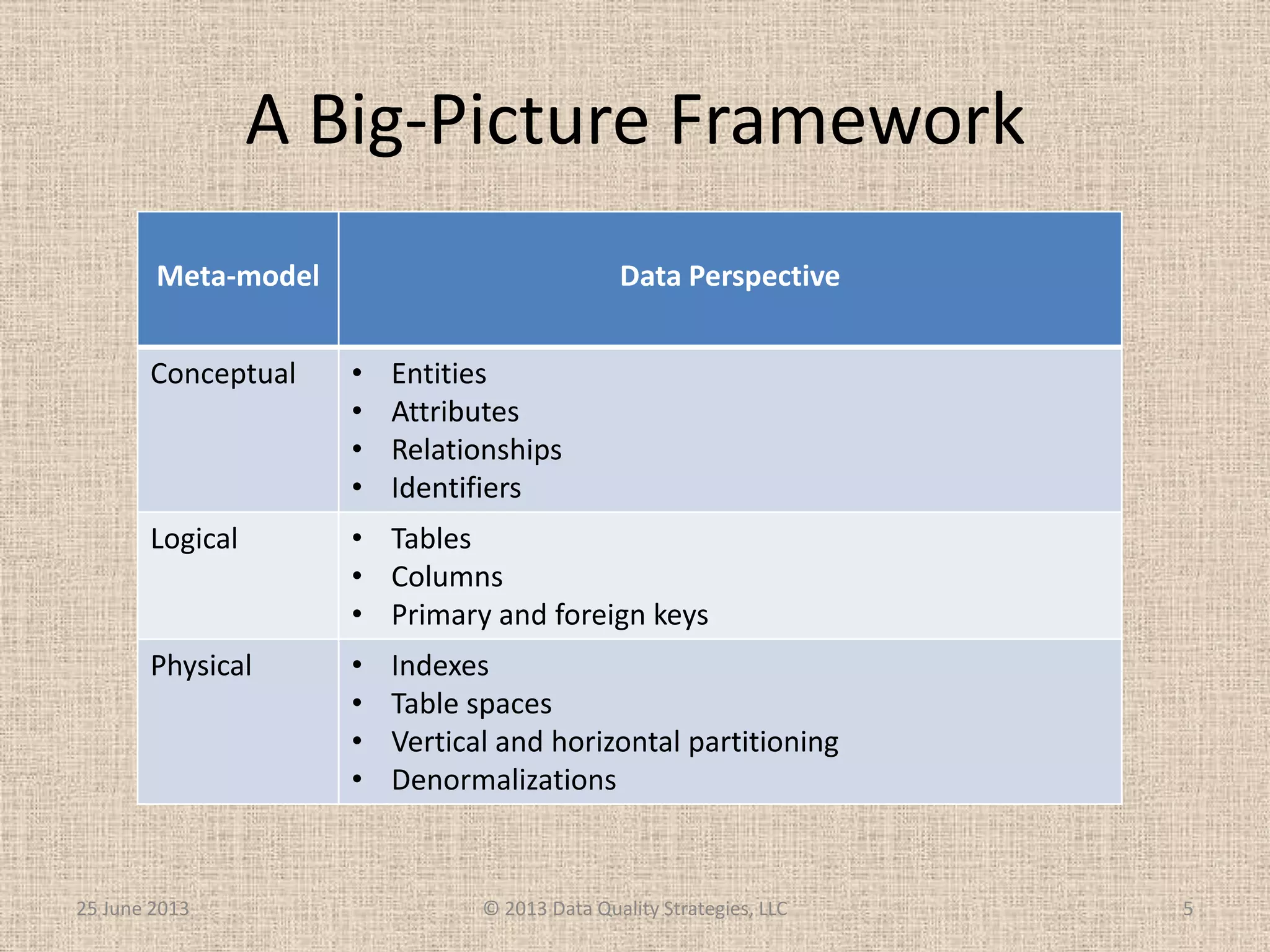
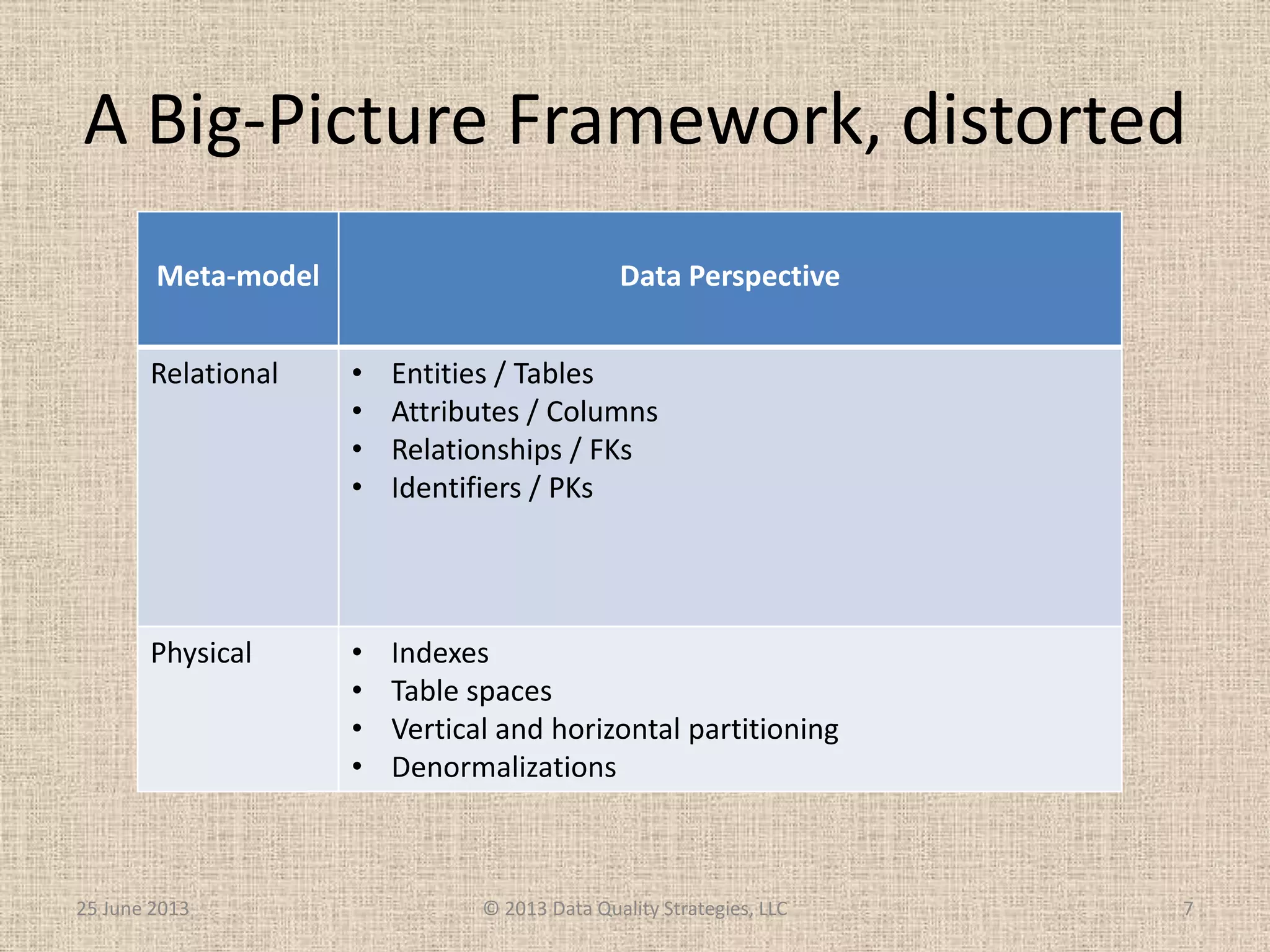
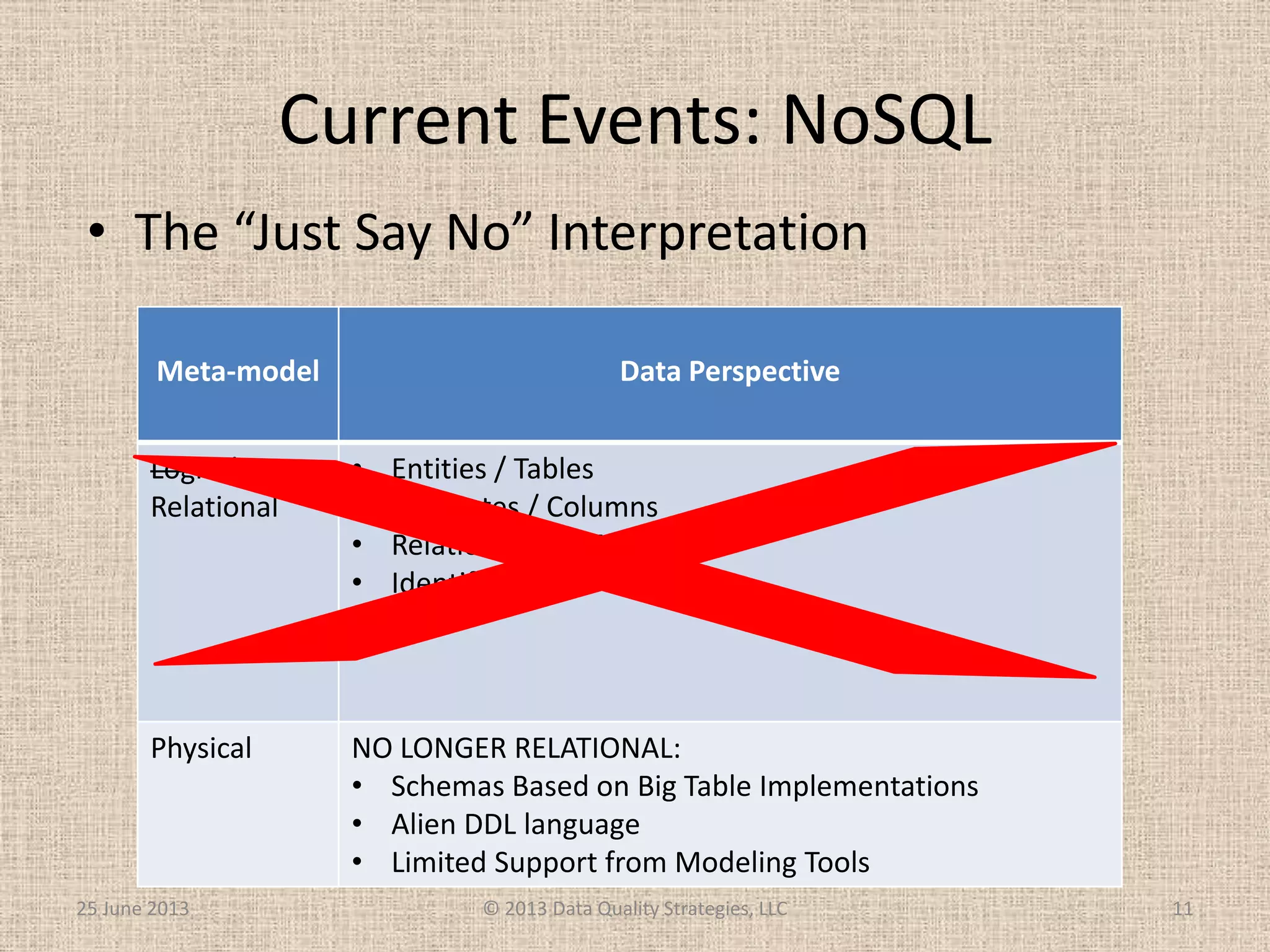
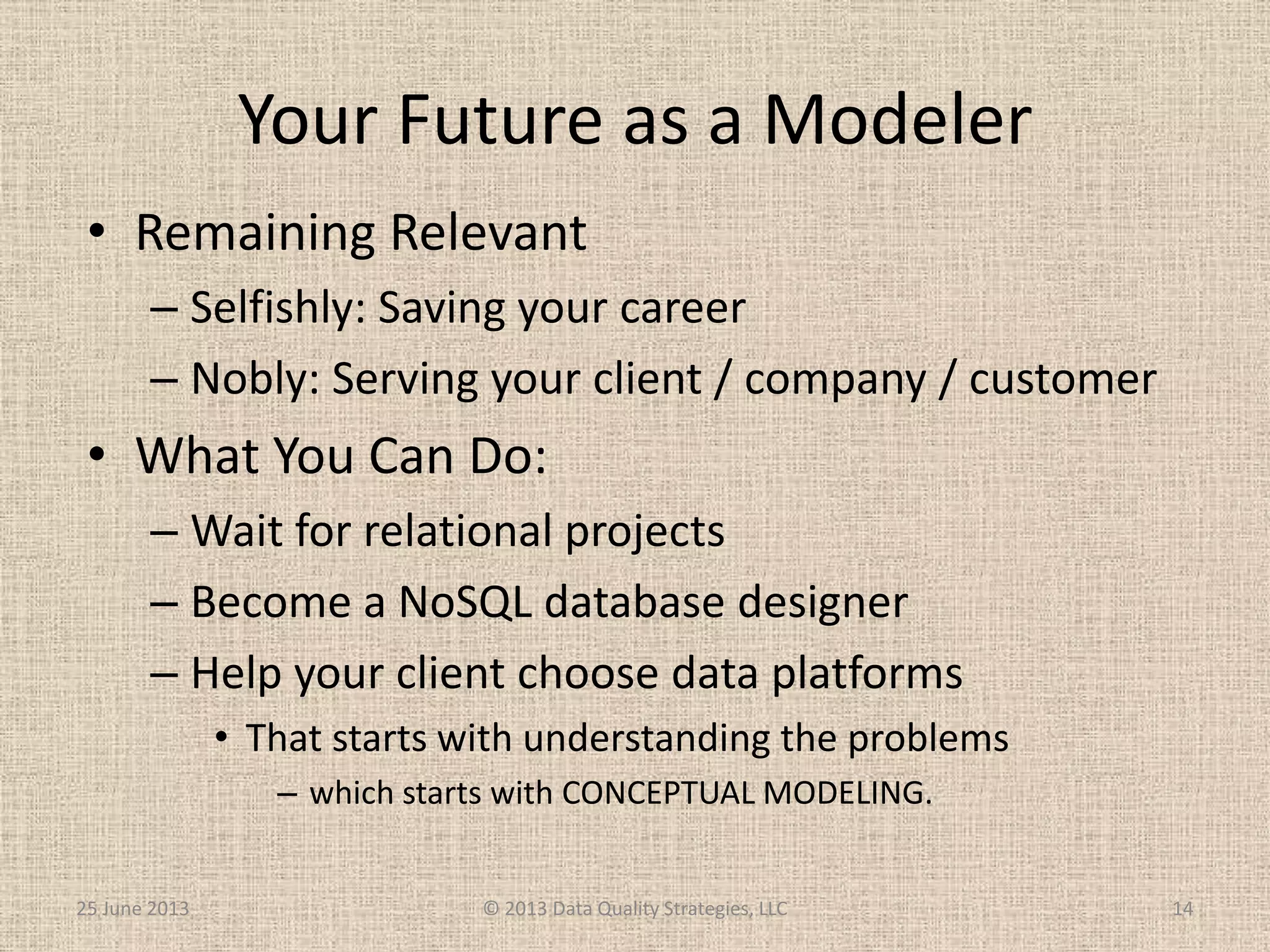
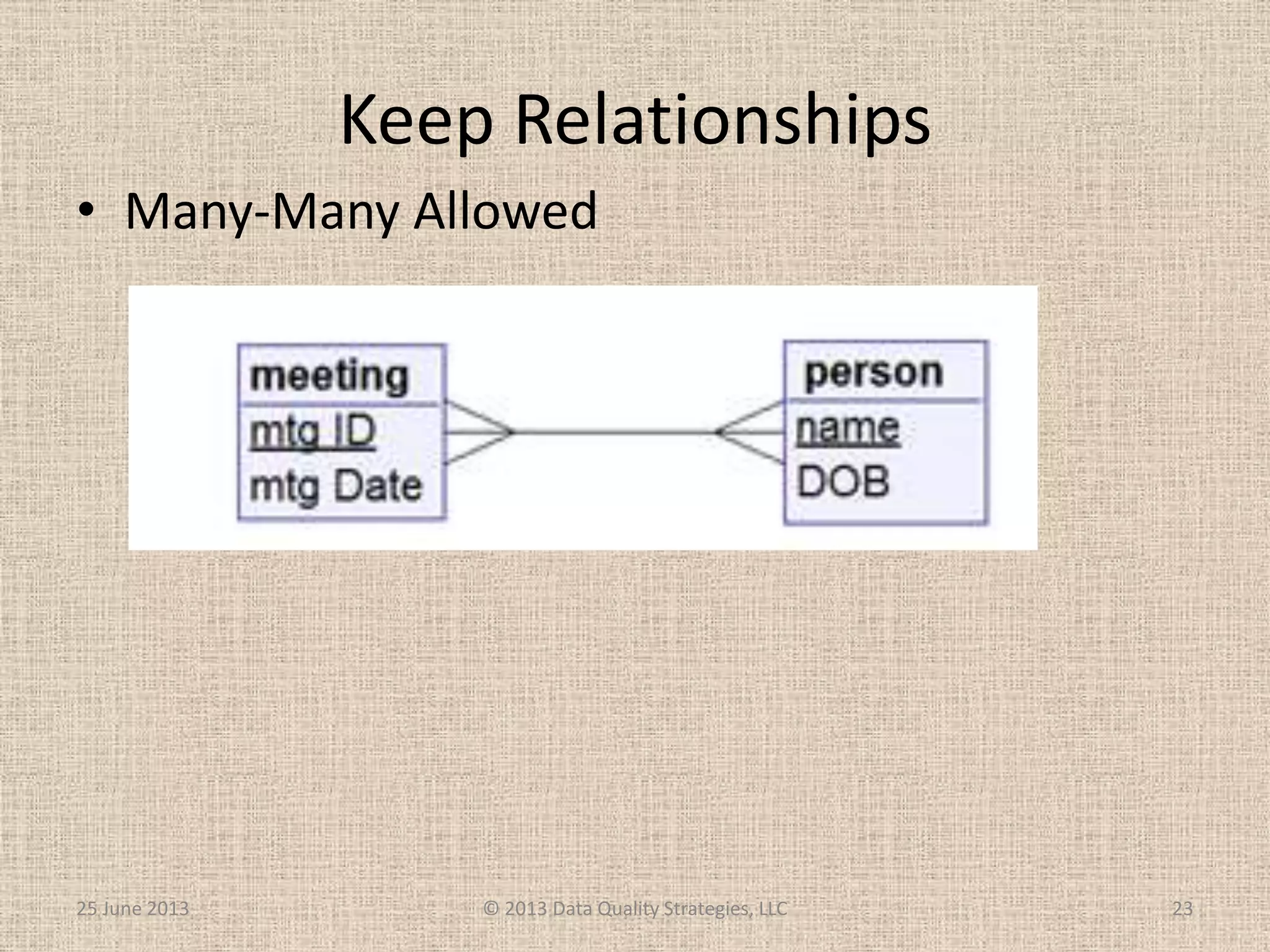
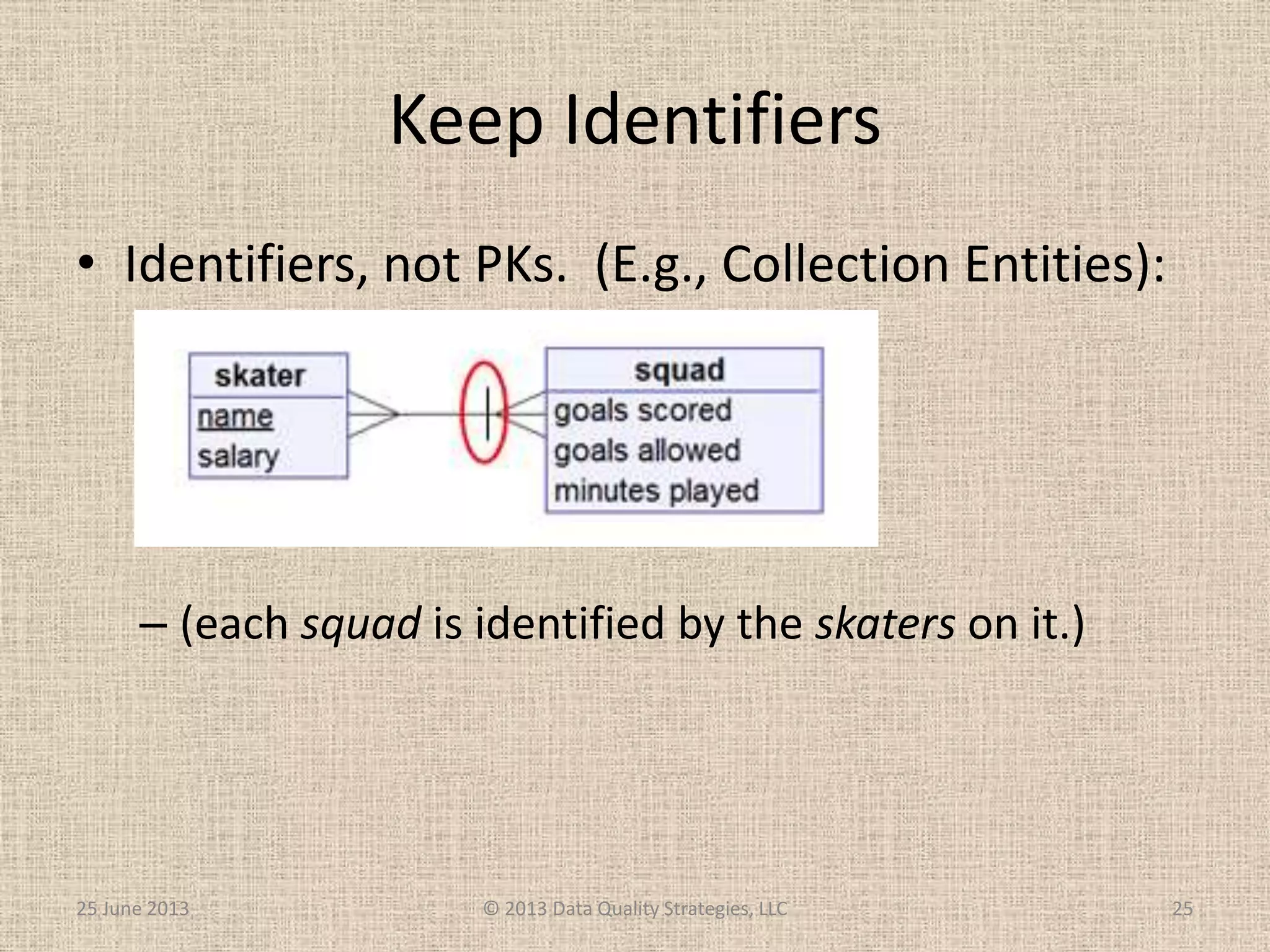
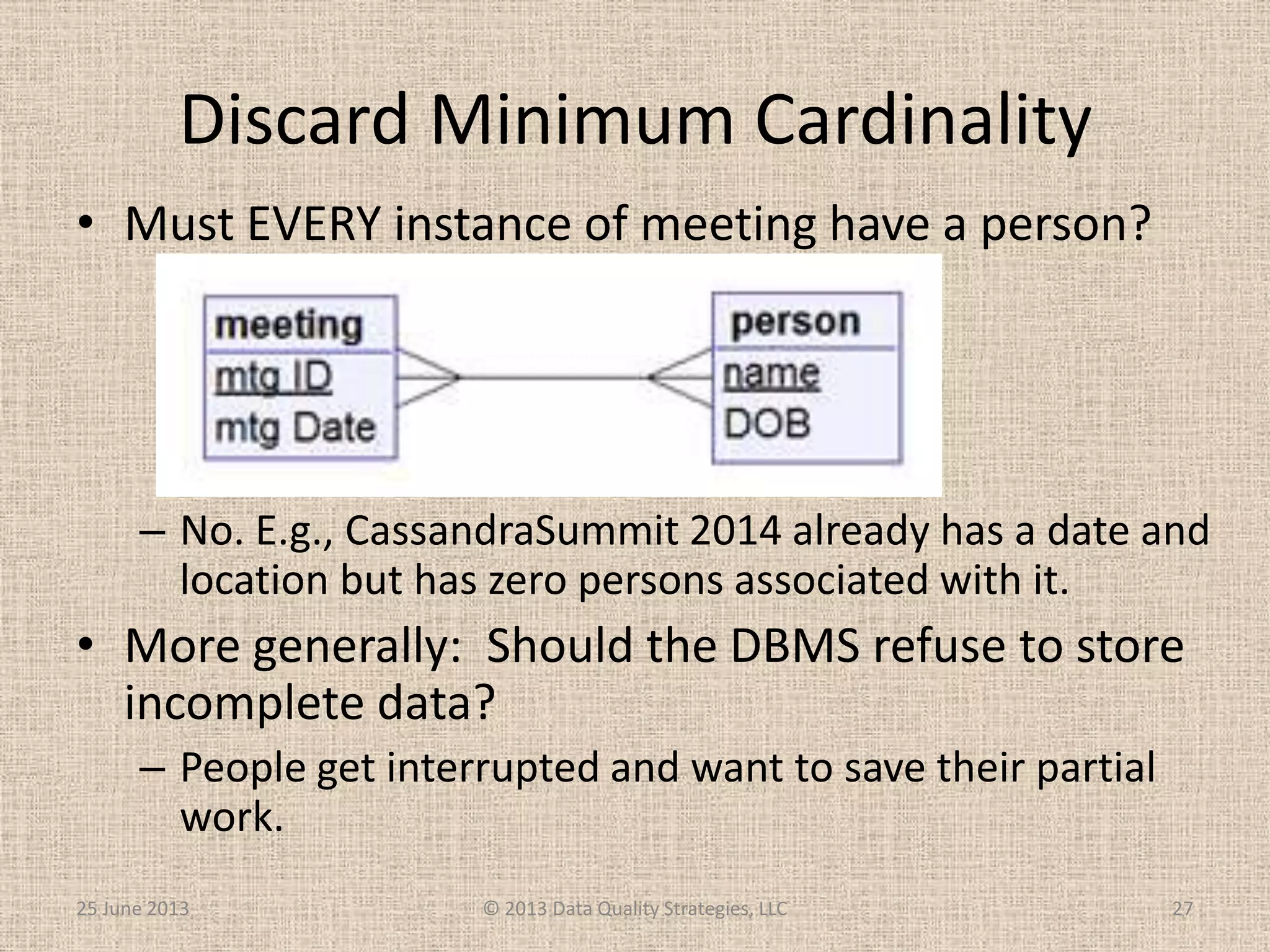
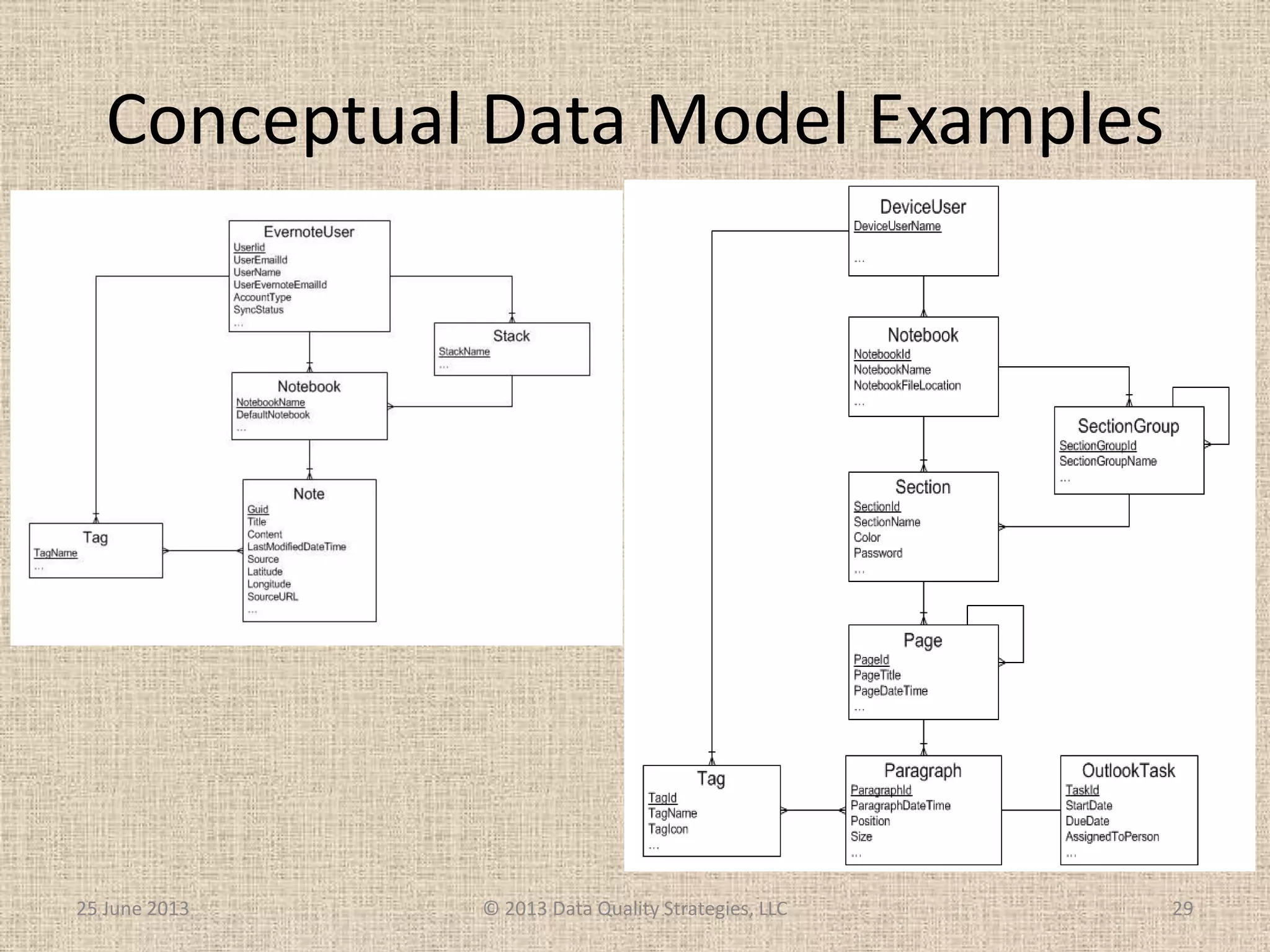
The document discusses how relational database management systems and relational modeling have dominated in the past but are declining with the rise of NoSQL databases. It argues that data modelers can save their careers by returning to focus on conceptual modeling rather than assuming relational modeling. Conceptual modeling involves communicating with users to understand entities, attributes, and relationships without implementation details. This will help data modelers choose the appropriate logical data model and adapt to changes in technologies.