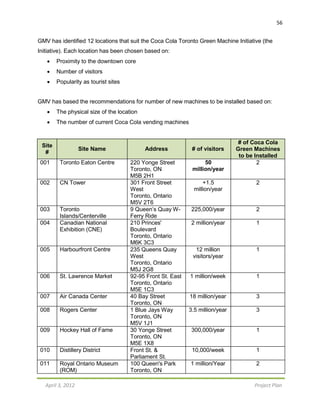
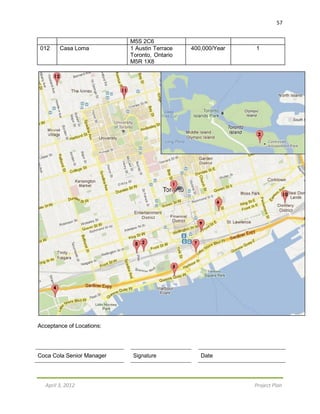
The project plan outlines the Coca-Cola green vending machine initiative by Green Machine Vending Co. (GMV) in Toronto, aimed at replacing 20 old vending machines with eco-friendly models to significantly reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. The project budget is $845,000, with a timeline from February 1, 2012, to April 30, 2012, and includes comprehensive management plans for scope, cost, quality, human resources, communication, risk, and procurement. It emphasizes the importance of stakeholder training, media promotion, and post-project evaluations to ensure successful implementation.










![15
April 3, 2012 Project Plan
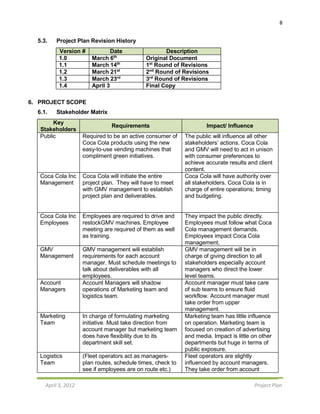
B4) On-Site Training $20,000
D) Media $200,000
D1) Print Advertising $29,000
D2) Interactive Advertising $49,000
D3) Billboard $24,000
D4) TTC Signage $23,000
D5) Trade Show $75,000
TOTAL $845,000 $845,000
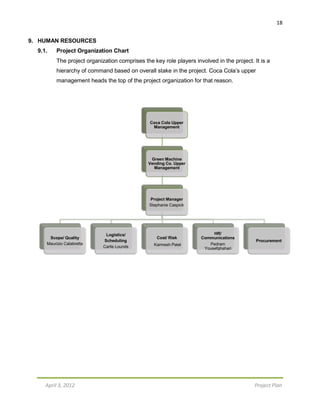
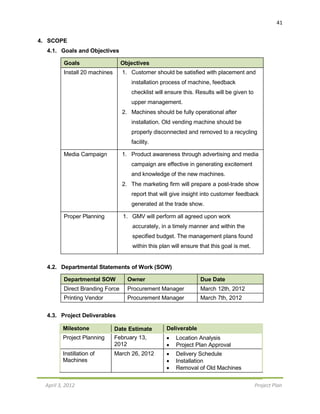
8.3. Cost Baseline (Bi-Weekly)
COSTS AT EXACT
DATES
February
[1st
-15th
]
February
[16th
-29th
]
March
[1st
-15th
]
March
[16th
-31st
]
April
[1st
-15th
]
April
[16th
-31st
]
Fri 2/3/12 $400
Mon 2/6/12 $0
Wed 2/8/12 $200
Thu 2/9/12 $14,000
Tue 2/14/12 $250
Thu 2/9/12 $150,000
Fri 2/17/12 $150
Wed 2/22/12 $7,200
Thu 2/23/12 $28,800
Thu 3/1/12 $0
Tue 3/13/12 $0
Wed 3/14/12 $500
Thu 3/15/12 $0
Mon 3/19/12 $84,000
Fri 3/16/12 $1,500
Wed 4/4/12 $500,000
Apr 4/3/12 $8,000
Thu 4/5/12 $500,000
Tue 4/30/12
TOTAL $164,850 $36,150 $500 $85,500 $558,000 $0
CUMULATIVE $164,850 $201,000 $201,500 $287,000 $845,000 $845,000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectproposal-cocacolagreenvendingmachine-161031200709/85/Project-Proposal-Coca-Cola-Green-Vending-Machine-15-320.jpg)
![16
April 3, 2012 Project Plan
$1,000,000
$800,000
$600,000
$400,000
$200,000
$0
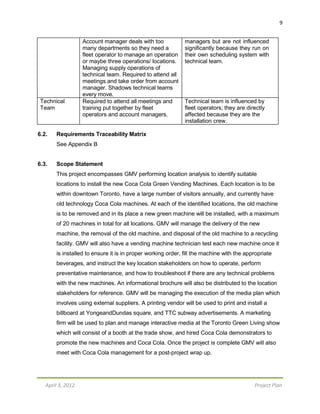
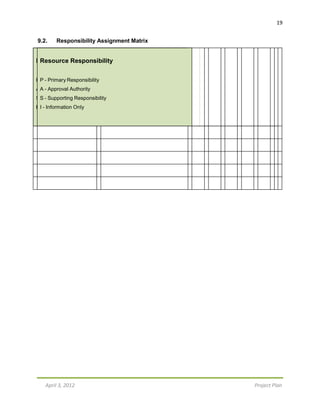
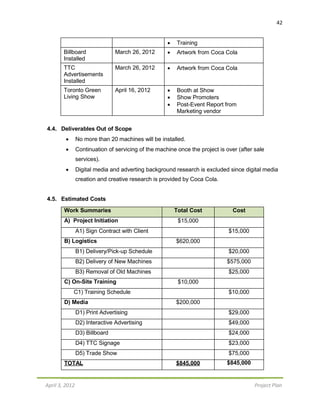
S-curve for Green Machine Vending Company
$845,000
February [1st- February [16th March [1st- March [16th- April [1st- April [16th-
15th ] -29th ] 15th] 31st] 15th] 31st]
MONTHS [X-Axis] CUMULATIVE COSTS [Y-Axis]
February [1st
-15th
] $164,850
February [16th
-29th
] $201,000
March [1st
-15th
] $201,500
March [16th
-31st
] $287,000
April [1st
-15th
] $845,000
April [16th
-31st
] $845,000
Cost Breakdown
After estimating the bi-weekly costs for the project, it has been identified that the most
expensive time frame for the project is during the first two weeks of April. The total cost
for the first 2 weeks of April is $558,000; which accumulates for 66%
($558,000/$845,000) of the total estimated budget for the project. The least expensive
week for the project is the first 2 weeks of March, where costs add up to only $500.
Bi-WeeklyBreakdown
February 1st
– 15th
: $164,850
This cost is primarily made up of preparing for the project with activities such as
identifying Toronto locations, presenting the project plan to the client, and finally
contacting the Toronto locations to ensure they permit the installation of the eco-friendly
machines on their property. The largest contributor to the cost is performing interactive
advertising. The interactive advertising costs $150,000, and is one of the most important
costs the company must sustain.
February 16th
– 29th
:$36,150
CumulativeCosrs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectproposal-cocacolagreenvendingmachine-161031200709/85/Project-Proposal-Coca-Cola-Green-Vending-Machine-16-320.jpg)

![26
April 3, 2012 Project Plan
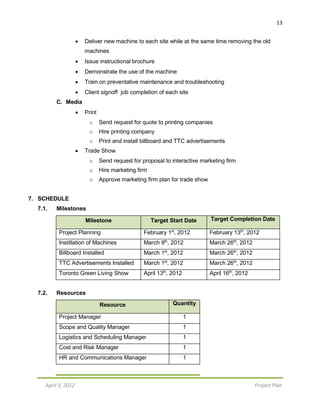
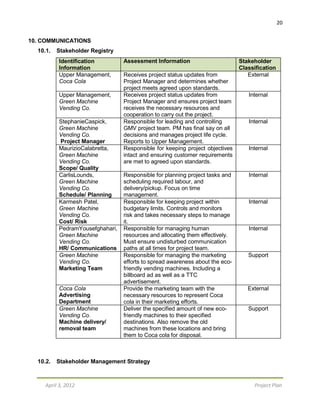
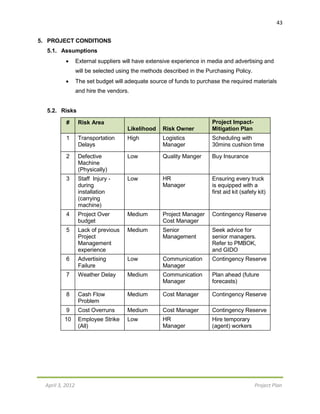
12.2. Risk Register
# Risk Event Probability
(%)
Impact
[cost]
Severity Response Who is
Responsible?
1 Employee Strike
(All)
5 $345,000 $17,250 Hire temporary
(agent) workers
HR
Manager
2 Cost Overruns 20 $100,000 $20,000 Contingency
Reserve
Cost Manager
3 Cash Flow Problem 15 $150,000 $22,500 Contingency
Reserve
Cost Manager
4 Lack of previous
Project Management
experience
5 $250,000 $12,500 Seek advice for
senior managers.
Refer to PMBOK,
and GIDO
Senior
Management
5 Defective Machine
(Physically)
15 $25,000 $3,750 Quality Checklists Quality Manger
6 Project Under
budget
15 $30,000 $4,500 Contingency
Reserve
Project
Manager
Cost Manager
7 Advertising Failure 25 $10,000 $2,500 Contingency
Reserve
Communication
Manager
8 Weather Delay 35 $2,000 $700 Plan ahead (future
forecasts)
Communication
Manager
9 Staff Injury - during
installation (carrying
machine)
10 $4,500 $450 Ensuring every
truck is equipped
with a first aid kit
(safety kit)
HR
Manager
10 Transportation
Delays
75 $1,000 $750 Scheduling with
30mins cushion
time
Schedule
Manager
TOTAL - $917,500 $84,900 - -
The Risk Register for GMV provides information on the potential risk events, the
probability of those risks, the impact, the response to the event, and finally who is
responsible for monitoring and ensuring that each event does not occur.
The probability section provides the chance of each event, if it were to occur. This
section depicts the likelihood of each event happening, and helps determine which
events should be closely monitored. A rating is given in the form of a percentage to help
show the project team a broader idea of how likely an event is.
The impact section defines the effect that each event could cause on the project. A
rating is given in terms of how much money GMV would suffer if the event took place.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectproposal-cocacolagreenvendingmachine-161031200709/85/Project-Proposal-Coca-Cola-Green-Vending-Machine-26-320.jpg)





















![58
April 3, 2012 Project Plan
APPENDIX F
Schedule Baseline
[See Hard Copy Report or MS Project File Submitted]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectproposal-cocacolagreenvendingmachine-161031200709/85/Project-Proposal-Coca-Cola-Green-Vending-Machine-58-320.jpg)
![59
April 3, 2012 Project Plan
APPENDIX G
Resource Calendar
[See Hard Copy Report or MS Project File Submitted]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectproposal-cocacolagreenvendingmachine-161031200709/85/Project-Proposal-Coca-Cola-Green-Vending-Machine-59-320.jpg)