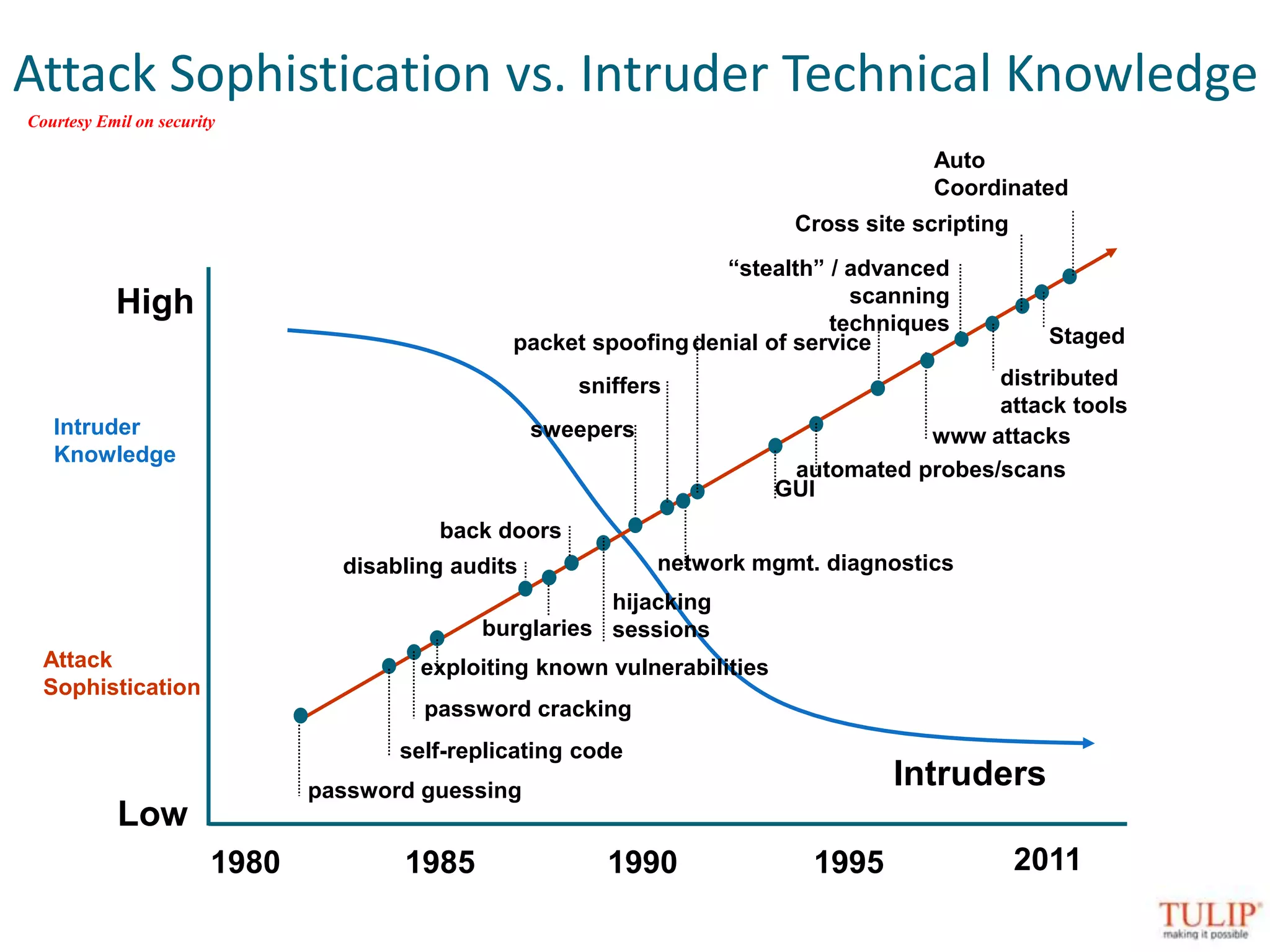
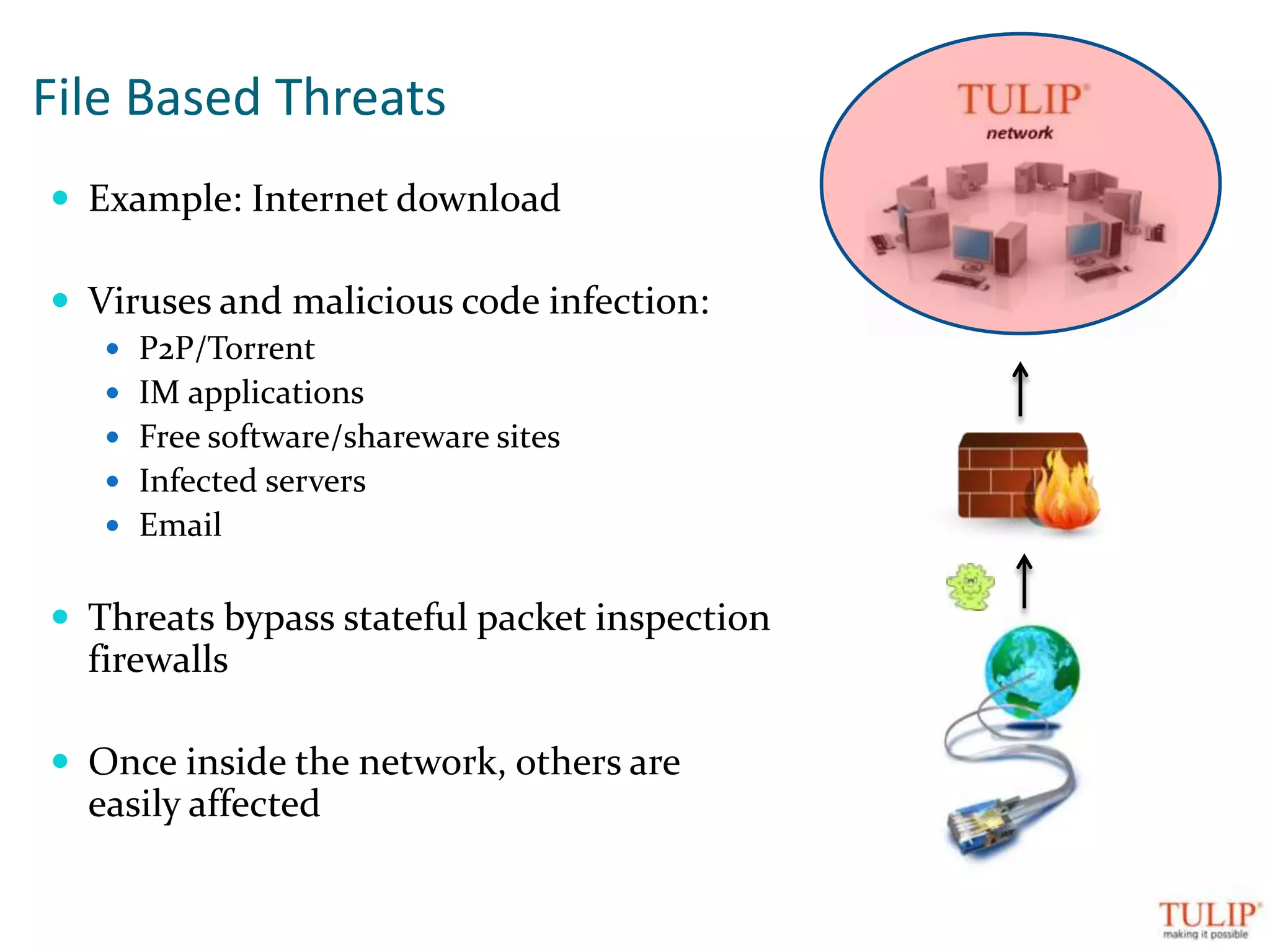
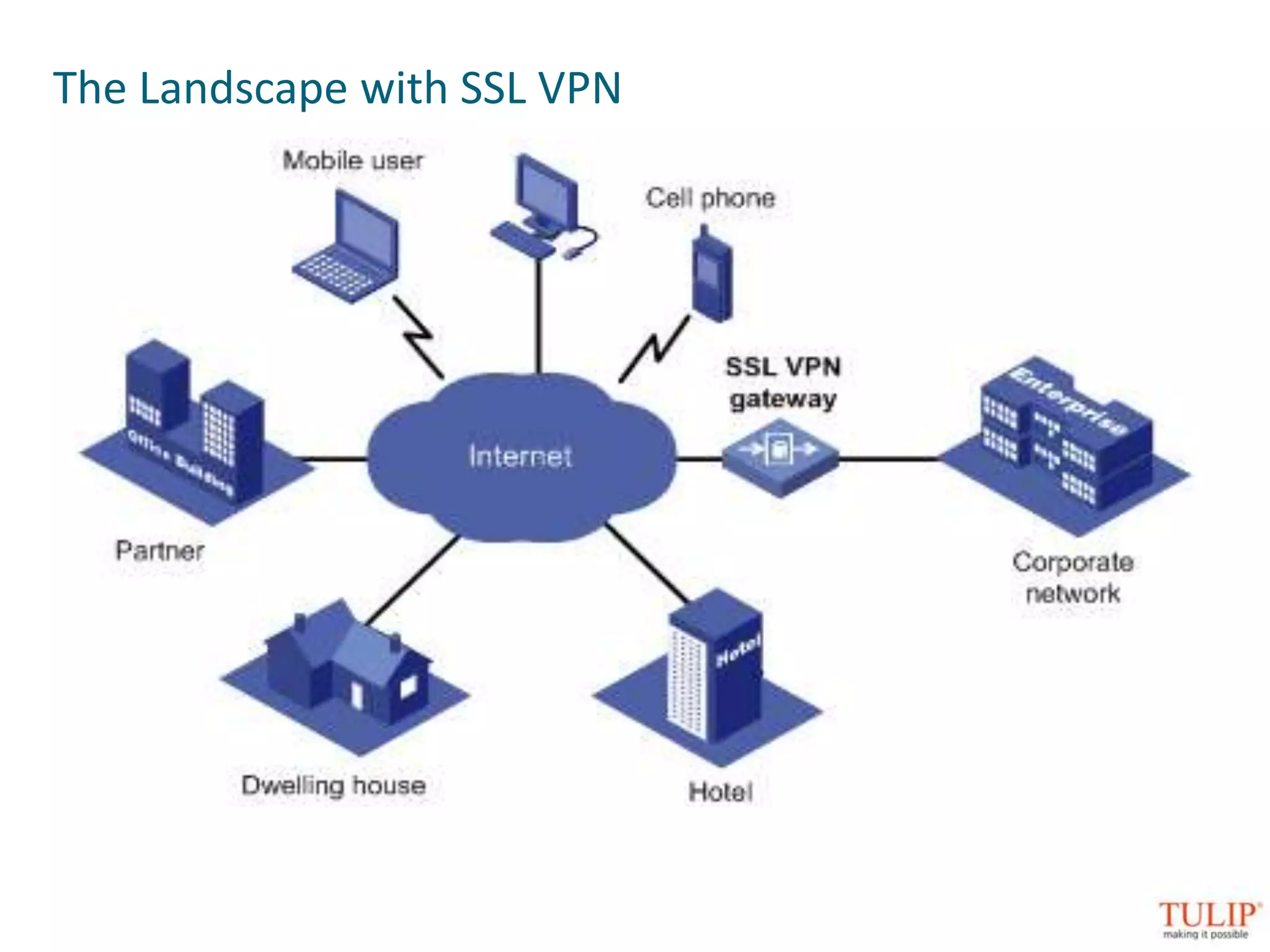
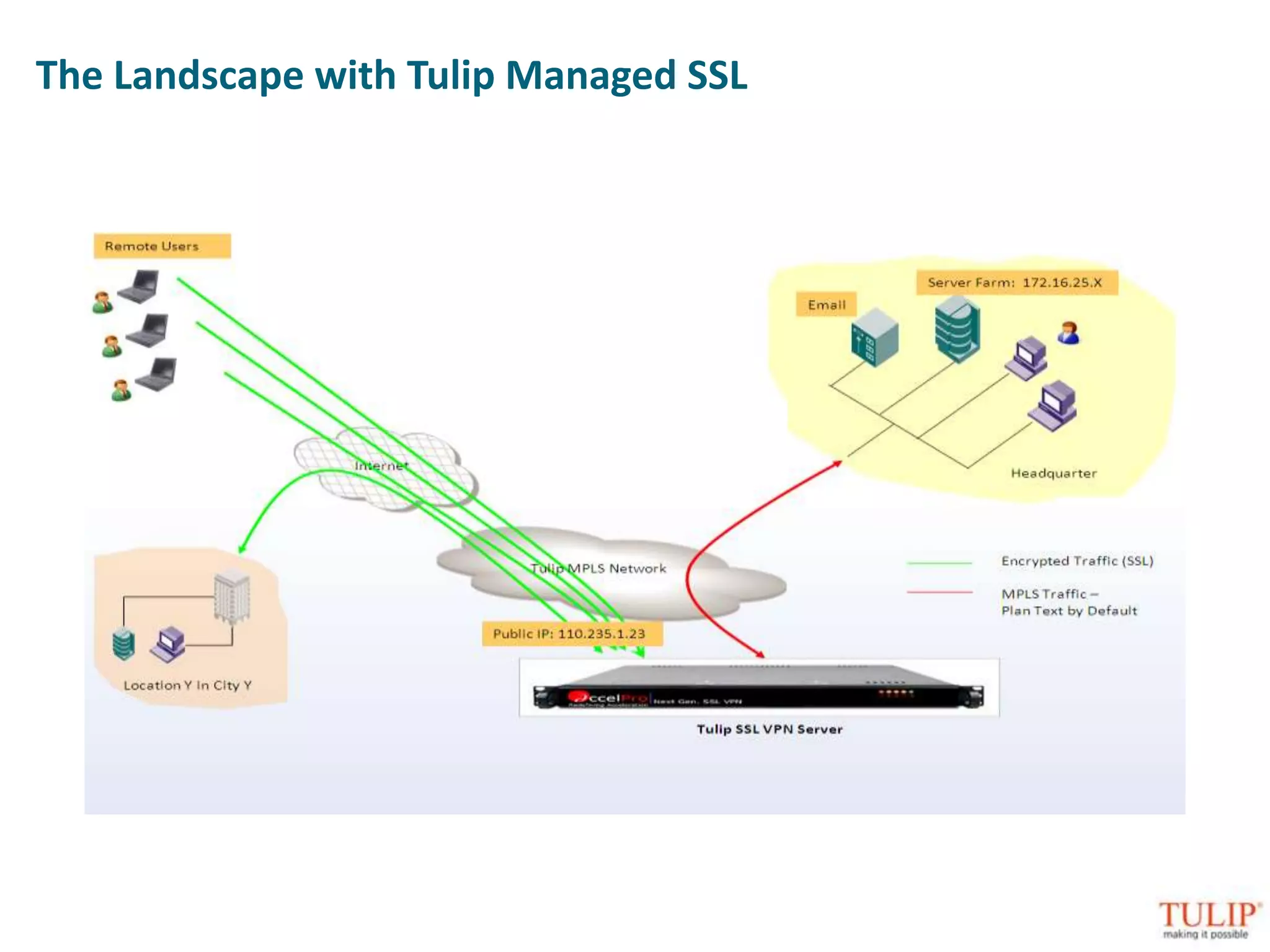
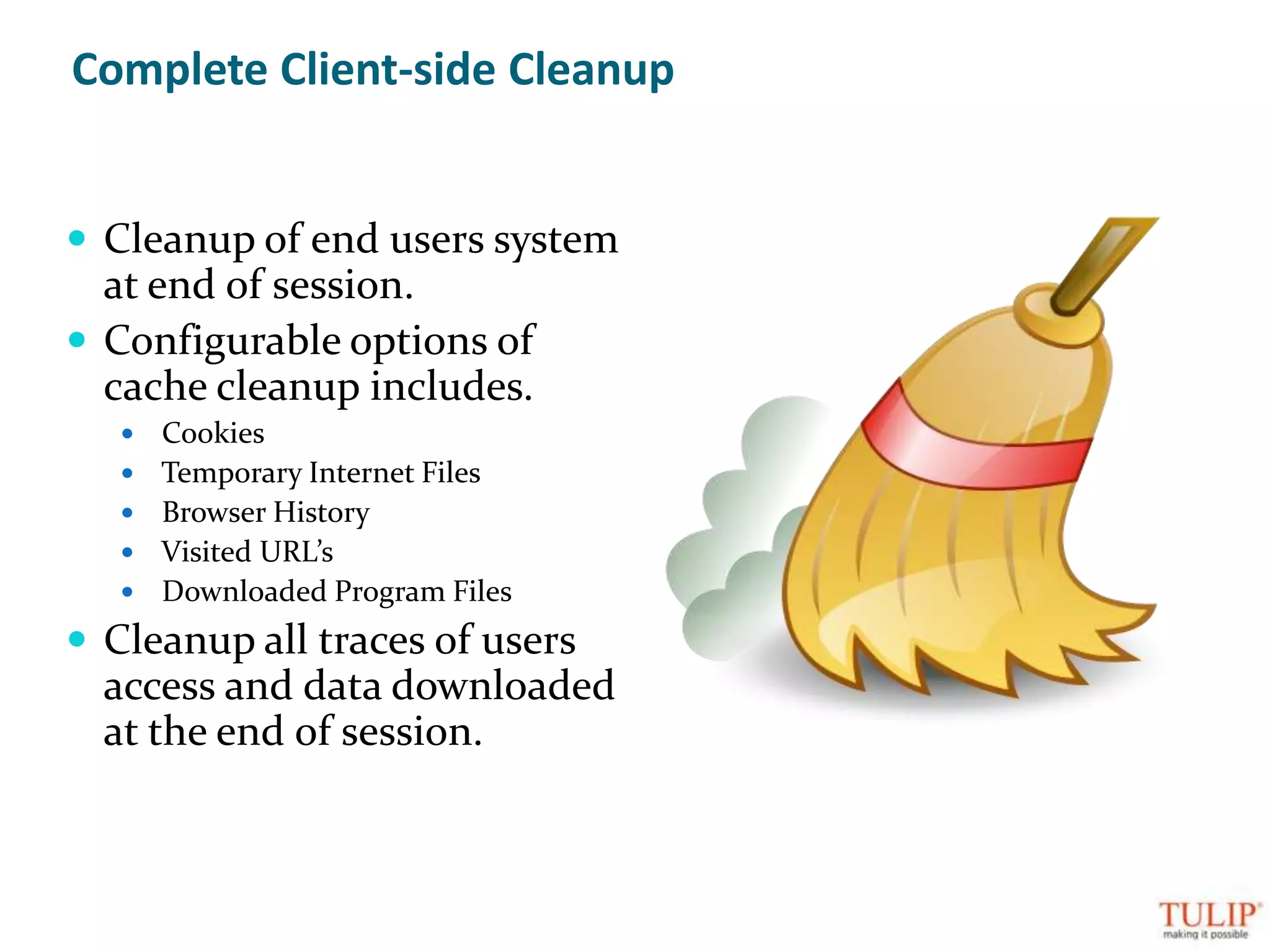
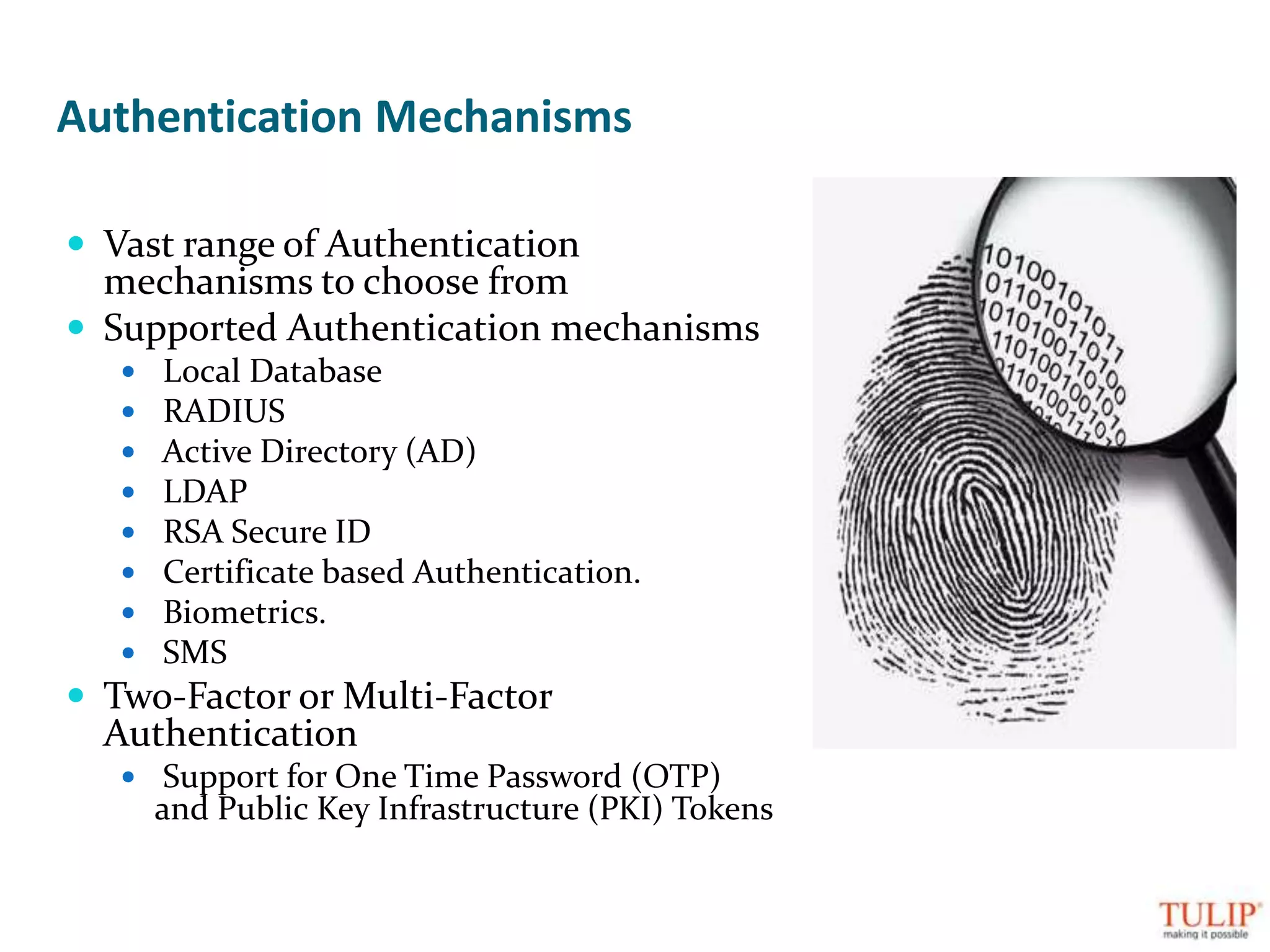
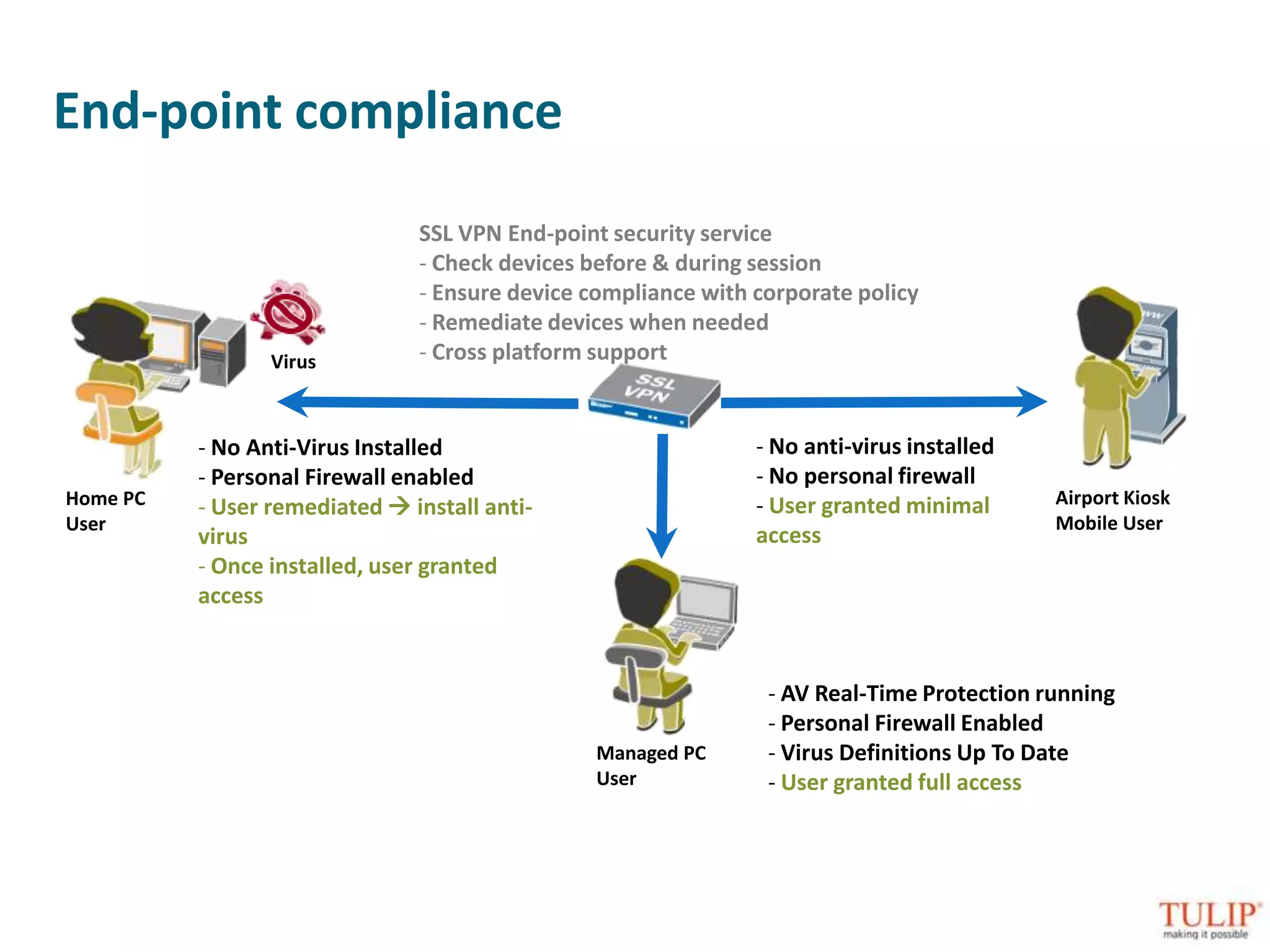
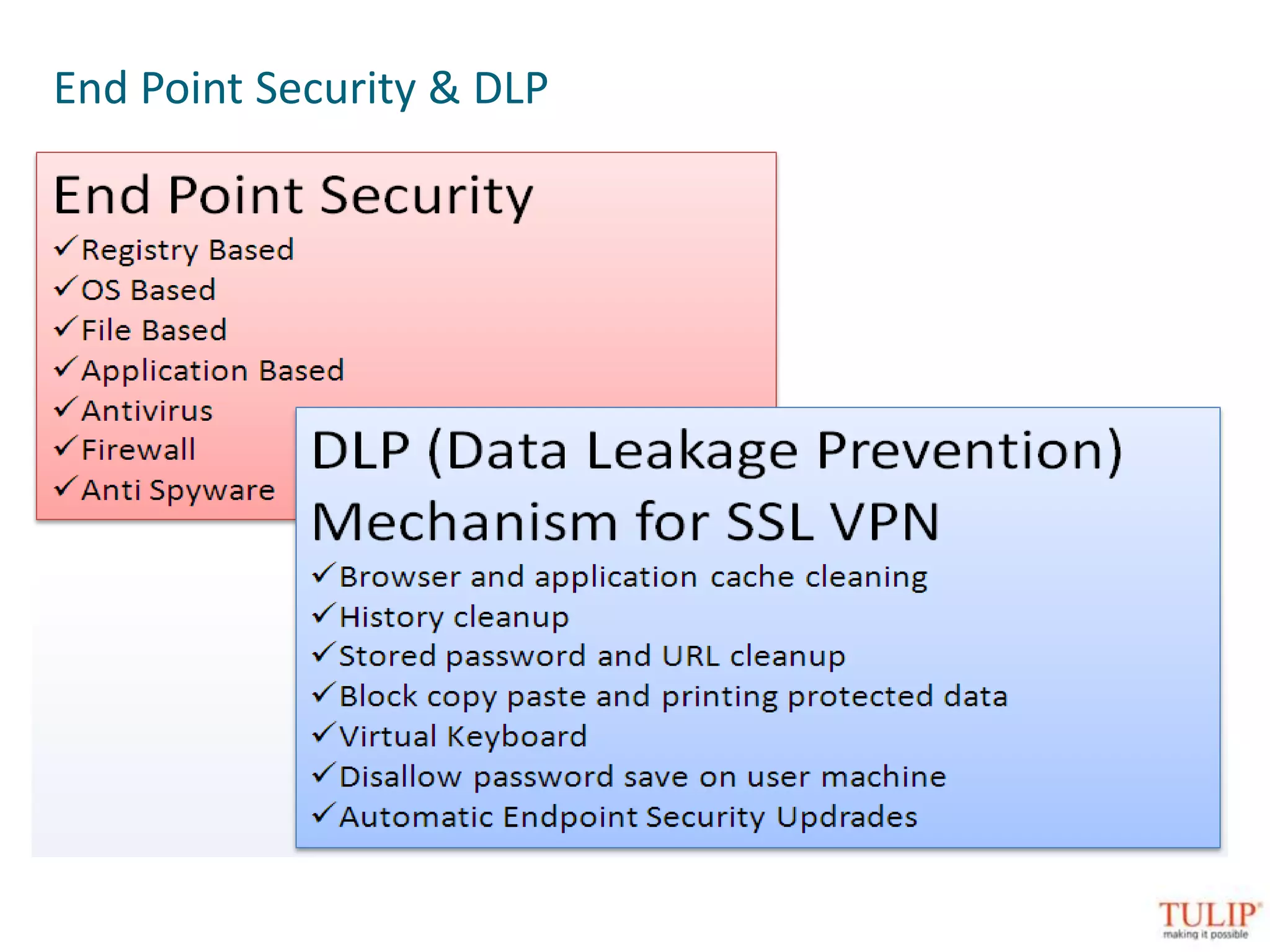
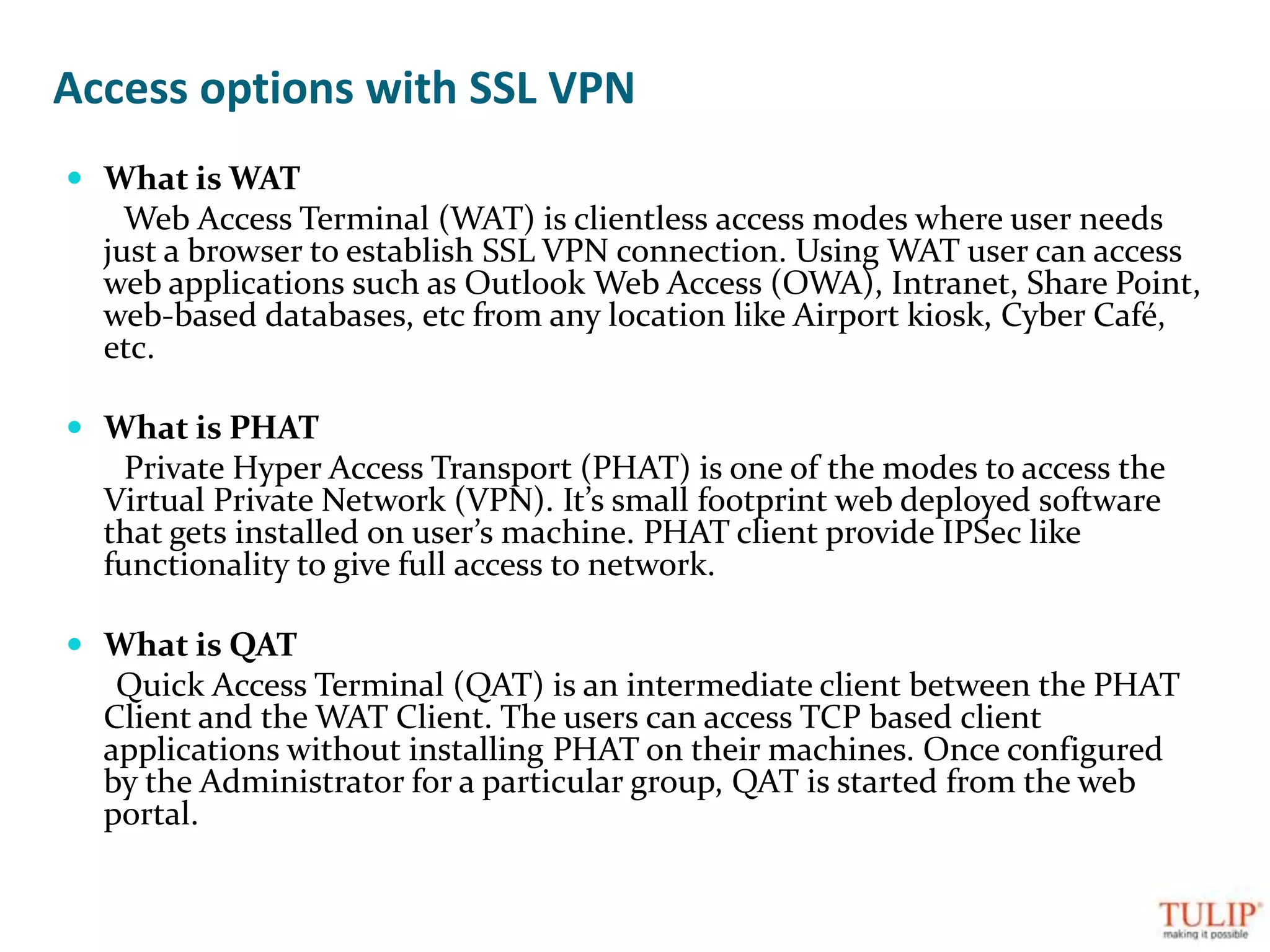
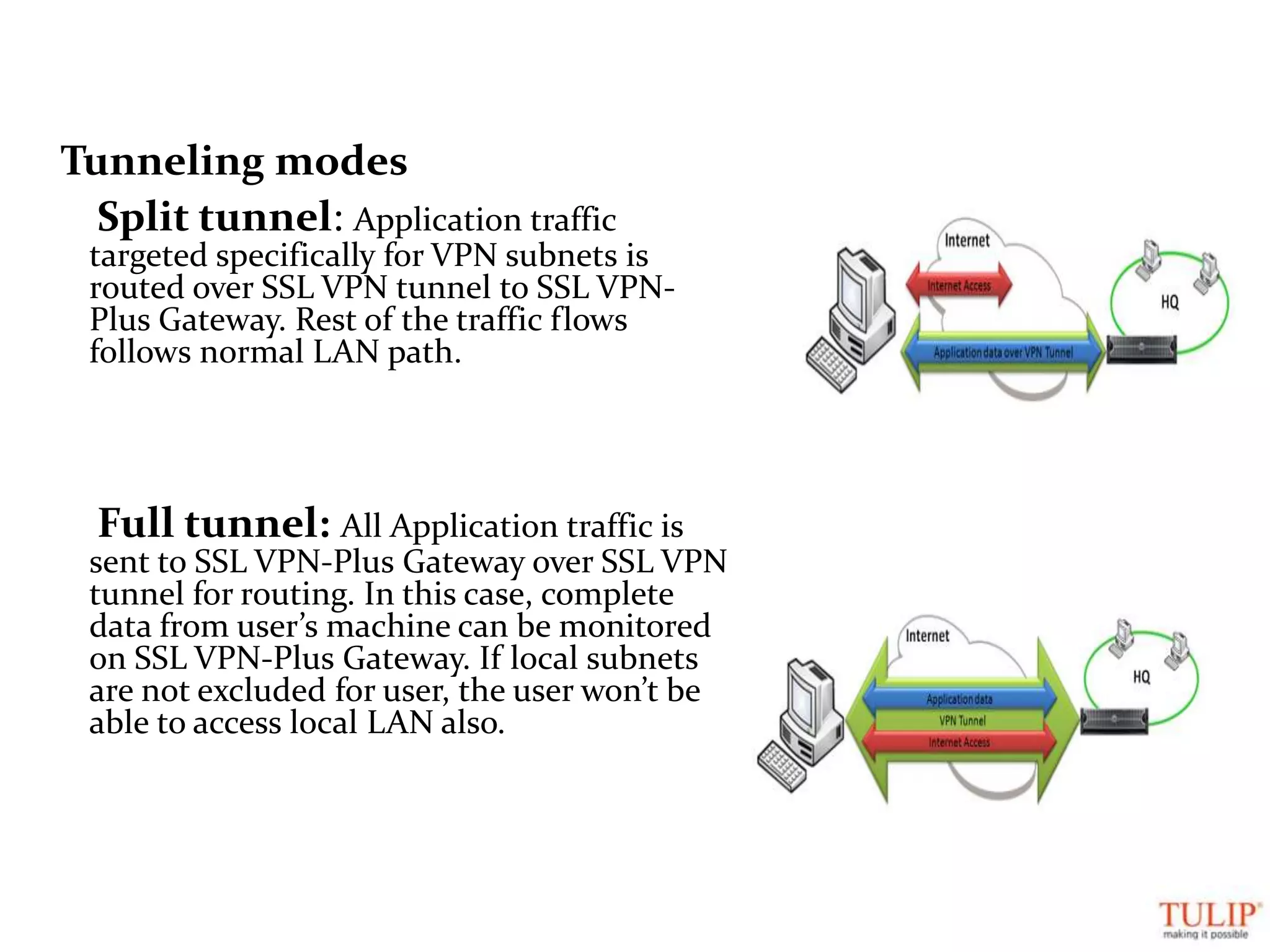
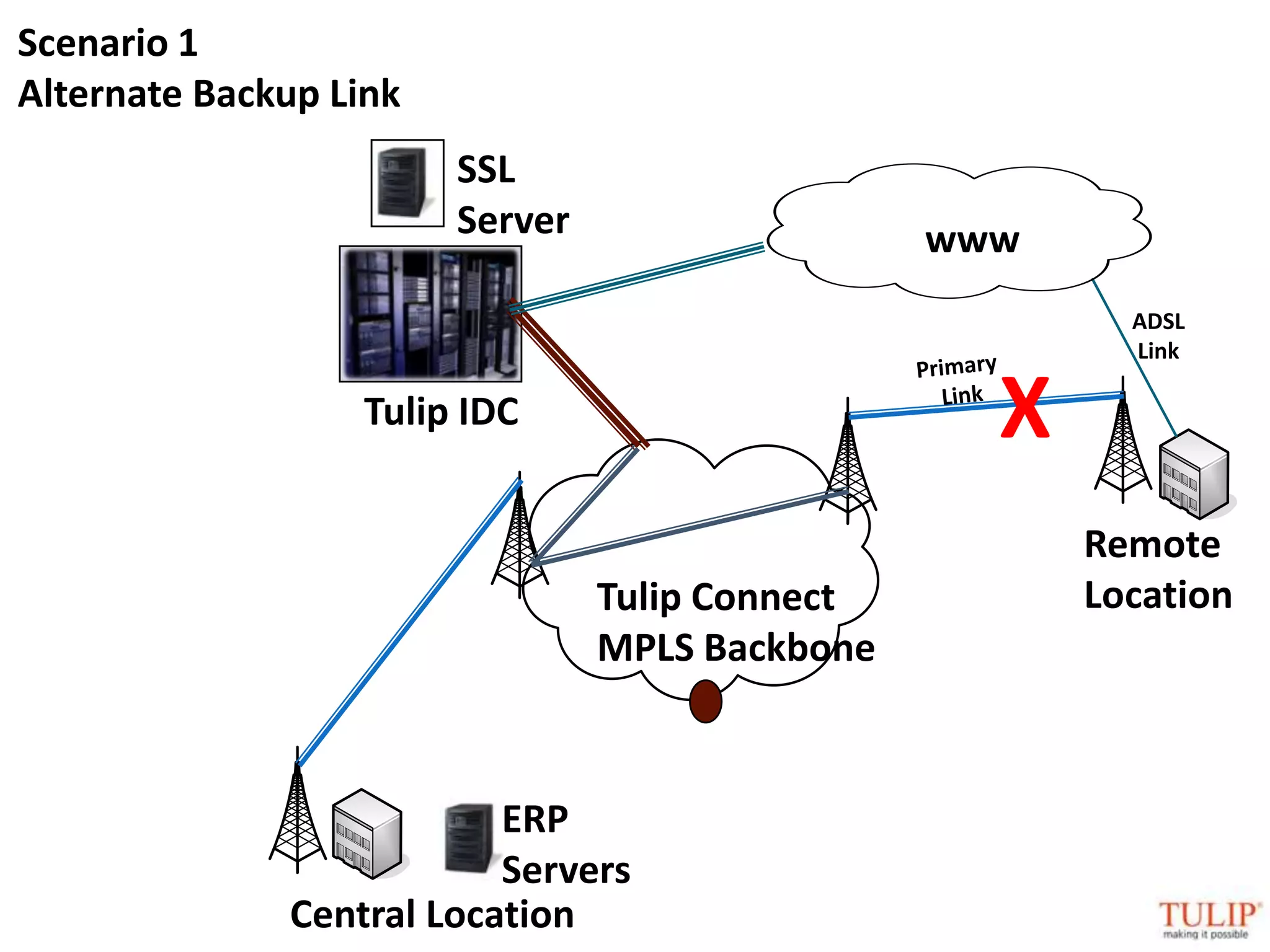
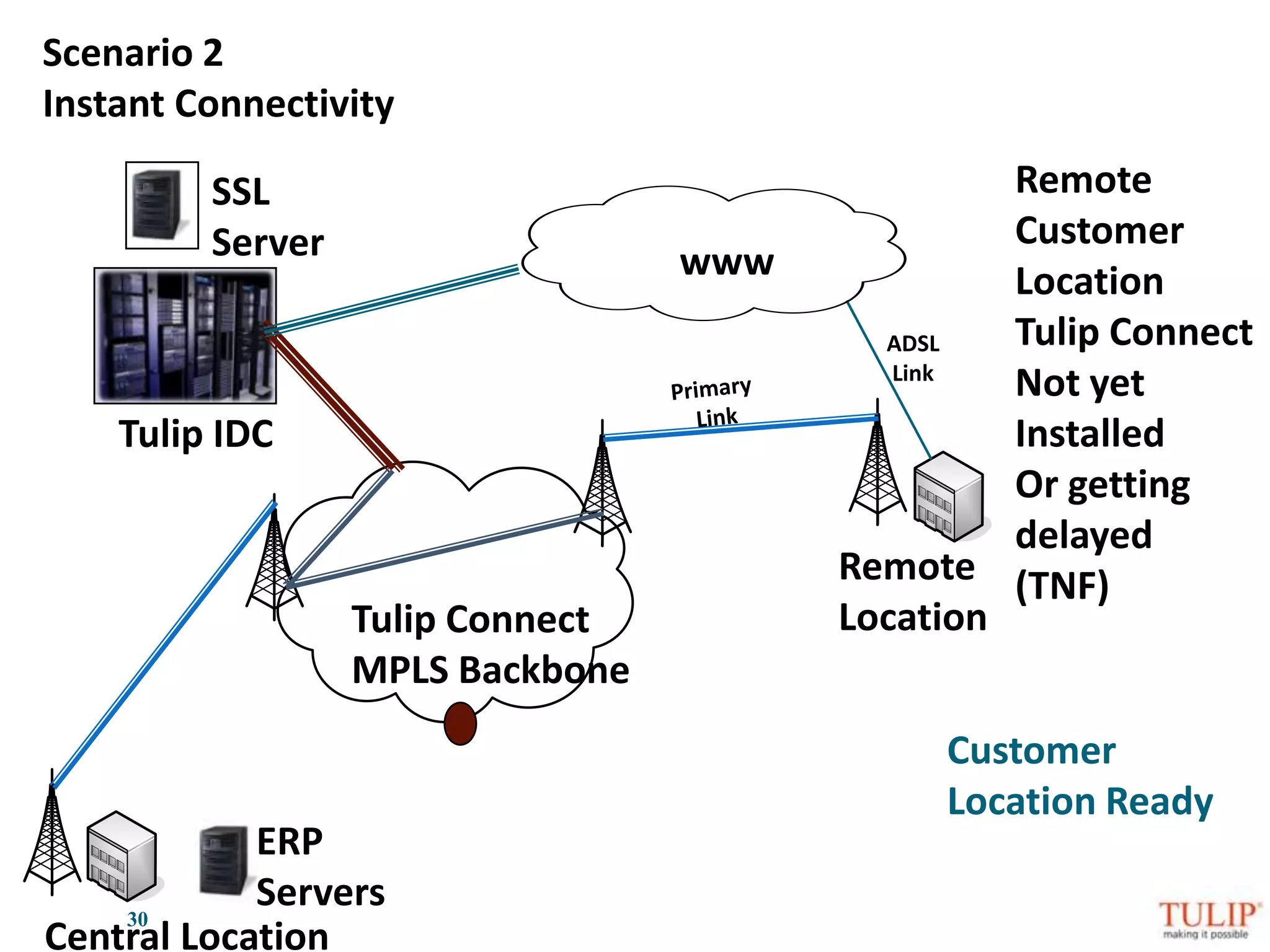
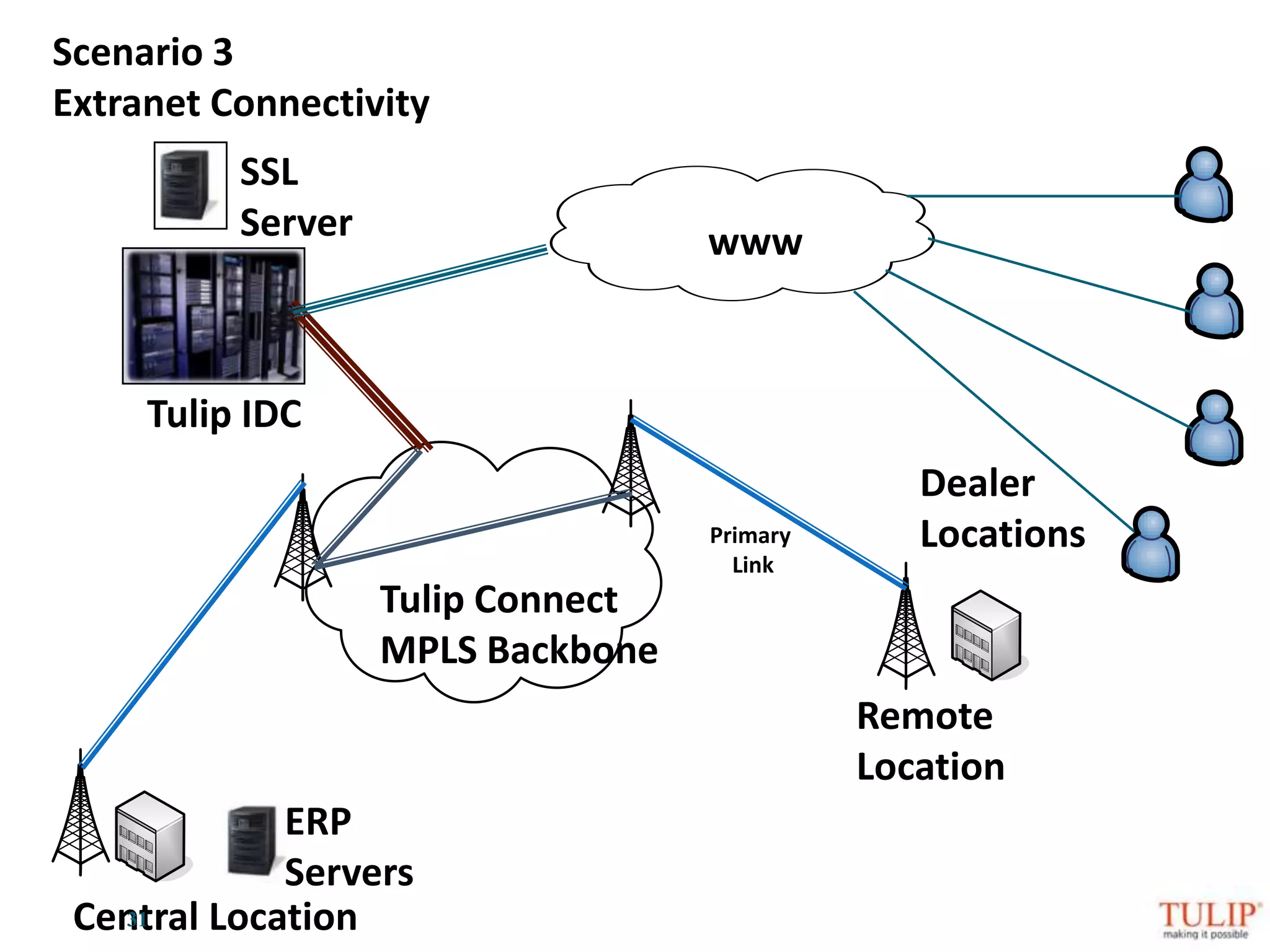
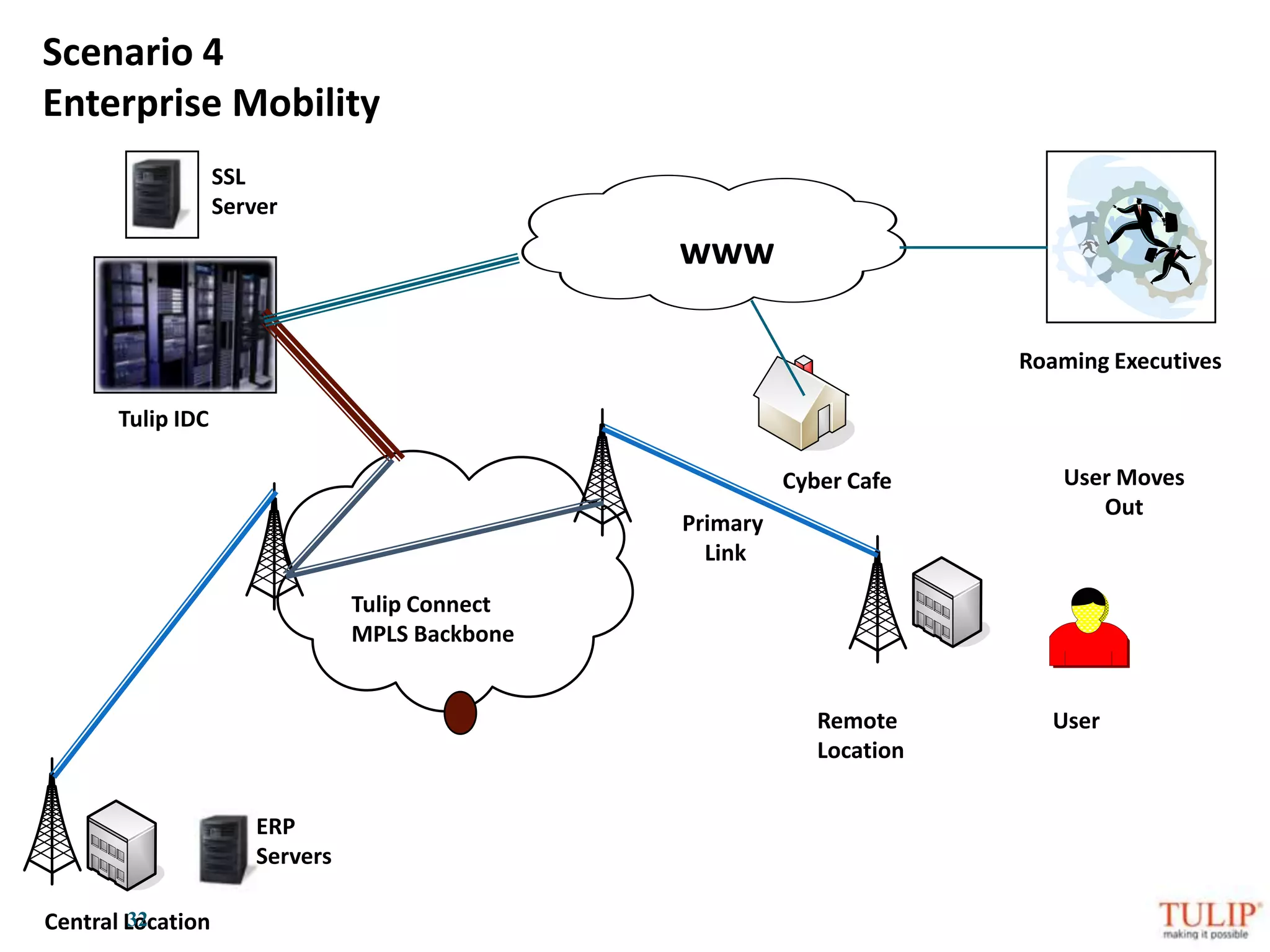
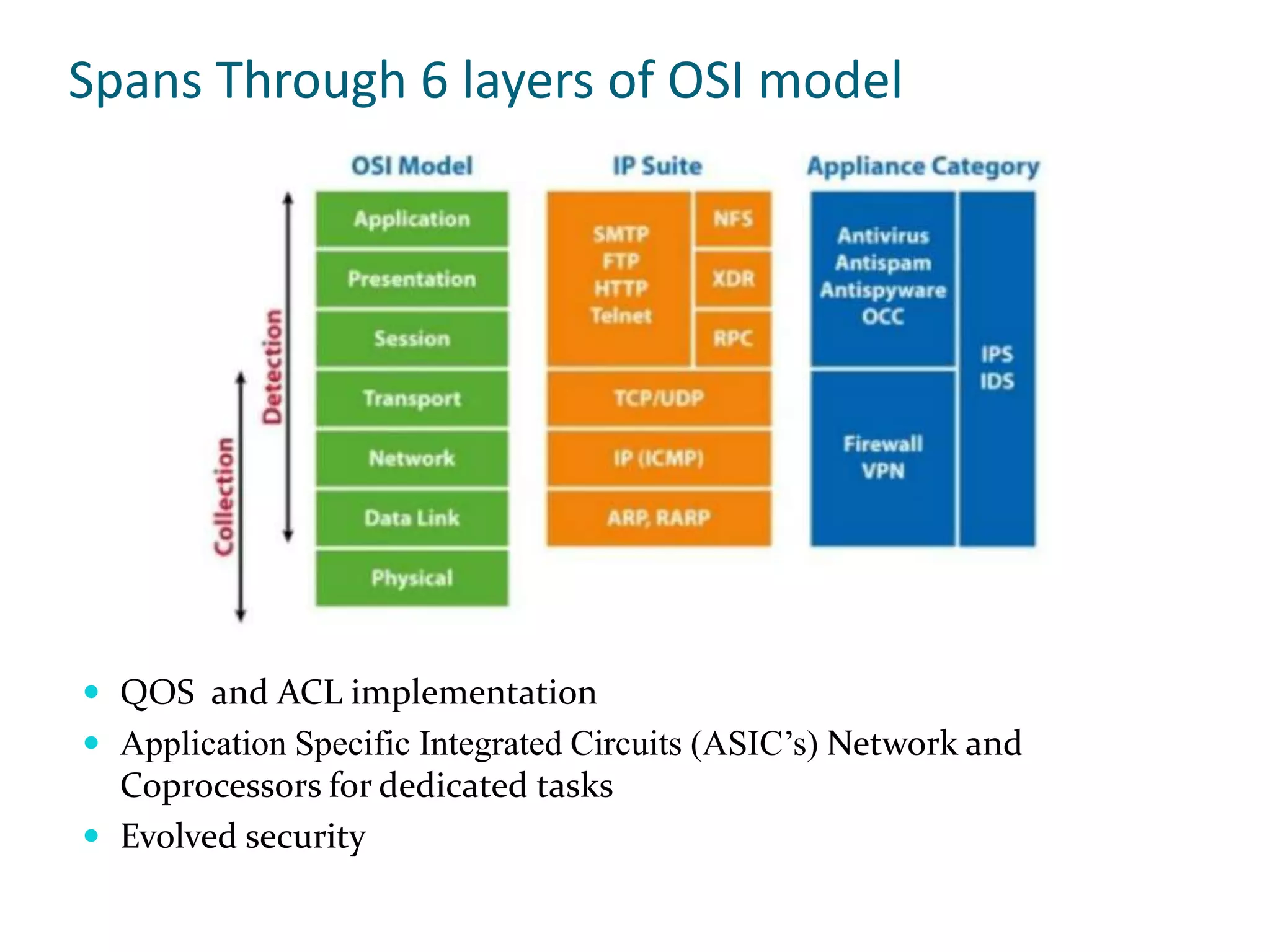
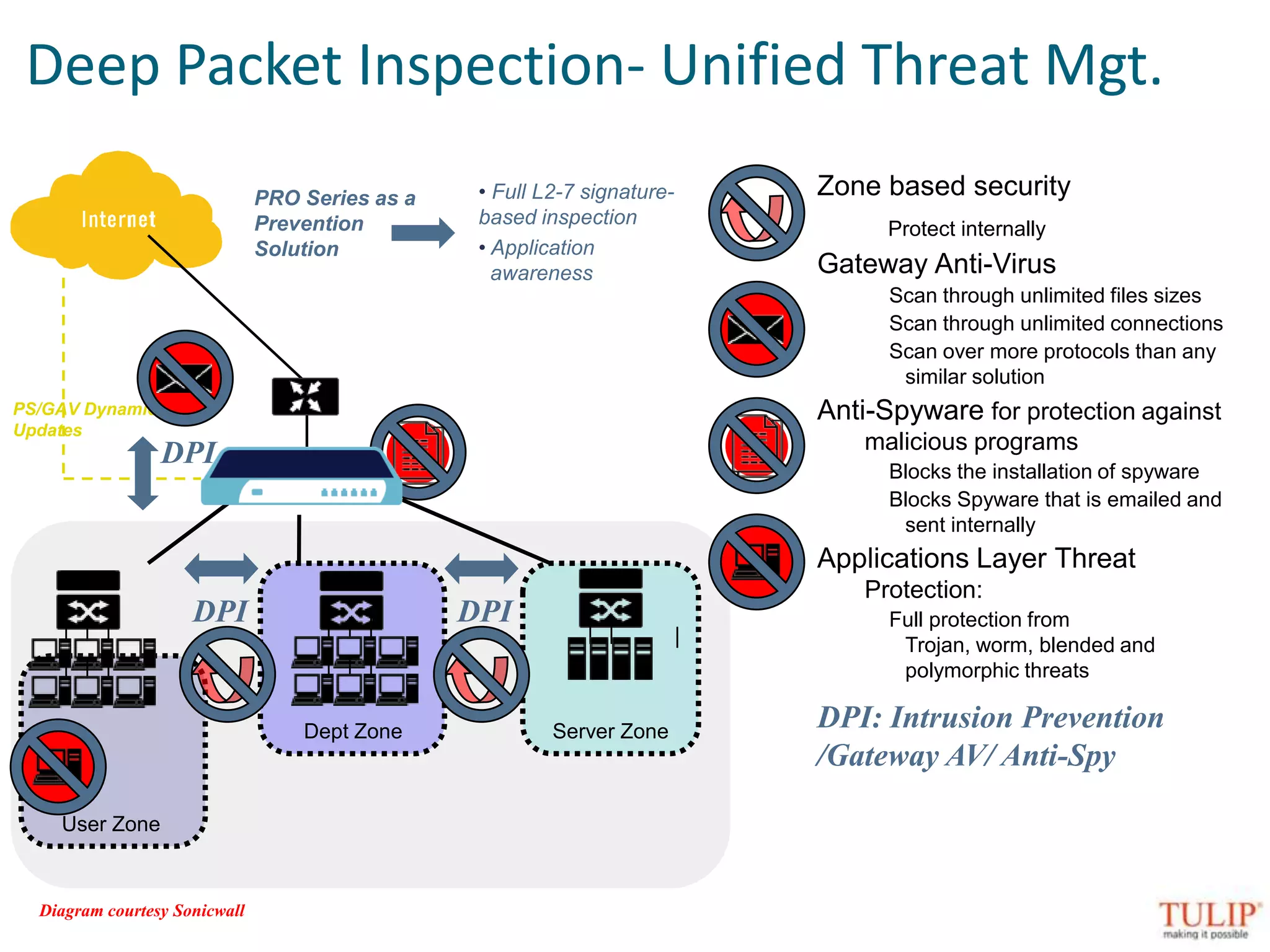
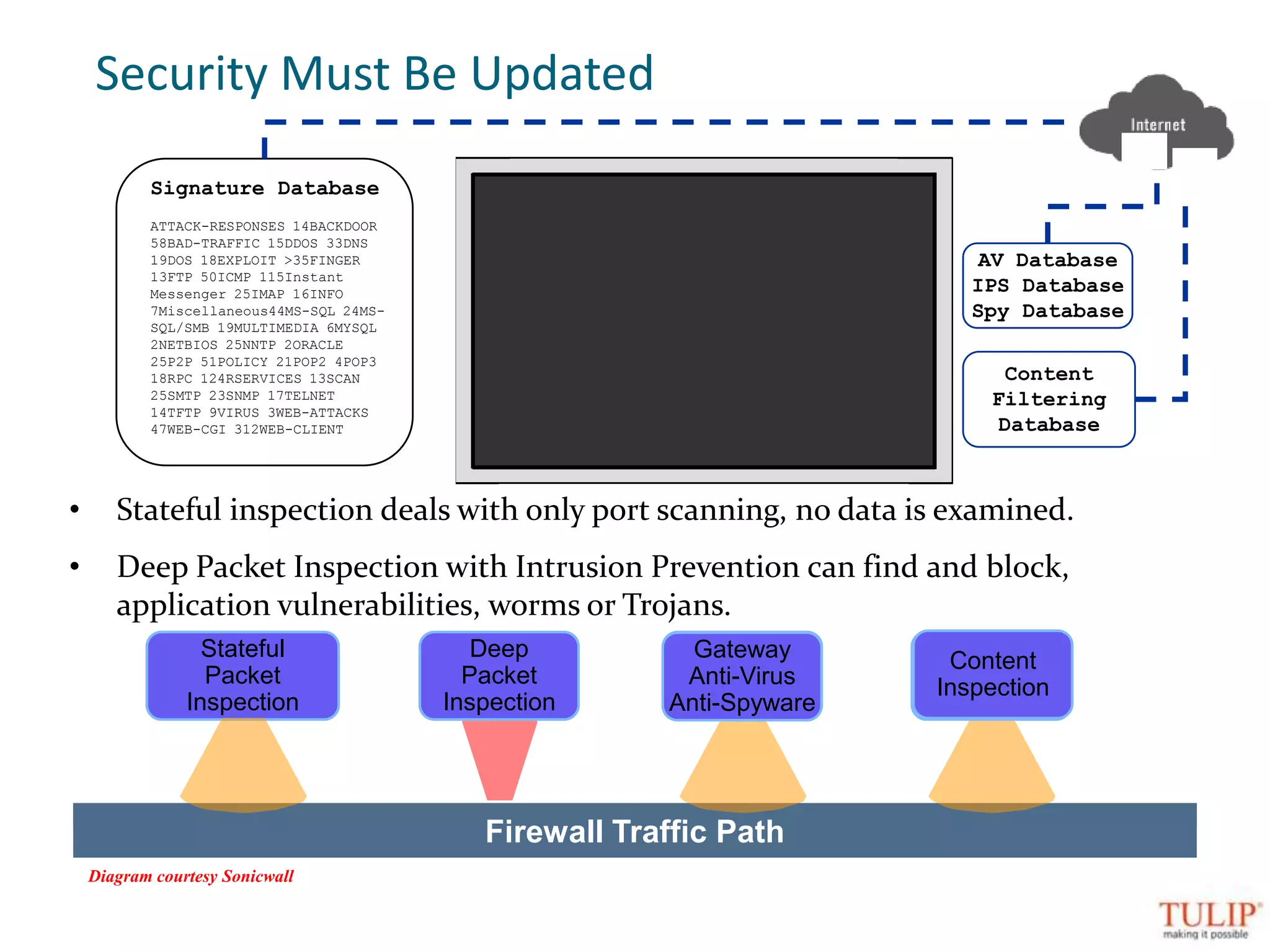
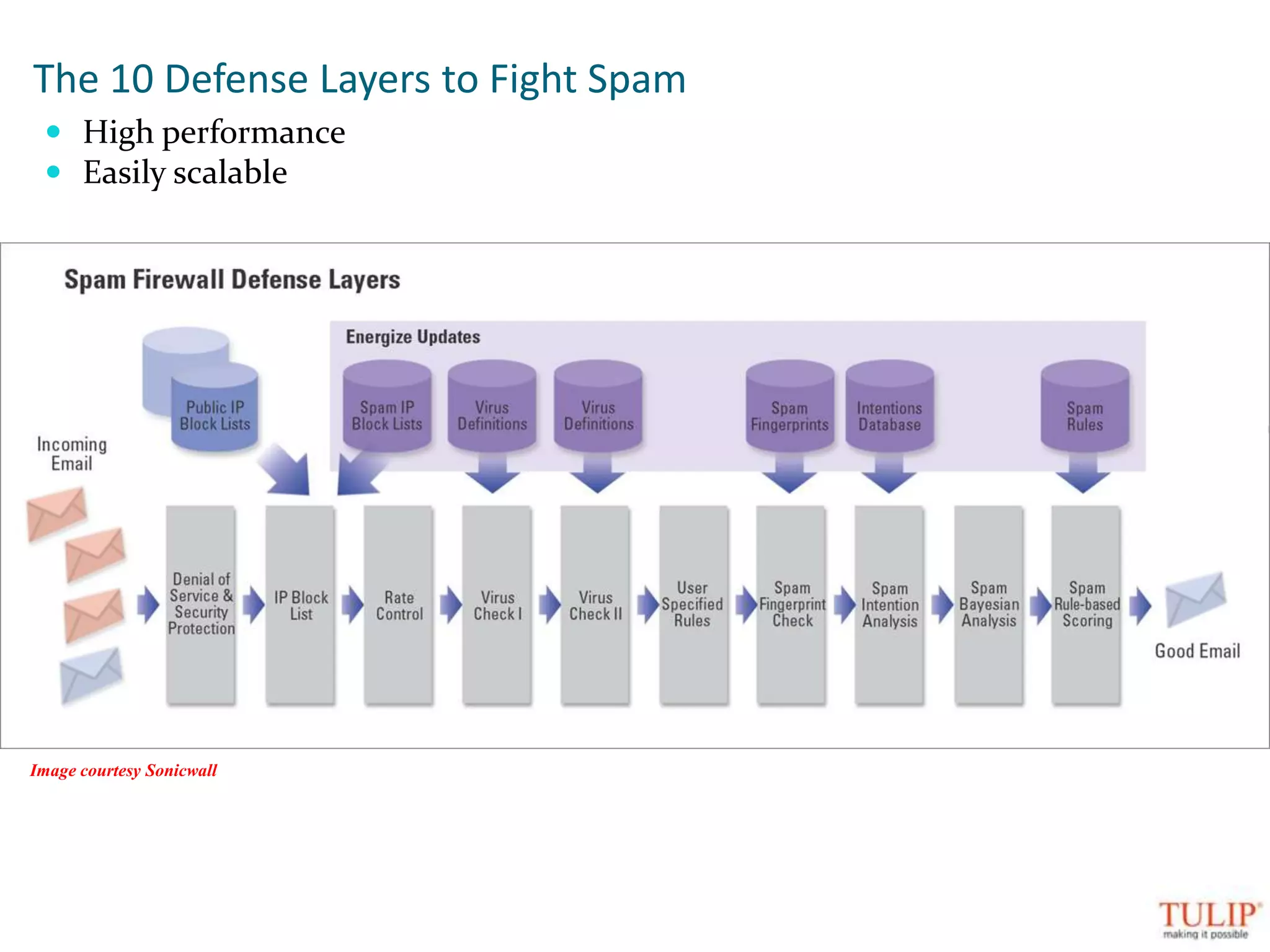
The document discusses training on unified threat management systems and SSL VPN by Tulip Telecom, focusing on the increasing sophistication of security threats and the importance of cybersecurity for ISPs. It highlights the role of security as a service, SSL VPN technologies, and various access options for secure remote access to organizational resources. Additionally, the document outlines unified threat management strategies, including deep packet inspection, antivirus, and anti-spyware defenses to protect against complex cyber threats.