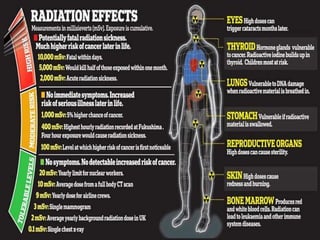
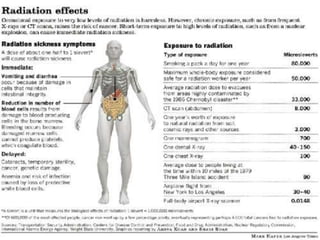
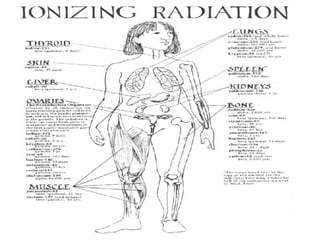
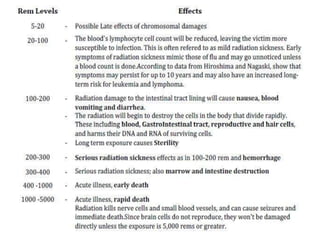
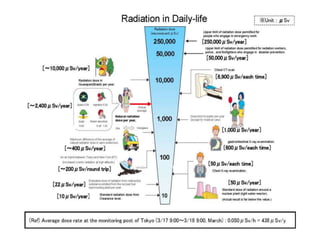
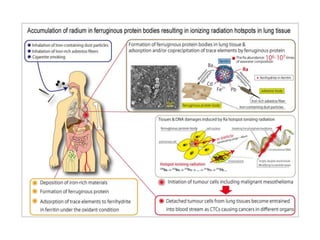
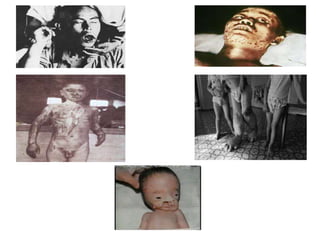
Radioactivity refers to the spontaneous emission of radiation from unstable atomic nuclei. The three main types of radiation emitted are alpha particles, electrons, and gamma rays. The curie and becquerel are units used to measure radioactivity, with 1 Bq being equal to 1 nuclear decay per second. Radiation dose is measured in rads or grays for absorbed dose, and rems or sieverts for biological dose. Radioactive contamination typically results from accidents during production or use of radionuclides. Cosmic rays originate from outside Earth's atmosphere and consist mainly of protons, helium nuclei, and electrons. Secondary cosmic rays like lithium and beryllium are produced when heavier cosmic rays interact with interstellar matter