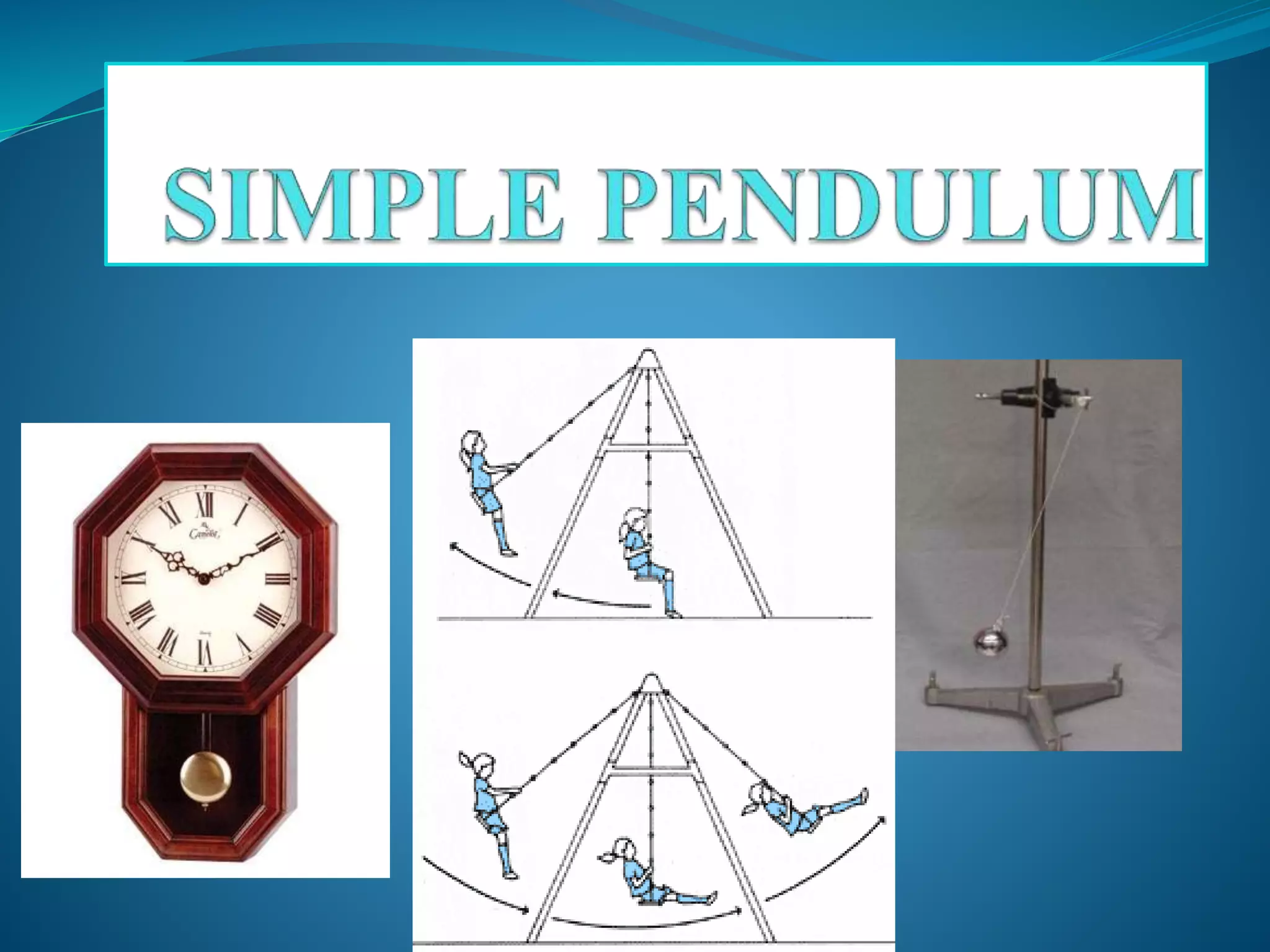
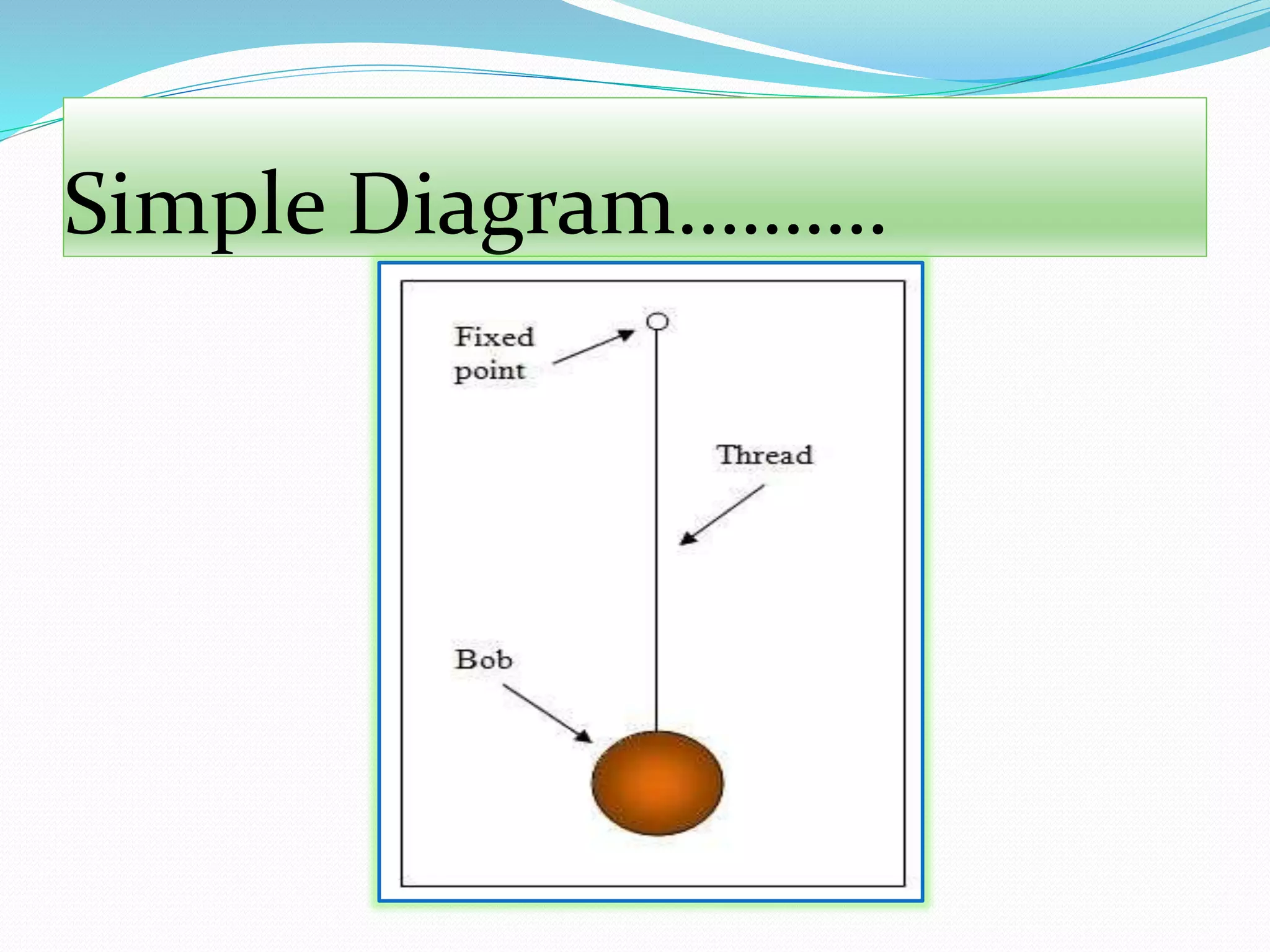
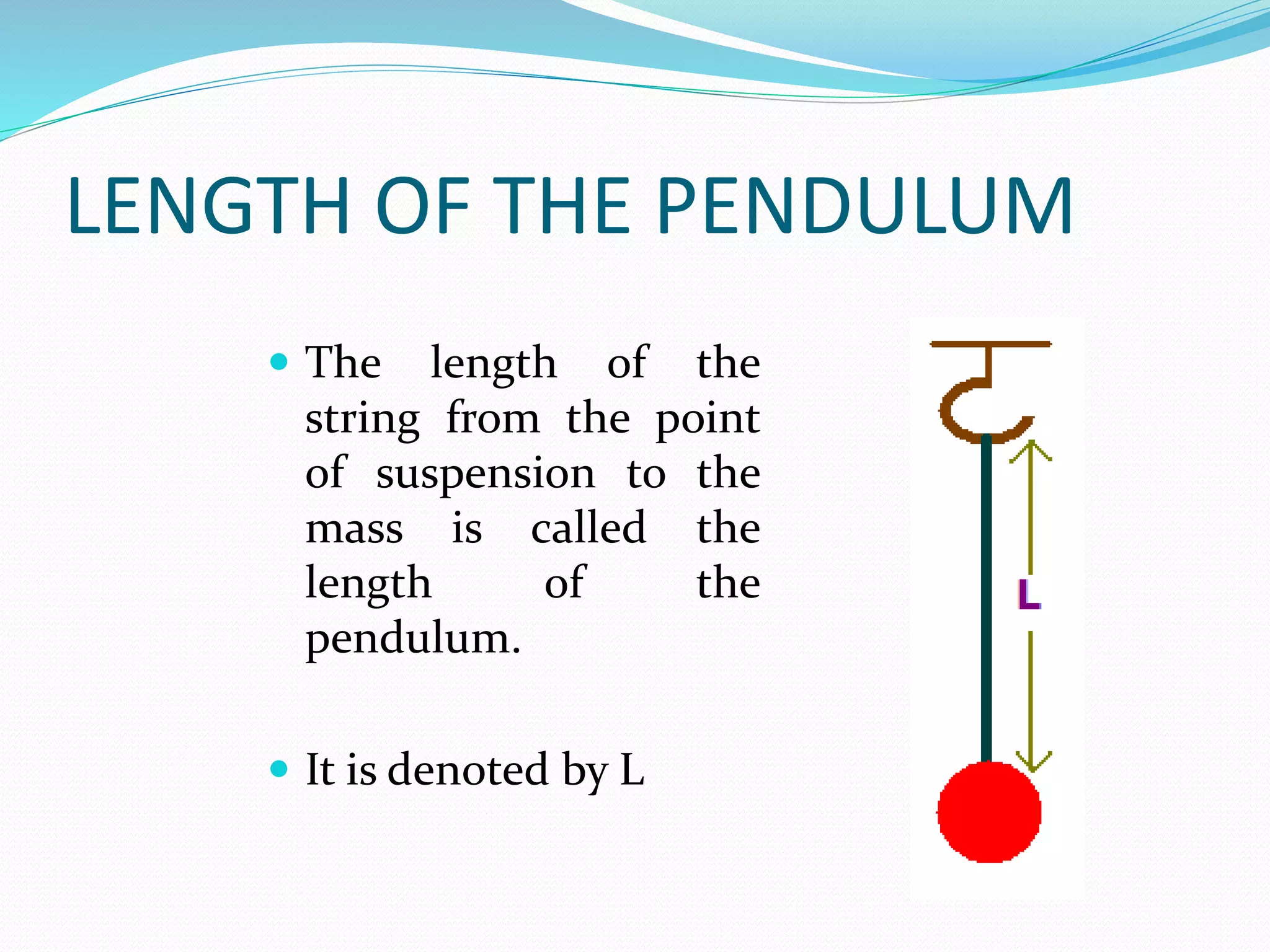
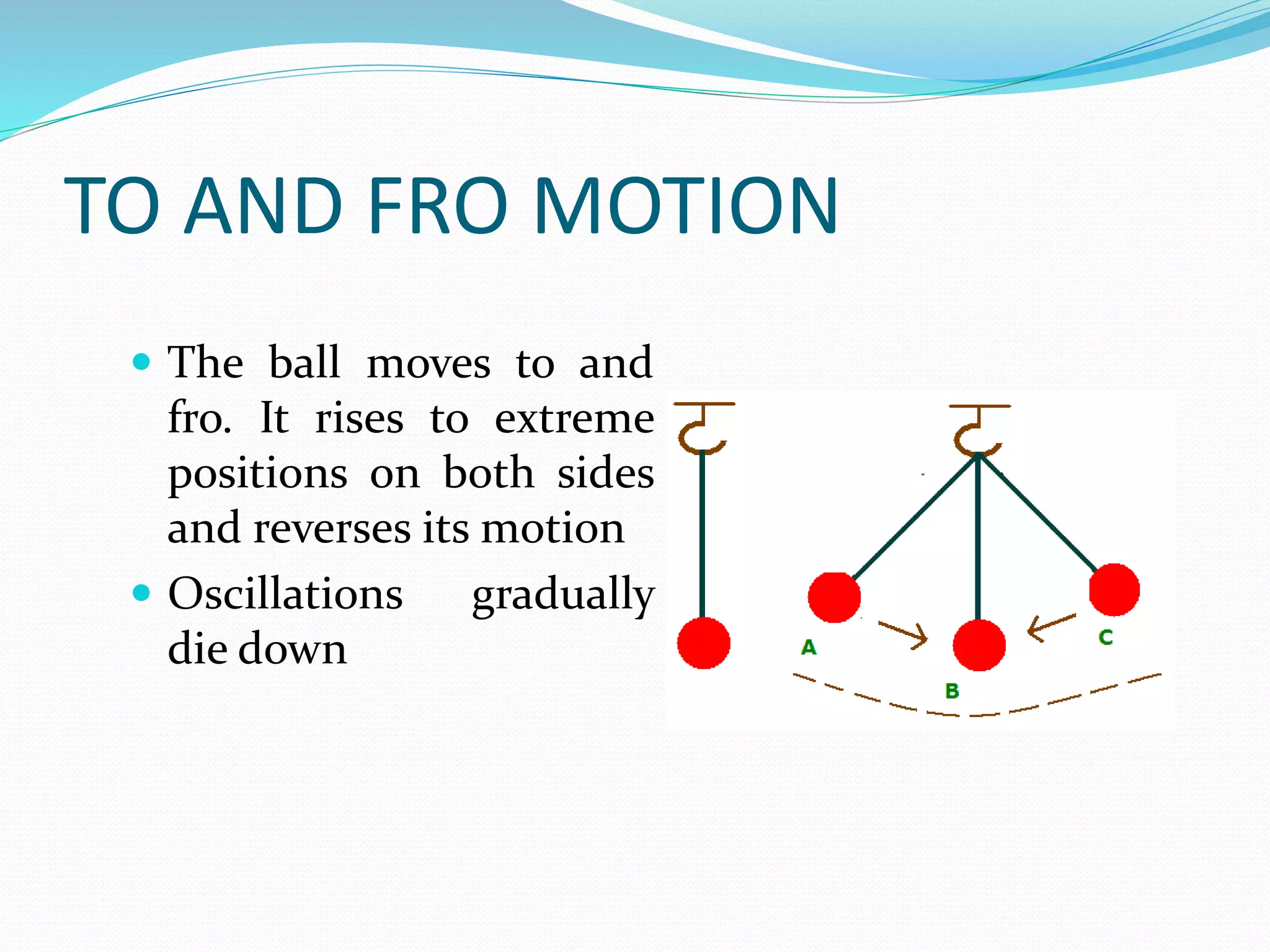
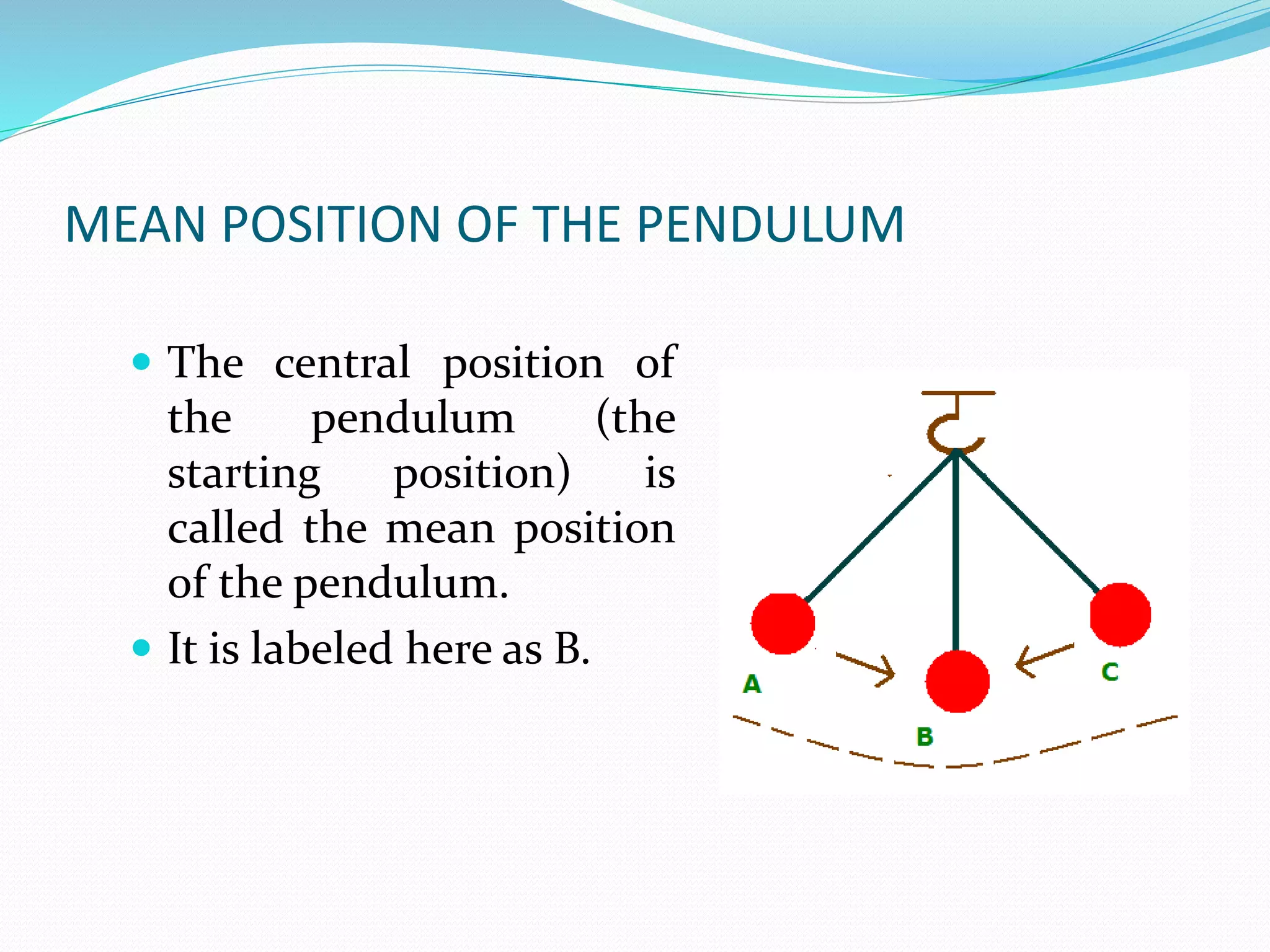
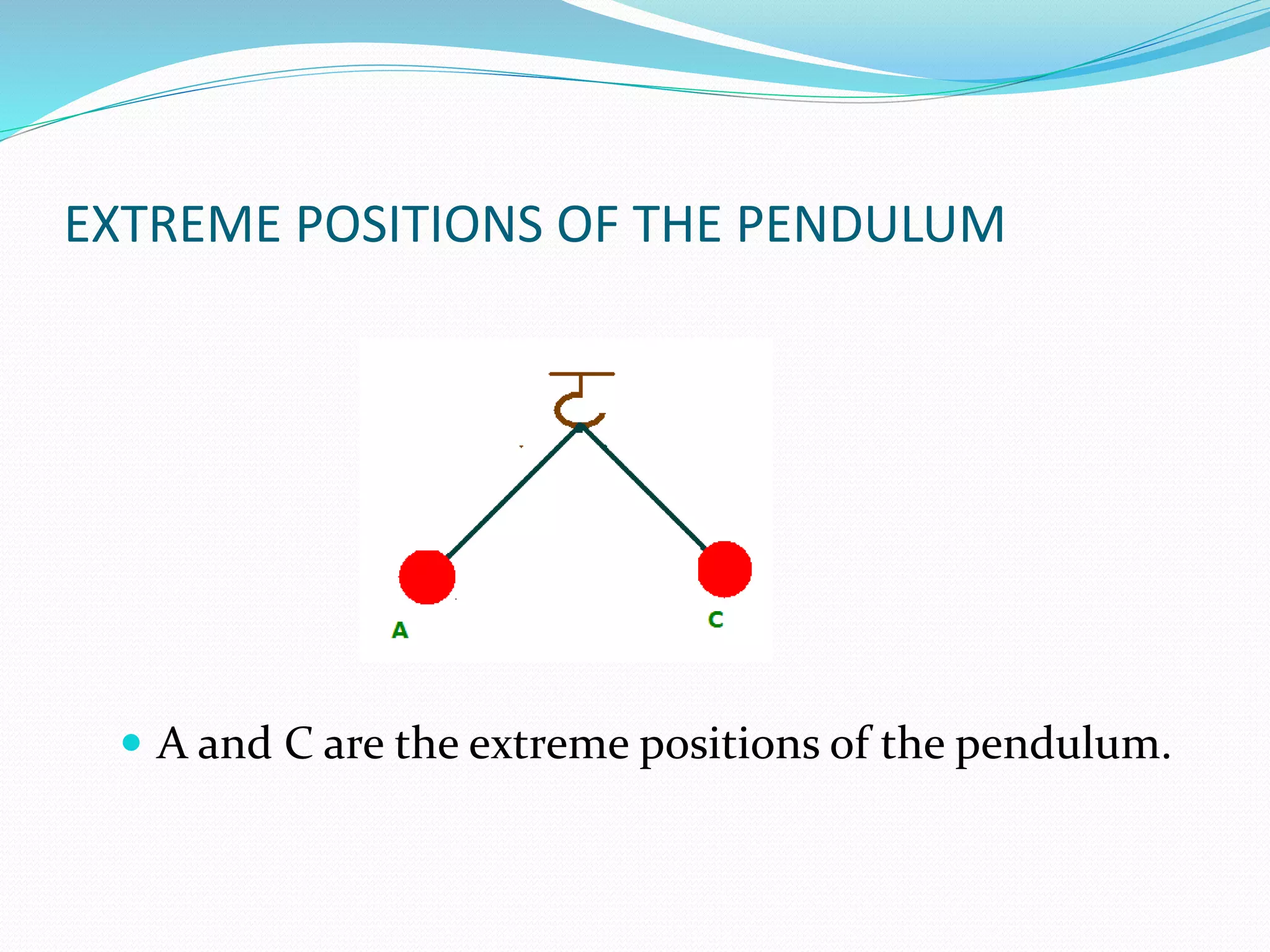
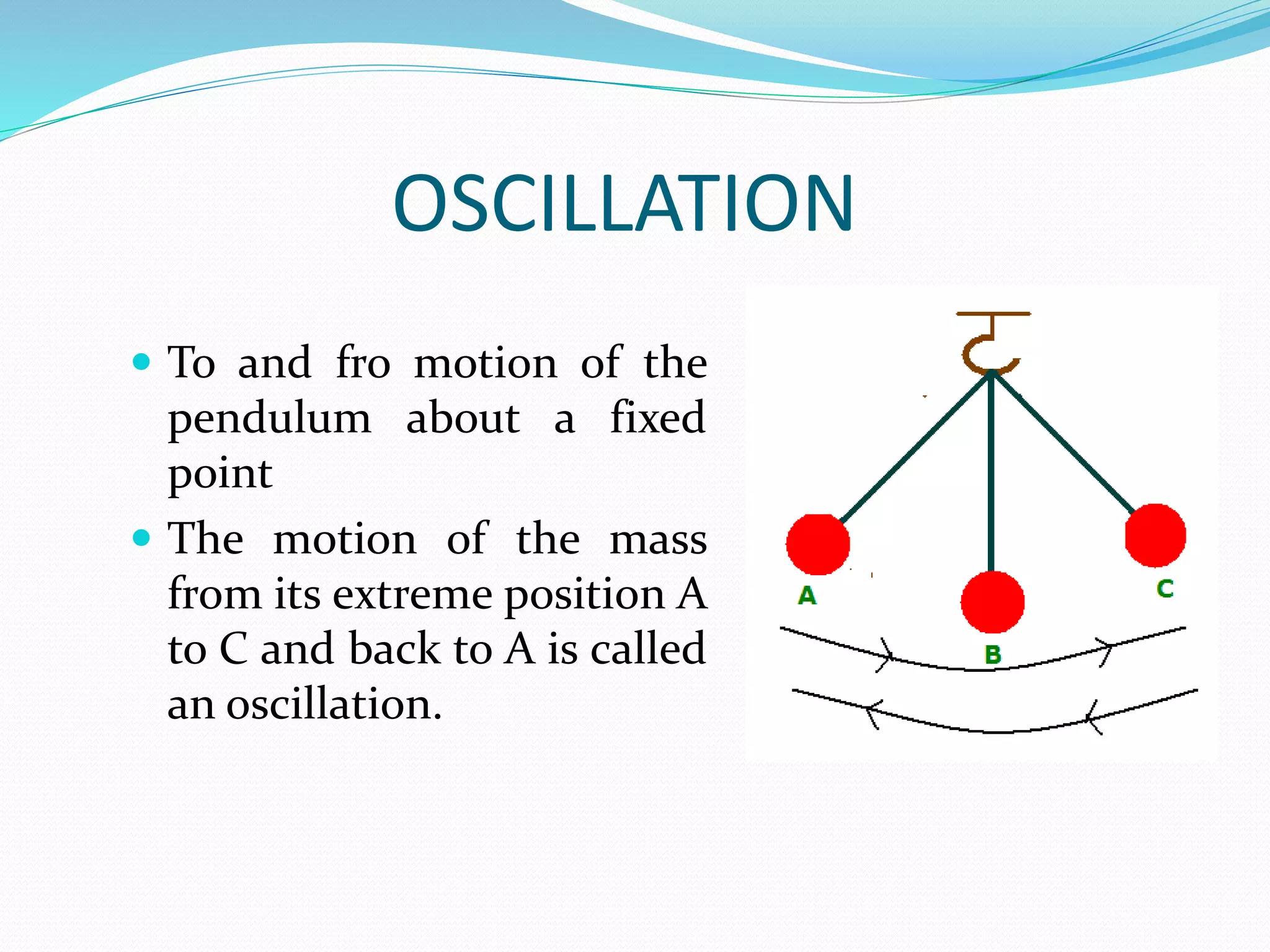
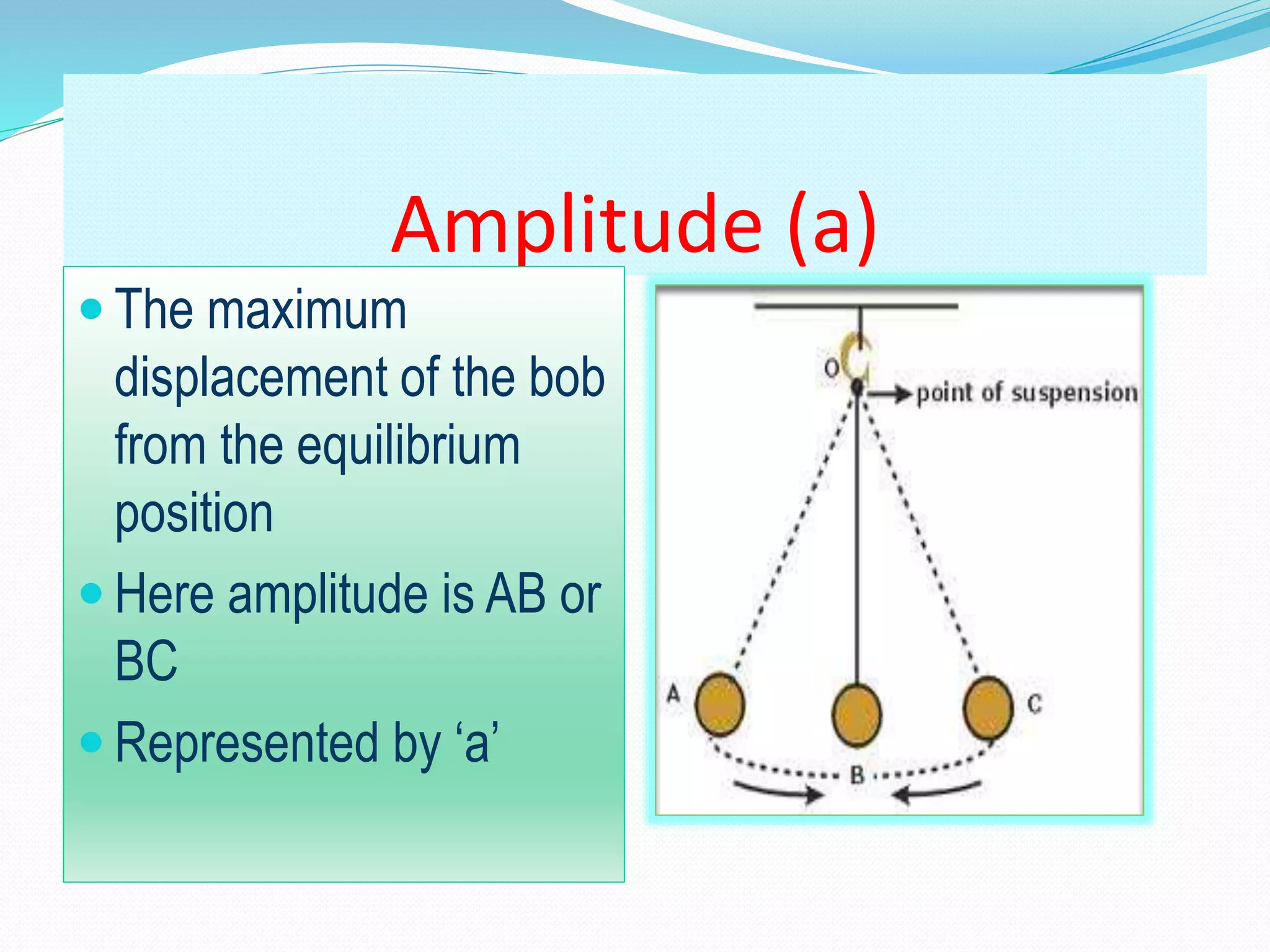
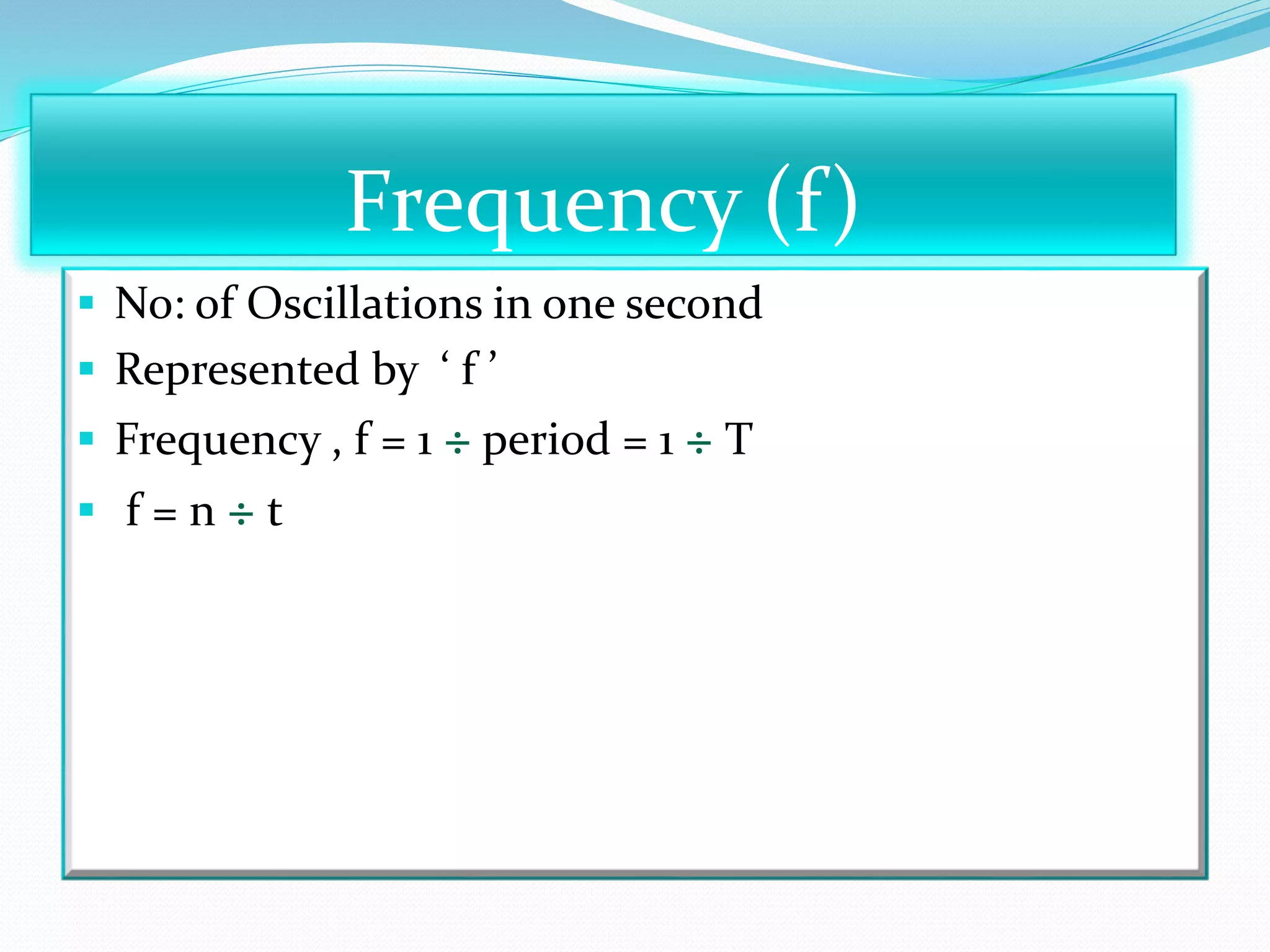
A simple pendulum consists of a bob suspended by a string from a fixed point, allowing it to swing freely. It undergoes periodic oscillations, moving back and forth between two extreme positions with its center point as the equilibrium position. The length of the string and mass of the bob are used to determine characteristics like the period of oscillation, which is the time taken for one complete oscillation, and the frequency, which is the number of oscillations per second.