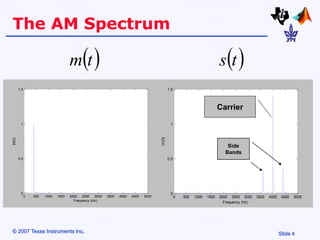
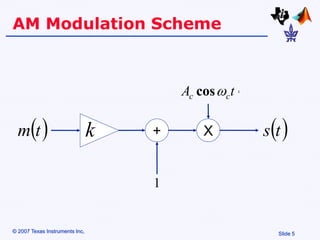
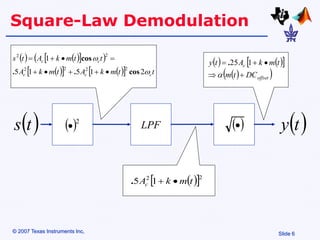
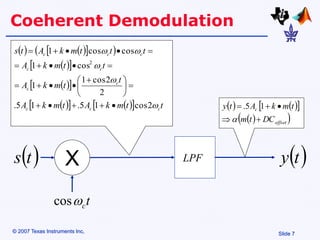
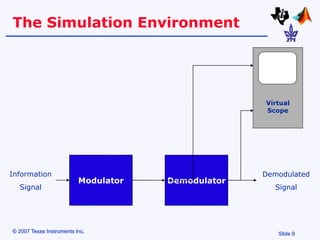
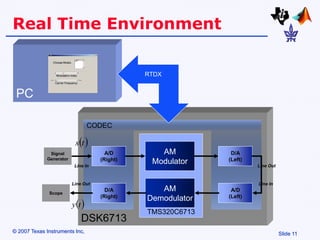
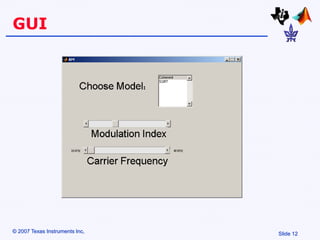
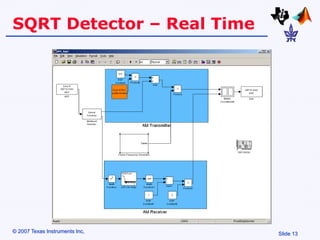
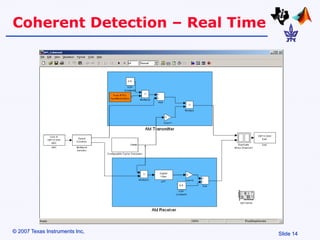
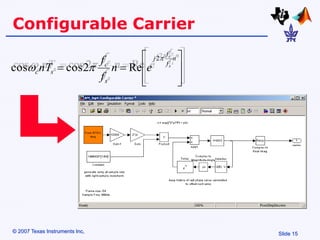
Amplitude modulation (AM) is a process where the amplitude of a carrier signal is altered according to an information-containing message signal. The carrier signal's frequency is usually much higher than the highest frequency of the message signal. There are two main types of AM demodulation: square-law demodulation and coherent demodulation. Square-law demodulation uses a diode and low-pass filter to extract the message signal from the AM signal. Coherent demodulation multiplies the AM signal with a reference carrier signal to directly extract the message signal. The document then describes using software simulation and a DSK6713 board to implement and observe AM modulation and these two demodulation techniques in real-time.