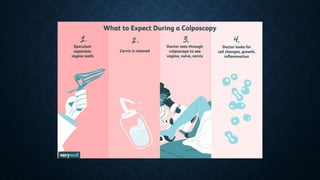
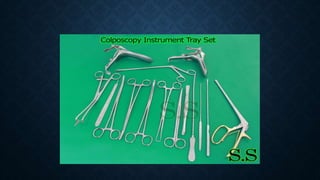
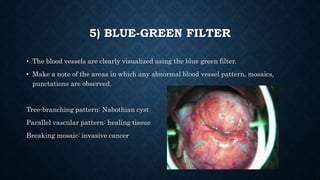
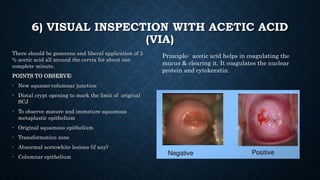
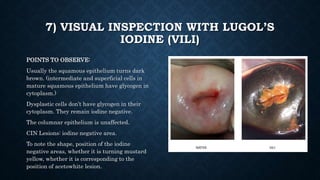
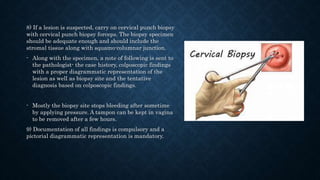
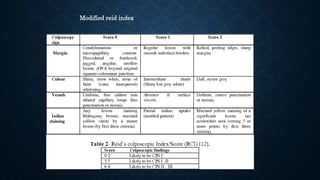
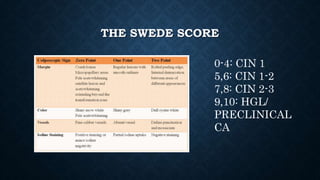
The document provides an overview of colposcopy, a diagnostic procedure to magnify and examine the cervix and vagina for precancerous and cancerous lesions. It details the indications, patient selection criteria, procedural steps, and necessary instruments involved in performing a colposcopy. Post-procedure care and advice for patients are also included, emphasizing the importance of follow-up and HPV vaccination.