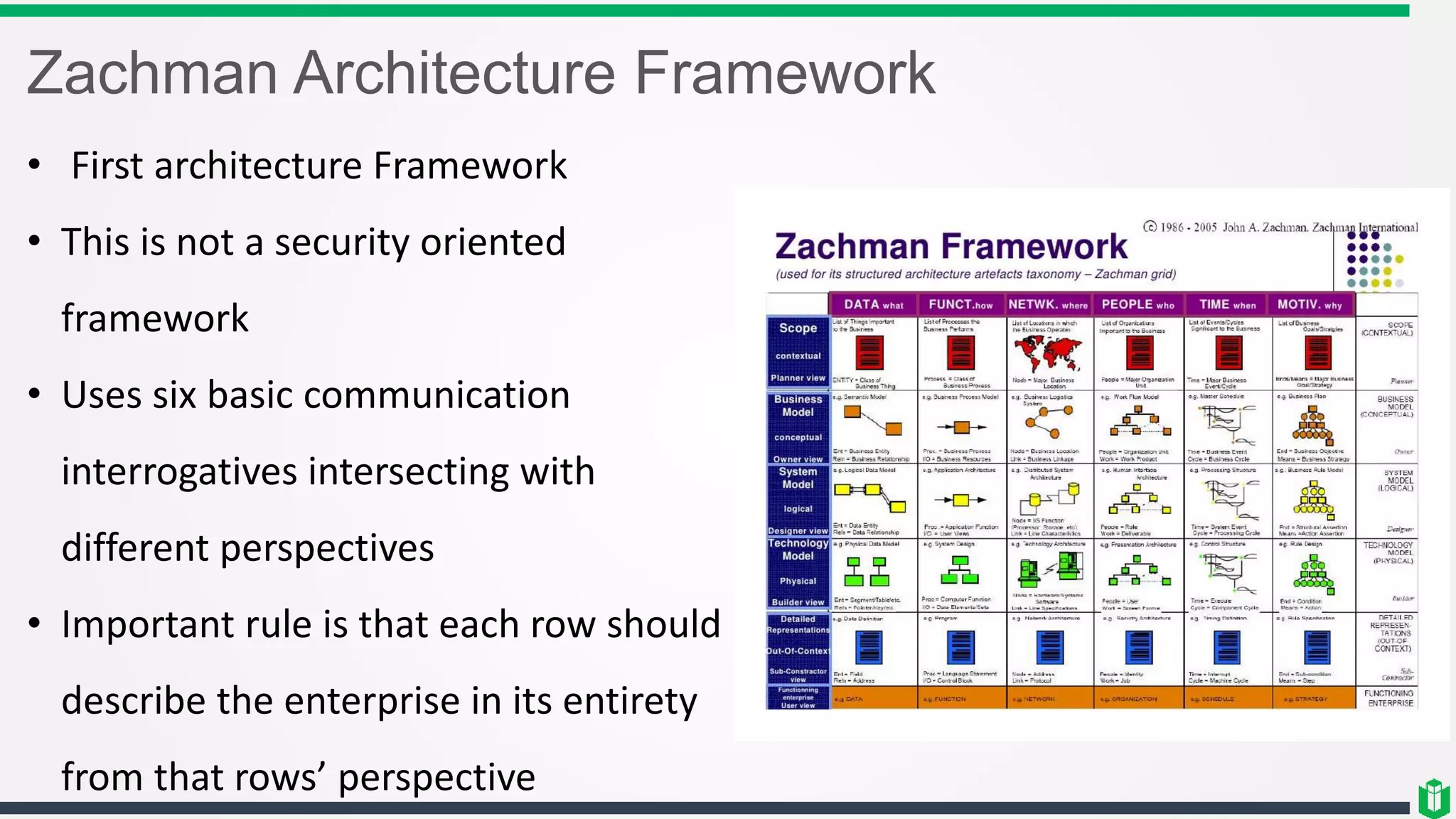
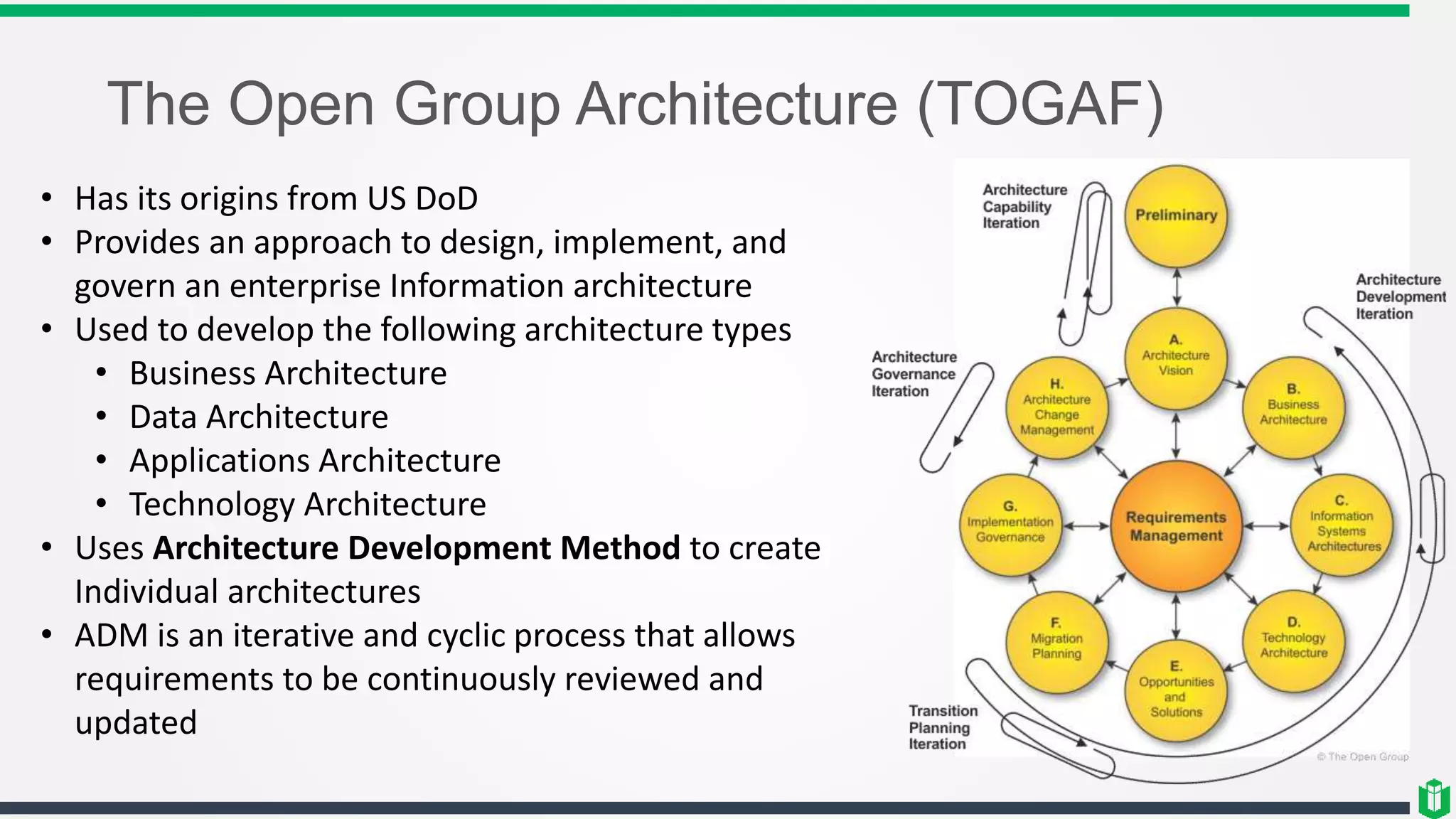
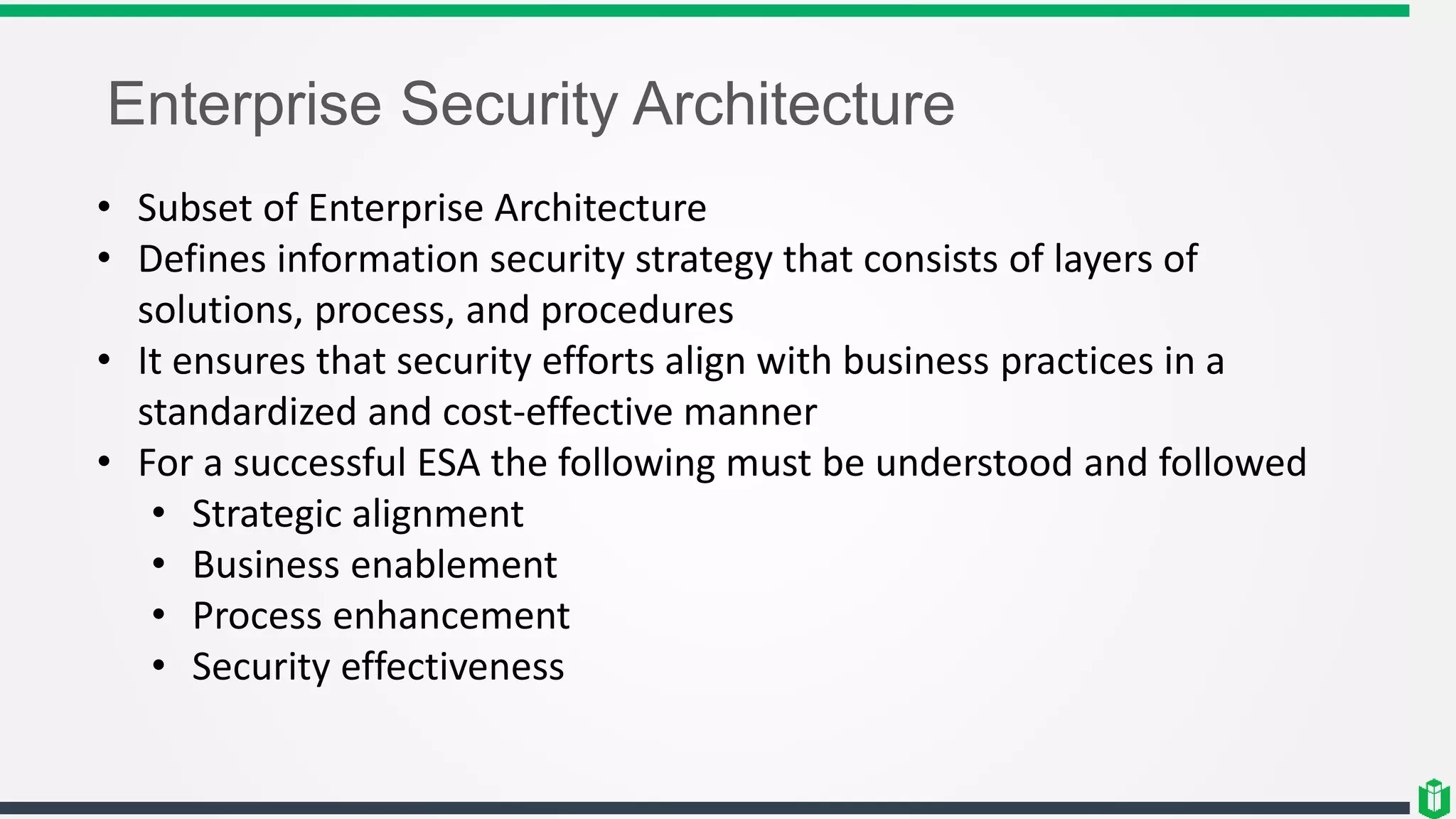
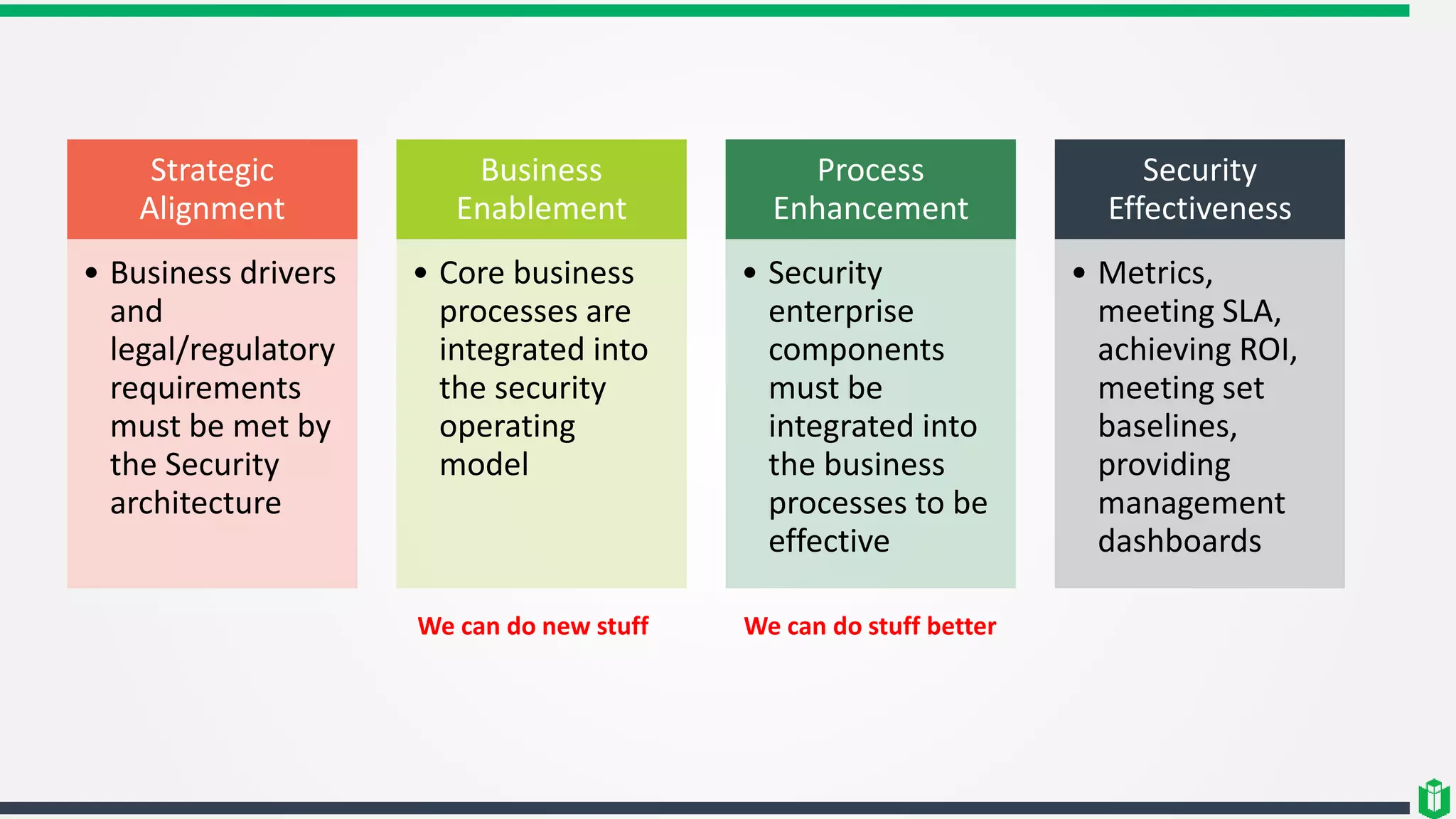
This document outlines several security frameworks that can be used to guide enterprise security architecture development. It discusses frameworks for information security management systems (ISO27000), enterprise architecture (Zachman, TOGAF), governance (COBIT, COSO), operational best practices (ITIL), and process improvement (Six Sigma, CMMI). The key aspects of a successful enterprise security architecture identified are strategic alignment with business needs, enabling business processes, enhancing existing processes, and ensuring security effectiveness through metrics and risk management.