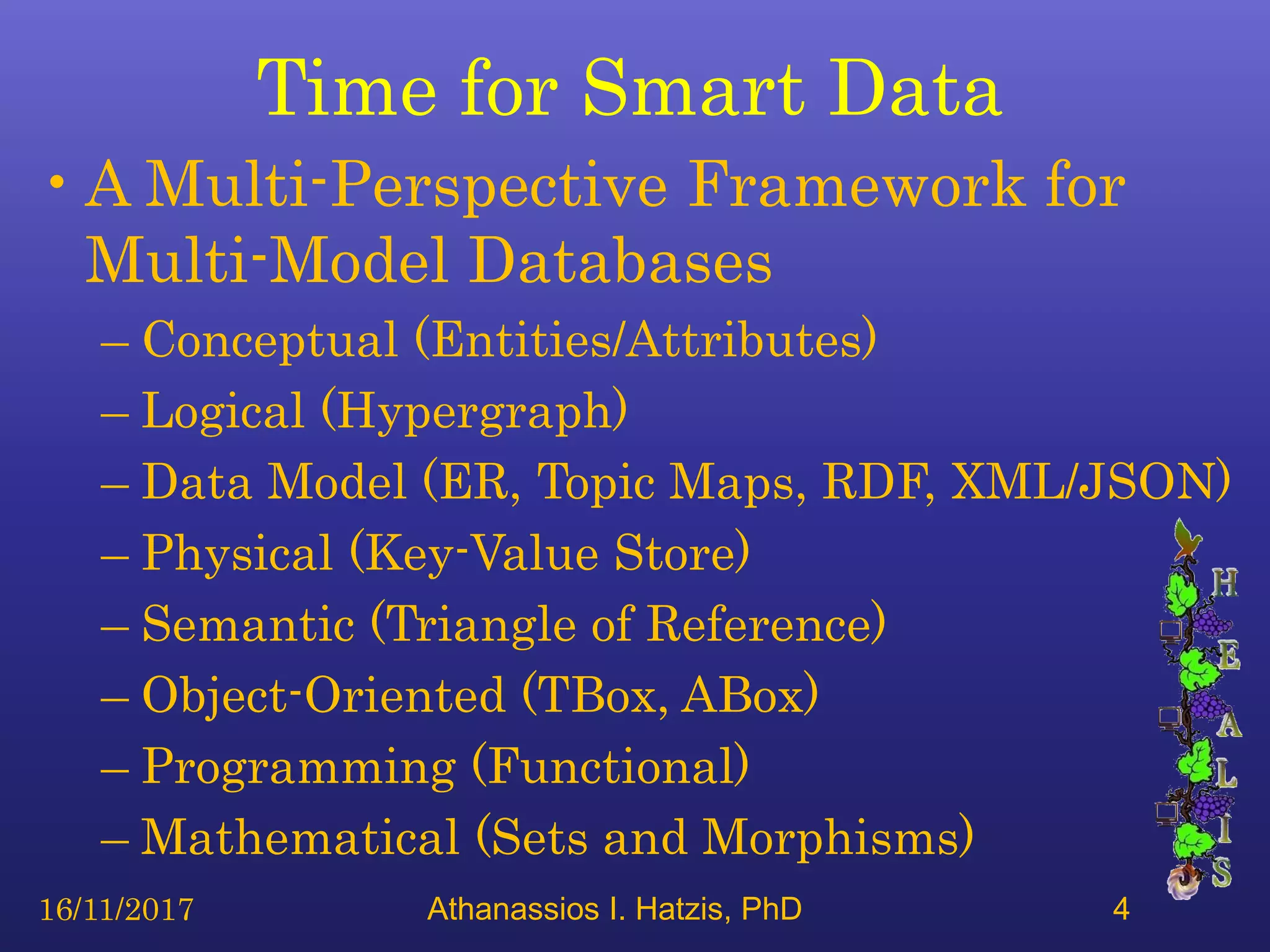
The document presents an associative semiotic hypergraph database that builds meaningful relationships easily in Intersystems Cache with Python Pandas. It discusses the database's multi-perspective framework that allows for conceptual, logical, data, semantic, object-oriented, and programming models. It also demonstrates the database's mapping, filtering, and traversal capabilities. The future plan is to develop a minimum viable product and collaborate with partners to build an open, self-service business intelligence system.