ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.pptx
- 1. ZERA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE OF HEALTH SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DR M.KATASO THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
- 2. INTRODUCTION 1. The nervous and endocrine systems act together to coordinate functions of all body systems. 2. The nervous system controls homeostasis through nerve impulses and neurotransmitters, which act locally and quickly. The endocrine system uses hormones, which act more slowly in distant parts of the body. 3. The nervous system controls neurons, muscle cells, and glandular cells; the endocrine system regulates virtually all body cells. 4. A hormone is a mediator molecule that is released in one part of the body but regulates the activity of cells in other parts of the body.
- 3. COMPARISON OF CONTROL BY THE NERVOUS SYSTEM & ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
- 4. ENDOCRINE GLAND 1. Exocrine glands (sudoriferous, sebaceous, mucous, and digestive) secrete their products through ducts into body cavities or onto body surfaces. Endocrine glands secrete hormones into interstitial fluid. Then, the hormones diffuse into the blood. 2. The endocrine system consists of endocrine glands (pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and pineal glands) and other hormone secreting tissues (hypothalamus, thymus, pancreas, ovaries, testes, kidneys, stomach, liver, small intestine, skin, heart, adipose tissue, and placenta).
- 5. HORMONE ACTIVITY 1. Hormones affect only specific target cells that have receptors to recognize (bind) a given hormone. The number of hormone receptors may decrease (down-regulation) or increase (up-regulation). 2. Circulating hormones enter the bloodstream; local hormones (paracrine and autocrine) act locally on neighboring cells. 3. Chemically, hormones are either lipid-soluble (steroids, thyroid hormones, and nitric oxide) or water-soluble (amines; peptides, proteins, and glycoproteins; and eicosanoids). 4. Water-soluble hormone molecules circulate in the watery blood plasma in a “free” form (not attached to plasma proteins); most lipid-soluble hormones are bound to transport proteins synthesized by the liver.
- 6. CHEMICAL CLASSES OF HORMONES
- 7. CHEMICAL CLASSES OF HORMONES
- 8. MEACHANISM OF ACTION OF HORMONES 1. Lipid-soluble steroid hormones and thyroid hormones affect cell function by altering gene expression. 2. Water-soluble hormones alter cell function by activating plasma membrane receptors, which elicit production of a second messenger that activates various enzymes inside the cell. 3. Hormonal interactions can have three types of effects: permissive, synergistic, or antagonistic.
- 9. MOA OF LIPID SOLUBLE
- 10. MOA OF WATER SOLUBLE
- 11. CONTROL OF SECRETION 1. Hormone secretion is controlled by signals from the nervous system, chemical changes in blood, and other hormones. 2. Negative feedback systems regulate the secretion of many hormones.
- 12. HYPOTHALAMUS & PITUITARY GLAND 1. The hypothalamus is the major integrating link between the nervous and endocrine systems. 2. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland regulate virtually all aspects of growth, development, metabolism, and homeostasis. 3. The pituitary gland is located in the hypophyseal fossa and is divided into the anterior pituitary (glandular portion), the posterior pituitary (nervous portion), and the pars intermedia (avascular zone in between). 4. Secretion of anterior pituitary hormones is stimulated by releasing hormones and suppressed by inhibiting hormones from the hypothalamus. 5. The blood supply to the anterior pituitary is from the superior hypophyseal arteries. Hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones enter the primary plexus and flow to the secondary plexus in the anterior pituitary by the hypophyseal portal veins.
- 13. CONT,,,, • The anterior pituitary consists of somatotrophs that produce human growth hormone (hGH); lactotrophs that produce prolactin (PRL); corticotrophs that secrete adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH); thyrotrophs that secrete thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH); and gonadotrophs that synthesize follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). • Human growth hormone (hGH) stimulates body growth through insulin like growth factors (IGFs). Secretion of hGH is inhibited by GHIH (growth hormone–inhibiting hormone, or somatostatin) and promoted by GHRH (growth hormone–releasing hormone). • TSH regulates thyroid gland activities. Its secretion is stimulated by TRH (thyrotropin-releasing hormone) and suppressed by GHIH. • FSH and LH regulate the activities of the gonads—ovaries and testes. Their secretion is controlled by GnRH (gonadotropin releasing hormone). • Prolactin (PRL) helps initiate milk secretion. Prolactin-inhibiting hormone (PIH) suppresses secretion of PRL; prolactin-releasing hormone (PRH) and TRH stimulate PRL secretion.
- 14. CONT,, • ACTH regulates the activities of the adrenal cortex and is controlled by CRH (corticotropin-releasing hormone). • Dopamine inhibits secretion of MSH. • The posterior pituitary contains axon terminals of neurosecretory cells whose cell bodies are in the hypothalamus. • Hormones made by the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary are oxytocin (OT), which stimulates contraction of the uterus and ejection of milk from the breasts, and antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which stimulates water reabsorption by the kidneys and constriction of arterioles. • Oxytocin secretion is stimulated by uterine stretching and suckling during nursing; ADH secretion is controlled by osmotic pressure of the blood and blood volume.
- 20. THYROID GLAND
- 21. THYROID HORMONE • The thyroid gland is located inferior to the larynx. • It consists of thyroid follicles composed of follicular cells, which secrete the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), and parafollicular cells, which secrete calcitonin (CT). • Thyroid hormones are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine within thyroglobulin (TGB). They are transported in the blood bound to plasma proteins, mostly thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG). • Secretion is controlled by TRH from the hypothalamus and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the anterior pituitary. • Thyroid hormones regulate oxygen use and metabolic rate, cellular metabolism, and growth and development. • Calcitonin (CT) can lower the blood level of calcium ions (Ca2+) and promote deposition of Ca2+ into bone matrix. Secretion of CT is controlled by the Ca2+level in the blood.
- 22. ACTIONS OF THYROID HORMONES 1. Thyroid hormones increase basal metabolic rate (BMR): When the basal metabolic rate increases, cellular metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins increases. 2. A second major effect of thyroid hormones is to stimulate synthesis of additional sodium- potassium pumps (Na/K ATPase), which use large amounts of ATP to continually eject sodium ions (Na+) from the cytosol into the extracellular fluid and potassium ions (K+) from the extracellular fluid into the cytosol. As cells produce and use more ATP, more heat is given off, and body temperature rises. This phenomenon is called the calorigenic effect. In this way, thyroid hormones play an important role in the maintenance of normal body temperature. 3. In the regulation of metabolism, the thyroid hormones stimulate protein synthesis and increase the use of glucose and fatty acids for ATP production. They also increase lipolysis and enhance cholesterol excretion, thus reducing blood cholesterol level. 4. The thyroid hormones enhance some actions of the catecholamines (norepinephrine and epinephrine) because they up-regulate beta receptors. 5. Together with human growth hormone and insulin, thyroid hormones accelerate body growth, particularly the growth of the nervous and skeletal systems.
- 23. PARATHYROID GLAND • The parathyroid glands are embedded in the posterior surfaces of the lateral lobes of the thyroid gland. They consist of chief cells and oxyphil cells. • Parathyroid hormone (PTH) regulates the homeostasis of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate ions by increasing blood calcium and magnesium levels and decreasing blood phosphate levels. PTH secretion is controlled by the level of calcium in the blood.
- 24. ADRENAL GLANDS
- 25. ADRENAL GLAND
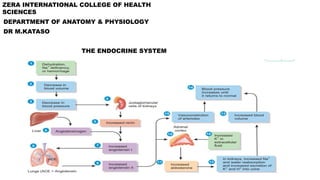
- 26. ADRENAL GLAND 1. The adrenal glands are located superior to the kidneys. They consist of an outer adrenal cortex and inner adrenal medulla. 2. The adrenal cortex is divided into a zona glomerulosa, a zona fasciculata, and a zona reticularis; the adrenal medulla consists of chromaffin cells and large blood vessels. 3. Cortical secretions include mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens. 4. Mineralocorticoids (mainly aldosterone) increase sodium and water reabsorption and decrease potassium reabsorption. Secretion is controlled by the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone (RAA) pathway and by K level in the blood. 5. Glucocorticoids (mainly cortisol) promote protein breakdown, gluconeogenesis, and lipolysis; help resist stress; and serve as anti-inflammatory substances. Their secretion is controlled by ACTH. 6. Androgens secreted by the adrenal cortex stimulate growth of axillary and pubic hair, aid the prepubertal growth spurt, and contribute to libido. 7. The adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine (NE), which are released during stress and produce effects similar to sympathetic responses
- 27. RAAS
- 28. PANCREATIC ISLETS • The pancreas lies in the curve of the duodenum. It has both endocrine and exocrine functions. • The endocrine portion consists of pancreatic islets or islets of Langerhans, made up of four types of cells: alpha, beta, delta, and F cells. • Alpha cells secrete glucagon, beta cells secrete insulin, delta cells secrete somatostatin, and F cells secrete pancreatic polypeptide. • Glucagon increases blood glucose level; insulin decreases blood glucose level. Secretion of both hormones is controlled by the level of glucose in the blood.
- 29. OVARIES & TESTIS • The ovaries are located in the pelvic cavity and produce estrogens, progesterone, and inhibin. These sex hormones govern the development and maintenance of female secondary sex characteristics, reproductive cycles, pregnancy, lactation, and normal female reproductive functions. • The testes lie inside the scrotum and produce testosterone and inhibin. These sex hormones govern the development and maintenance of male secondary sex characteristics and normal male reproductive functions.