The Anatomy and Development of Human Skin
- 1. SKIN - basic STRUCTURE DR.P.NIKHILESH REDDY
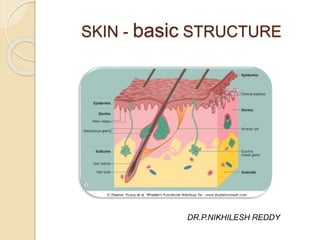
- 2. introduction Skin is the largest organ of the human body Accounts for 16-20% of body weight…it weighs twice as much as your brain For the average adult human, the skin has a surface area of between 1.5-2.0 sq.mtrs The skin is composed of two basic layers (regions).. ◦ Epidermis – outermost layer ◦ Dermis –underlying connective tissue Subcutaneous fat (Hypodermis),inspite of its close anatomic relationship and tendency to respond jointly to pathologic processes,is not a part of skin basic structure
- 3. EPIDERMIS Primarily made up of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium(keratinocytes) Gives strength to the skin. Varies in thickness from thick skin to thin skin Eyelids- 0.04 mm,Palms- 1.6 mm,average 0.1 mm It does not have any vascularization, so it relies on the connective tissues deep to it. Also contain melanocytes, merkel’s cells and Langerhans cell
- 4. Layers of epidermis Stratum basale (the deepest layer) Stratum spinosum Stratum granulosum Stratum lucidum (only in thick skin) Stratum corneum (most superficial layer of epidermis)
- 6. Stratum Basale The stratum germinativum (or basal layer, stratum basale) Consists of single layer of basophilic columnar or cuboidal cells. Along with S. spinosum, it is a component of Malpighian layer Cells are bound to each other by desmosomes and to basal lamina by hemidesmosomes. All cells contain intermediate keratin filaments, number of which increases as cells progress upward.
- 7. Stratum Spinosum Also contain the dividing cells as in basale. Cells contain bundles of intermediate filament (tonofilaments) projecting into the processses of cells which give attachment to the desmosomes, so giving spined appearance. Tonofilaments provide resistant to the abrasion so this layer is thicker in the areas prone to abrasion (thick skin) . Keratinization begins in the stratum spinosum.
- 8. stratum granulosum Consists of polygonal cells , cytoplasm of which is filled with the basophilic granule , keratohyaline granules. It is rich in phosphorylated histidine and cystine. Cells contain, lamellated bodies, made up of lipid. It fuses with the cell membrane and it come out of cells and function as a intercellular cement or sealing agent. This sealing effect is first evolutionary adaptation to terrestrial life
- 9. Stratum Lucidum More prominent in thick skin .Cellular organells and nuclei are not prominent. It is composed of clear non-nucleated cells. In the palms and soles, the stratum lucidum is present. The tan colored protein blocks the underlying melanocytes from view
- 10. Stratum corneum The main difference between thick skin and thin skin relates to the thickness of the Stratum corneum. These are the dead cells, flaking off. The cells lose their nucleus and fuse to form squamous sheets, which are eventually shed from the surface (desquamation). The mean turnover or renewal time of epidermis is 39 days(13+12+14) i.e.,time for a cell to move from the stratum basale to the distal edge of the stratum corneum and shed 13 days for proliferative compartment( lower two rows),12 days for differentiated compartment,14 days for cornified layer
- 11. Dermis It is connective tissue that support the epidermis and attaches the epidermis to the hypodermis. Dermis is 15-40 times thicker than the epidermis Its surface consists of many ridges (dermal papillae) which interdigitate with epidermal ridges. The dermis is also the area where all the glands of the body are located. Has 2 layers/compartments 1. A thin zone immediately beneath the epidermis (the papillary dermis) and around adnexa ( the periadnexal dermis).The combination of papillary and periadnexal dermis is called Adventitial dermis 2. A thick zone of Reticular dermis that extends from the base of the papillary dermis to the surface of the subcutaneous fat
- 12. papillary dermis Papillary layer –The papillary dermis is the uppermost layer of the dermis,composed of thin haphazardly arranged collagen bundles,delicate branching elastic fibers,numerous fibrocytes,abundant ground substance.A highly developed microcirculation composed of arterioles,capillaries and venules Its superior surface is uneven (fingerlike projections) which forms the characteristic fingerprint of the finger. This layer provides the epidermis with nutrients. Pain and touch receptors are found here Together,the papillary dermis and epidermis form a morphologic and functional unit whose intimacy is reflected in their alteration jointly in various inflammatory processes A similar interrelationship exists b/w periadnexal layer and its adjacent epithelium
- 13. Reticular dermis Dense irregular Connective Tissue Has thick bundles of Collagen and coarse Elastic fibers.Proportionally, there are fewer fibrocytes and blood vessels and less ground substance compared to papillary dermis Arrangement of bundle in the direction of mechanical force give rise to the cleavage lines of Langer. Strongest layer of the Dermis.Gives the area strength.Contains sweat,sebaceous glands and pressure receptors Leather is made of this layer.
- 14. HYPODERMIS •Consists of loose connective tissue which helps in sliding the skin over the deep structure. •Consists of layer of fat according to the nutritional status of the person. •Also called as superficial fascia or panniculus adiposus VESSELS IN SKIN Arteries form the 2 plexuses. One at the junction of papillary and reticular layer( sub- papillary plexus) and another at junction of dermis and hypodermis (cutaneous plexus). Veins form the three plexuses – 2 in same position as for arterial and another in the middle of the dermis
- 16. Cutaneous Glands 1. Sebaceous (oil) glands-Sebaceous glands are microscopic glands in the skin which secrete an oily matter, called sebum, in the hair follicles to lubricate the skin and hair. In humans, they are found in greatest abundance on the face and scalp, though they are distributed throughout all skin sites except the palms and soles. An infection causes acne 2. Sweat (sudoriferous) glands - Sweat glands are exocrine glands, found in the skin , that are used for body temperature regulation. a) Eccrine glands -Eccrine glands (or merocrine glands) are found at virtually all sites on the human body. They produce clear liquid (perspiration), consisting of water, salts, and urea. b) Apocrine glands- Apocrine glands are found in axillary and genital areas, secrete a milky protein and fat substance. This mixture is an excellent source of nutrients for bacteria which produce body odour.
- 17. hair Follicle- A hair follicle is a part of the skin that grows hair by packing old cells together. Root Shaft Hair bulb Arrector pili -Arrectores pilorum (singular Arrector pili) are tiny muscle fibers attached to each hair follicle, which contract to make the hairs stand on end, causing goose bumps. Arrectores pilorum are smooth muscle, not skeletal muscle, which explains why humans cannot voluntarily give themselves goose bumps.
- 18. nails Fingernails and toenails are made of a tough protein called keratin. Along with hair and teeth they are an appendage of the skin. Free edge- The part of the nail that extends past the finger, beyond the nail plate. There should always be a free edge present to prevent infections. Nail folds (cuticle)- A fold of hard skin overlapping the base and sides of a fingernail or toenail Nail Matrix- This is the only living part of the nail. It is situated behind and underneath the Nail Fold and produces protein keratin which makes up the Nail Plate.
- 19. Embryology of skin DR.P.NIKHILESH REDDY
- 20. The skin of the embryo begins to form during the first 20 to 30 days of embryonic life, the period of active organogenesis in human development. The skin arises by the juxtaposition of two major embryological elements: The prospective epidermis, originates from a surface area of the early gastrula; ectoderm. The prospective mesoderm, which is brought into contact with the inner surface of the epidermis. The neural crest also makes contribution to the skin
- 21. Derivates of germinal layers Ectoderm: Epithelial structures like Epidermis Folliculo-sebaceous-apocrine units Eccrine units Nail units & Merkel Cells ( From Primitive Ectodermal Cells From Embryonic Epidermis) Neuroectoderm: Melanocytes Nerves & Specialised sensory receptors
- 22. Mesoderm: Langerhans cells Macrophages Mast cells Fibrocytes Blood vessels Lymph vessels Muscles adipocytes
- 24. Development of epidermis In about the third week of fetal life, the epidermis consists of a single layer of undifferentiated, glycogen-filled, a single layer of cells. Present only in prekeratinized, developing skin sloughed to amniotic fluid. The periderm: In a 4- to 6-week-old fetus, two layers of cells can be distinguished, the periderm or epitrichial layer and a stratum germinativum ( basal germinative epithelium)
- 26. Development of epidermis EGA EVENTS 3 Weeks Single Layer Of Flattened Epithelial Cells 4 Weeks Basal Germinative Layer & Periderm 3 Months Intermediate Cells ,Tonofilaments-desmosomes 5 Months Keratohyaline Granules, signs Of Cornification Starts 6 Months Cornification Completed Term Increase In Thickness Of Cornified Layers
- 28. Development of cells in epidermis Melanocytes: Derived from Neural Crest cells 8 weeks - Reach epidermis 4-6 Months - Become dendritic, synthesize & transfer melanosomes Langerhans cells : Derived from Bone marrow ( Mesoderm) In fetal life : yolk sac and/or Liver 6-7 weeks – Appear 12-14 wks - mature Merkel cells : Derived from neural crest ?? Evidence points towards origin from primitive ectodermal cells within embryonic epidermis 12 wks – appear in plantar skin 16 wks – palmar skin ( as early as 9th week in Hair )
- 29. Development of dej EGA EVENTS Early Flat Interface 1st Trimester Basal Lamina 12 Wks Interface Undulated End Of 12 Wks Mature DEJ ( As Viewed Through An Electron Microscope) 6 Months Dermal Papillae
- 30. development of dermis Intially, embryonic dermis comsists of stellate mesenchymal cells suspended in acid muco substance EGA EVENTS 12 weeks fibrocyte produce delicate collagen bundles 16 weeks i. Mature collagen bundles ii. Dermis with papillary (thin collagen bundles) and Reticular (thicker collagen bundles) becomes recognizable 24 weeks Fibrocyte derived elastic fibres appear interspread among collagen bundles
- 31. Devp. Of blood vessels,cells of dermis and sub cutaneous fat EGA EVENTS 1st Trimester Dermal network of blood & lymph vessels 1st appears 2nd Trimester Mast cells and macrophages appear in the dermis Late 2nd Trimester Beneath the dermis, mesenchymal cells surrounding BV begin to differentiate into lipid filled primitive adipocytes,as a consequence subcutaneous fat comes into being 3rd Trimester Arborizing arterial and Venous plexuses
- 32. Develeopment of neural network Origin-ectoderm of neural crest 5th week – detectable in the embryonic dermis In succeeding weeks, elaborate neural network develop consisting of autonomic motor nerves that innervate i. Blood vessels ii. Hair erector muscles iii. Eccrine & apocrine glands iv. Somatic sensory nerves v. Specialised sensory end organs ( pacini corpuscle, meissner corpuscle,mucocutaneous end organs)
- 33. Development of adnexa Folliculo-sebaceous-apocrine unit Hair follicle The earliest development of the hair rudiments occurs at about 9 weeks in the regions of the eyebrow, upper lip and chin. The bulk of the remaining follicles begin to develop at approximately 4 to 5 months gestation in a cephalad- to-caudad direction. By 17th week-first fine wisps of hair emerge from ostia on the eyebrows and forehead and cover the entire scalp by 18 weeks By 20 weeks,these lanugo hairs cover the whole cutaneous surface,except for the palms,soles,terminal phalanges of the digits,glans penis and labia minora
- 34. Follicular germ stage condensation of mesenchymal cells just beneath the slight downgrowth or “bud” of fetal basal keratinocytes.
- 35. Follicular peg stage, organization of keratinocytes in the follicle and the mesenchyme of the follicular sheath and follicular papilla located at the tip of the follicle.
- 36. Bulbous hair peg stage,(near 16th week). Two prominent bulge outgrowths the uppermost becoms the sebaceous gland and the lowermost is the insertion site of the arrector pili muscle as well as the presumptive site of the hair follicle stem cells. In many follicles, a third bud later appears above the sebaceous gland; this is the rudiment of the apocrine gland.
- 38. Sebaceous glands The sebaceous glands become differentiated at 13-15 weeks, and are then large and functional. These are, at first, solid, hemispherical protuberances on the posterior surfaces of the hair pegs. The cells contain moderate amounts of glycogen, but soon the cells in the centre lose this, and become larger and foamy as they accumulate droplets of lipid. Apocrine glands • Anlagen of apocrine glands probably develop in all hair follicles, but after the fifth month,most begin to regress,so that by term they persist in only a few sites namely the axillae,areola and the periumbilical and anogenital skin • At 24 weeks,cord of cells which becomes coiled at its base • Although the apocrine secretory segment secretes a milky fluid beginning at 7 months,apocrine glands are dormant postnatally until they resume secretory function around puberty
- 39. Eccrine glands In embryos of 12 weeks, the rudiments of eccrine sweat glands are first identifiable as regularly spaced undulations of the stratum germ. These start to develop on the palms and soles at about 3 months, but not over the rest of the body until the fifth month. Cells forming them lie palisading and closely together, but otherwise they do not differ from the rest of the stratum germinativum. By 14-15 weeks, the tips of the eccrine sweat-gland rudiments have penetrated deeply into the dermis, and have begun to form the coils
- 41. nails The nail apparatus develops during the 9th embryonic week from the epidermis of the dorsal tip of the digit as a rectangular area, the nail field. The proximal border of the nail field extends downward and proximally into the dermis to form the nail matrix primordium. at 13 weeks, four morphologic components are recognizable in the epithelium of a developing nail unit. They are the basal zone,the spinous zone,the granular zone and the cornified zone.This region now termed e[ithelium of nail bed, loses its granular zone by the twentieth week At 14 weeks,cornified cells mature at the proximal end of nail bed to form nail plate By 16 weeks,nail plate advances to cover proximal half of the nail bed By 20th week,covers its completely at which time the fetal nail resembles that of the adult
- 43. Mechanism that govern embryonal development of skin I. Mesenchyme Epithelial interaction Can occur via direct cell to cell contact or diffusible macromolecules This interdependence is exemplified by embryogenesis of follicular unit Epithelial unit will not develop from epidermis in absence of mesenchymal papilla and conversely a follicular papilla will not form in the absence of a covering epithelium II. Stratification of epidermal cells is dependant on the intactness of basal lamina Seen in re epithelisation of healing wounds The reconstitution of epidermis from keratinocytes of all ectodermally derived epithelial structures of adnexa demonstrates the pluripotentiality of adnexal keratinocytes
- 44. In conclusion The development & maintenance of skin depend on interactions between epithelium and mesenchyme,between generative epithelium cells & components of their basal lamina,and of epithelial cells with one another. These interactions collectively result in a heterogenous but unified structure i.e., skin with marked regional differentiation in form,color,consistency References i. Samuel L. Moschella and Harry J. Hurley Dermatology 3/e ii. Jean L Bolognia MD ,Joseph L Jorizzo MD ,Ronald P Rapini MD Dermatology 3/e