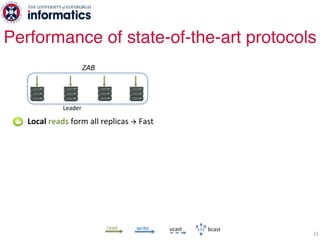
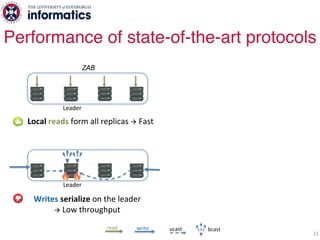
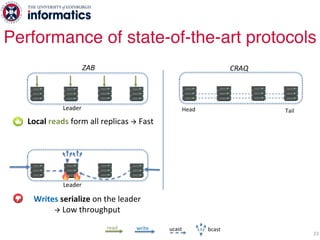
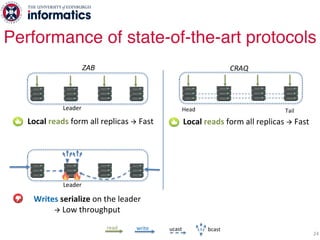
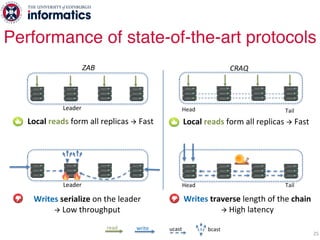
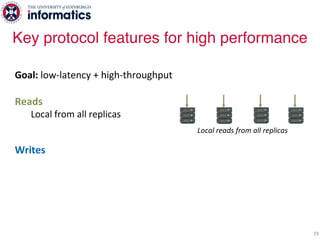
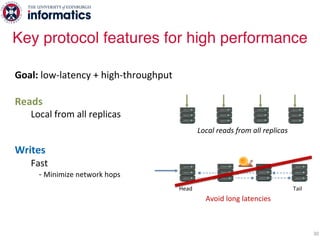
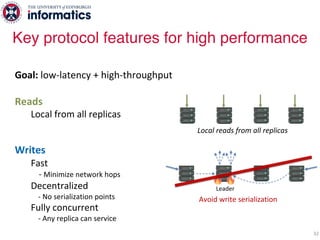
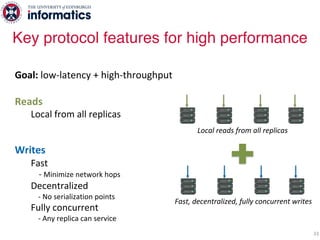
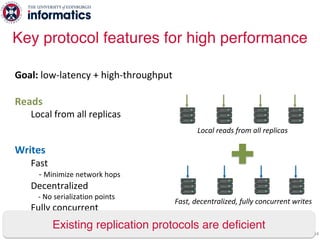
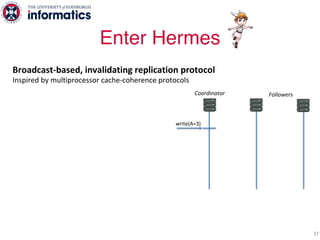
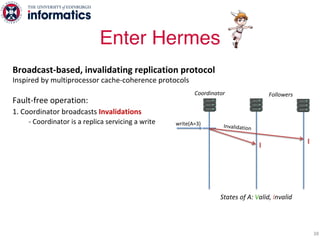
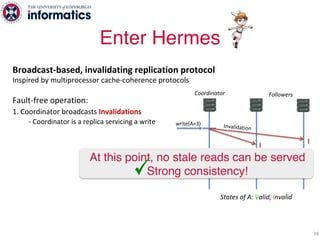
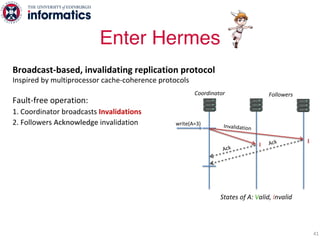
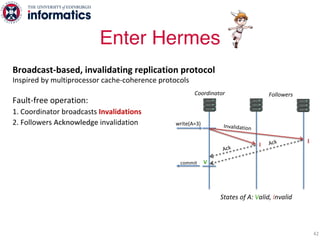
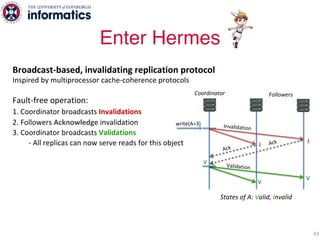
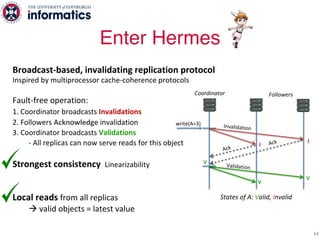
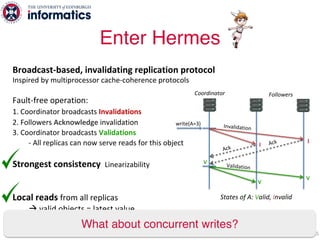
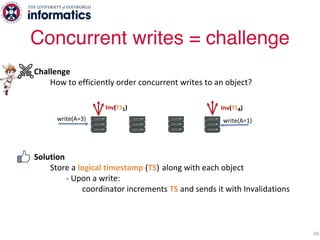
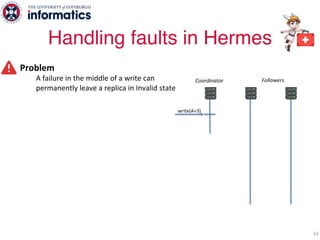
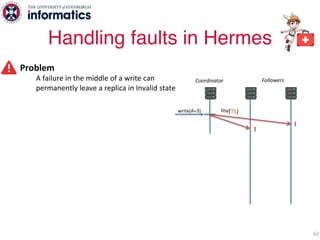
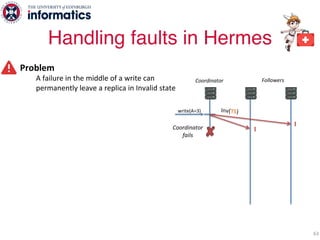
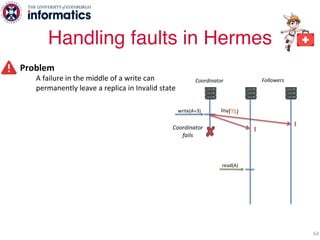
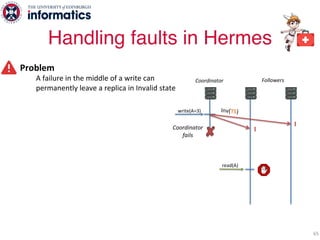
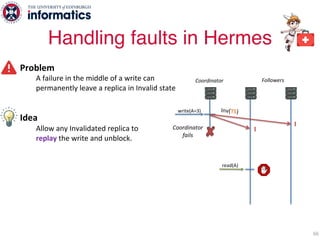
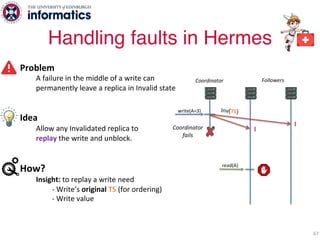
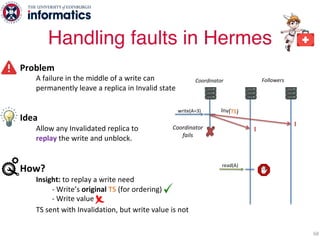
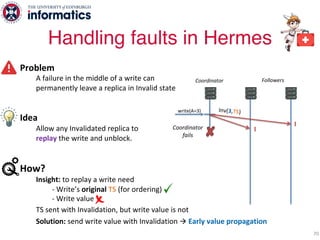
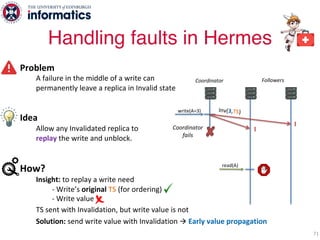
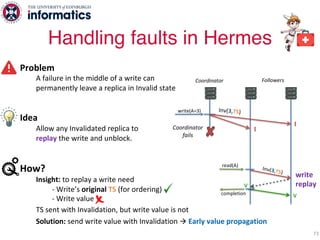
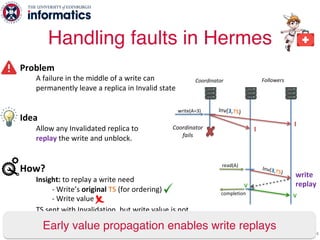
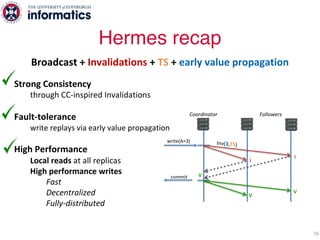
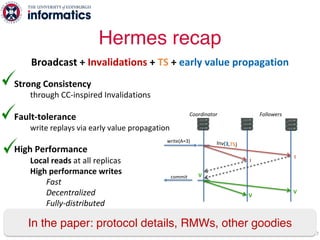
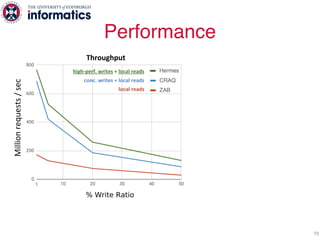
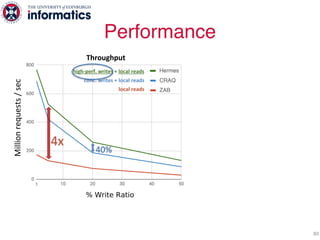
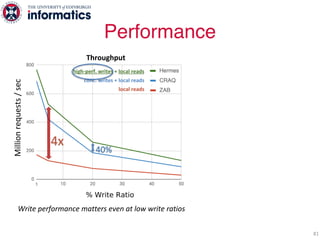
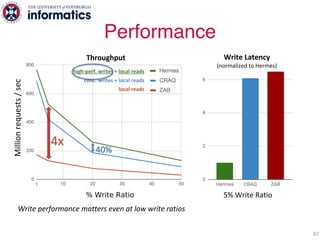
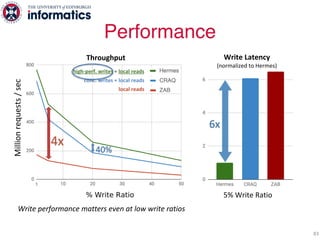
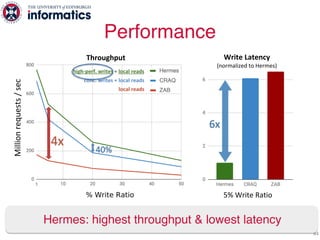
The document describes Hermes, a new replication protocol that aims to provide high performance, strong consistency, and fault tolerance for distributed datastores. Hermes uses an invalidating broadcast-based approach where writes are coordinated by a replica that broadcasts invalidations and value updates to other replicas. It allows for local reads from any replica and fast, decentralized, fully concurrent writes that commit in one network round trip. To handle faults, Hermes propagates write values with invalidations to allow replicas to recover from failures without blocking. The goal is to improve on existing protocols by avoiding serialization bottlenecks while maintaining strong consistency under both normal operation and replica failures.