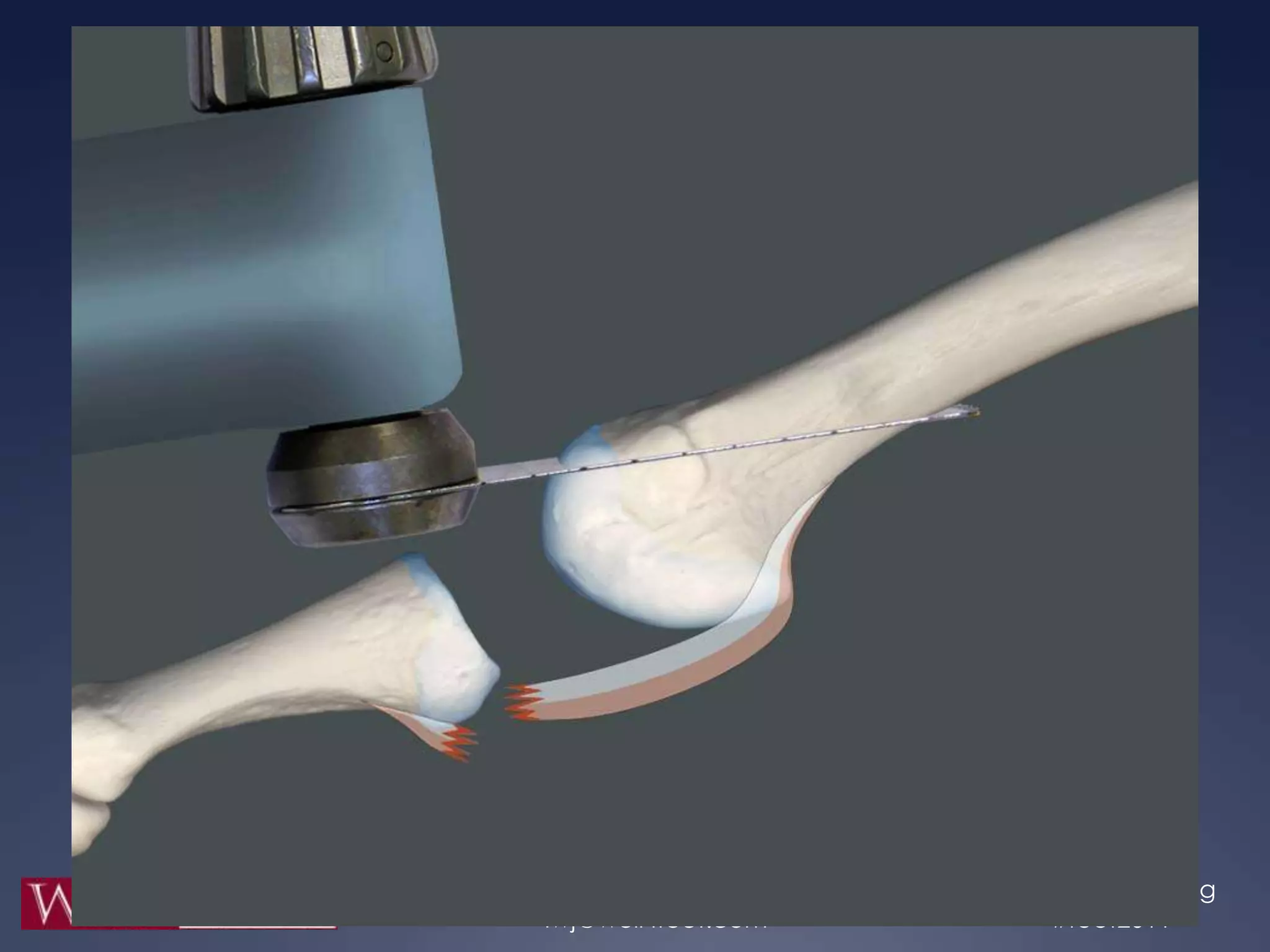
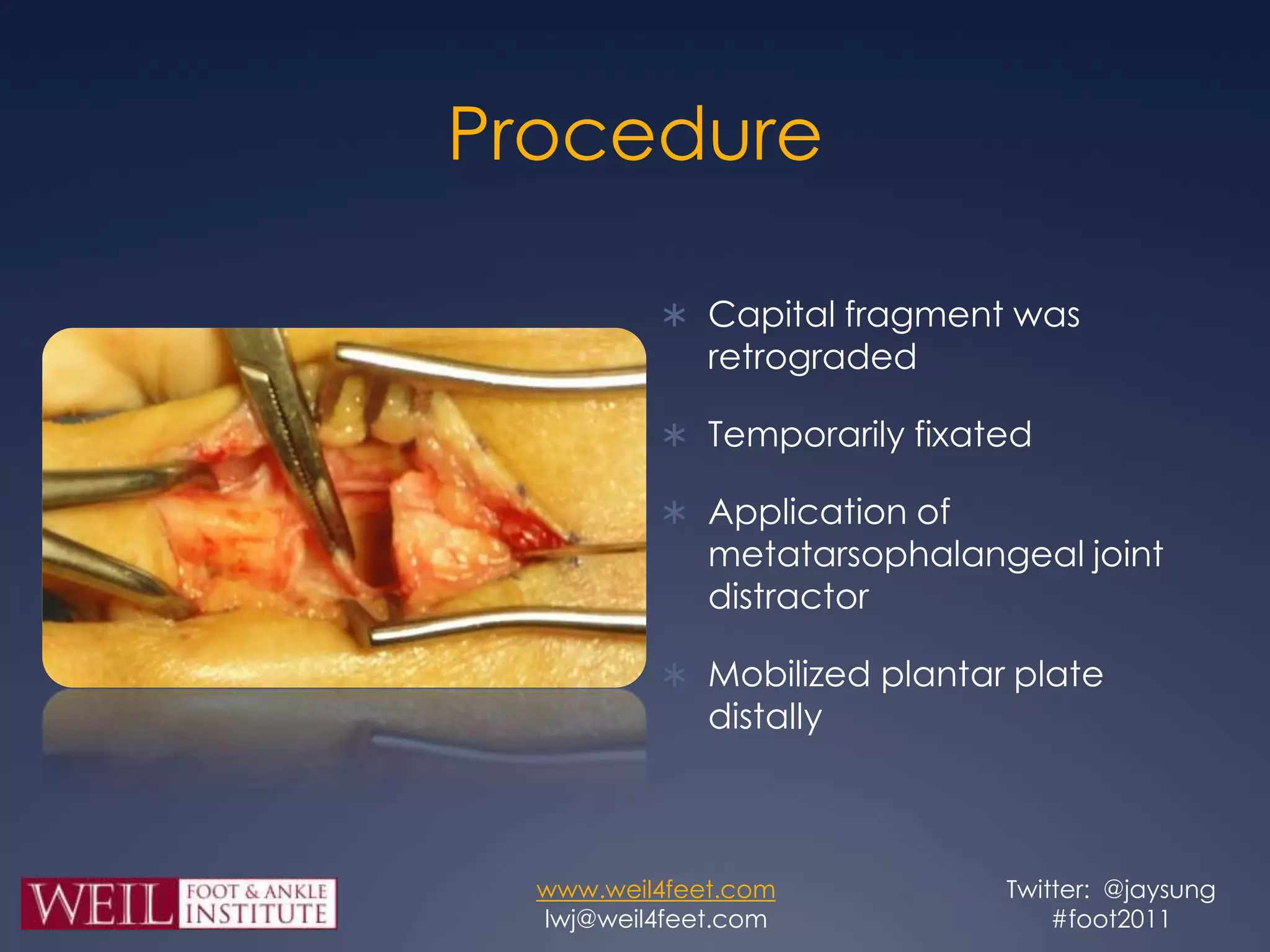
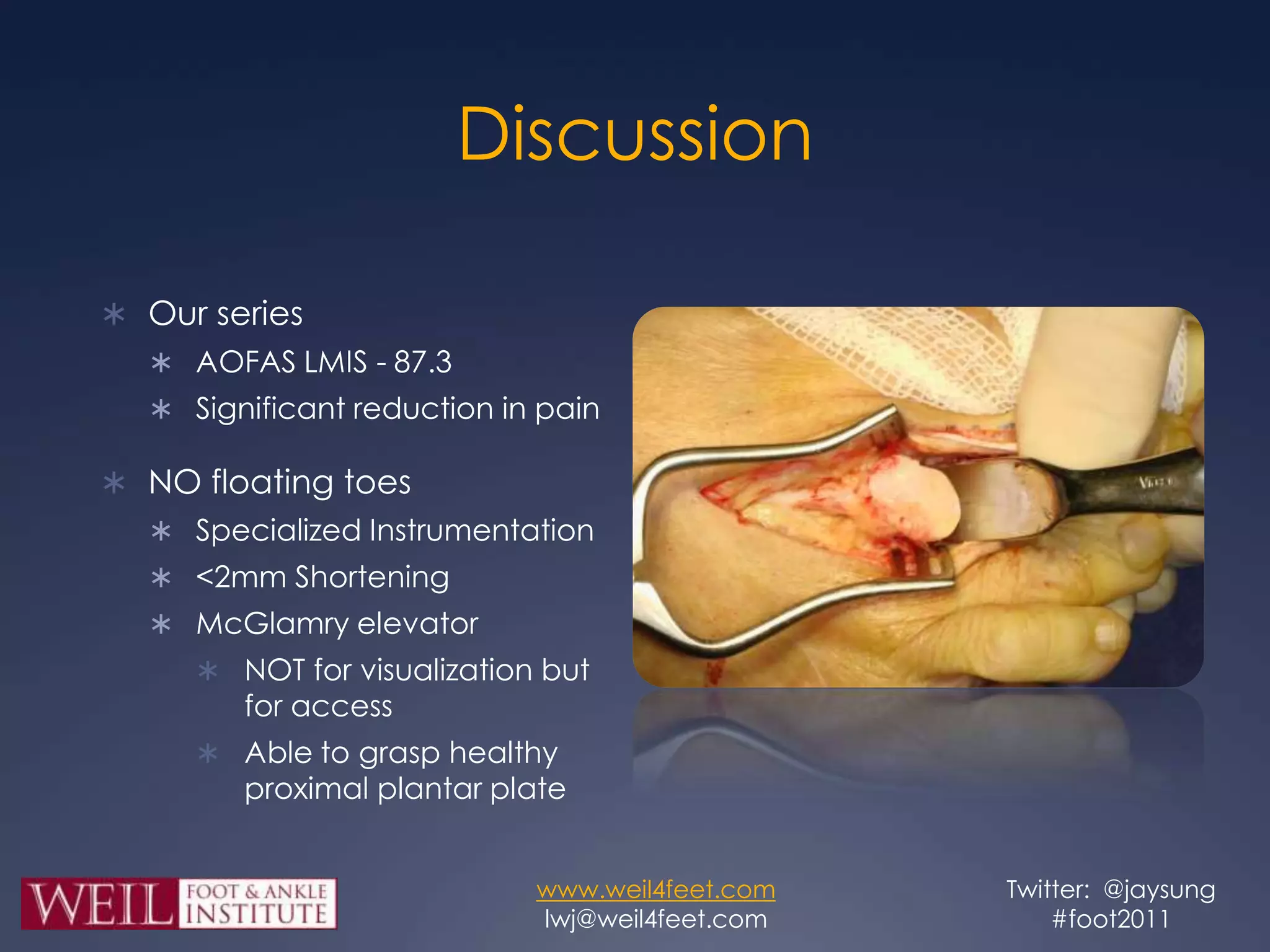
This study retrospectively reviewed 29 patients (32 feet) who underwent dorsal anatomic plantar plate repair (DAPPR) in conjunction with a Weil osteotomy to treat instability of the second metatarsophalangeal joint. Post-operatively, patients had significantly reduced pain based on VAS and improved function based on AOFAS scores. Complications included three cases each of painful stiffness and painful hardware, and one painful scar, but there were no cases of floating toes or recurrence of instability. The authors conclude that DAPPR enhances visualization and repair of plantar plates compared to plantar approaches, with favorable post-operative outcomes.