Comparing Equatorial, Humid Tropical, Savannah and Hot Desert Climates
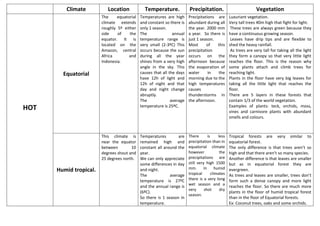
- 1. Climate Location Temperature. Precipitation. Vegetation The equatorial climate extends roughly 5º either side of the equator. It is located on the Amazon, central Africa and Indonesia. Temperatures are high and constant so there is only 1 season. The annual temperature range is very small (2-3ºC) This occurs because the sun during all the year shines from a very high angle in the sky. This causes that all the days have 12h of light and 12h of night and that day and night change abruptly. The average temperature is 25ºC. Precipitations are abundant during all the year. 2000 mm a year. So there is just 1 season. Most of this precipitation occurs on the afternoon because the evaporation of water in the morning due to the high temperatures causes thunderstorms in the afternoon. Luxuriant vegetation. Very tall trees 40m high that fight for light. These trees are always green because they have a continuous growing season. Leaves have drip tips and are flexible to shed the heavy rainfall. As trees are very tall for taking all the light they form a canopy so that very little light reaches the floor. This is the reason why some plants attach and climb trees for reaching light. Plants in the floor have very big leaves for taking all the little light that reaches the floor. There are 5 layers in these forests that contain 1/3 of the world vegetation. Examples of plants: teck, orchids, moss, vines and carnivore plants with abundant smells and colours. This climate is near the equator between 10 degrees shout and 25 degrees north. Temperatures are remained high and constant all around the year. We can only appreciate some differences in day and night. The average temperature is 27ºC and the annual range is (6ºC). So there is 1 season in temperature. There is less precipitation than in equatorial climate however the precipitations are still very high 1500 mm. In humid tropical climates there is a very long wet season and a very shot dry season. Tropical forests are very similar to equatorial forest. The only difference is that trees aren’t so high and that there aren’t so many species. Another difference is that leaves are smaller but as in equatorial forest they are evergreen. As trees and leaves are smaller, trees don’t form such a dense canopy and more light reaches the floor. So there are much more plants in the floor of humid tropical forest than in the floor of Equatorial forests. Ex: Coconut trees, oaks and some orchids. Equatorial HOT Humid tropical.
- 2. Dry tropical (Savannah) The savannah climates is located between latitudes 15º and 30º north and south the equator. It is mostly founded on eastern and west Africa, South America and Australia. Temperatures are very high during all the year around 18ºC. However we find that we can appreciate a small difference between summer and winter so we can say that there are 2 seasons: a mild winter and a hot summer. This occurs because the temperature range is of 8ºC. The hot desert climate is found around the tropics of Capricorn and Cancer. 25º North and South Equator. Examples are the Thar desert in Pakistan, the Atacama desert in Chile, the Rocky Mountains, the Arabian desert, Afghanistan, Iran, Sahara and the Kalahari desert. Temperatures on hot deserts are very high all around the year. However there are huge temperature oscillations every day of 40ºC. During the day this temperatures are of 50ºC and during the night of 5ºC. This occurs because there aren’t clouds in the sky. However the annual temperature average is of 25ºC. HOT Hot Desert The savannah has a mild very dry season that coincides with dry prevailing winds. However when the winds end a hot rainy season comes and the rivers flows increases significantly. We find that in savannah climate the dry season lasts longer than the wet season. The precipitations are between 8001000mm. Precipitations are very few. Only of 250mm every year. However very dry deserts such as the Atacama desert have precipitations of 100mm a year. The savannah landscape is a transition between the hot dessert and the tropical rainforest. In it we can find grassland 5m tall with few scattered trees that have to adapt to a very dry season and a rainy season. We find with the baobab that has a 10m diameter trunk that stores water and with the acacia trees that have leafy and flat canopies that protects animals from the sun. We find that acacia trees have like this their canopies due to wind. Trees normally have few leaves for losing little water and are not evergreen. Also we find with bushes. Vegetation is very scarce and it has adapted to the few precipitations by having long roots to search for moisture. Others such as cacti store water in their trunk and have very little leaves for losing little water. Ex: Esparto grass, palm trees...