lec6.ppt
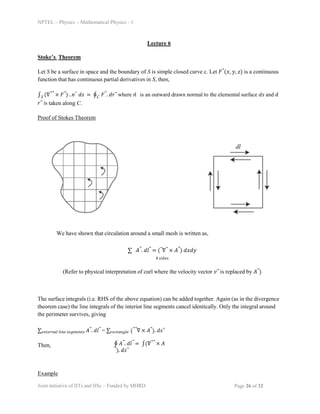
- 1. NPTEL – Physics – Mathematical Physics - 1 Lecture 6 Stoke’s Theorem Let S be a surface in space and the boundary of S is simple closed curve c. Let 𝐹⃗(𝑥, 𝑦, 𝑧) is a continuous function that has continuous partial derivatives in S, then, ∫𝑆 (∇⃗⃗ × 𝐹⃗) . nˆ 𝑑𝑠 = ∮𝐶 𝐹⃗. 𝑑𝑟⃗ where 𝑛̂ is an outward drawn normal to the elemental surface 𝑑𝑠 and 𝑑 𝑟⃗ is taken along C. Proof of Stokes Theorem We have shown that circulation around a small mesh is written as, ∑ 𝐴⃗. 𝑑𝑙⃗ = (⃗∇⃗ × 𝐴⃗) 𝑑𝑥𝑑𝑦 4 𝑠𝑖𝑑𝑒𝑠 (Refer to physical interpretation of curl where the velocity vector 𝑣⃗ is replaced by 𝐴⃗) The surface integrals (i.e. RHS of the above equation) can be added together. Again (as in the divergence theorem case) the line integrals of the interior line segments cancel identically. Only the integral around the perimeter survives, giving ∑𝑒𝑥𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑛𝑎𝑙 𝑙𝑖𝑛𝑒 𝑠𝑒𝑔𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑠 𝐴⃗. 𝑑𝑙⃗ = ∑𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒 (⃗⃗∇ × 𝐴⃗). 𝑑𝑠⃗ Then, ∮ 𝐴⃗. 𝑑𝑙⃗ = ∫(∇⃗⃗ × 𝐴 ⃗). 𝑑𝑠⃗ Example Joint initiative of IITs and IISc – Funded by MHRD Page 26 of 32
- 2. NPTEL – Physics – Mathematical Physics - 1 Verify Stokes theorem for 𝐹⃗ = (2𝑥 − 𝑦)𝑖̂ − 𝑦𝑧2𝑗̂ − 𝑦2𝑧𝑘̂ for the paraboloid S devoted by 𝑧 = 𝑓(𝑥, 𝑦) = 1 − (𝑥2 + 𝑦2) 𝑧 ≥ 0 Or the upper half surface of a sphere. In z = 0 plane the boundary c of the surface S is a circle 𝑥2 + 𝑦2 = 1 A convenient way to determine the line integral (refer to Stoke’s theorem) is to substitute 𝑥 = cos 𝑡, 𝑦 = 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑡. 0 ≤ 𝑡 ≤ 2𝜋 and 𝑧 = 0. Thus ∮ 𝐹⃗. 𝑑𝑟⃗ = ∮(2𝑥 − 𝑦). (𝑑𝑥 iˆ + 𝑑𝑦 ˆj + 𝑑𝑧 kˆ ) 𝑐 𝑐 = ∮ (2𝑥 − 𝑦)𝑑𝑥 = ∫ 2𝜋 (2𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑡 − 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑡)(−𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑡)𝑑𝑡 𝑐 0 =𝜋 Also ⃗∇⃗ × 𝐹⃗ = Kˆ (𝑧̂), 𝑆𝑜 ∫(∇⃗⃗ × 𝐹⃗). 𝑑𝑠⃗ = ∫ 𝑧̂. nˆ 𝑑𝑠 = ∫ 𝑑𝑥𝑑𝑦 = ∫𝑥=−1 1 ∫𝑦=−√1−𝑥2 𝑑𝑥𝑑𝑦 √1−𝑥2 = 𝜋. (verified) Joint initiative of IITs and IISc – Funded by MHRD Page 27 of 32
- 3. NPTEL – Physics – Mathematical Physics - 1 Green’s theorem in a plane Let R be a closed bounded region in the 𝑥𝑦 plane which has a boundary C. Let 𝐹1(𝑥, 𝑦) and 𝐹2(𝑥,𝑦) functions that are continuous partial derivatives in a domain that contains R, then ∫ ( − ) 𝑑𝑥𝑑𝑦 = ∮(𝐹1𝑑𝑥 + 𝐹2 𝑑𝑦) 𝛿𝐹2 𝛿𝑥 𝛿𝑦 𝛿𝐹1 𝑅 𝑐 We shall present this theorem without proof. Example Verify Green’s theorem for, 𝐹1(𝑥, 𝑦) = 𝑦2 − 7𝑦 𝐹2(𝑥, 𝑦) = 2𝑥𝑦 + 2𝑥 And C is a circle 𝑥2 + 𝑦2 = 1 Thus, ∫ (𝛿𝐹2 − 𝛿𝑥 𝛿𝑦 𝑅 𝛿𝐹1 )𝑑𝑥𝑑𝑦 = ∫𝑅 [(2𝑦 + 2) − (2𝑦 − 7)]𝑑𝑥𝑑𝑦 = 9 ∫ 𝑑𝑥𝑑𝑦 = 9𝜋 Where 𝜋 is the area of the circle of unit radius. Since C is a circle, it is convenient to introduce 𝑥 = 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑡, 𝑦 = 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑡, 𝑑𝑥 = −𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑡, 𝑑𝑦 = 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑡 So, 𝐹1 = 𝑠𝑖𝑛2𝑡 − 7𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑡, 𝐹2 = 2𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑡 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑡 + 2𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑡 2𝜋 ∮(𝐹1𝑑𝑥 + 𝐹2 𝑑𝑦) = ∫ (𝑠𝑖𝑛2𝑡 − 7𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑡)(−𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑡) + (2𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑡 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑡 + 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑡)(𝑐𝑜𝑠𝑡)𝑑𝑡 𝐶 0 = 9𝜋 Thus Green’s theorem is verified. Joint initiative of IITs and IISc – Funded by MHRD Page 28 of 32
- 4. NPTEL – Physics – Mathematical Physics - 1 Vector calculus in curvilinear coordinate system It is very important for the students to understand vector calculus in curvilinear systems where the basis vectors (such as 𝑟̂, ̂ etc) are not constants. For a point in eartesian coordinate space, 𝑟⃗ = (𝑥, 𝑦, 𝑧) is used to denote the distances from the three orthogonal axes. In cylindrical coordinates, the same point is denoted by (𝜌, 𝜑, 𝑧). While these quantities are not necessarily distances (such as 𝜑 being an angle), however to convert them to distances, we use the relations, 𝑥 = 𝜌𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜑, 𝑦 = 𝜌𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜑, 𝑧 = 𝑧 So the same point in space in terms of distances is (𝜌𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜑, 𝜌𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜑, 𝑧). Let us now discuss the scenario for basis vectors. A coordinate system {𝑥𝑖} allows us to define bases for all of these vector spaces through. ê = 𝑒 i 𝜕𝑟 𝜕𝑥𝑖 For Cartesian systems, the basis vectors are eˆ iˆ , eˆ ˆj and eˆ kˆ pointing along the three x y z orthogonal coordinate axes. They are also constants, that is their directions do not change with the point 𝑟 . Now for curvilinear coordinates, such as for a cylindrical polar coordinate system, the basis vectors are given by, ê 1 r sinê cosê p x y x y z z ê r cosê sinê ê ê The in the definition of 𝑒̂𝜑 is needed for the vector to be properly normalized to 1. Joint initiative of IITs and IISc – Funded by MHRD Page 29 of 32 1 An inversion of the above relations is also possible which will yield eˆx , eˆy and eˆz in terms of eˆ , 𝑒̂ 𝜑and eˆz . Similarly a vector field 𝐹 , can be written in the cylindrical polar coordinates as {(𝐹𝑥𝑐𝑜𝑠 + 𝐹𝑦𝑠𝑖𝑛), (−𝐹𝑥𝑠𝑖𝑛 + 𝐹𝑦𝑐𝑜𝑠), 𝐹𝑧} The basis vectors obey the usual relations for an orthogonal right handed bases, that is
- 5. NPTEL – Physics – Mathematical Physics - 1 eˆ .eˆ and eˆ eˆ ˆ 𝜀𝛼𝛽𝛾 = 1 𝑖𝑓 𝛼, 𝛽, 𝛾 are cyclic = −1 otherwise = 0 if two indices are same Partial derivatives: Partial derivatives with respect to the coordinates can be a good starting point for our present discussion. For example, 𝜕𝑝 = 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜕𝑥 + 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜕𝑦 𝜕𝜙 = − 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜕𝑥 + 𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜕𝑦 𝜕𝑧 = 𝜕𝑧 While the inverse relations are, 𝑃 𝜕𝑥 = 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝜕𝑝 − 𝜕 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝜙 𝜕𝑦 = 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜕𝑝 + 𝜕 𝑐𝑜𝑠 𝜙𝑃 and 𝜕𝑧 = 𝜕𝑧 Thus the del (⃗∇⃗) operator is written by using the relations, 𝜕𝑥 ∇⃗⃗= (𝜕𝑦) = eˆx 𝜕𝑥 + eˆy 𝜕𝑦 + eˆz 𝜕𝑧 𝜕𝑧 ê 1 ê ê p p p z z z Thus gradient of a scalar field is written as, 𝐴 = 𝜋𝑟2 ∇⃗⃗𝑣(𝜌, 𝜑, 𝑧) = eˆ 𝑣 + 𝑣 + eˆz z 𝑣 Joint initiative of IITs and IISc – Funded by MHRD Page 30 of 32 ê While the divergence is written as,
- 6. NPTEL – Physics – Mathematical Physics - 1 ∇⃗⃗. 𝐹 = (𝑃𝐹𝜌) + 𝐹 + z 𝐹𝑧 A derivation of the divergence formula can be shown as follows. There are two non zero partial derivatives of the unit vectors, namely 1 eˆp =-cos 𝜑 eˆx -sin𝜑 eˆy =- eˆ 𝜑 𝑒̂ = −𝑠𝑖𝑛ϕ eˆ + 𝑐𝑜𝑠φ eˆ = − eˆ x y Thus the divergence in general is NOT given by ∇⃗⃗. 𝐹 (𝛾 ) = ∑𝑖 𝜕𝑖𝐹𝑖 (𝛾 ) which is only true for an orthogonal coordinate system where the basis vectors are constant in space. Hence using the product rule, ∇⃗⃗. 𝐹 = [ eˆ + + eˆz z ] . [𝐹𝑃 eˆ + 𝐹 eˆ + 𝐹 eˆz ] ê = 𝐹 + . [ (𝐹 ê ) + (𝐹 ê )] + z 𝐹𝑧 ê = (𝐹) 𝐹 + + z 𝐹 𝑧 For the curl working along similar lines, ⃗∇⃗x𝐹 = [ eˆ + + eˆz z ] [𝐹 eˆ + 𝐹 eˆ + 𝐹 eˆz ] ê = ê 𝑥 [ ê 𝐹 + êz 𝐹 𝑧 ] + ê 𝑥[ eˆ 𝐹 − eˆ 𝐹 + eˆz 𝐹𝑧 ] Thus ∇⃗⃗x𝐹 = eˆ [ 𝐹𝑧 − z 𝐹] + eˆ [− 𝐹𝑧 + z 𝐹] + eˆz [ (𝐹) − 𝐹 ] Also a Laplacian ∇⃗⃗2 is defined as, ∇⃗⃗2= ⃗∇⃗. ∇⃗⃗= 1 . ( ) + 2 + 2 Joint initiative of IITs and IISc – Funded by MHRD Page 31 of 32 2 1 z
- 7. NPTEL – Physics – Mathematical Physics - 1 Example A vector field is given by, 𝐹 = 𝛼 ê where 𝛼 is a constant The divergence of 𝐹 is ∇. 𝐹 = [ ⃗⃗ ê + ê z z ê + ] . 𝛼 ê = 0 The corresponding expressions in spherical polar coordinates are given by, (the reader should work them out) ∇⃗⃗. 𝐹 = 1 (𝑟2𝐹 ) + 𝑟 2 r 𝑟 1 1 𝑟𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃 𝑟𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝜃 𝜃 (𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃𝐹 ) + 𝐹 Also ∇⃗⃗x𝐹 = (𝛾𝐹𝜃) − 𝐹𝑟 ] Joint initiative of IITs and IISc – Funded by MHRD Page 32 of 32 1 𝑟𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝜃 eˆ [ (𝐹 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃) − 𝐹 ] + 1 eˆ [− (𝛾𝐹 + r 𝜙 𝜃 𝜙 𝑟 1 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃 𝑟 𝐹 ] + 1 ê [ 𝑟 And the Laplacian, ∇⃗⃗2= 1 𝑟2 (𝑟 𝜕 ) + 2 𝑟 1 𝑟 𝑠𝑖𝑛 𝜃 2 (𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃 ) + 1 𝑟2𝑠𝑖𝑛2 𝜃 2
