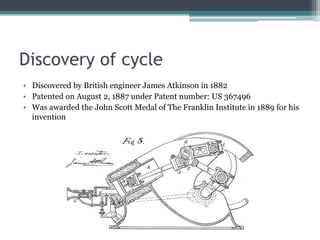
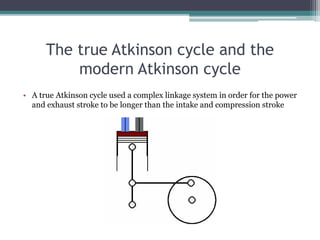
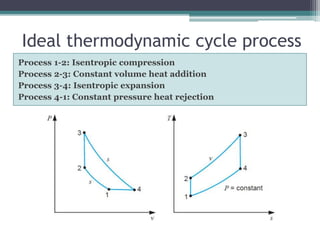
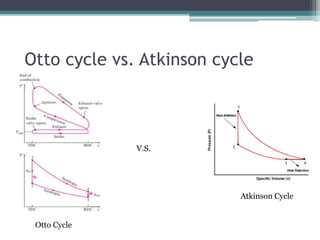
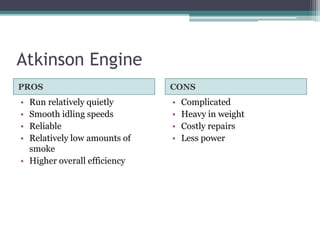
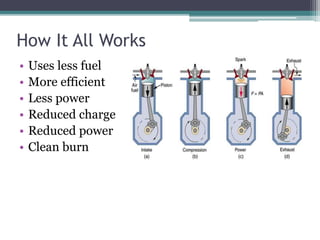
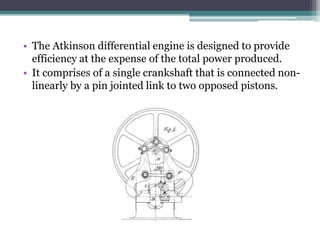
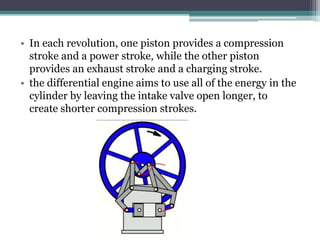
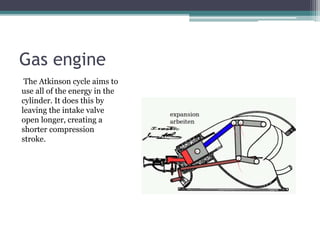
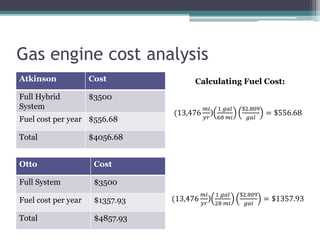
The Atkinson cycle was discovered in 1882 by British engineer James Atkinson. It achieves higher efficiency than the Otto cycle by using a longer exhaust and intake stroke compared to the compression and power strokes. The modern Atkinson cycle uses variable valve timing to keep the intake valve open longer during the compression stroke, allowing some of the air-fuel mixture to re-enter the exhaust. It provides benefits like reduced fuel consumption and emissions but with reduced power output. Toyota was an early adopter of the Atkinson cycle, using it in engines like their 1.2-liter turbocharged engine to improve efficiency.