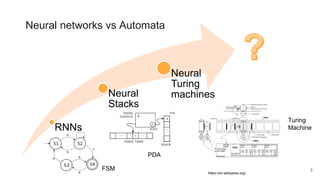
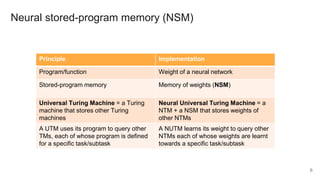
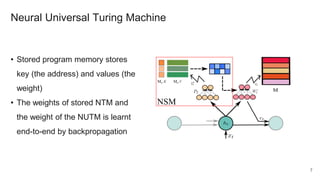
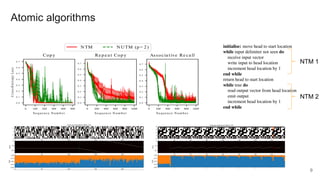
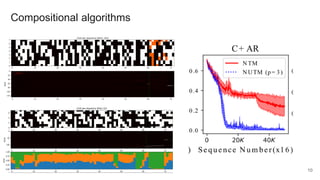
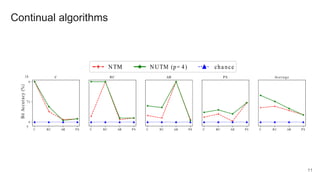
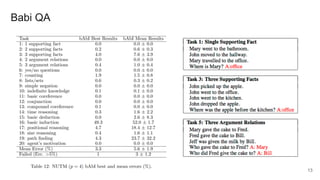
The document proposes a neural stored-program memory (NSM) that allows a neural network to simulate a universal Turing machine. The NSM stores the weights of other neural Turing machines (NTMs), with each NTM trained for a specific subtask. This allows a neural universal Turing machine (NUTM) to learn to query the appropriate NTM weights stored in memory to complete complex, multi-step tasks by breaking them into subtasks. Experiments show NSM enables NUTMs to learn atomic algorithms, compositional algorithms, continual learning, few-shot learning, and question answering—demonstrating its computational universality.