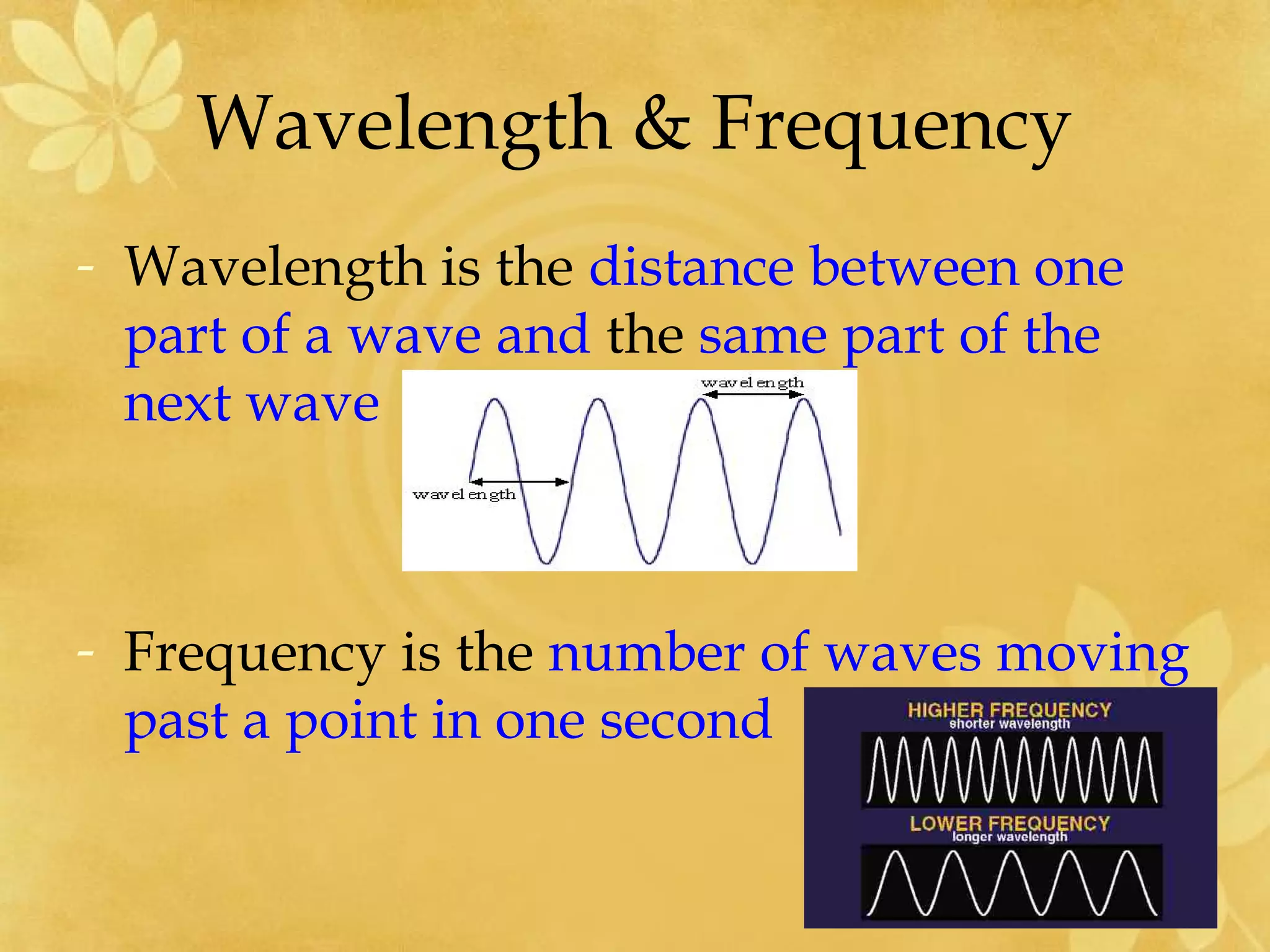
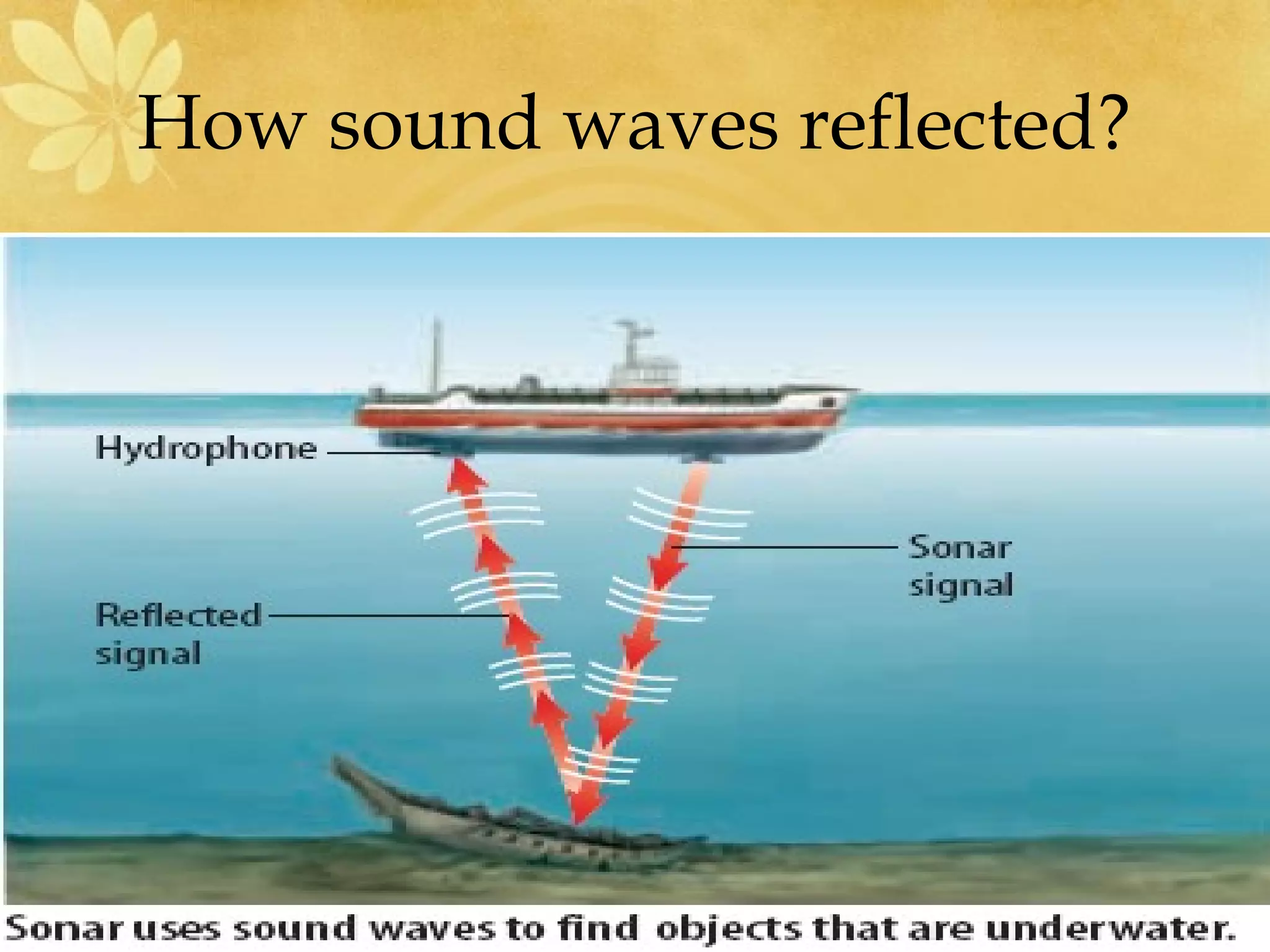
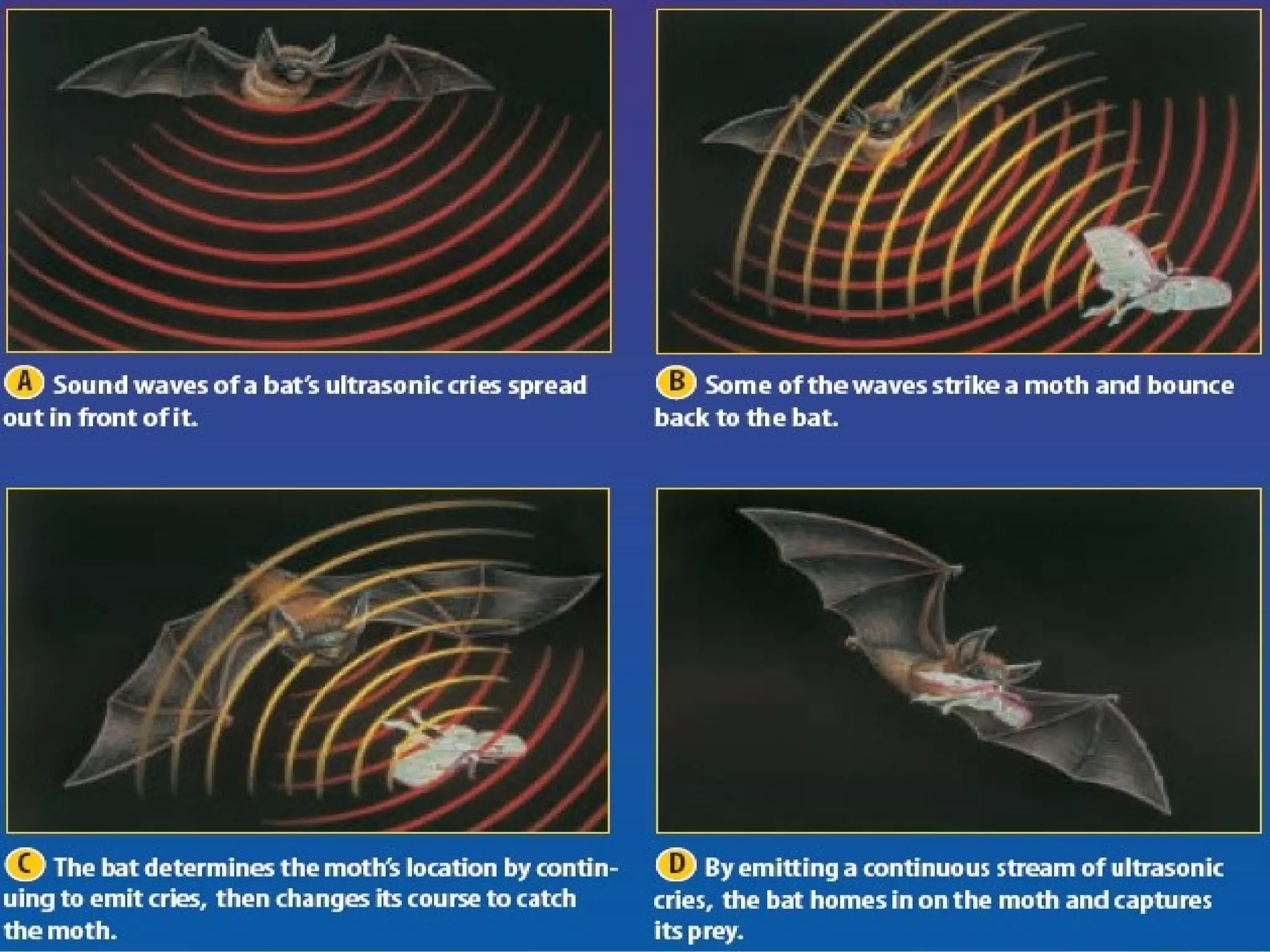
1) Sound is a form of energy that travels in waves and more quickly through solids than liquids or gases. There are two main types of sound - musical sounds produced by regular vibrations and noise sounds from irregular vibrations.
2) The ear takes in sound waves and converts them to signals sent to the brain. Sound waves move through three parts of the ear - the outer, middle, and inner ear.
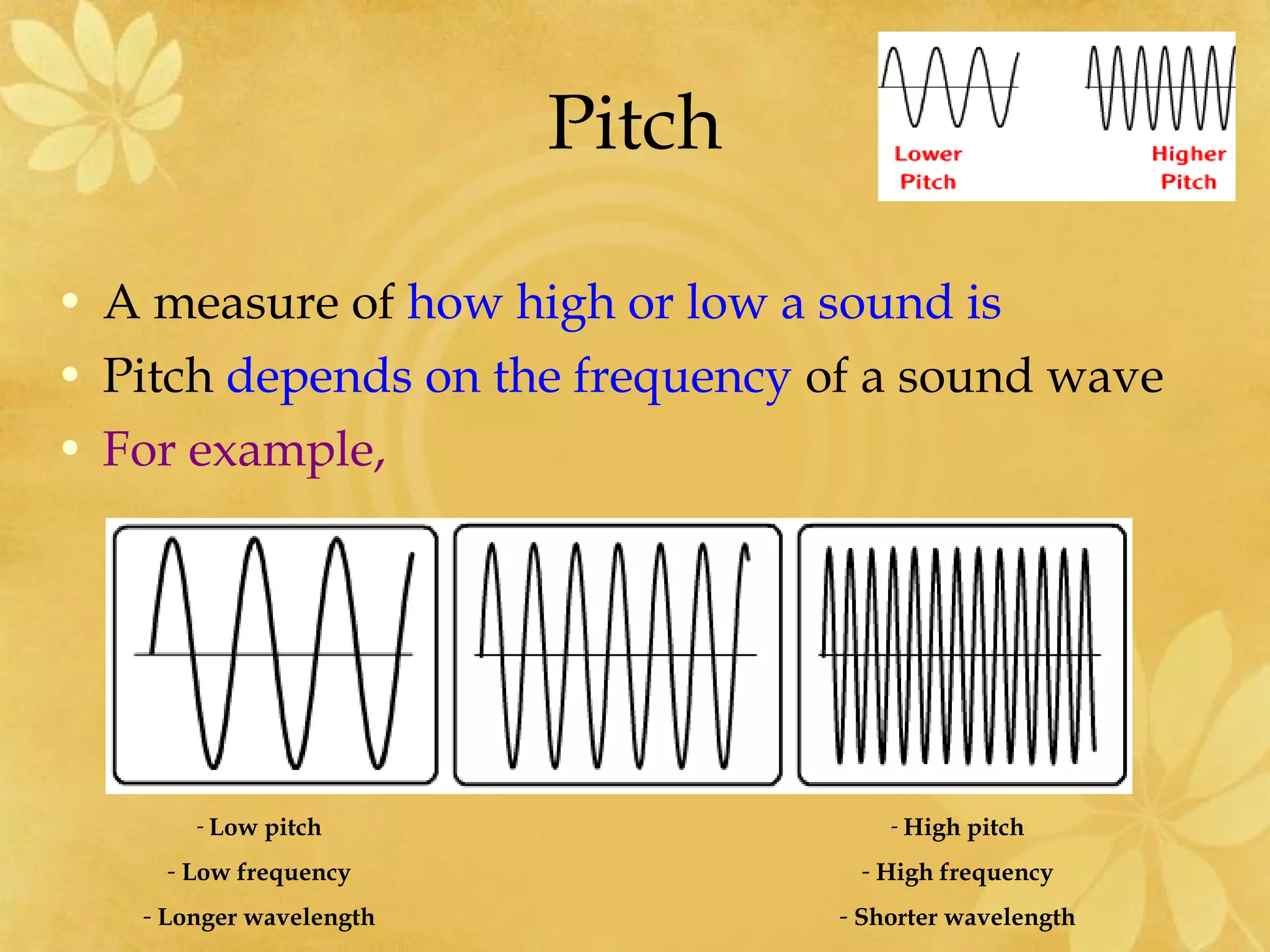
3) Pitch depends on the frequency of a sound wave, with a higher pitch associated with a higher frequency and shorter wavelength. Musical instruments can be played at different pitches by changing the lengths or thicknesses of their parts.