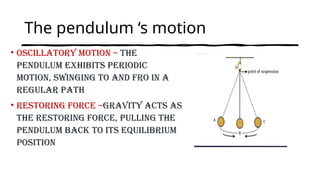
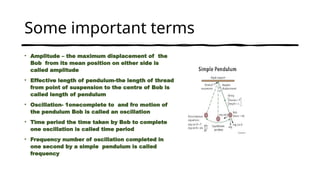
The document discusses the concept of a simple pendulum, originally discovered by Galileo Galilei, and its fundamental properties including components, oscillation, and motion characteristics. It emphasizes key terms such as amplitude, effective length, time period, and frequency, alongside the equations governing the pendulum's behavior. Lastly, it highlights factors affecting the time period of a pendulum's oscillation.