This document provides guidance on managing change, restructuring, and redundancy. It discusses:
- Planning change carefully using models like Kotter's 8 steps for leading change. This includes forming a team, establishing urgency, and communicating vision.
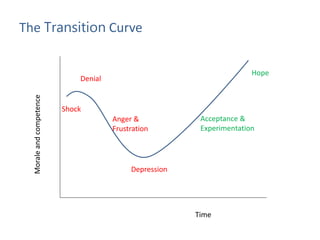
- Managing risks like disruptive behavior, legal issues, and loss of productivity through thoughtful communication, consultation, and support for employees.
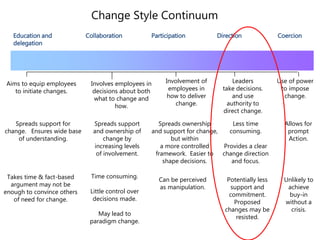
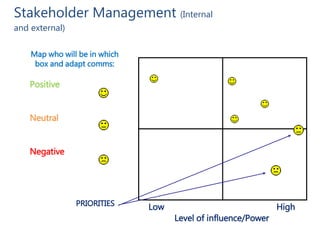
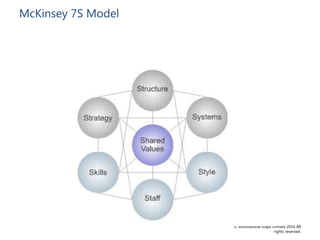
- Tailoring the approach to each situation and different stakeholders. Methods may range from education to direction depending on influence and power.
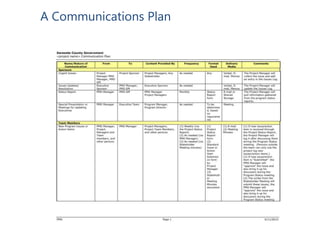
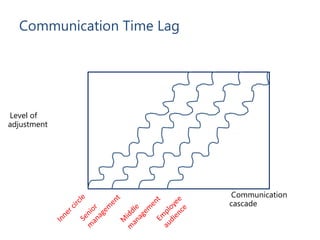
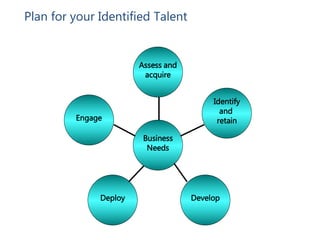
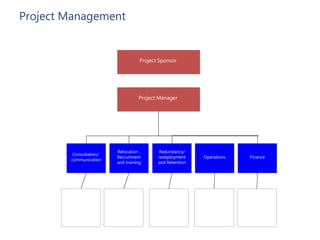
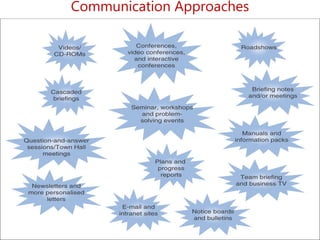
- Key steps include mapping stakeholders, developing a communications plan, manager training, project management, and addressing business needs like identifying and retaining talent.
- The ultimate goal is to help the company and employees through change while maintaining