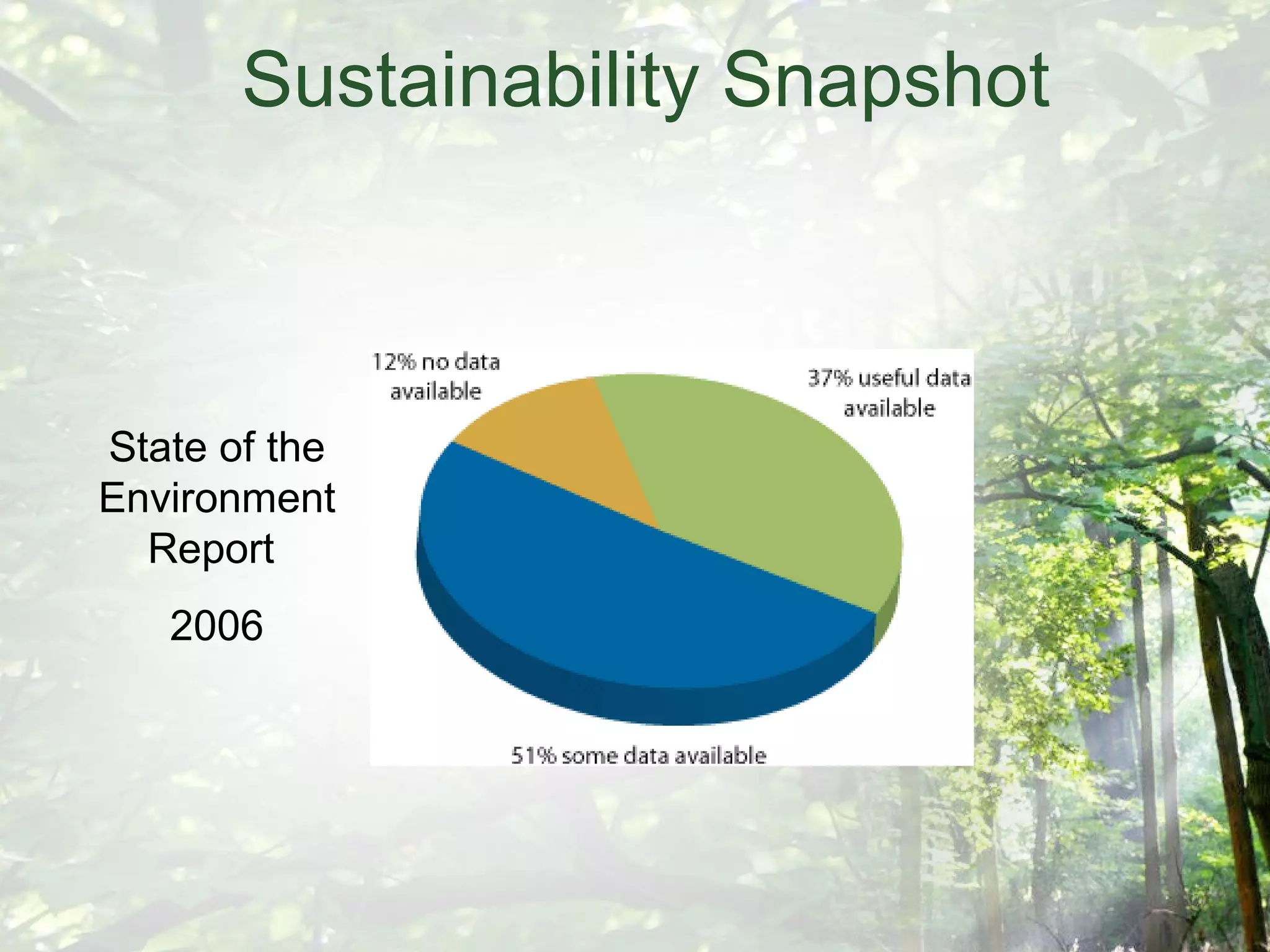
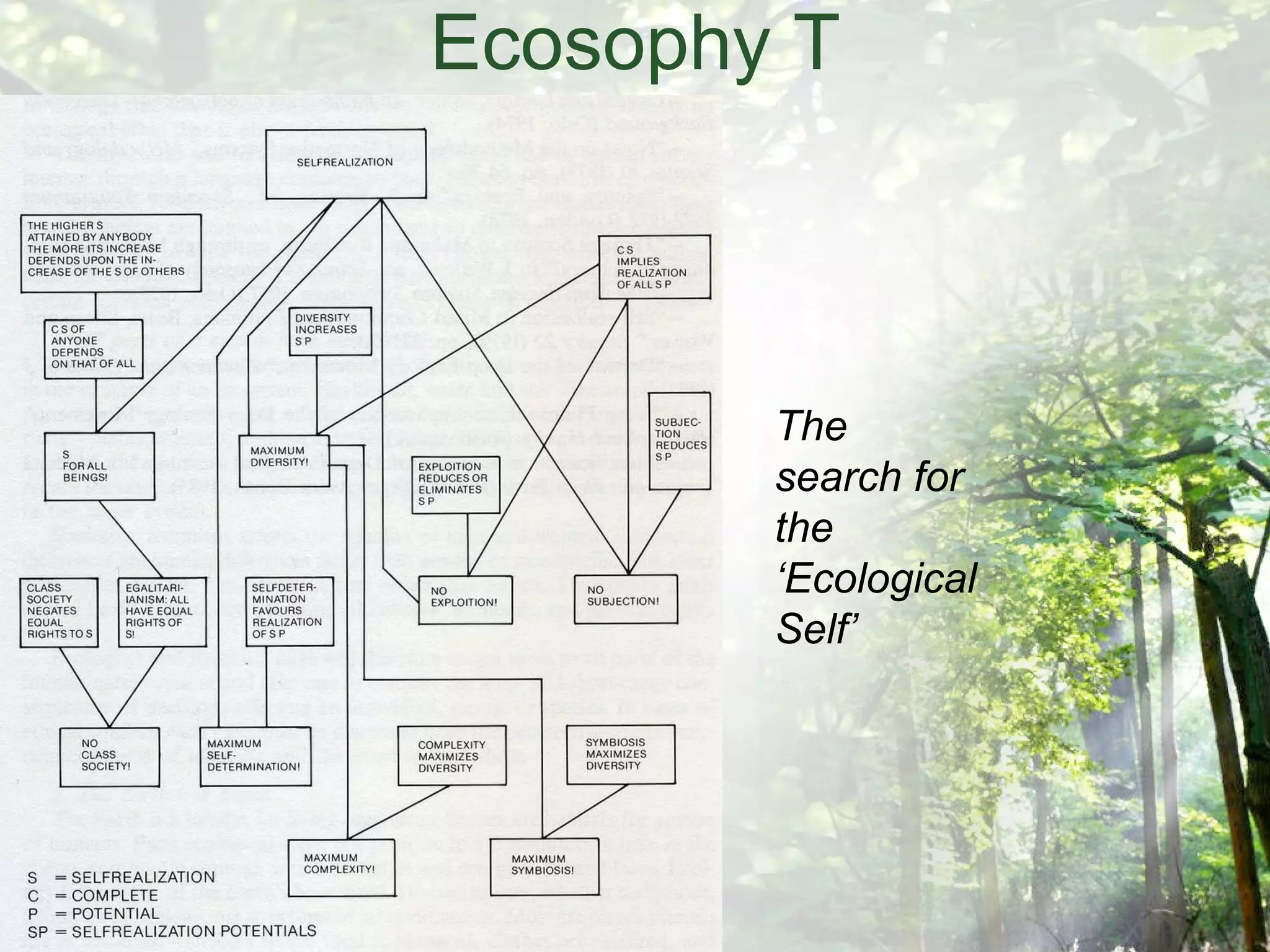
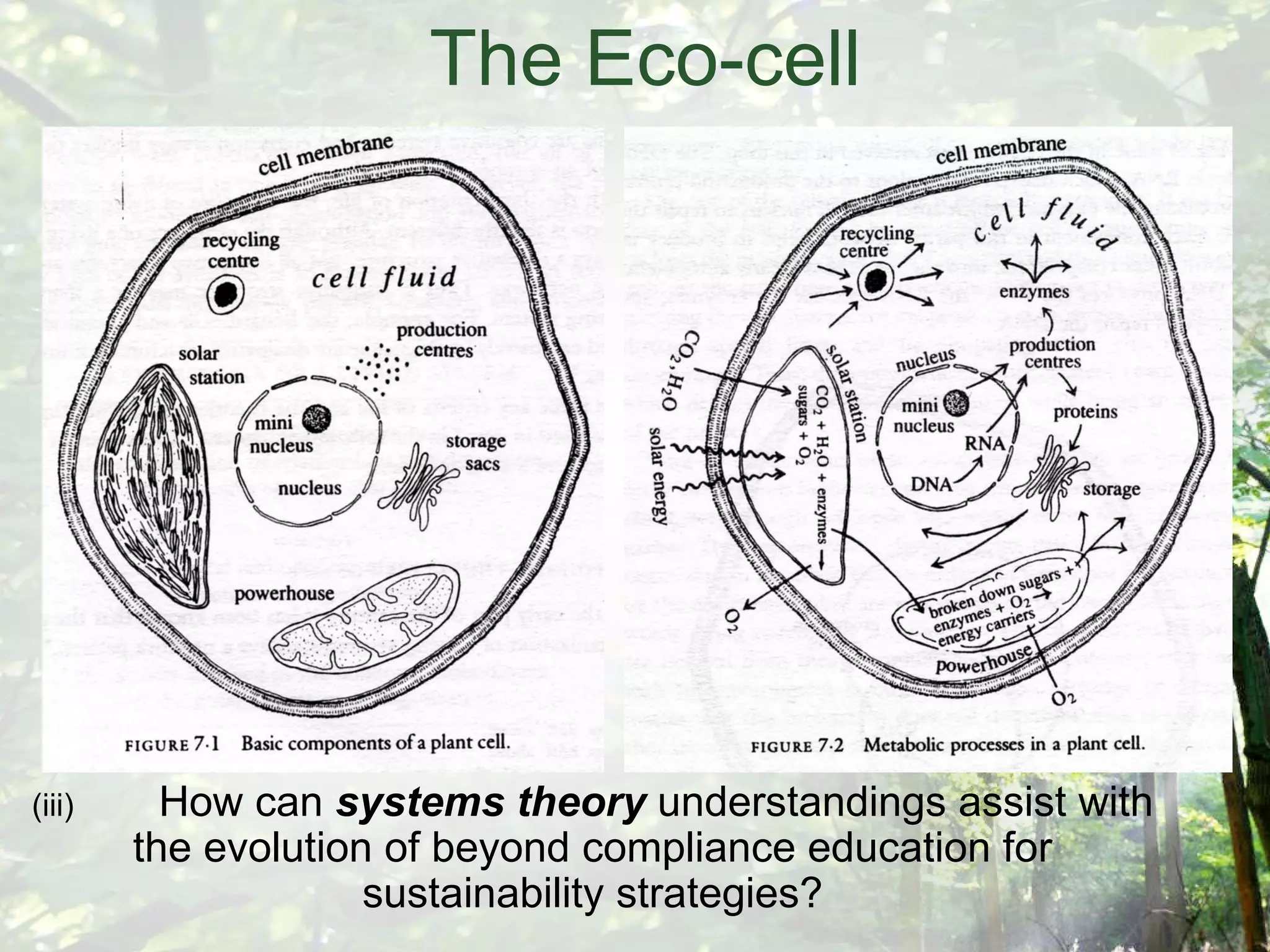
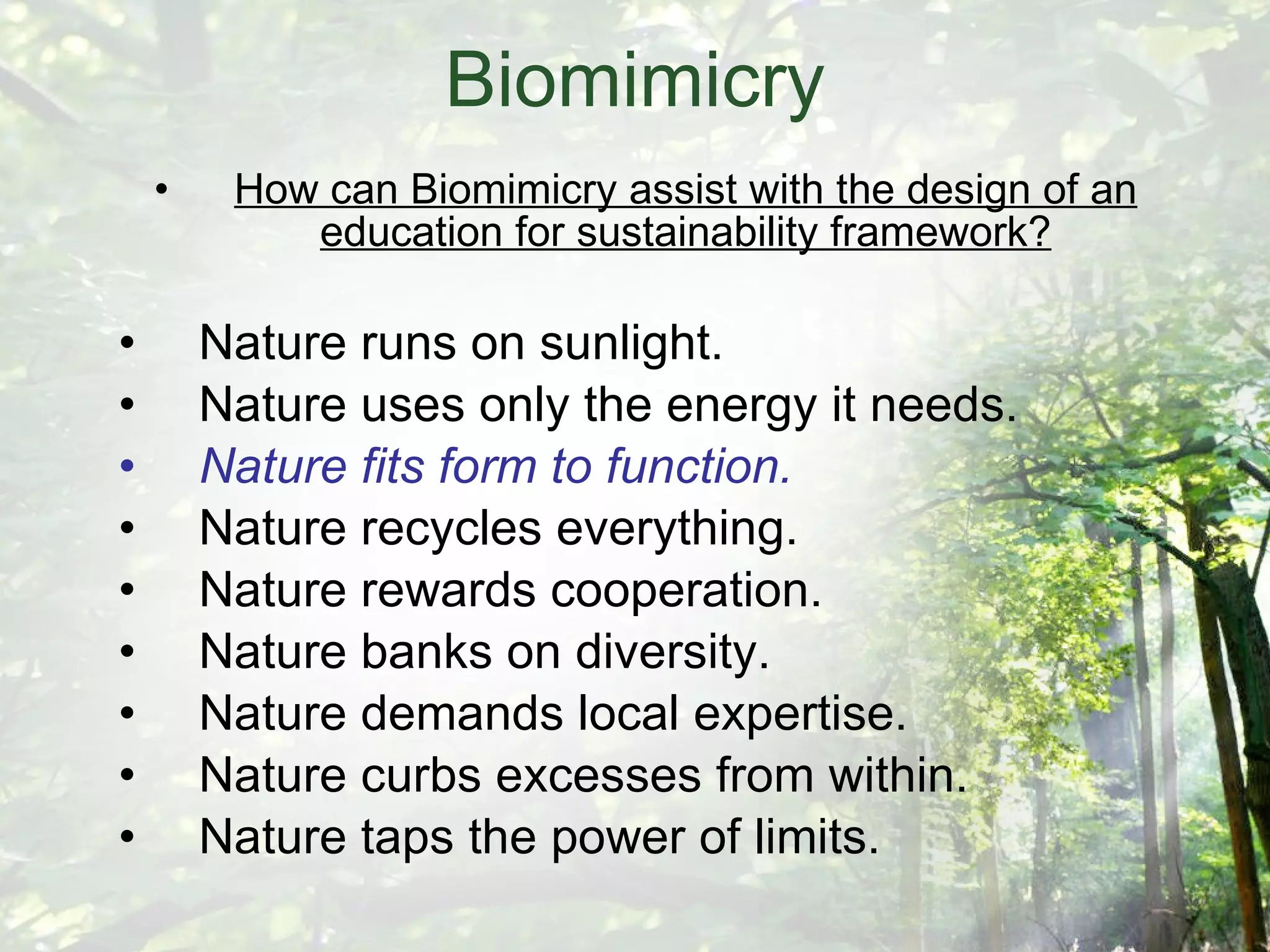
The document discusses the design of an "Eco-cell", which is a framework for education for sustainability. It will be developed based on research into how deep ecology, Buddhist philosophy, systems theory, and biomimicry can assist in evolving strategies beyond mere compliance. The Eco-cell will include components like a nucleus for self-realization, a cell membrane for reconnecting to deep ecology, and a powerhouse utilizing permaculture design principles. It aims to foster an ecological self through experiential learning and an integrated holistic systems perspective.