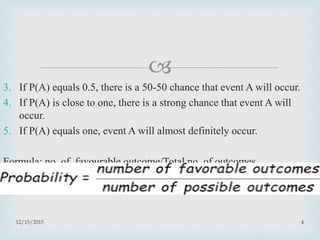This document presents information on probability and its uses. It defines probability as the chances of an event occurring from a sample space. Probability is expressed as a number from 0 to 1, with 0 meaning an event will not occur and 1 meaning it will definitely occur. The document discusses types of probability such as mathematical, statistical, and subjective probabilities. It also defines key probability terminology like sample space, outcomes, events, and complementary events. Finally, it discusses how probability is useful for business decision making, risk evaluation, and predicting demand and markets.