Embed presentation

![Axiomatic approach
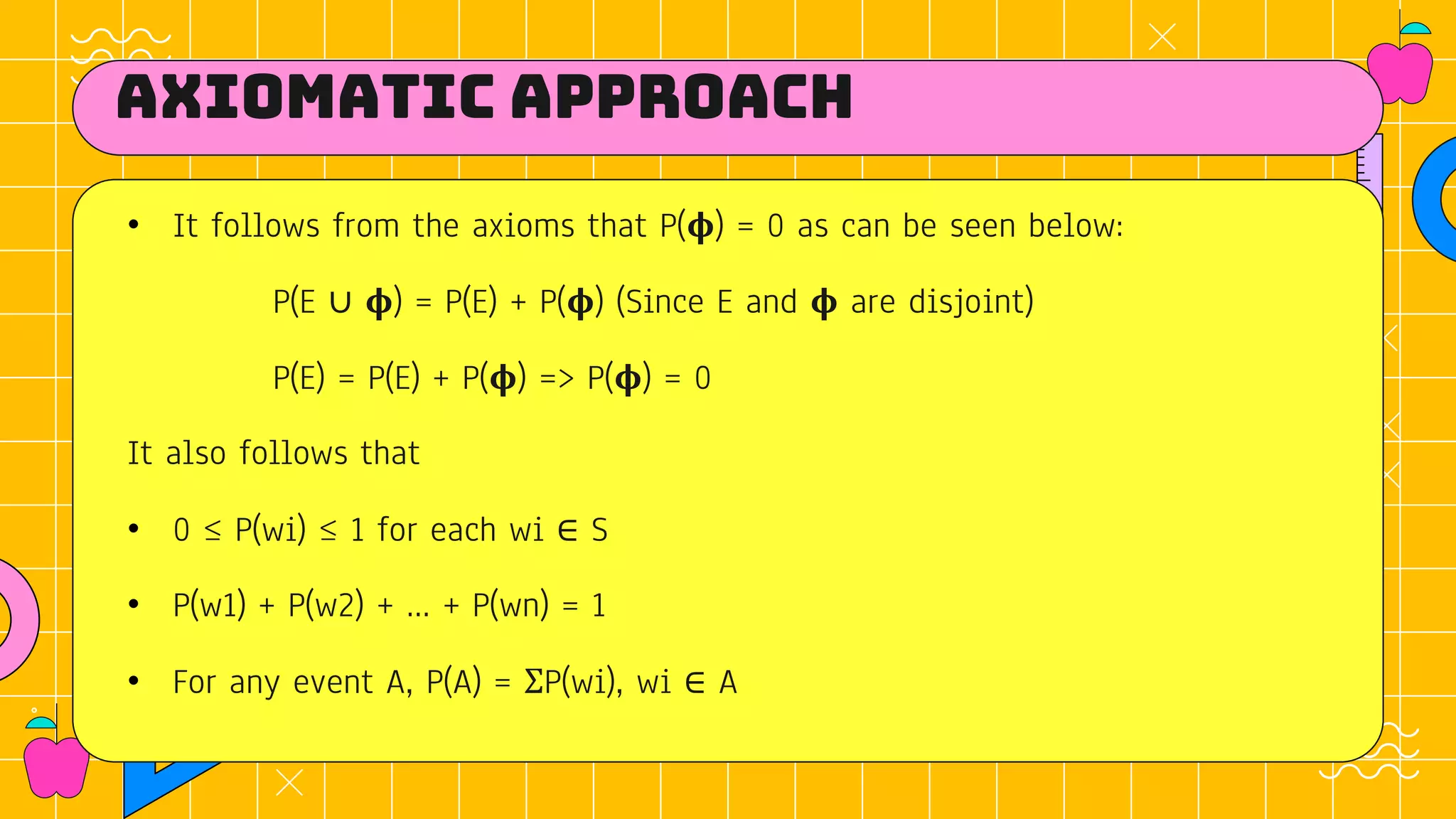
• Let S be the sample space of a random experiment.
• The probability P is a real valued function whose domain is the power set
of S and range is the interval [0,1] satisfying the following axioms:
i. For any event E, P (E) ≥ 0
ii. P(S) = 1
iii. If E and F are mutually exclusive events, then P(E ∪ F) = P(E) + P(F)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10axiomaticapproachtoprobability-220112050543/75/10-axiomatic-approach-to-probability-2-2048.jpg)


The document outlines the axiomatic approach to probability, defining key concepts such as sample space, probability as a real-valued function, and the axioms that govern it. It explains that the probability of any event is non-negative, that the sum of probabilities of mutually exclusive events equals the probability of their union, and highlights the properties of exhaustive and mutually exclusive events. The author, Dhruv Sethi, offers contact information for private or group tutoring.

![Axiomatic approach
• Let S be the sample space of a random experiment.
• The probability P is a real valued function whose domain is the power set
of S and range is the interval [0,1] satisfying the following axioms:
i. For any event E, P (E) ≥ 0
ii. P(S) = 1
iii. If E and F are mutually exclusive events, then P(E ∪ F) = P(E) + P(F)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/10axiomaticapproachtoprobability-220112050543/75/10-axiomatic-approach-to-probability-2-2048.jpg)


