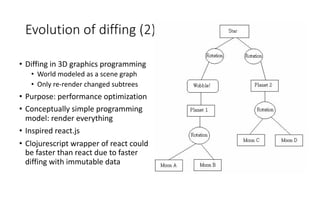
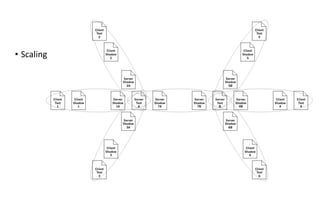
The document discusses data diffing-based software architecture patterns, detailing the evolution of diffing from its inception in the 1970s to its application in modern programming frameworks like React and ClojureScript. It highlights the benefits of diffing in decoupling system components, encouraging data model reuse, and facilitating scalable state management in applications. Several case studies illustrate the practical implementations of diffing, such as in collaborative editing and state externalization.















![Case study: reduce component dependency
• Stateful components depend on one another
• Introducing user invokable system functions,
leads to circular dependency, e.g.
(juji.func.system/cleanup-chat rep)
System
Rep
Reps
Rep
Subs
func.system
[:rt jujiid]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diffing-200623215705/85/Data-Diffing-Based-Software-Architecture-Patterns-17-320.jpg)





![Data modeling guideline: Don’t use vector
• Minimize unnecessary use of ordered data structure, e.g. vector or
list
• Diffing algorithm is slow for ordered data, because order is a strong
constraint to satisfy
• Ordered O(mn) vs. Unordered O(m+n)
• The implicit order of data elements are often source of incidental complexity
• Meaningful order is often based on data fields
• Sets or maps suffice in most cases
[ {} {} {} … ]
Bad
{ {} {} {} … } #{ {} {} {} … }
Good](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diffing-200623215705/85/Data-Diffing-Based-Software-Architecture-Patterns-24-320.jpg)

