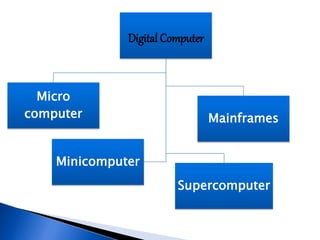
Digital computers use electronic technology to process data represented as strings of 1s and 0s. There are several types of computers:
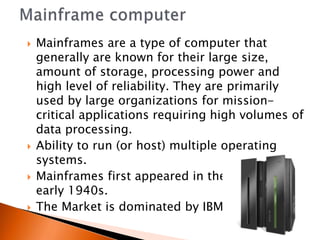
Microcomputers are small and inexpensive, containing a microprocessor, memory, and input/output devices like PCs. Minicomputers emerged in the 1960s, filling the space between mainframes and microcomputers. Mainframes are large, reliable computers used for mission-critical tasks requiring high volumes of data. Supercomputers have tens of thousands of processors capable of billions of calculations per second, used for massive computing tasks.