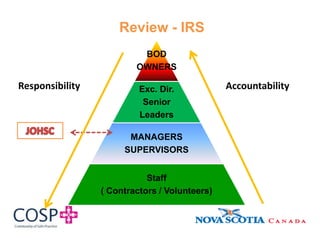
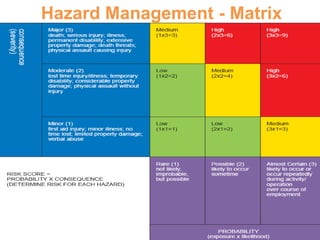
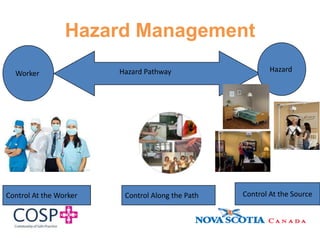
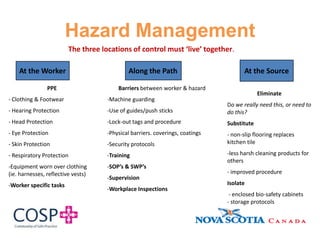
This document discusses hazard identification and control in the workplace. It reviews key elements of a hazard management system including internal responsibility systems, responsibilities of employers and employees, and relevant occupational health and safety laws. Main hazards in healthcare settings like overexertion, falls, violence, and infectious diseases are identified. The process of identifying, assessing, and controlling hazards is explained through a hazard matrix. Challenges of hazard management in healthcare and ways to improve control of hazards are also covered.