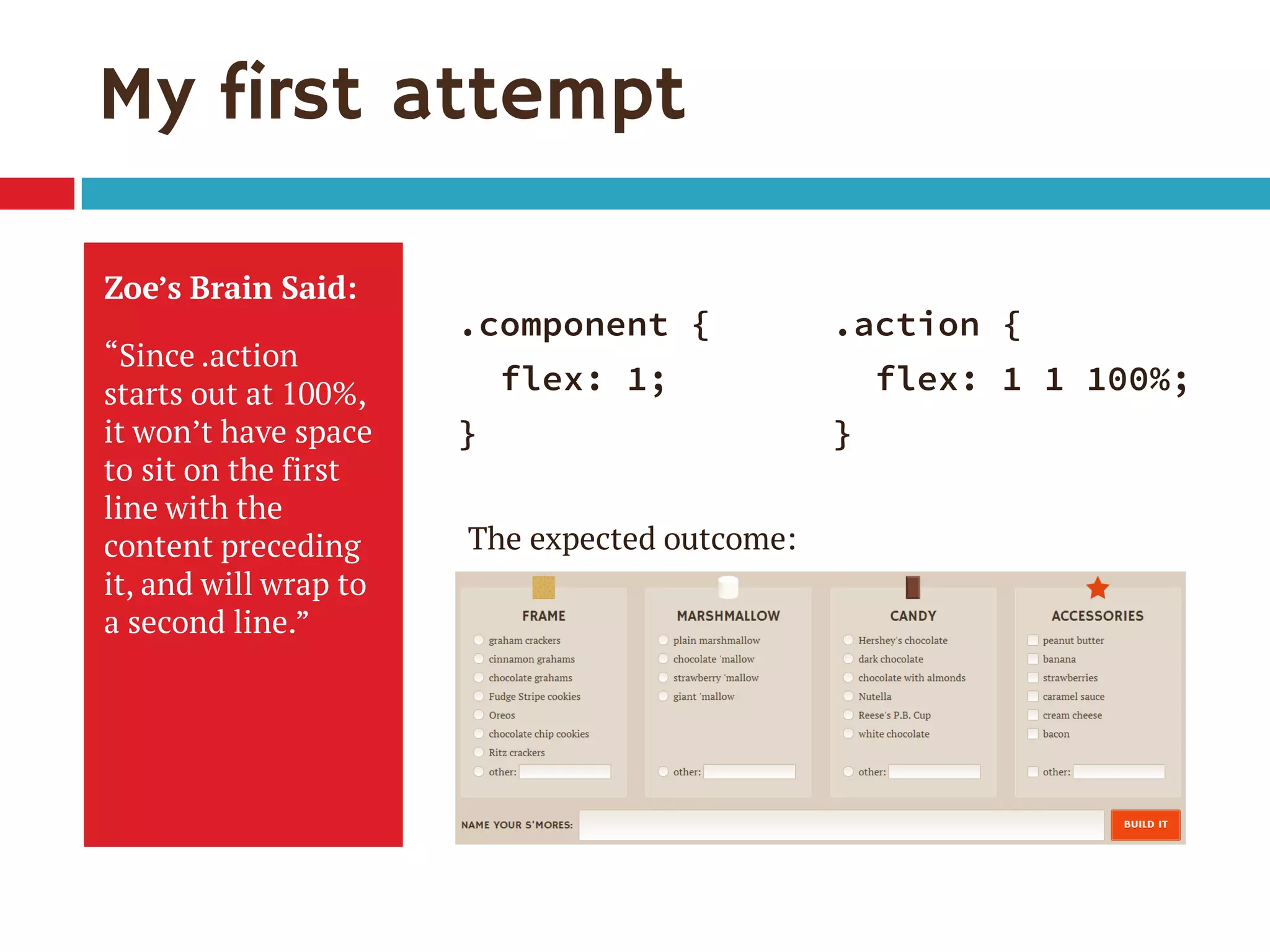
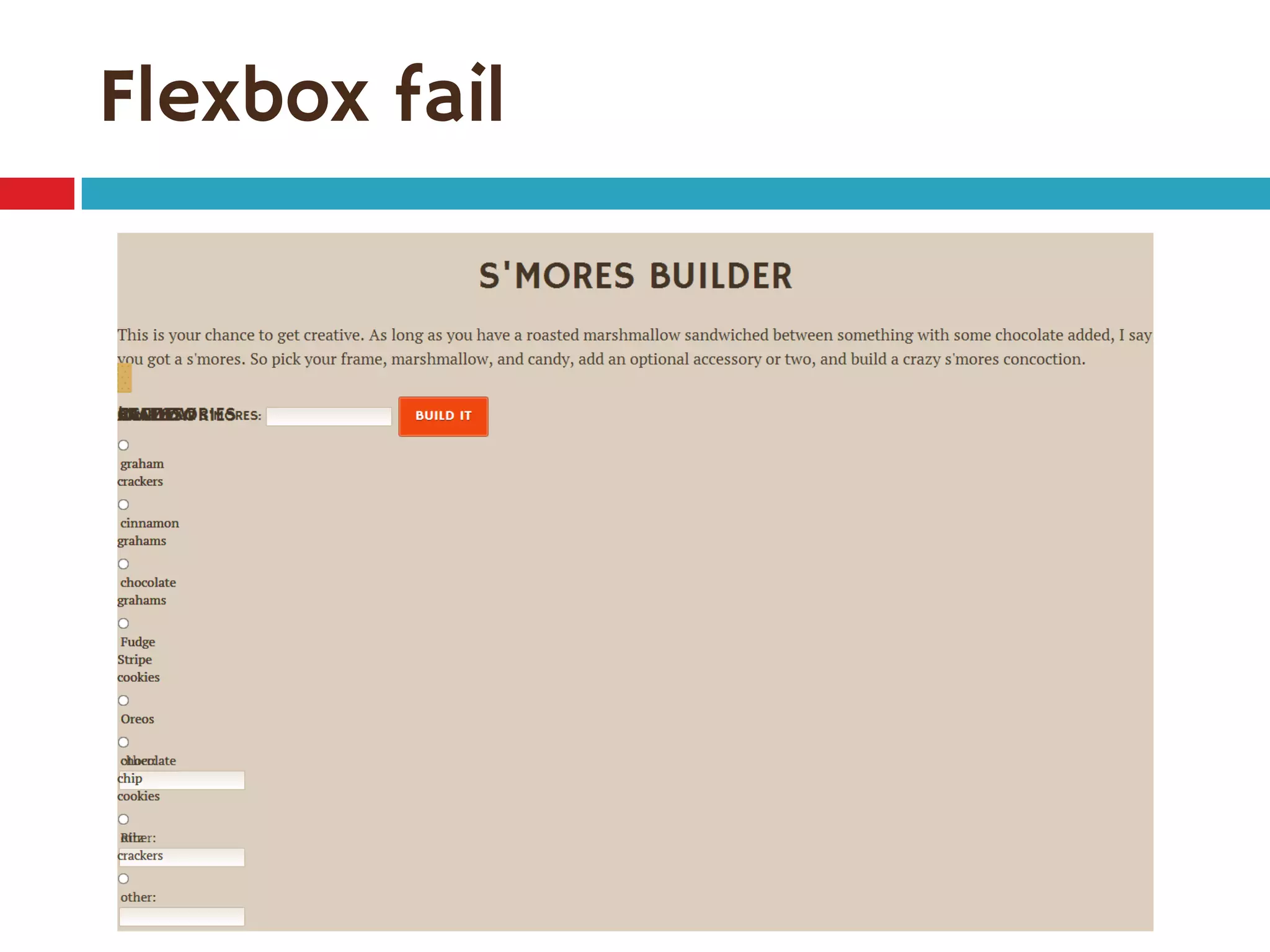
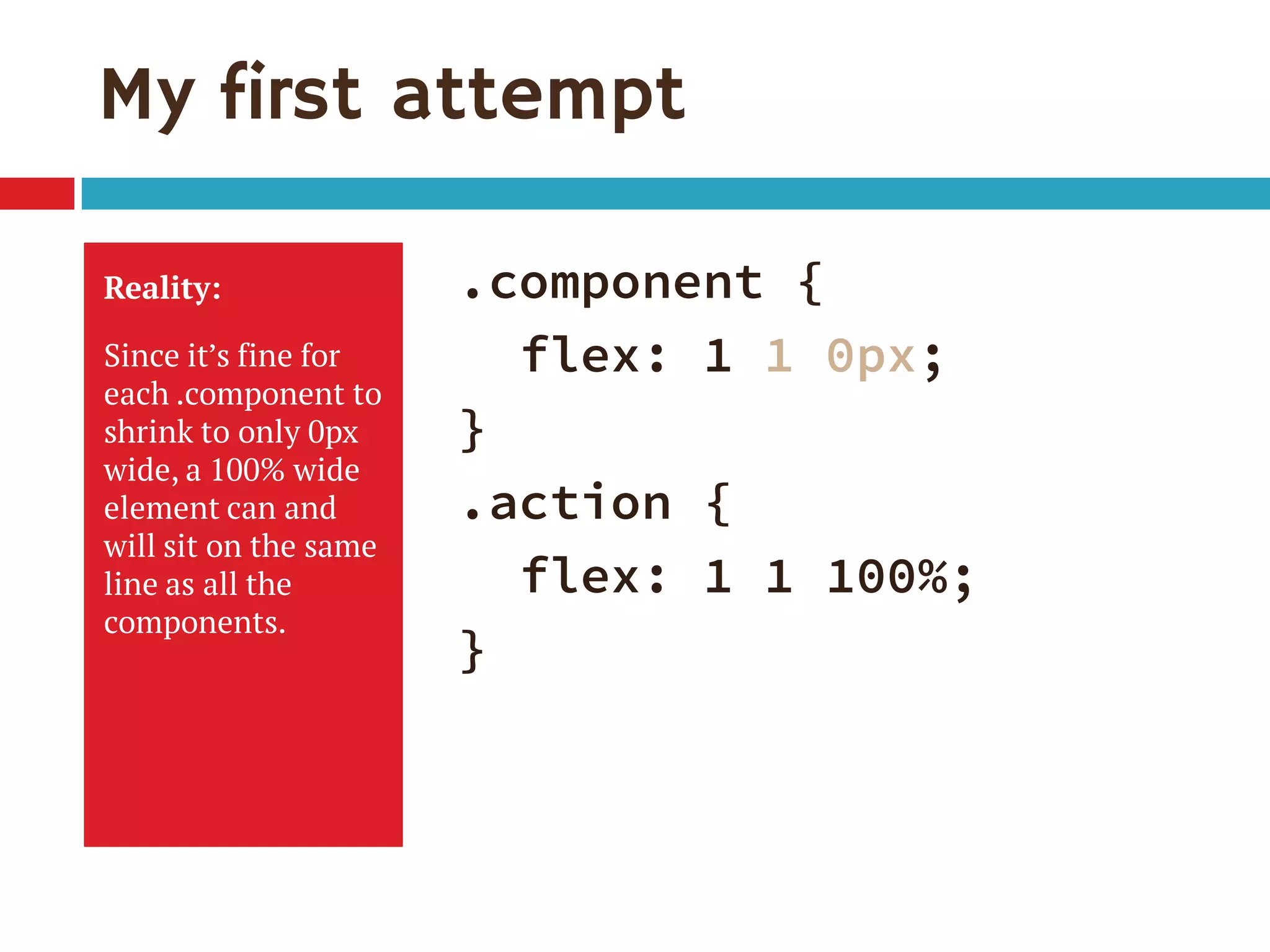
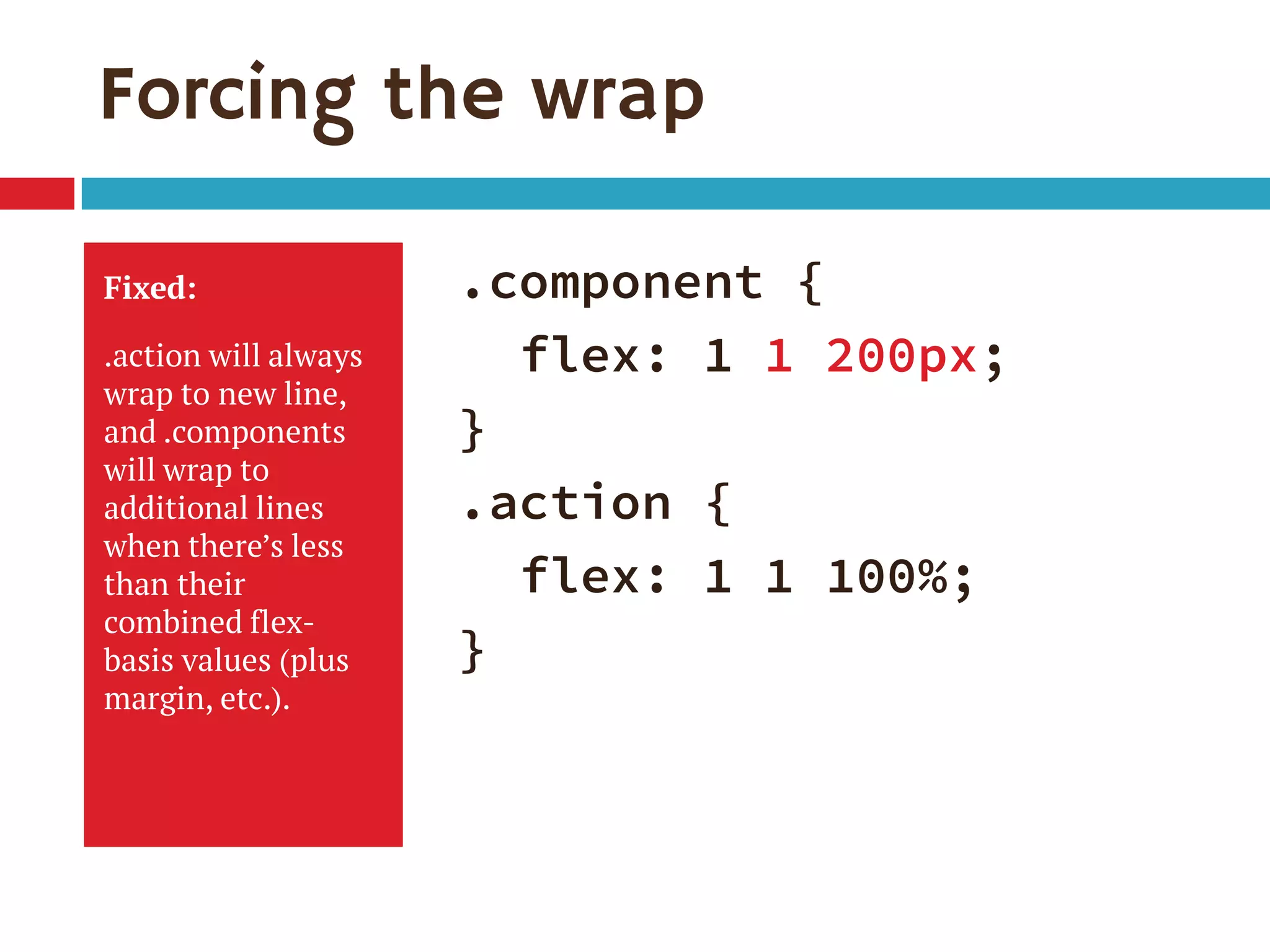
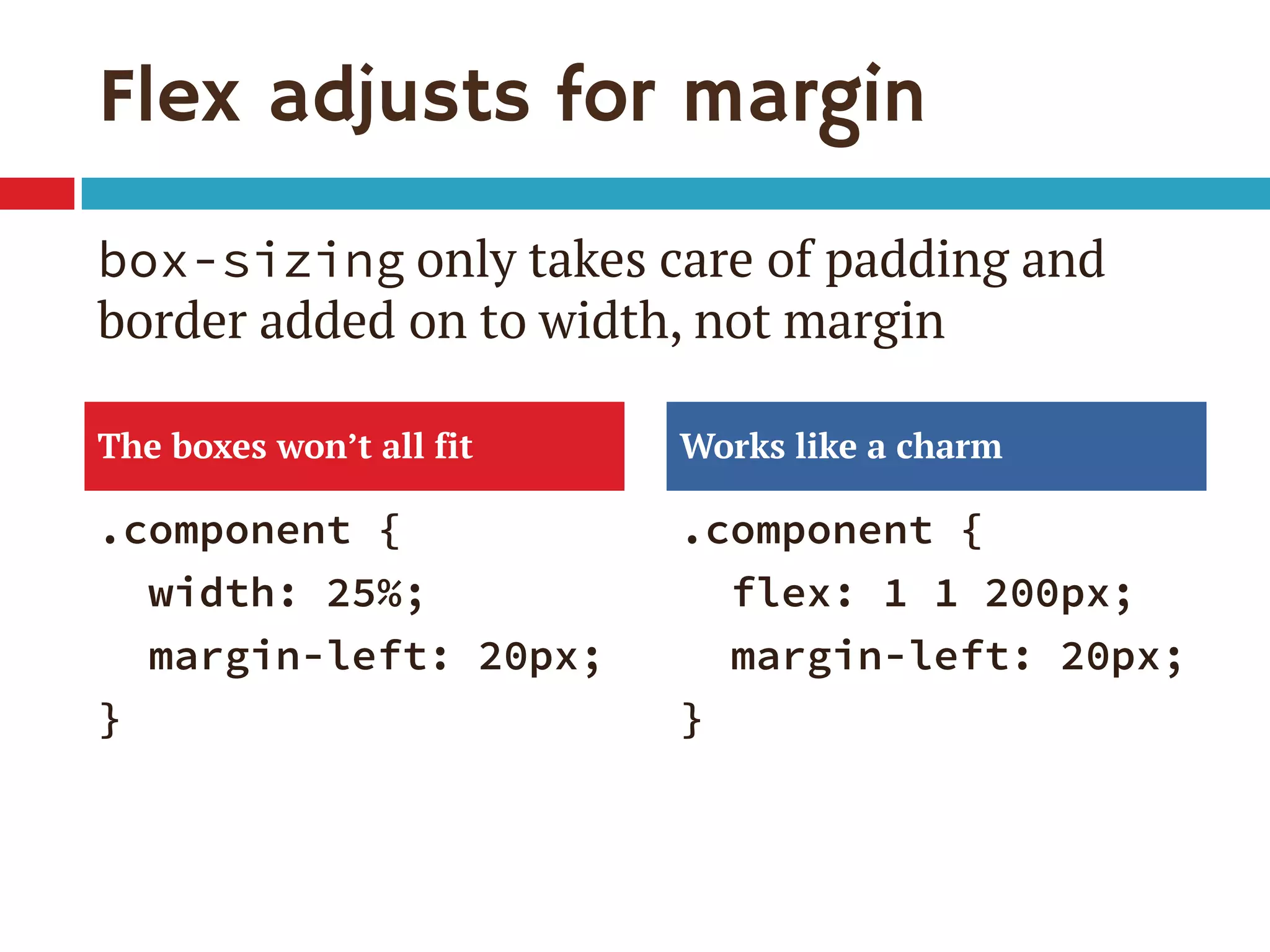
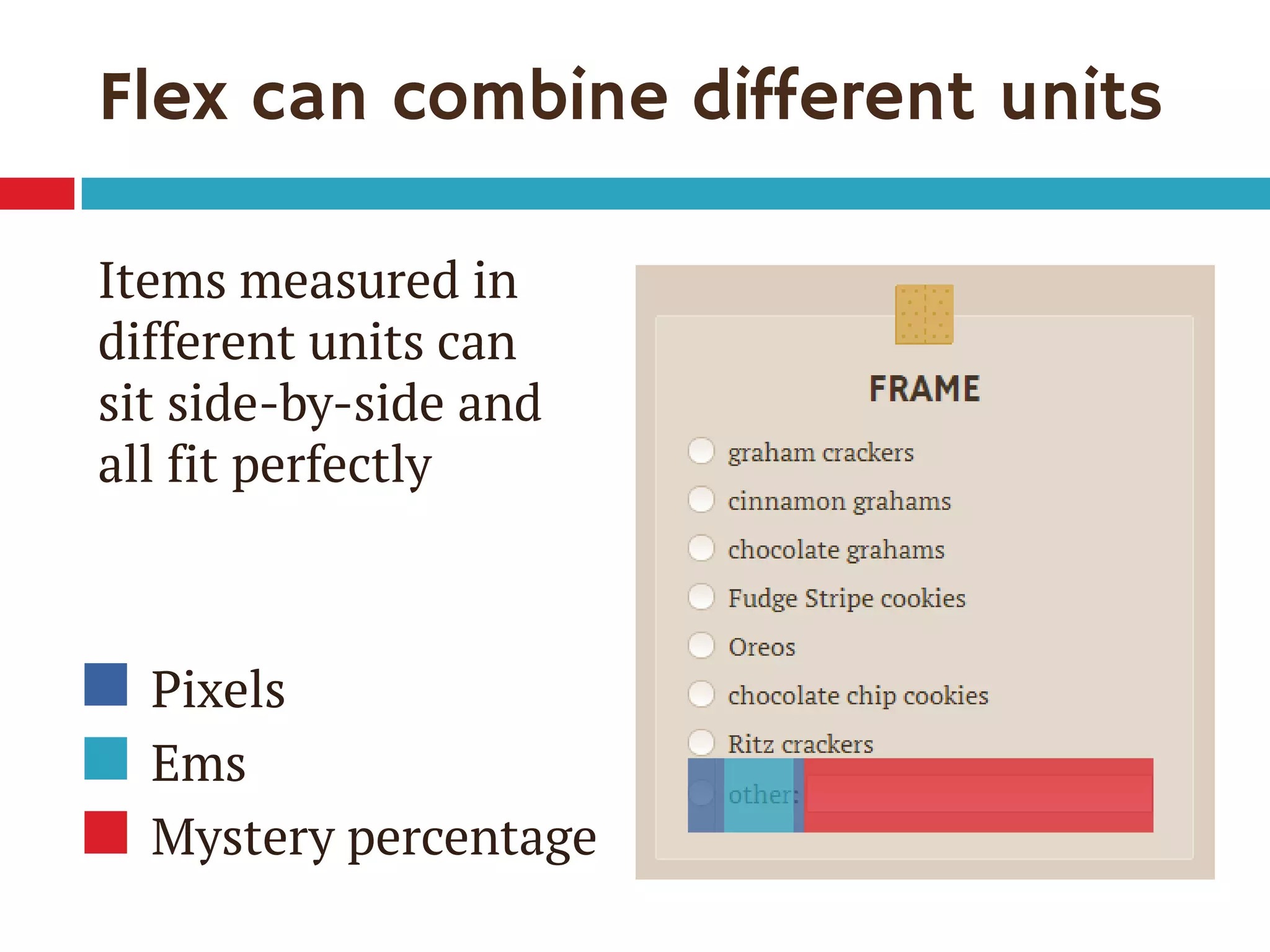
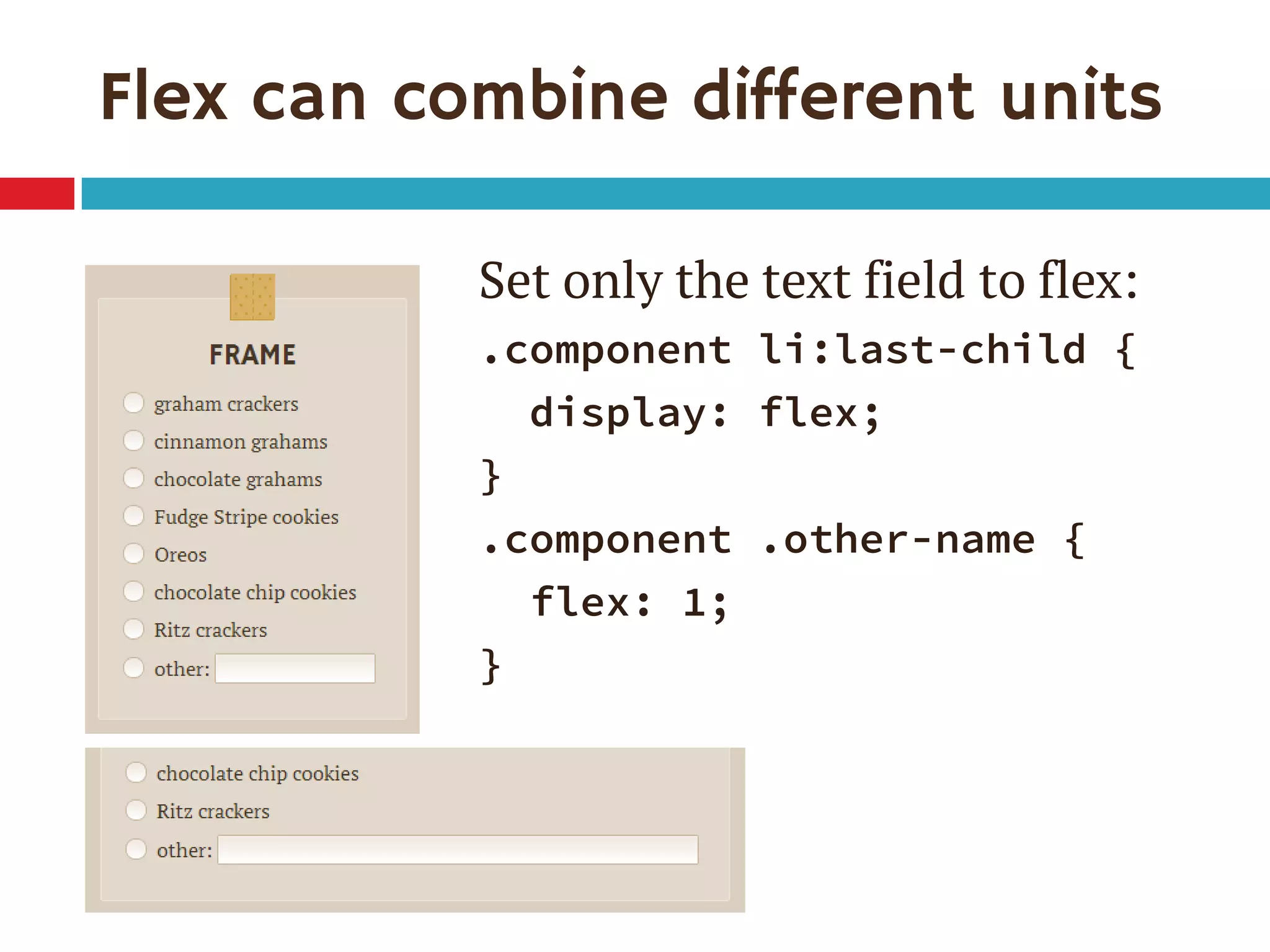
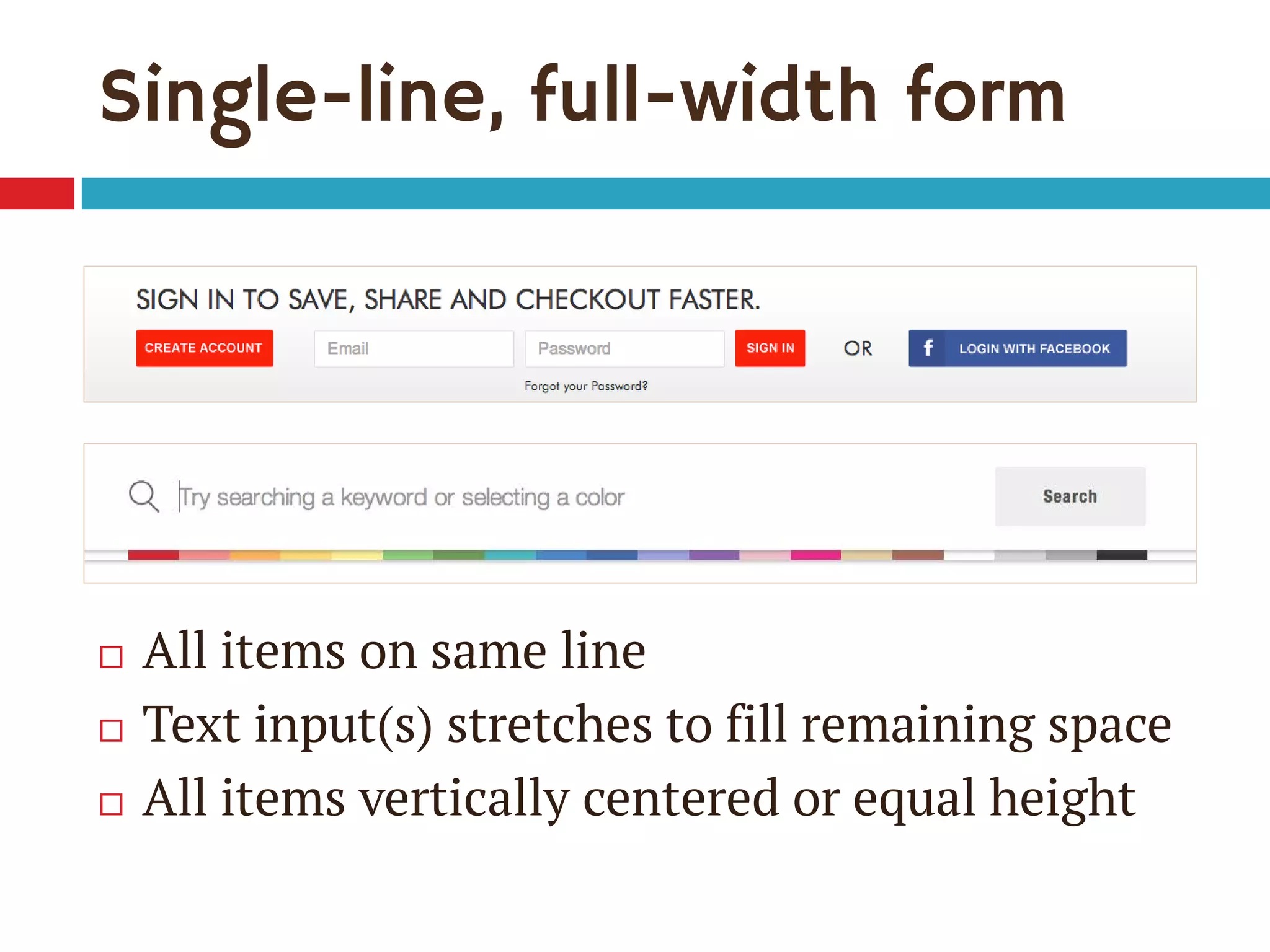
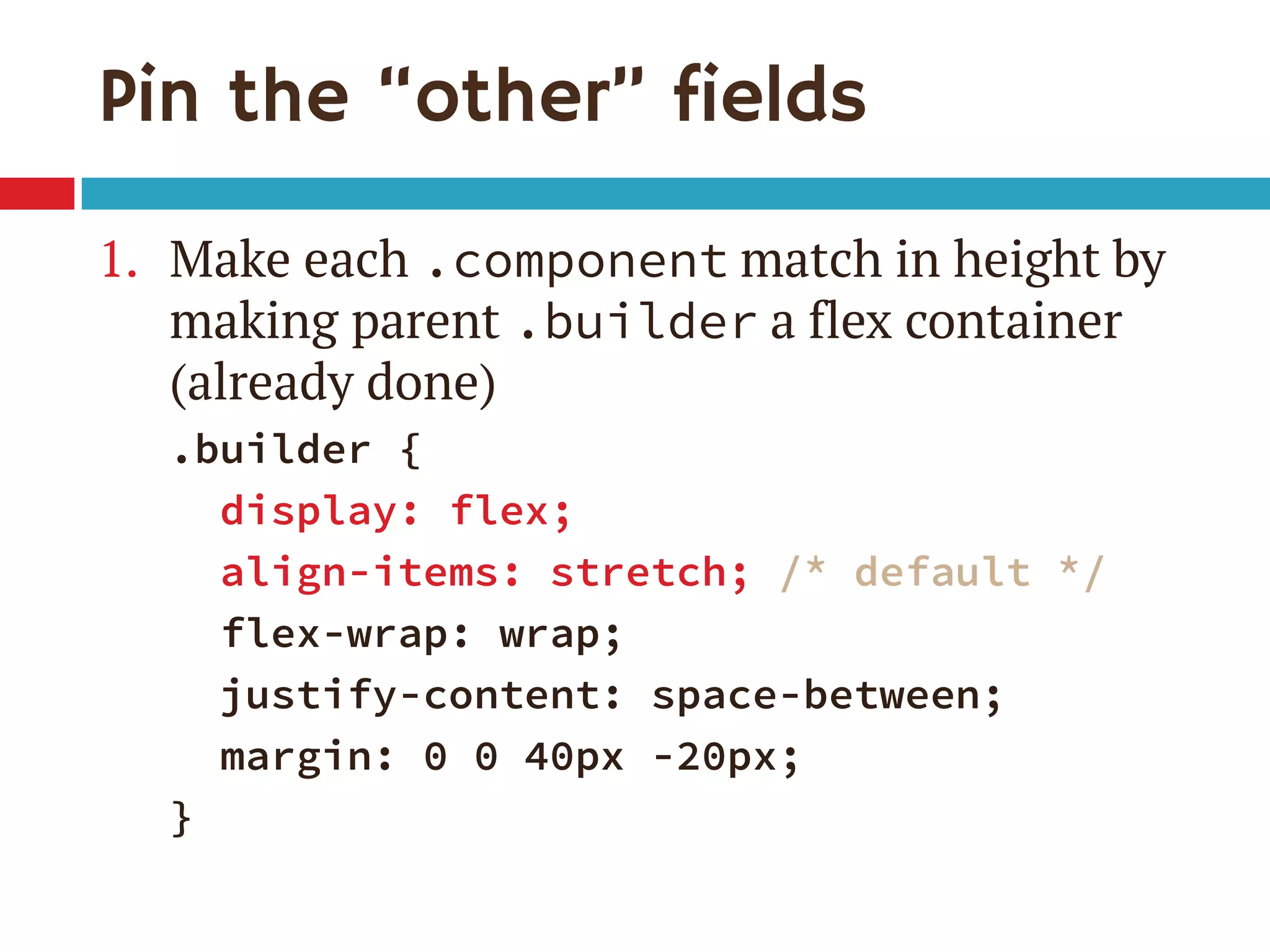
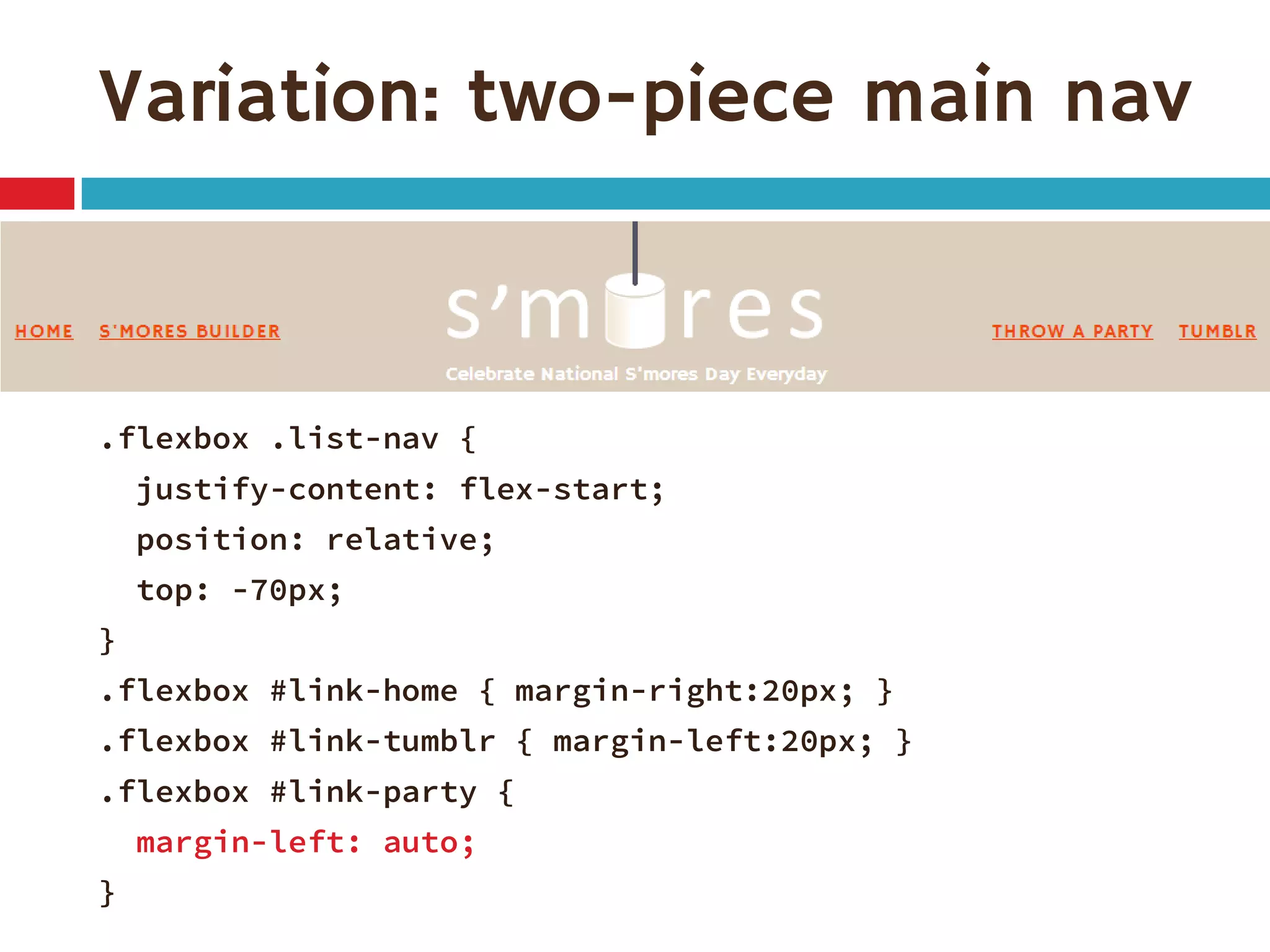
1. The document discusses the CSS Flexible Box Layout Module (flexbox) and how to implement it.
2. Flexbox allows items to be laid out flexibly on a page and makes it easier to create responsive page layouts without needing many media queries.
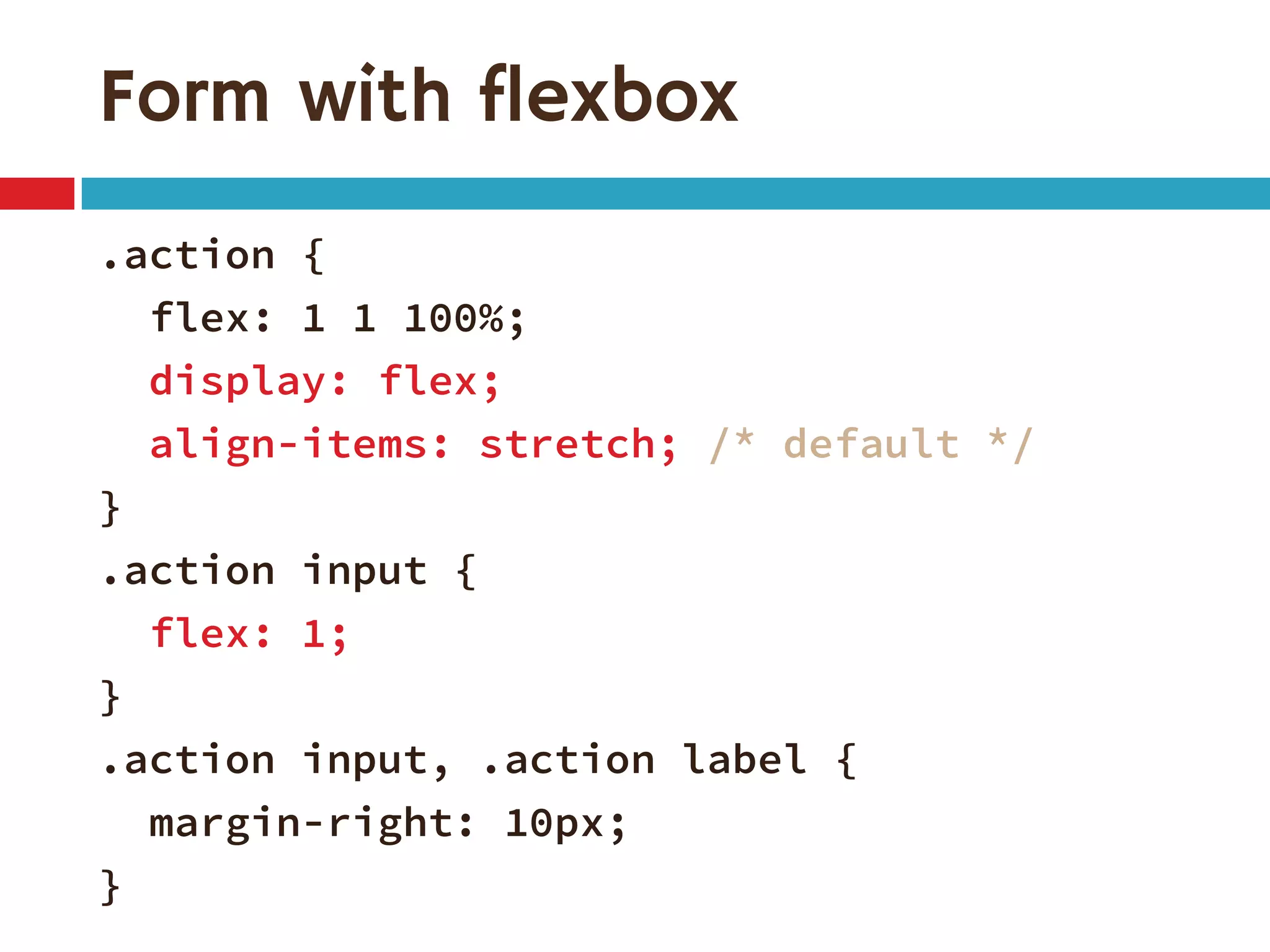
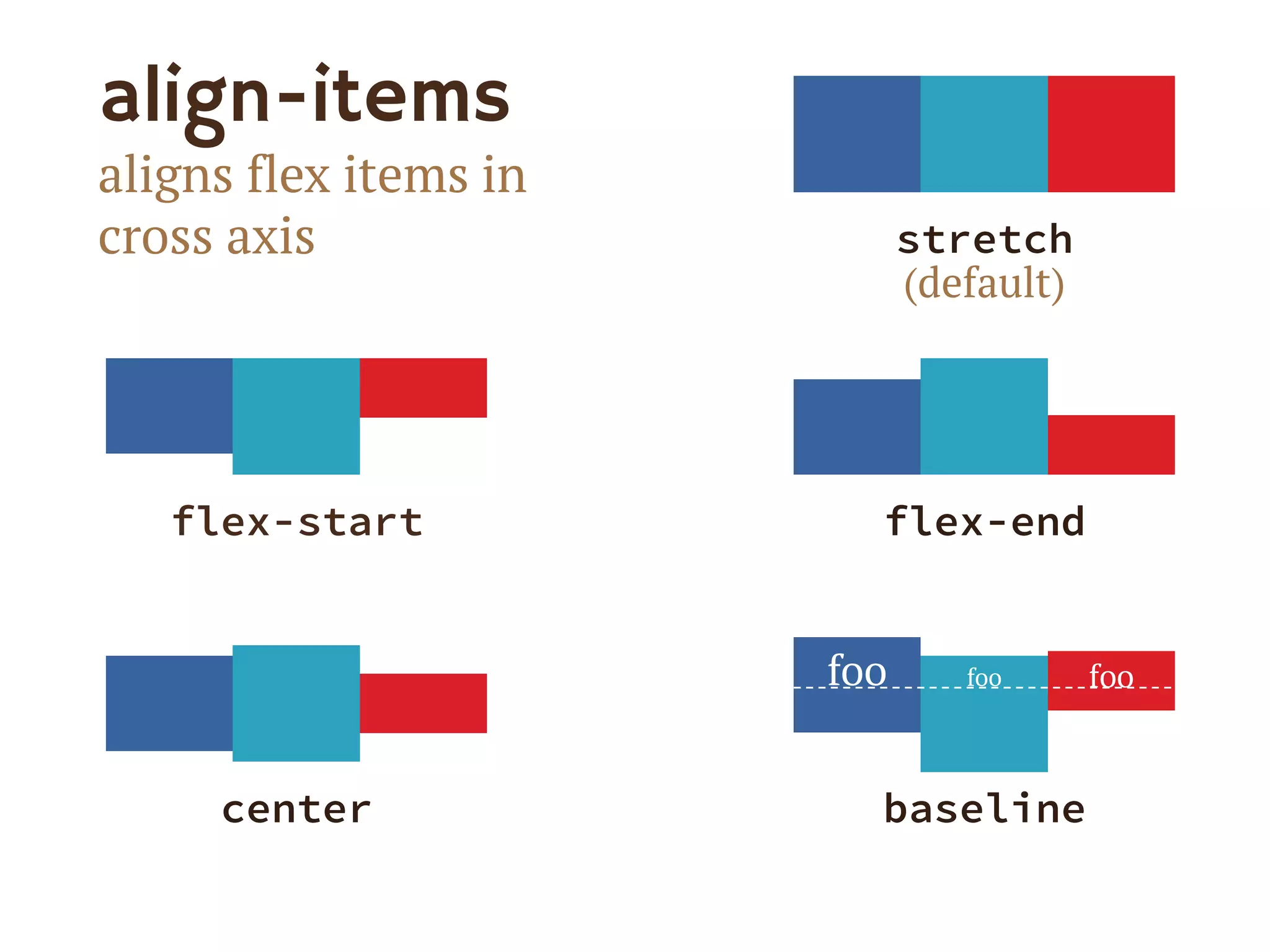
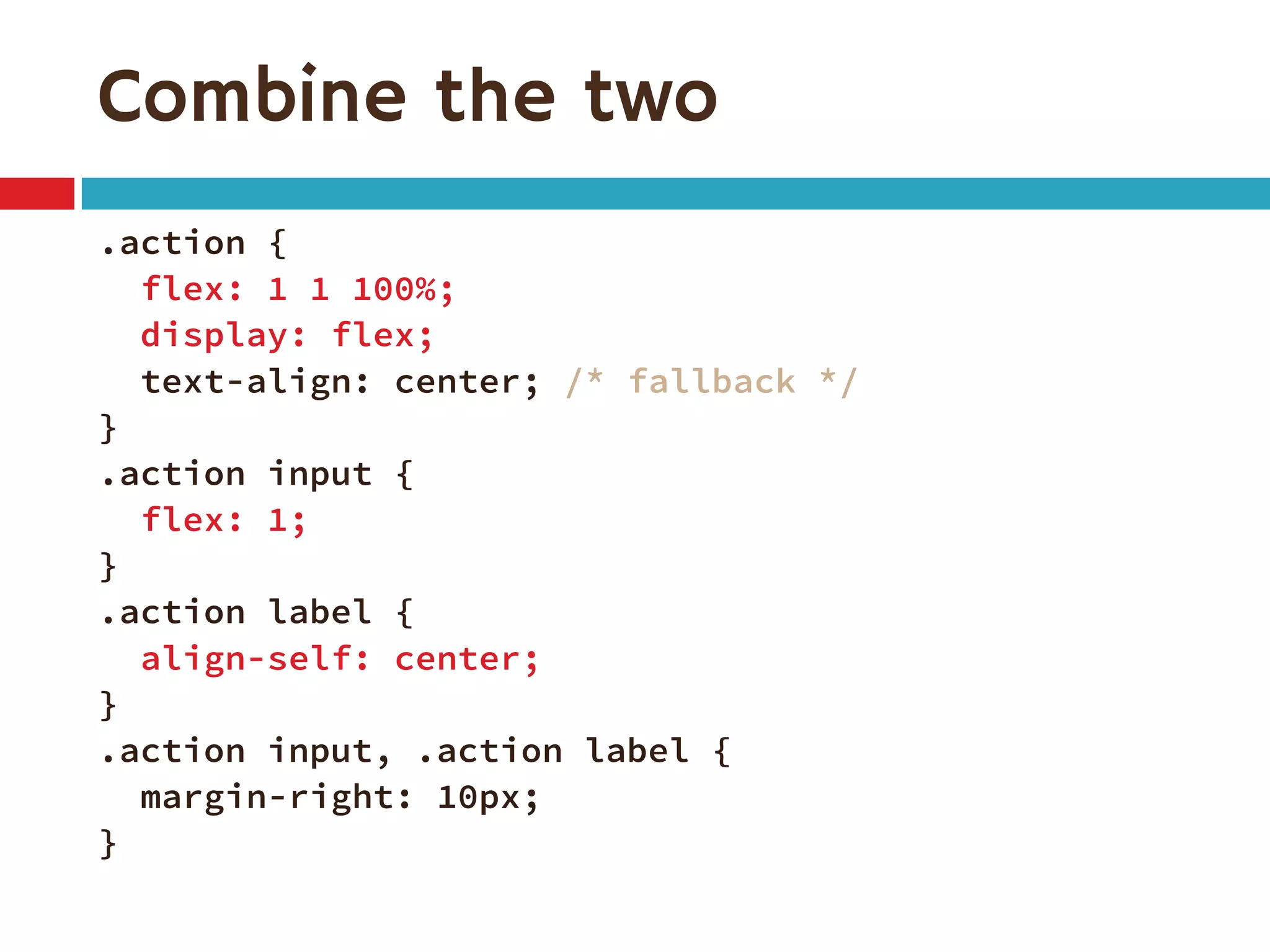
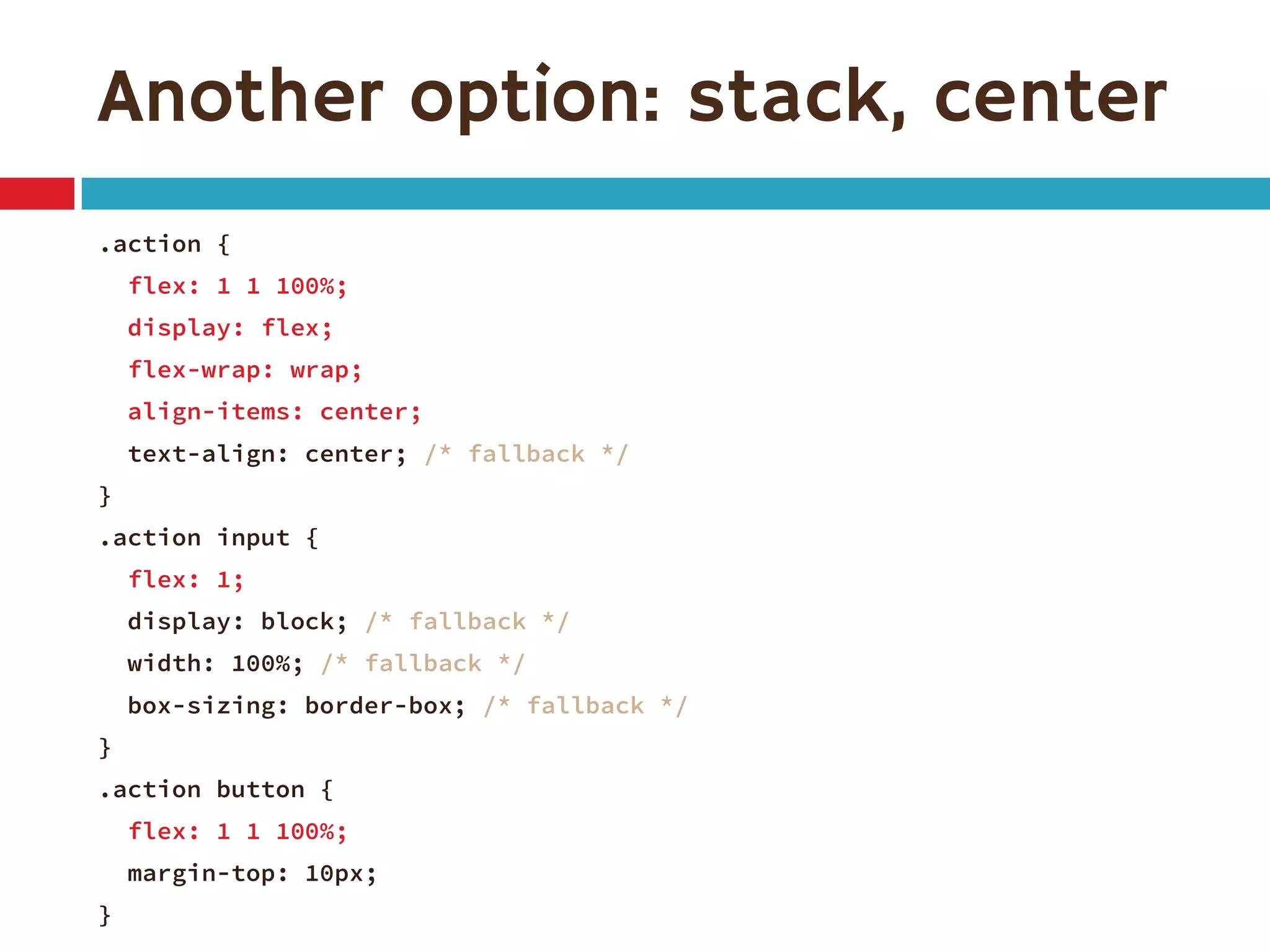
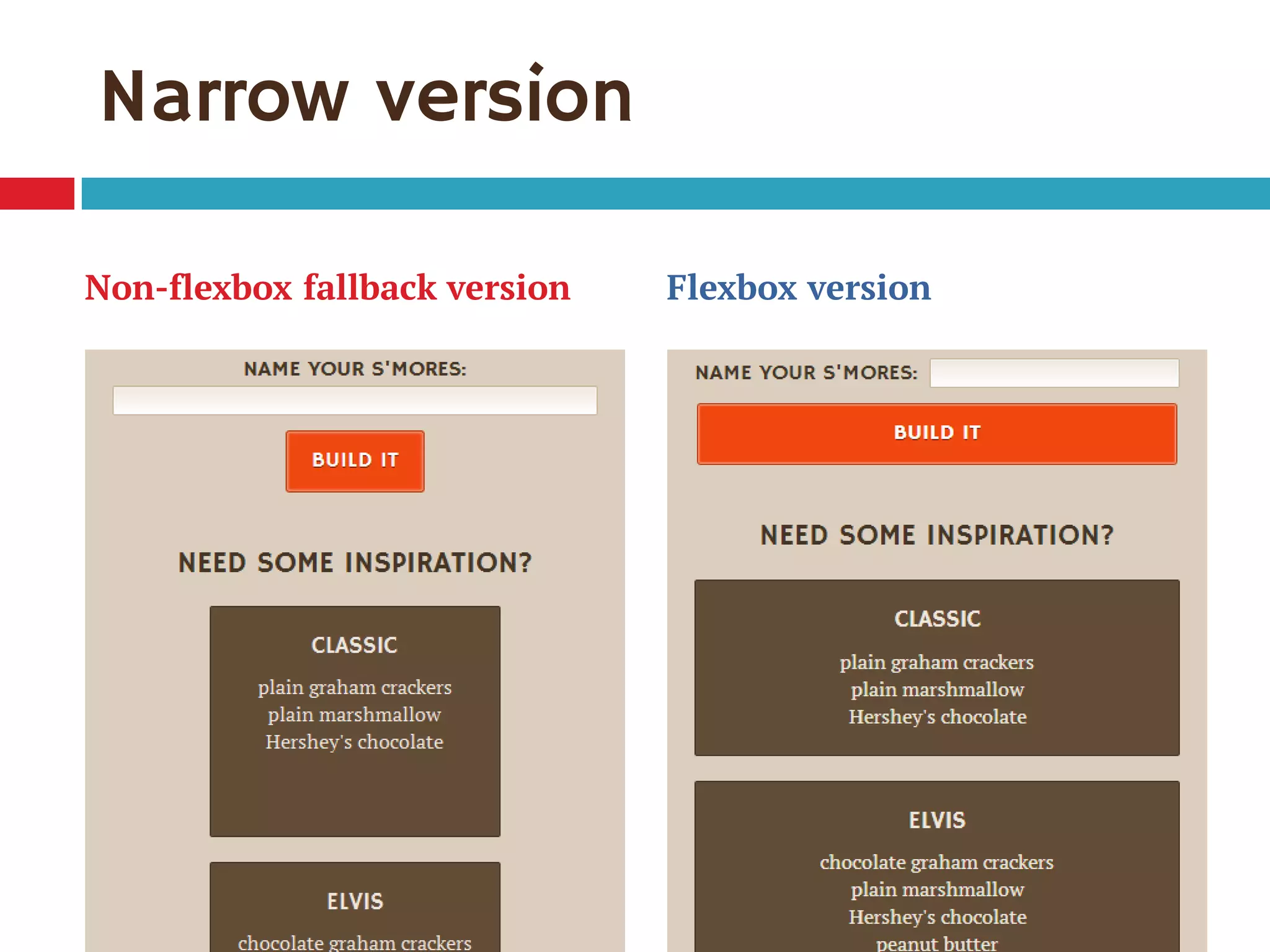
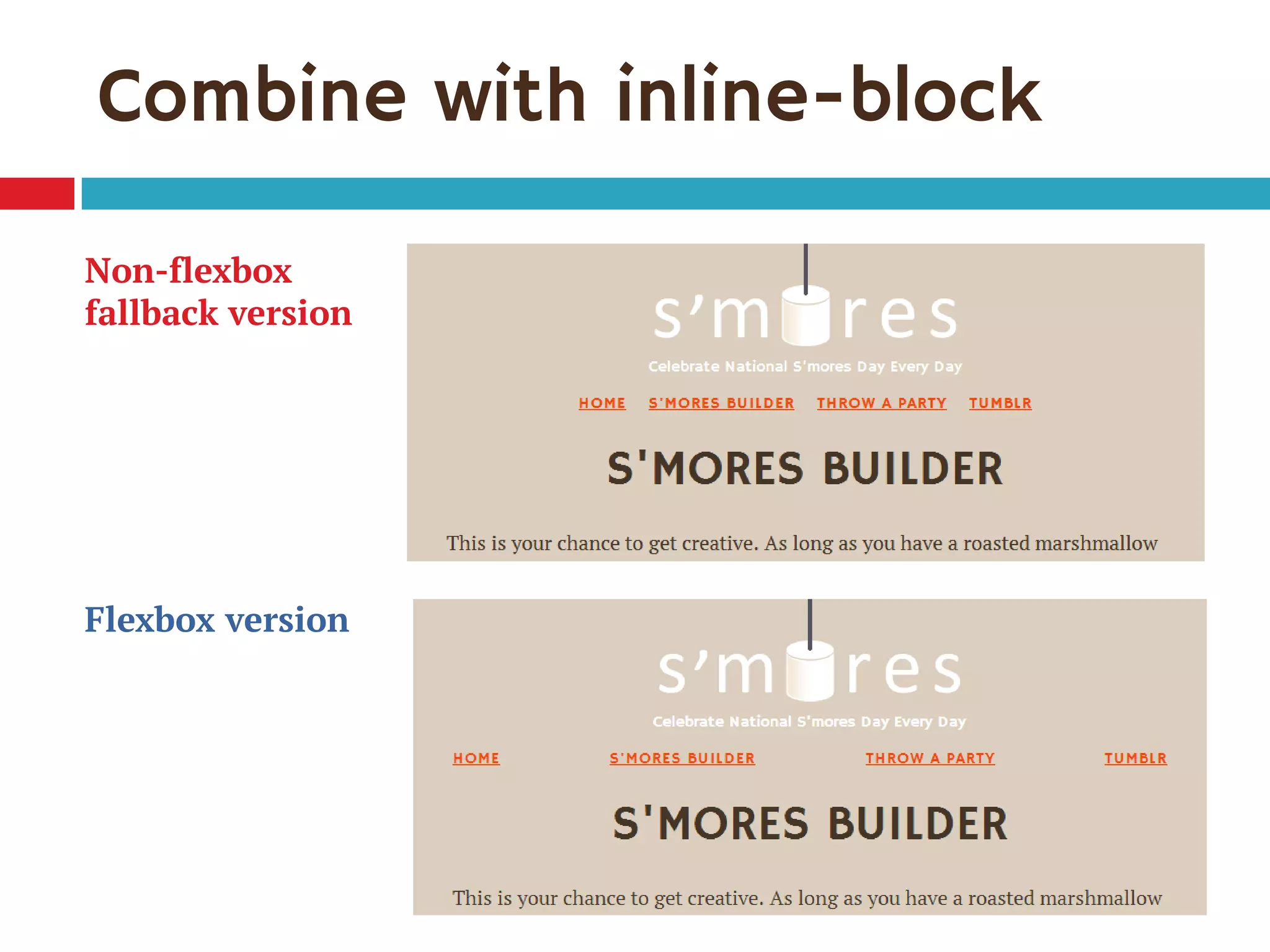
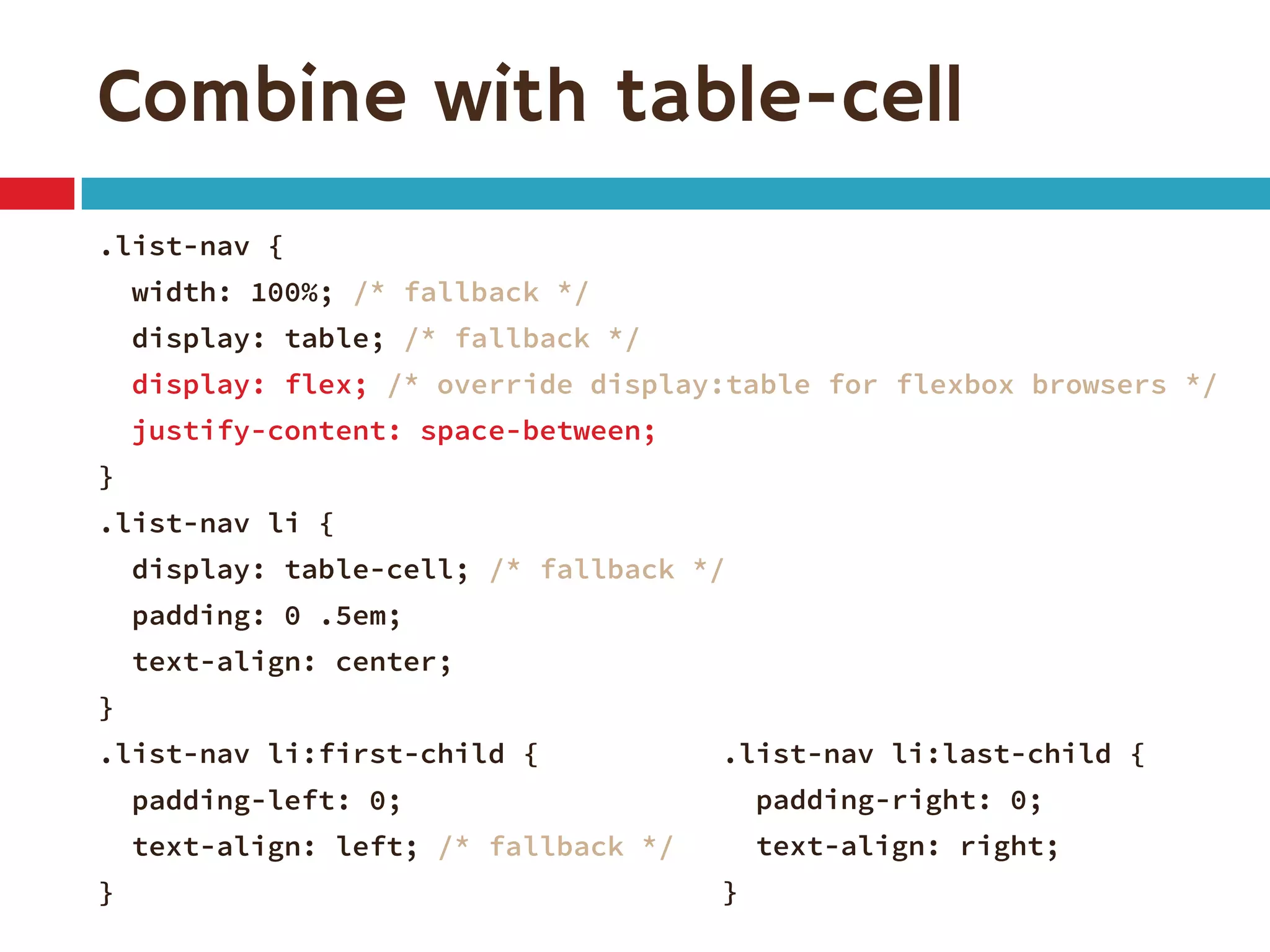
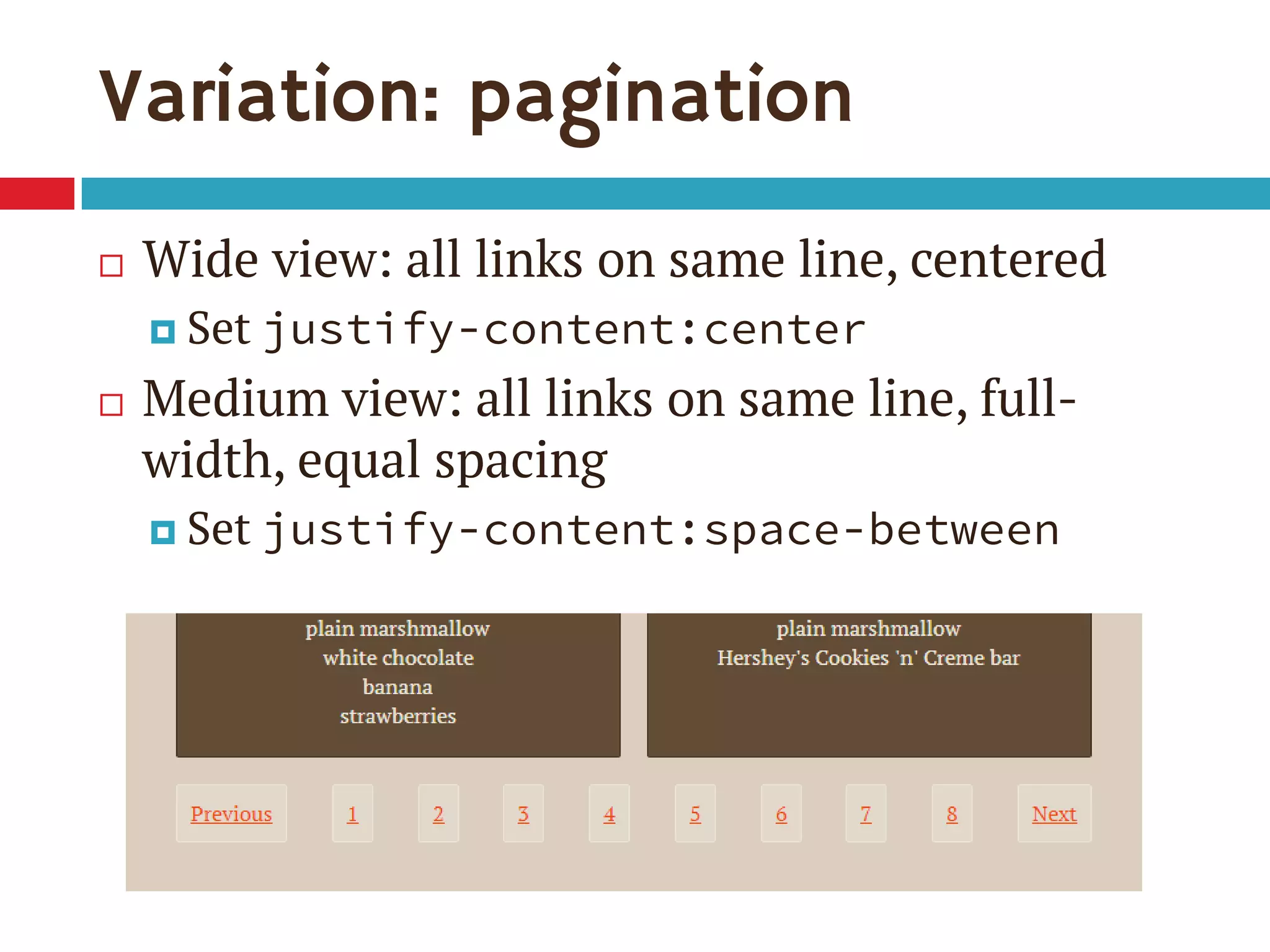
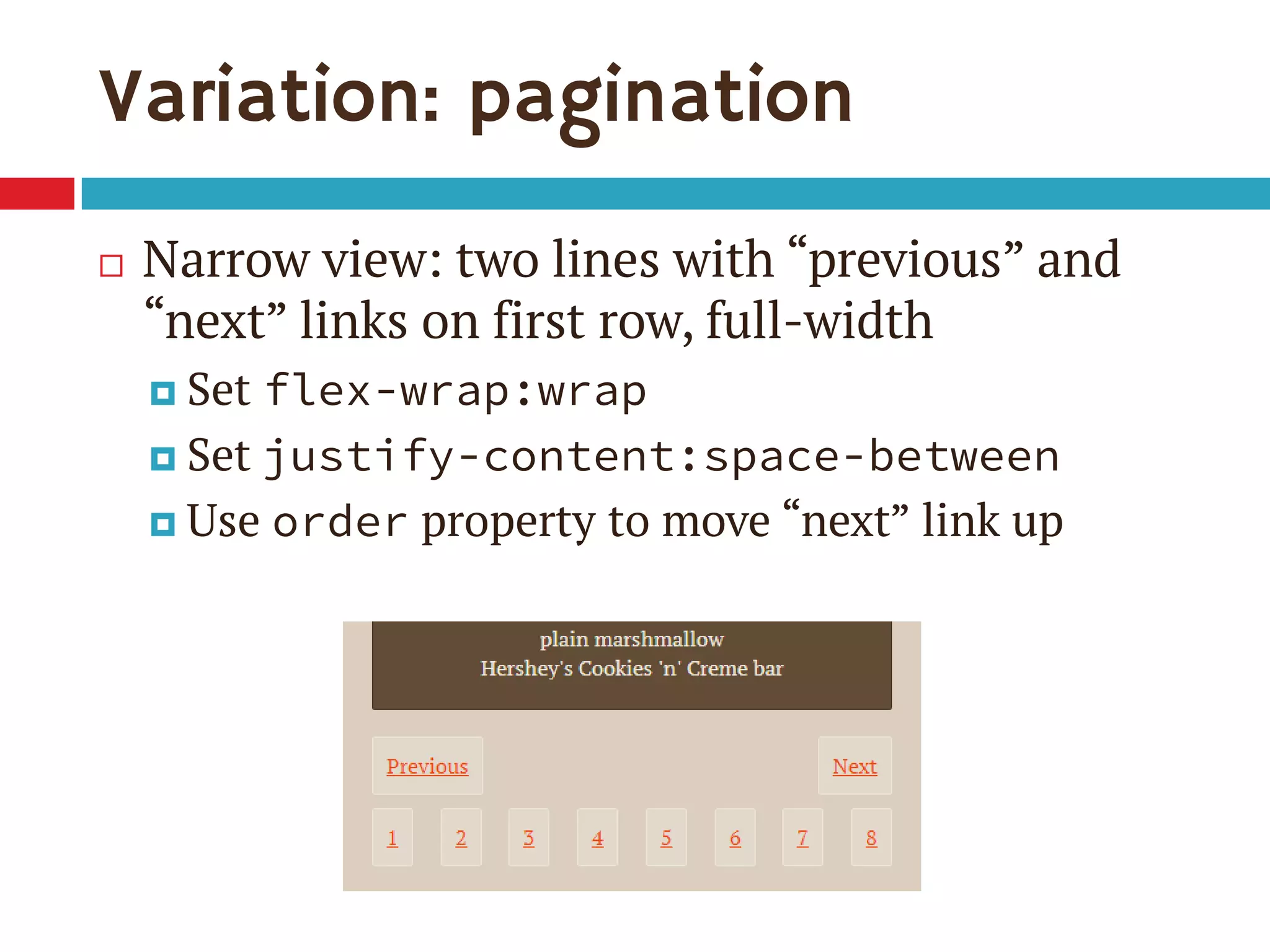
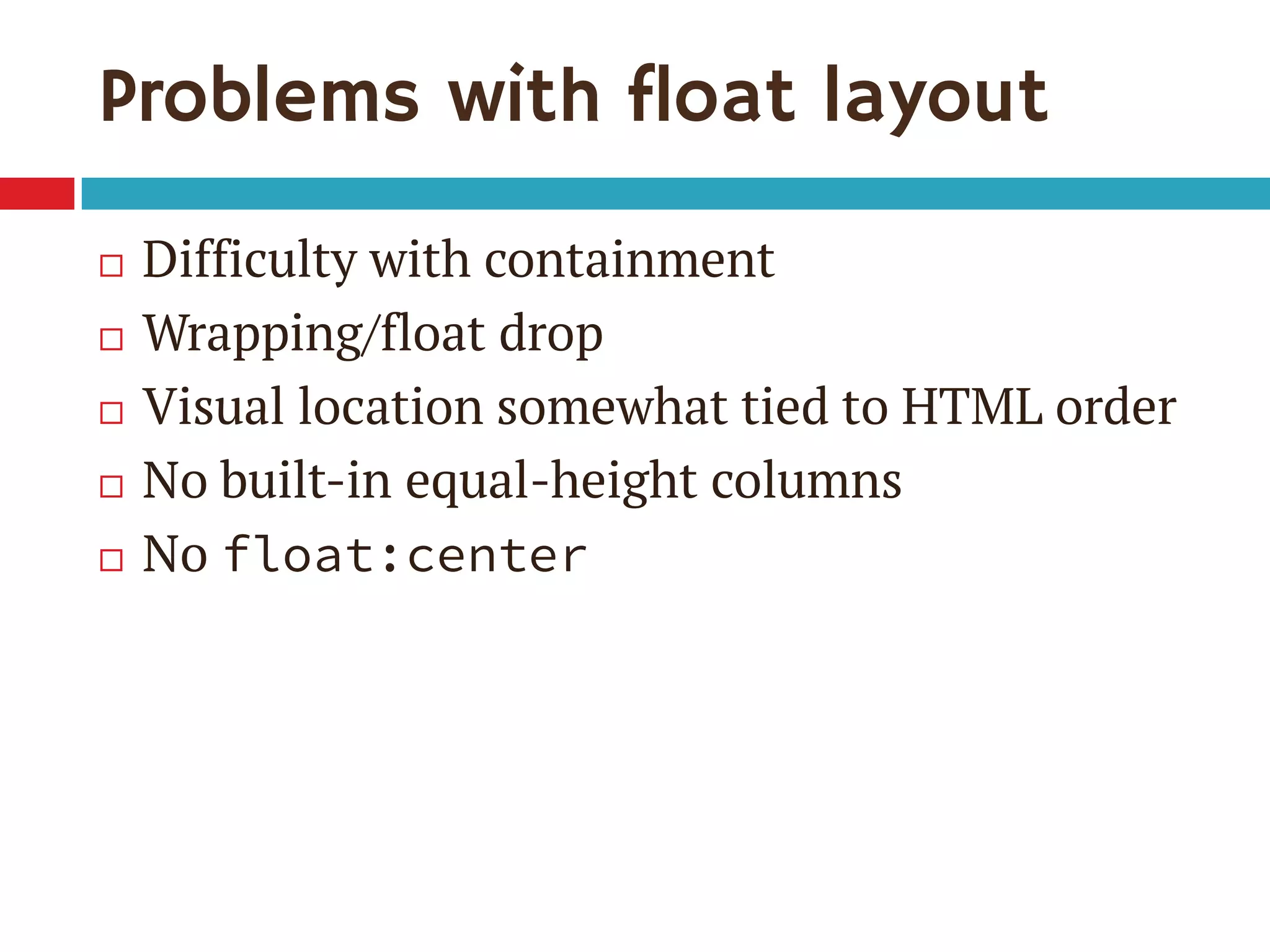
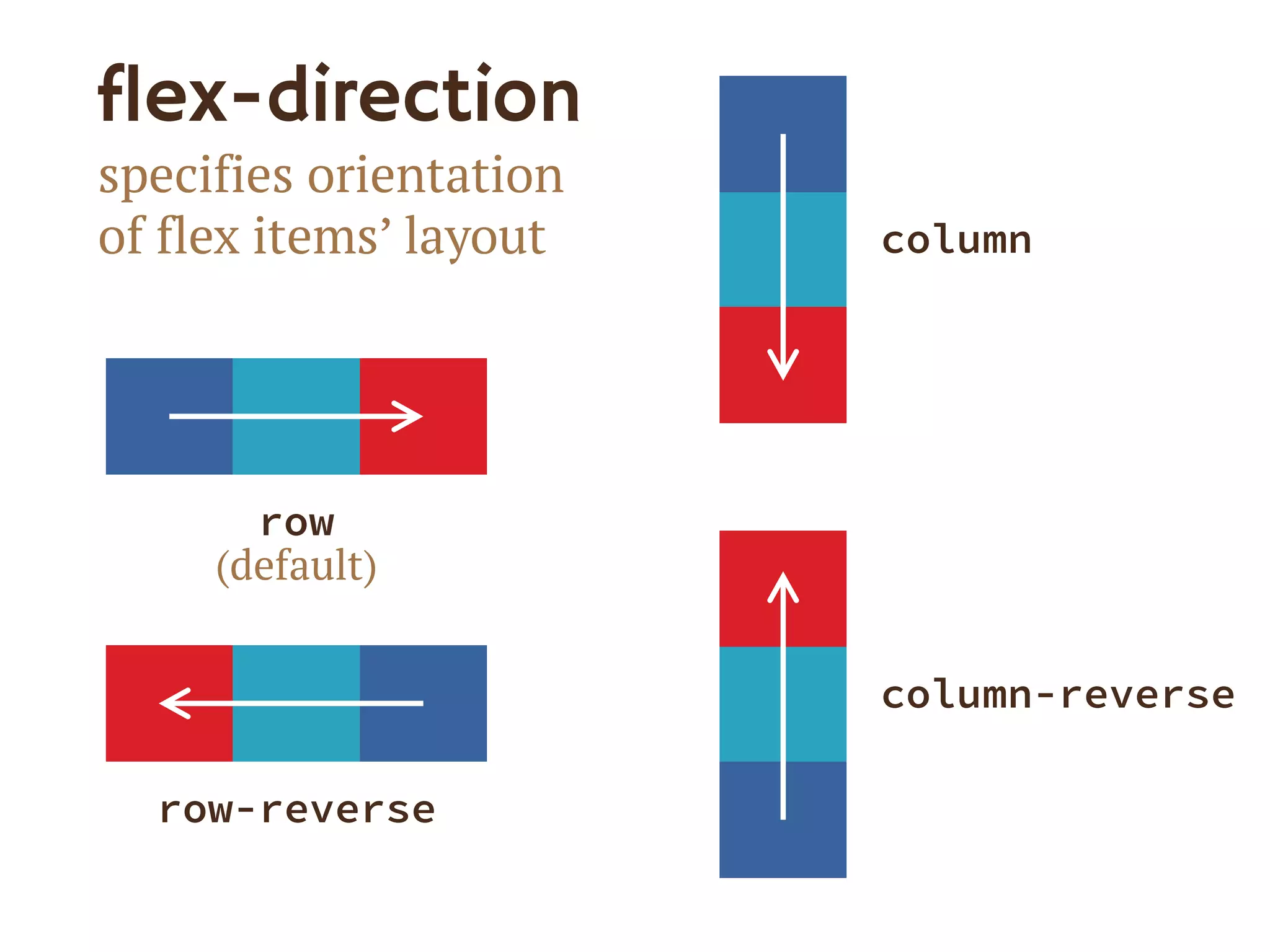
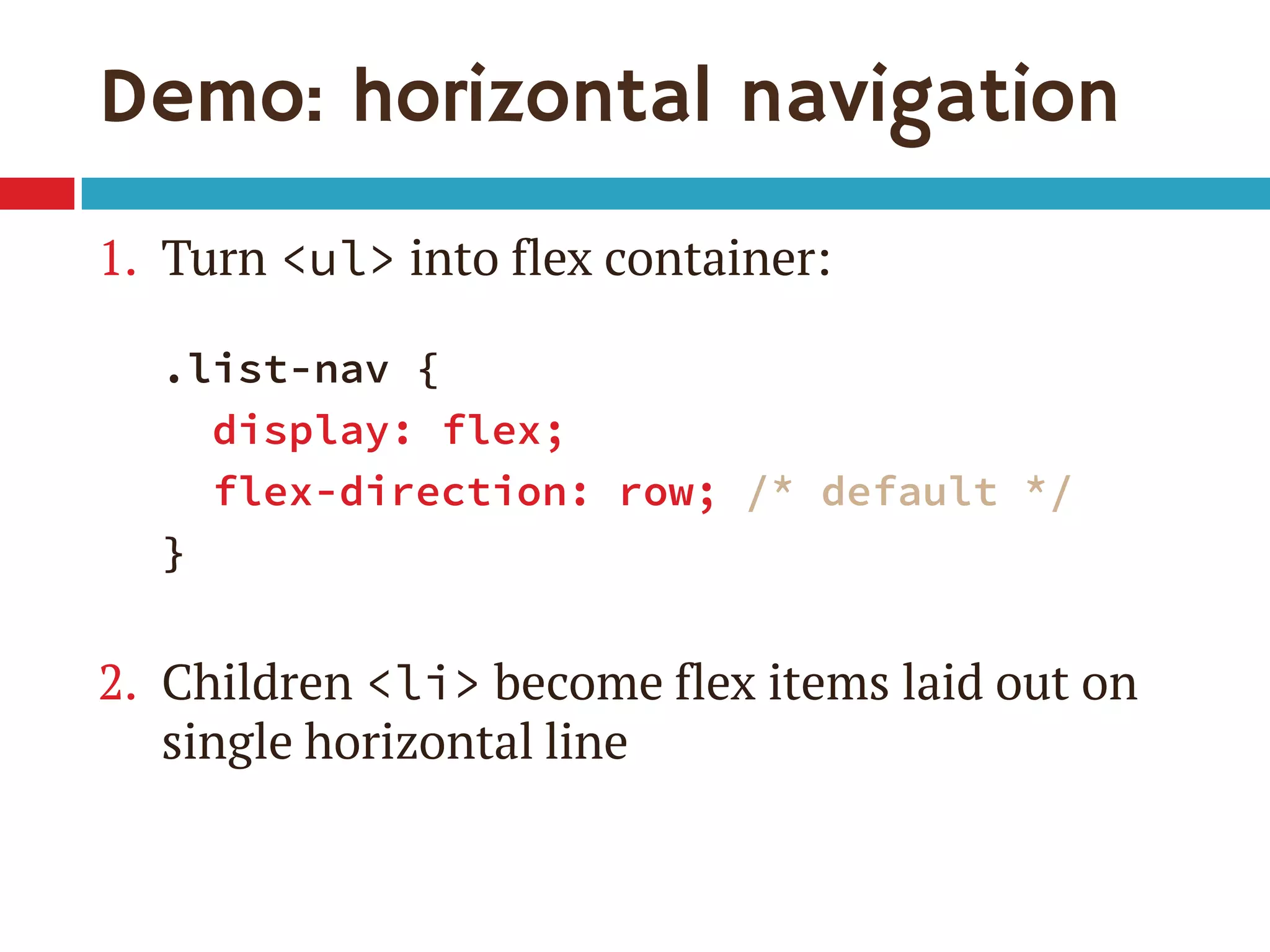
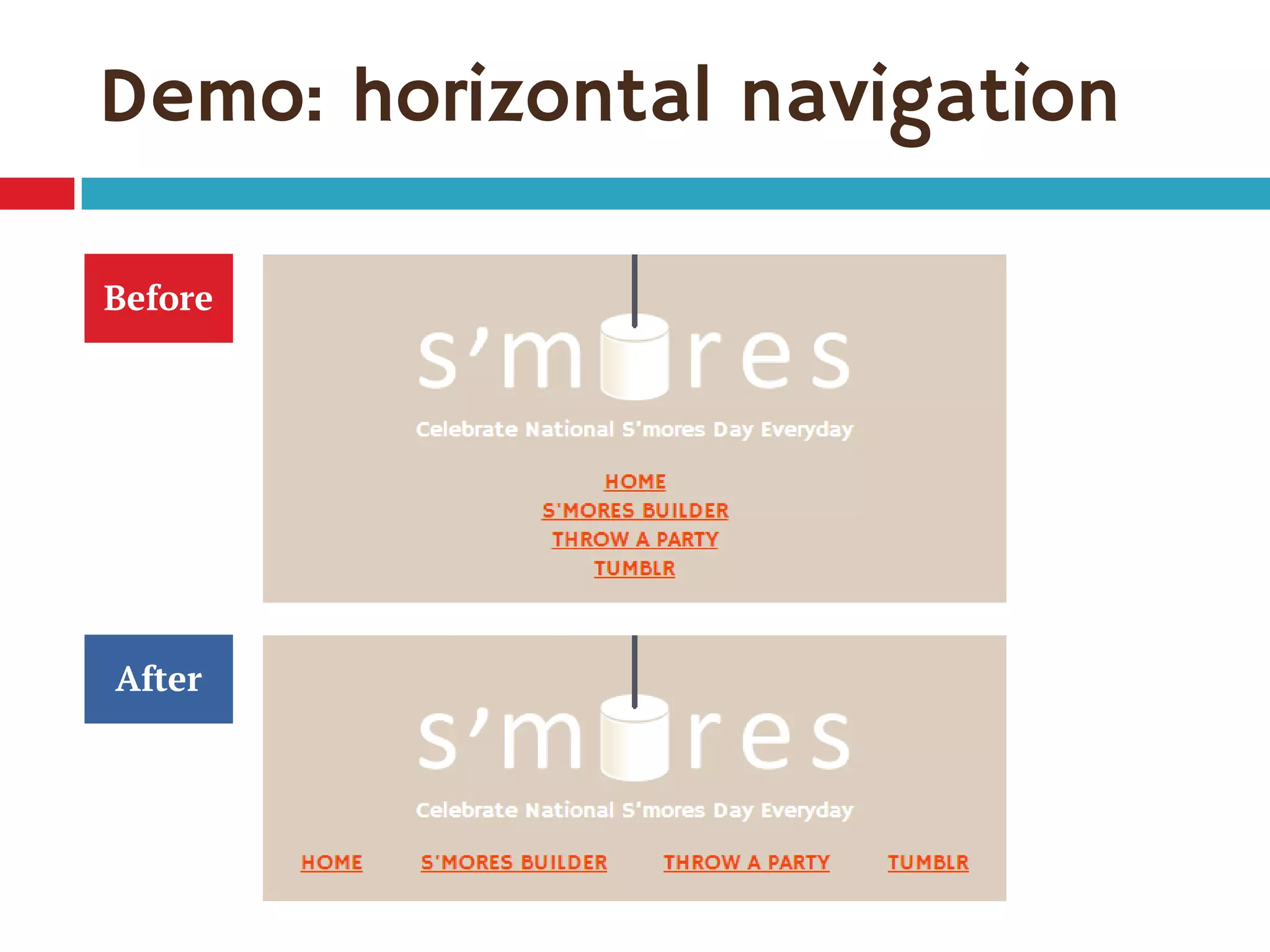
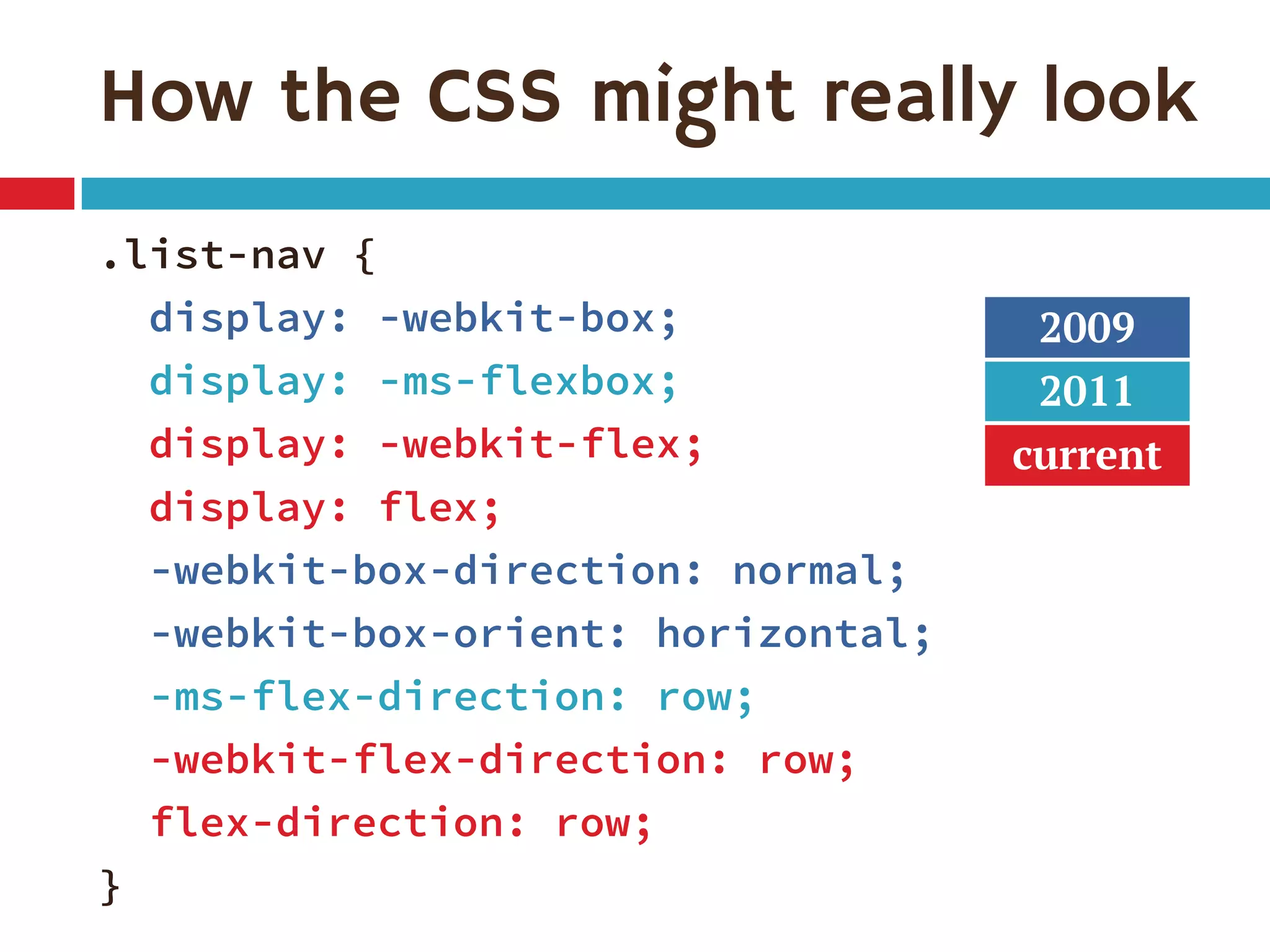
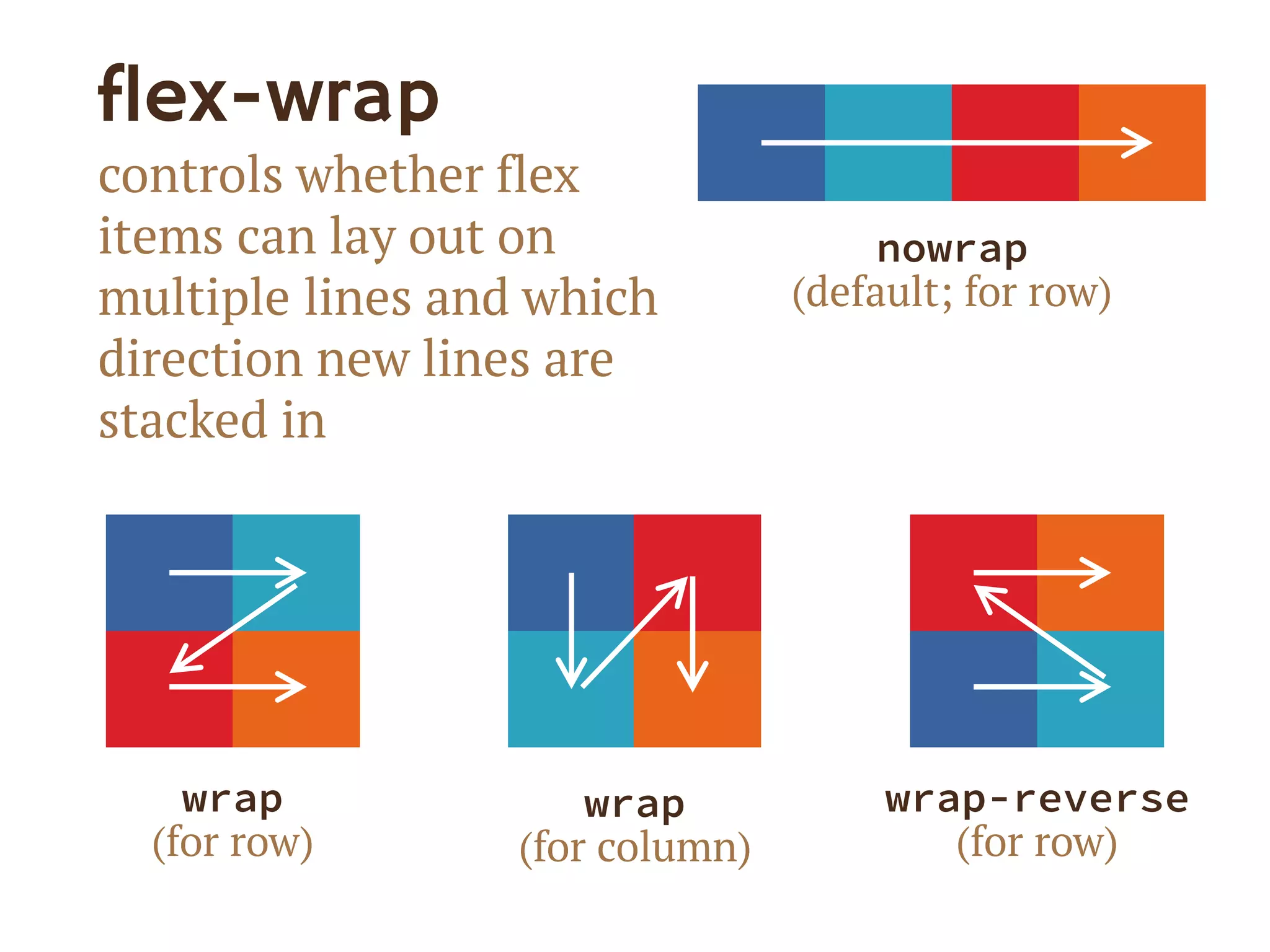
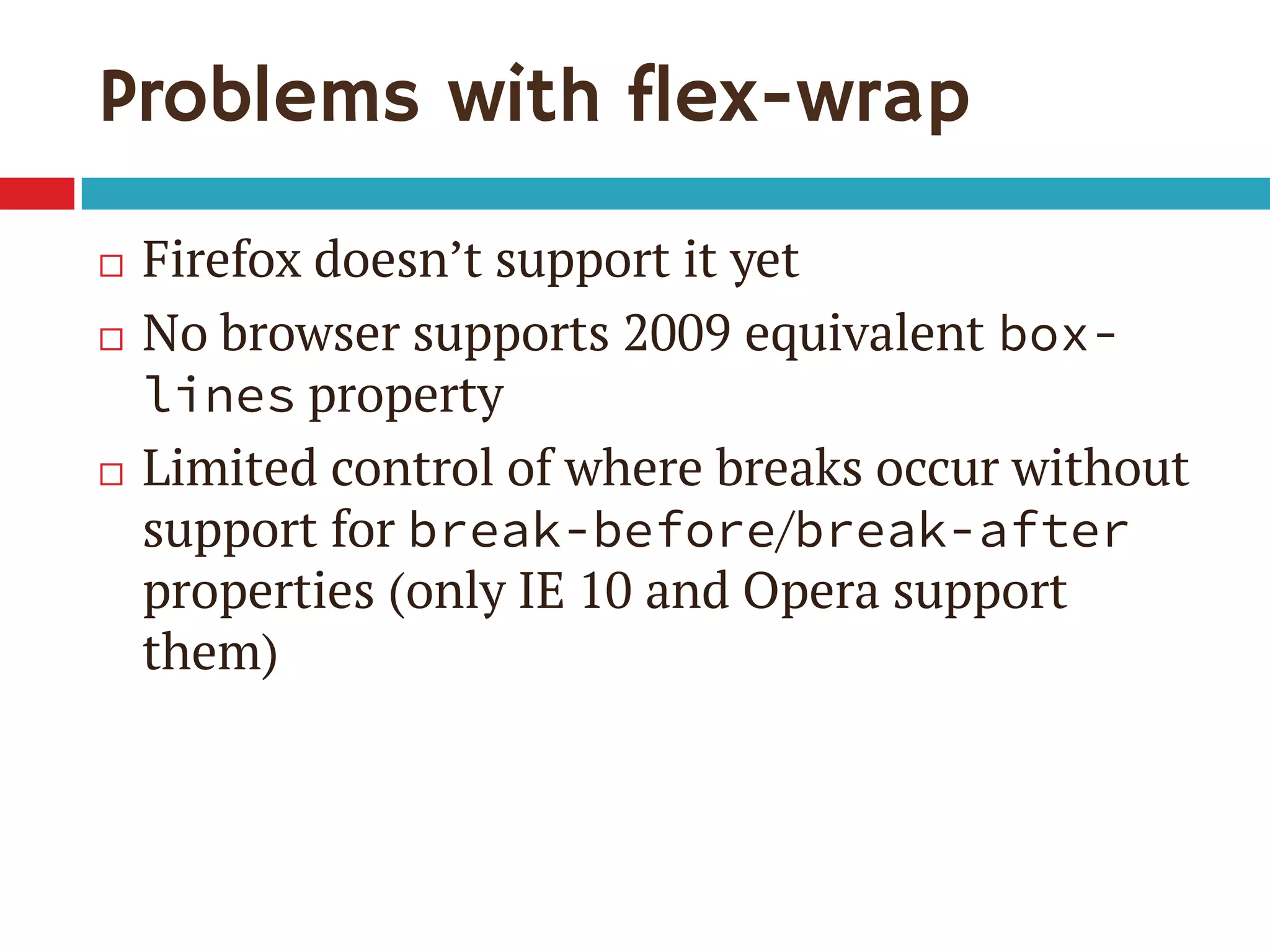
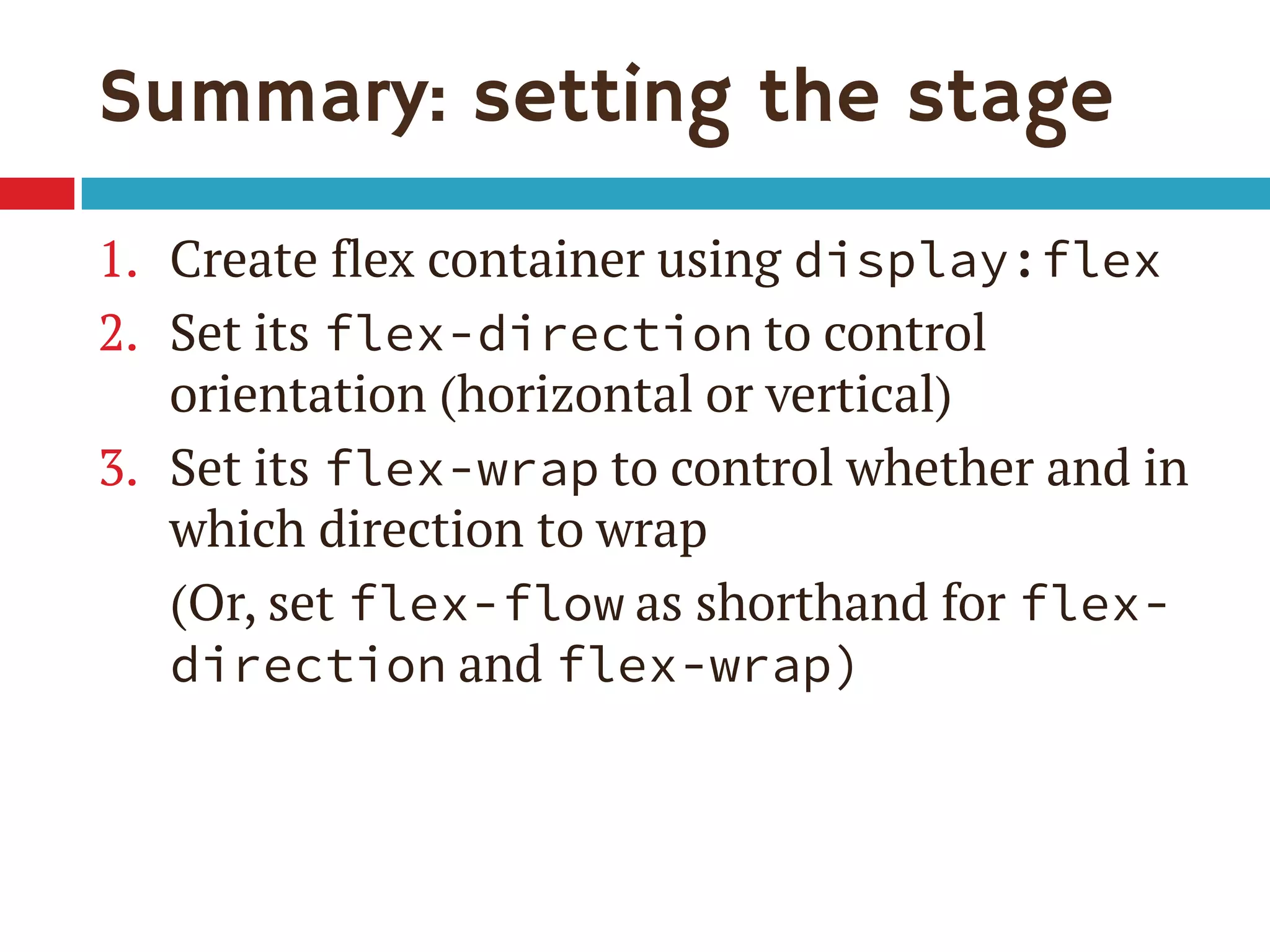
3. The document demonstrates how to use various flexbox properties like flex-direction, flex-wrap, justify-content, and order to create common layouts like navigation bars, forms, and grids.


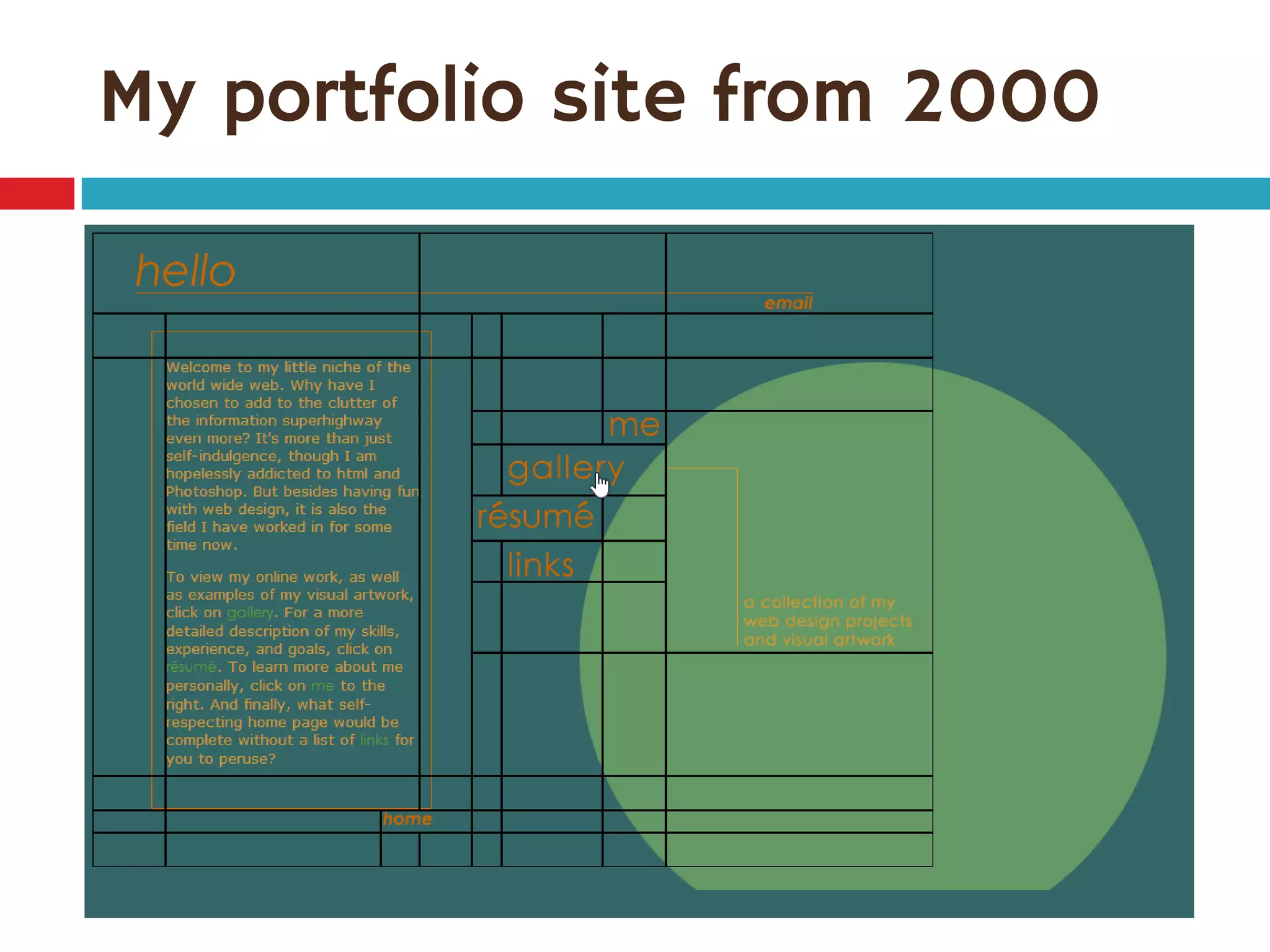






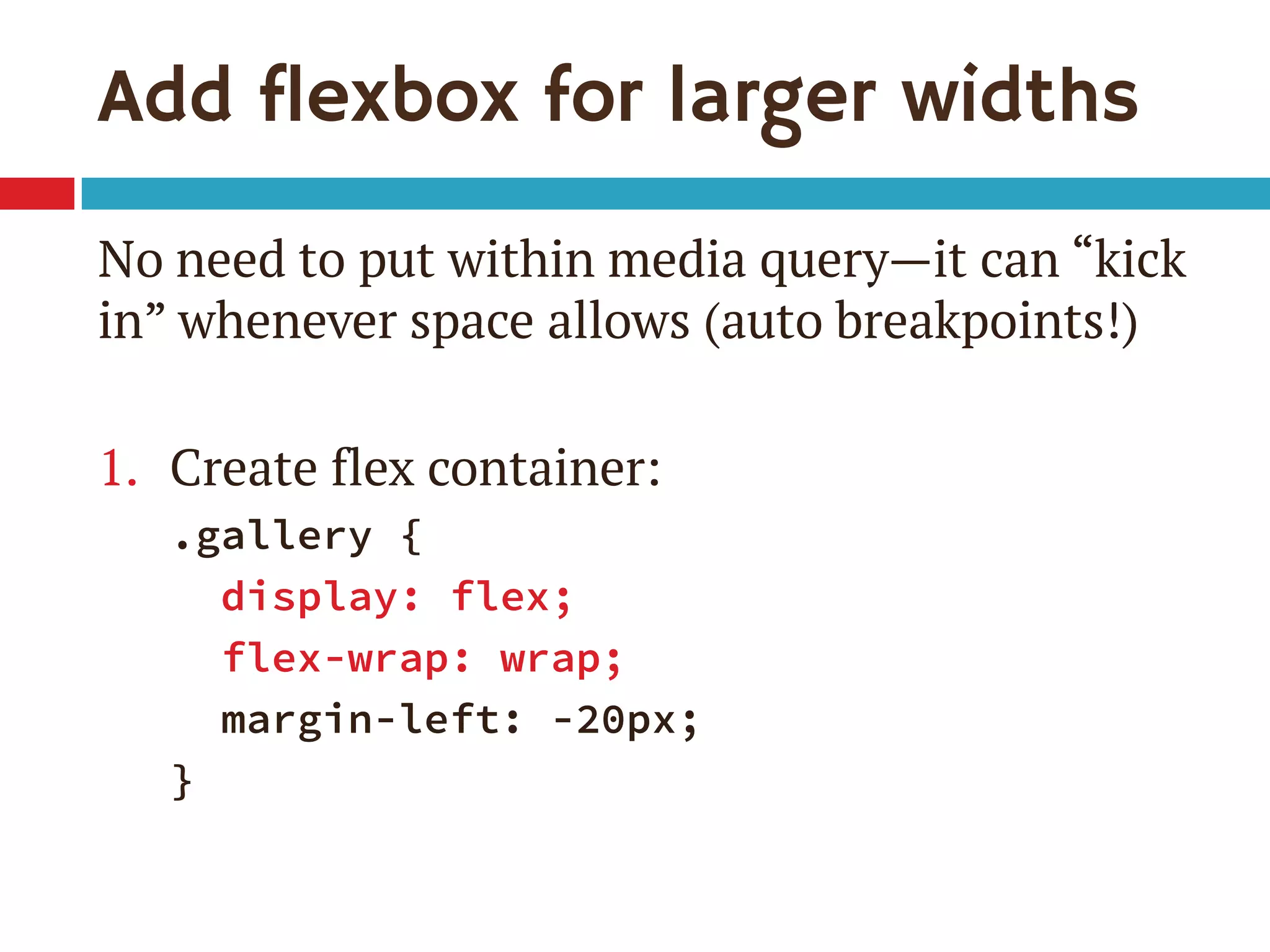




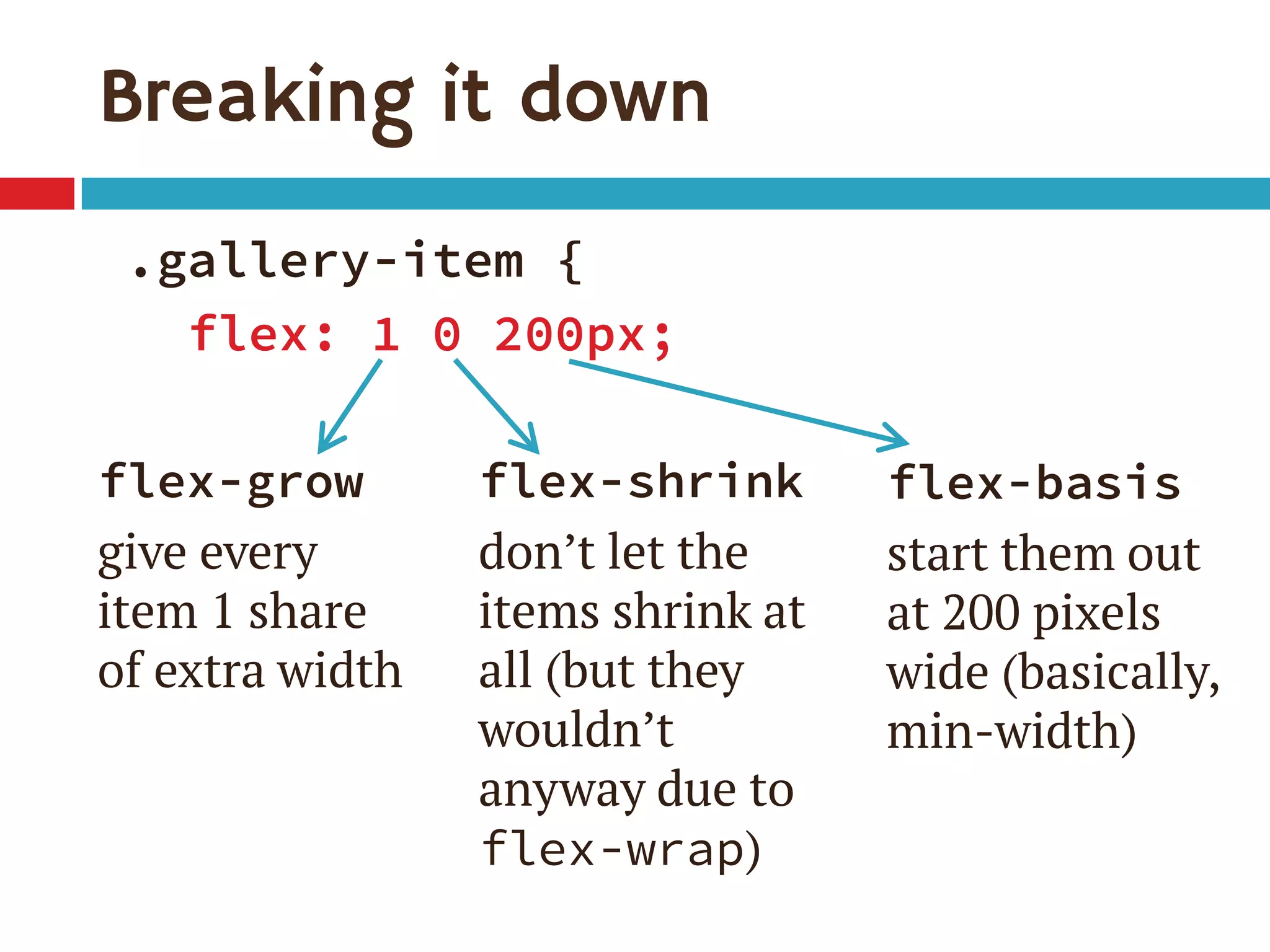

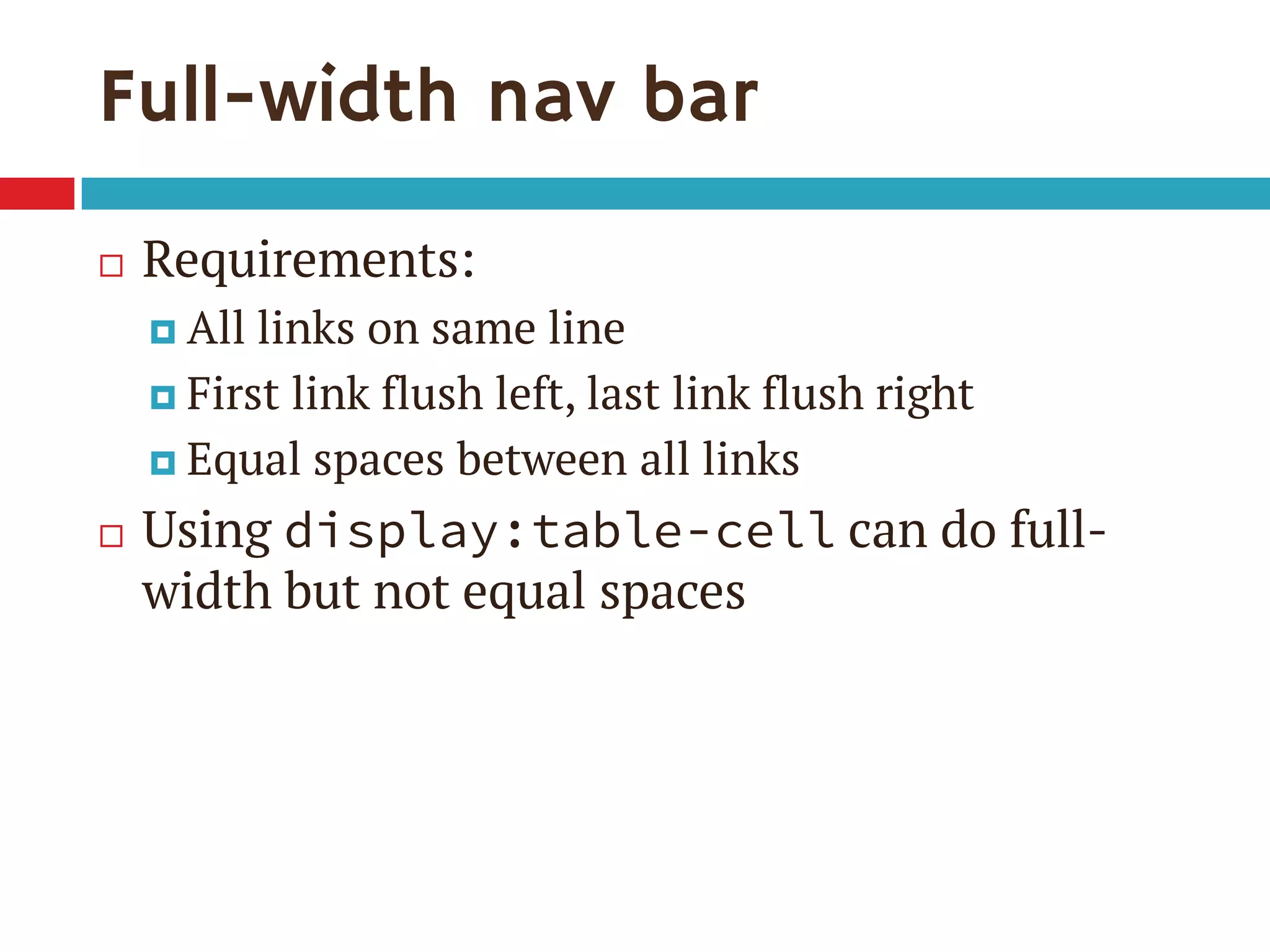
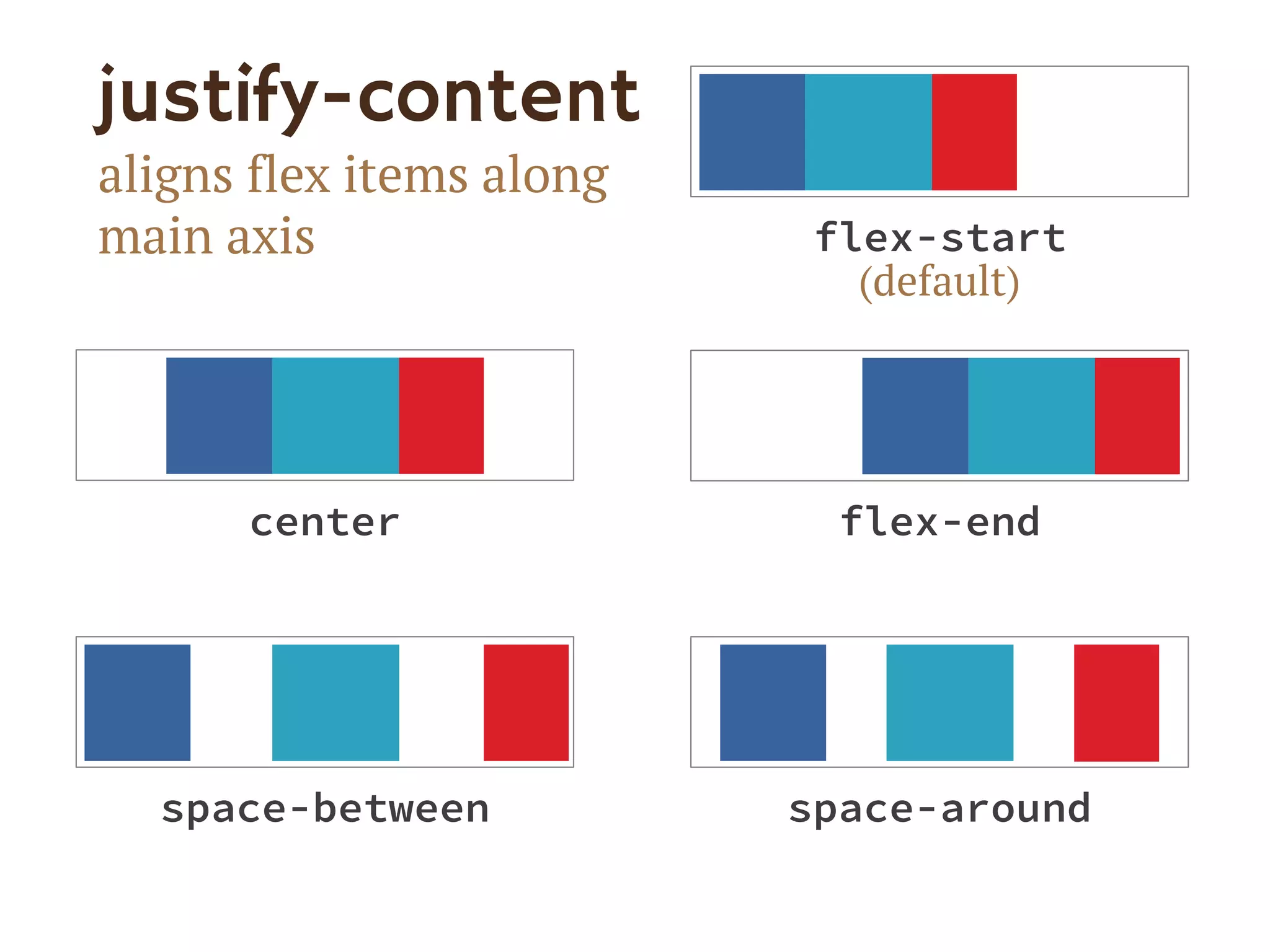
![Single-digit flex values
Common to see flex: 1 in demos
flex: [number] is equivalent to
flex: [number] 1 0px
Be sure you really want flex-basis to be 0
When wrap on, essentially min-width
0px therefore means items can shrink to 0px
If everything can get down to 0px, nothing ever
has a reason to wrap](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/putting-flexbox-into-practiceblend-conf130907-130908160522-/75/Putting-Flexbox-into-Practice-30-2048.jpg)