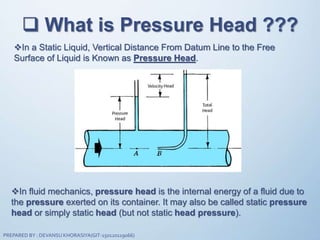
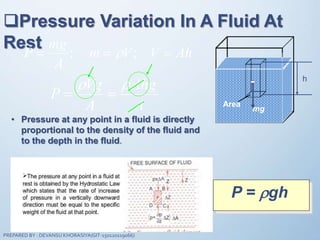
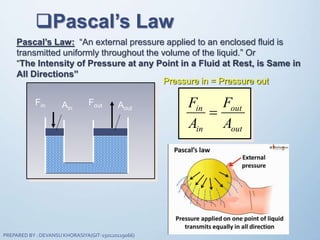
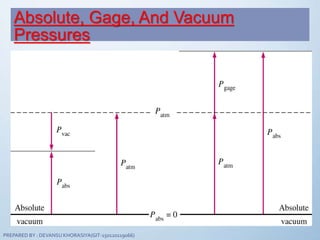
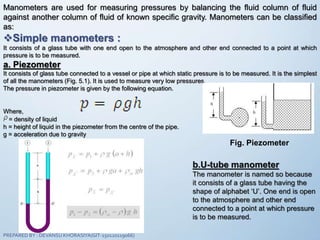
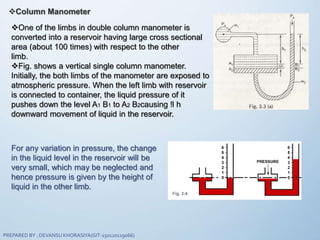
The document discusses fluid mechanics, specifically focusing on pressure and head. It defines pressure as a normal force exerted by a fluid per unit area, outlining its properties, types, and measurement methods. Additionally, it explains concepts like pressure head and Pascal's law, emphasizing the importance of fluid pressure and its application in various contexts.