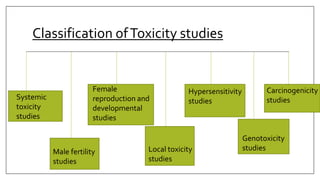
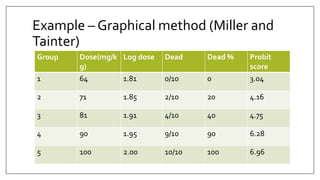
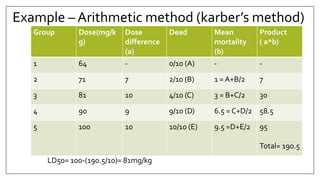
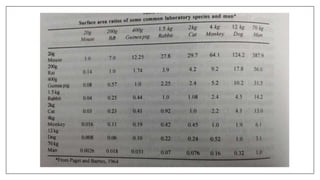
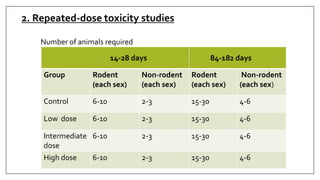
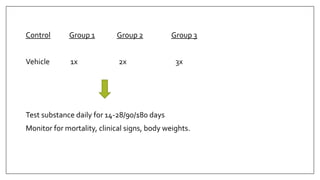
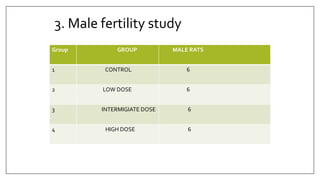
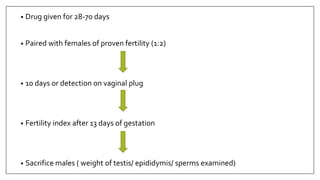
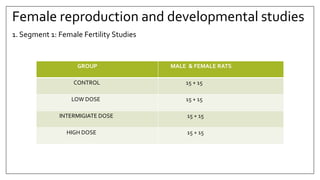
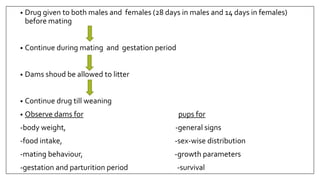
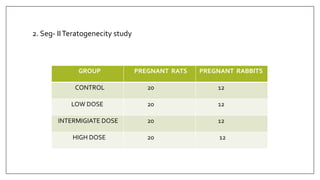
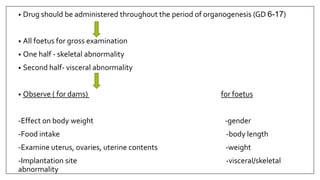
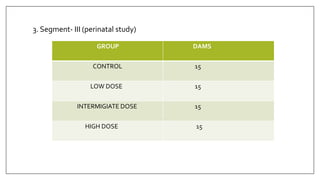
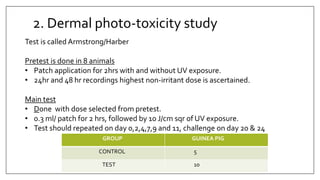
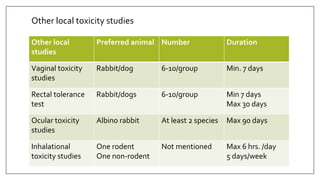
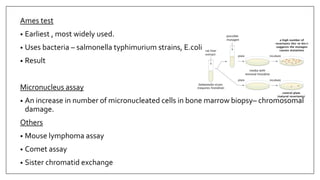
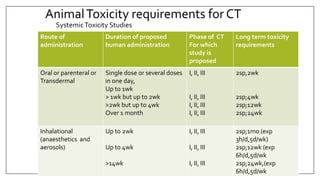
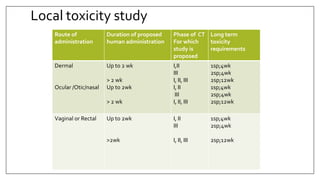
The document provides an overview of animal toxicity studies, detailing objectives, classifications, methodologies, and requirements for preclinical assessment of toxic substances. It describes various toxicity study types such as systemic, male fertility, female reproduction, and local studies, along with methods for calculating lethal doses and monitoring effects. Comprehensive guidelines are outlined for compliance with good laboratory practices, study design, dosing, and data preservation over a five-year period.