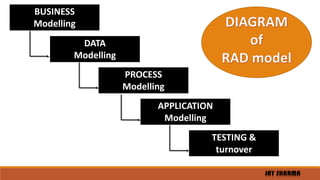
The document discusses the Rapid Application Development (RAD) model. It describes the RAD model as an incremental development model where components are developed in parallel as mini-projects and delivered quickly to get early customer feedback. The phases of the RAD model include business modeling, data modeling, process modeling, application generation, and testing. The RAD model aims to reduce development time, increase reusability, and encourage early customer feedback through quick iterations. However, it requires highly skilled developers and designers and is costly to implement.