monkeys, apes, humans
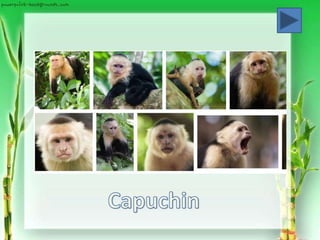
Superfamily Ceboida: New World Monkeys
(ex. marmosets, capuchin)
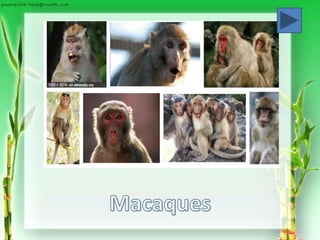
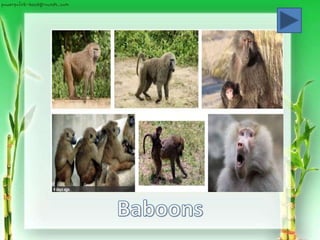
Superfamily Cercopithecoida: Old World Monkeys
(ex. Macaques, baboons)
Superfamily Hominoida
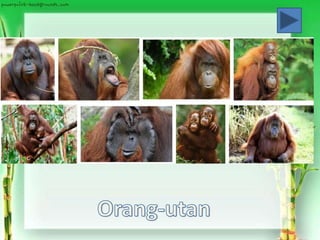
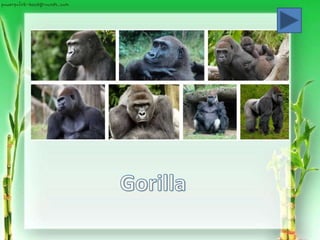
Family Anthropoidii: the Anthropoid apes
(ex. Gibbon, orang-utan,
gorilla and chimpanzee.)
Family Hominidae:
Austropithecus [extinct Prehumans]
Homo habilis, H. Erictus. H. Sapiens](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ceps112primates-180724140845/85/different-primates-all-over-the-world-4-320.jpg)