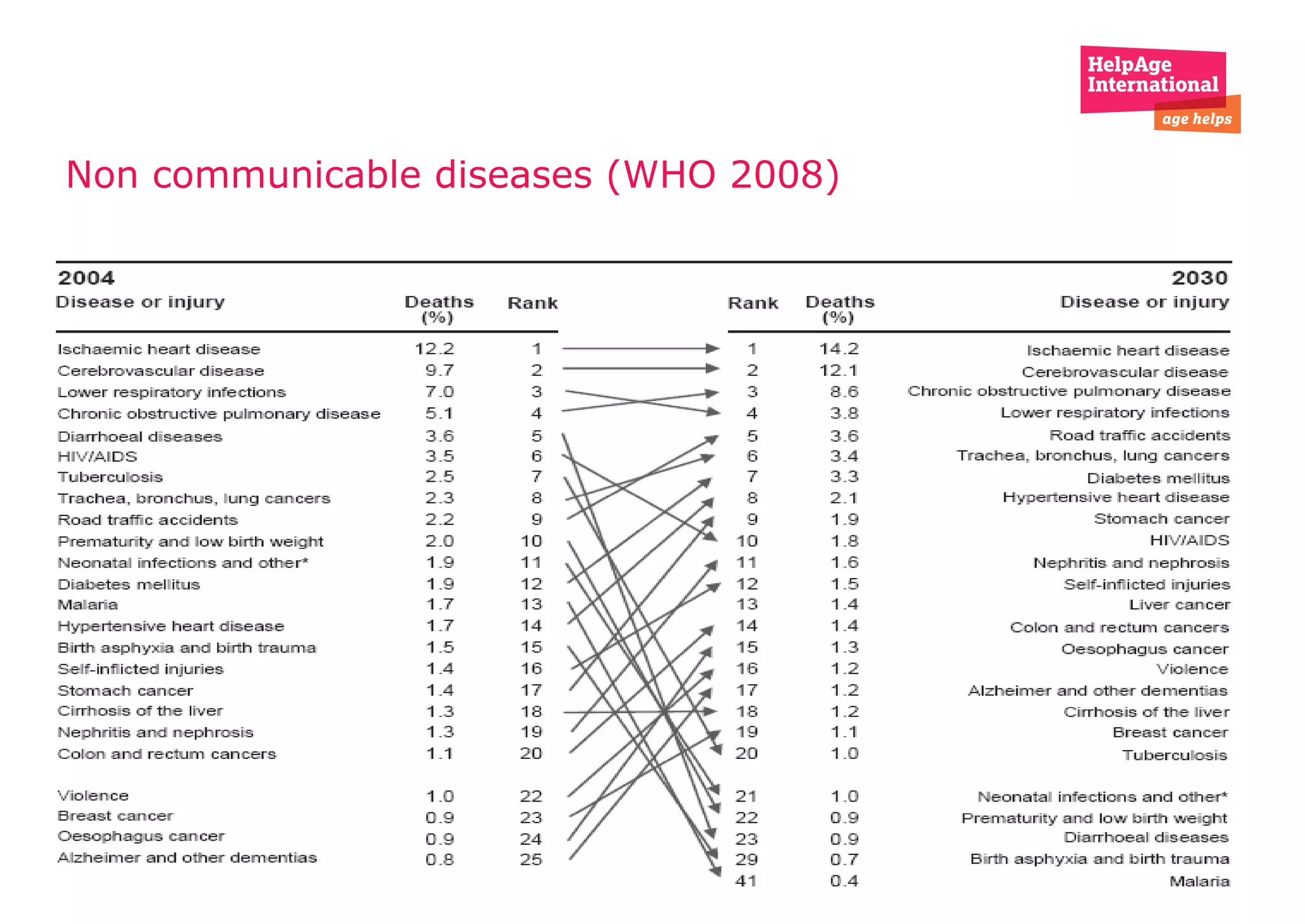
The document discusses aging, disability, and development. It notes that disability is an umbrella term covering impairments, activity limitations, and participation restrictions due to problems with body function/structure, task execution difficulties, and life situation involvement problems respectively. Disability is a complex phenomenon influenced by both individual and societal factors. Common causes of disability and loss of livelihood among older adults include hearing loss, vision problems, and mental disorders. Fewer than 25% of those affected by conditions like Alzheimer's and depression have access to adequate treatment. The document calls for a focus on chronic but treatable conditions and wider access to low-cost interventions to help older adults live productively.
![Ageing, disability and development Disability Mainstreaming Forum DFID 3 rd March 2009 Sylvia Beales HelpAge International [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationageinganddisabilitysylviabeales-111124080411-phpapp01/75/Presentation-ageing-and-disability-1-2048.jpg)