The document explores the significance of blogs as information sources in both work and everyday life, highlighting their role in journalism, public opinion, and personal expression. It presents a framework for understanding blogs by categorizing them alongside traditional information sources, discussing their unique properties and complexities. The document concludes with a proposed classification of blog content and a call for further study on how blogs function as information sources.
















![References
Hertzum, M., Andersen, H. H. K., Andersen, V., & Hansen, C. B. (2002). Trust in information sources: Seeking
information from people, documents, and virtual agents. Interacting with Computers, 14(5), 575-599.
doi:10.1016/S0953-5438(02)00023-1
Kline, D., Burstein, D., De Keijzer, A. J., & Berger, P. (2005). Blog! :How the newest media revolution is changing
politics, business, and culture. New York: CDS Books in association with Squibnocket Partners LLC.
Leckie, G. J., Pettigrew, K. E., & Sylvain, C. (1996). Modeling the information seeking of professionals: A general
model derived from research on engineers, health care professionals, and lawyers. The Library
Quarterly, 66(2), 161-193. Retrieved from http://www.jstor.org/stable/4309109
Lenhart, A., & Fox, S. (2006). Bloggers: A portrait of the internet’s new storytellers. Pew Internet & American Life
Project. Retrieved from
http://www.pewinternet.org/~/media//Files/Reports/2006/PIP%20Bloggers%20Report%20July%2019%202006.
pdf.pdf
Maxwell, R. (2008). Flash and substance: Blogs as alternative sources of legal information. The CRIVSheet, The
Newsletter of American Association of Law Libraries [AALL] ‘s Committee on Relations with Information
Vendors, 30 (2), 9-10. Retrieved 8/17/2012, from http://www.aallnet.org/main-
menu/Publications/spectrum/Archives/Vol-12/pub_sp0802/pub-sp0802-criv.pdf
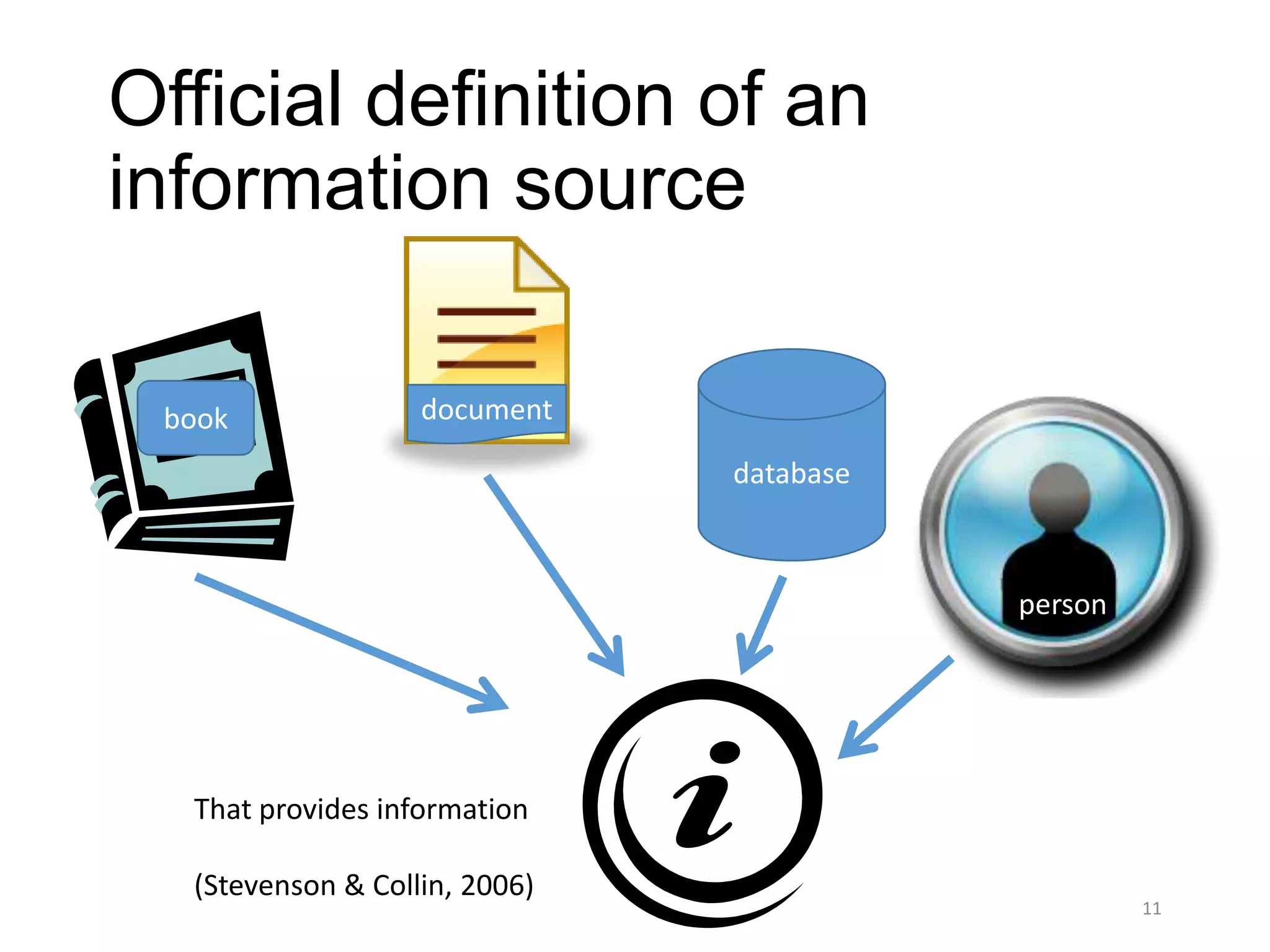
Stevenson, J. & Collin, P. H. (2006). Dictionary of information and library management (2nd ed.). London: A & C
Black.
Vaughan, L., Tang, J., & Du, J. (2010). Constructing business profiles based on keyword patterns on web sites.
Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 61(6), 1120-1129. doi:
10.1002/asi.21321
Zhuo, X., Wellman, B., & Yu, J. (2011). Egypt: The first Internet revolt? Peace Magazine, 27(3), 6-10. Retrieved
from http://peacemagazine.org/archive/v27n3p06.htm
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/influence12blogs3-120929224340-phpapp01/75/Categorizing-blogs-as-information-sources-Implications-for-collection-development-policies-of-libraries-25-2048.jpg)