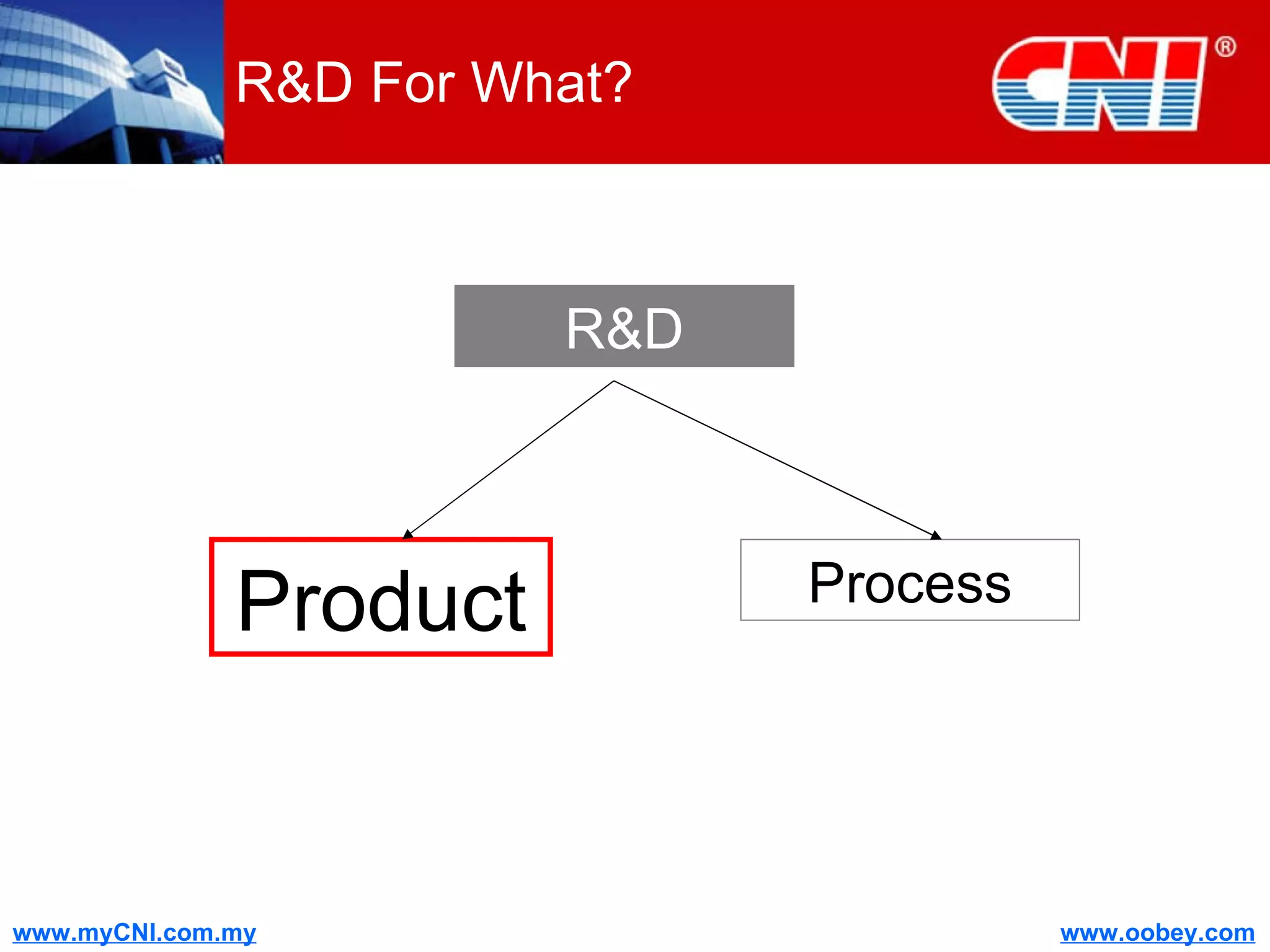
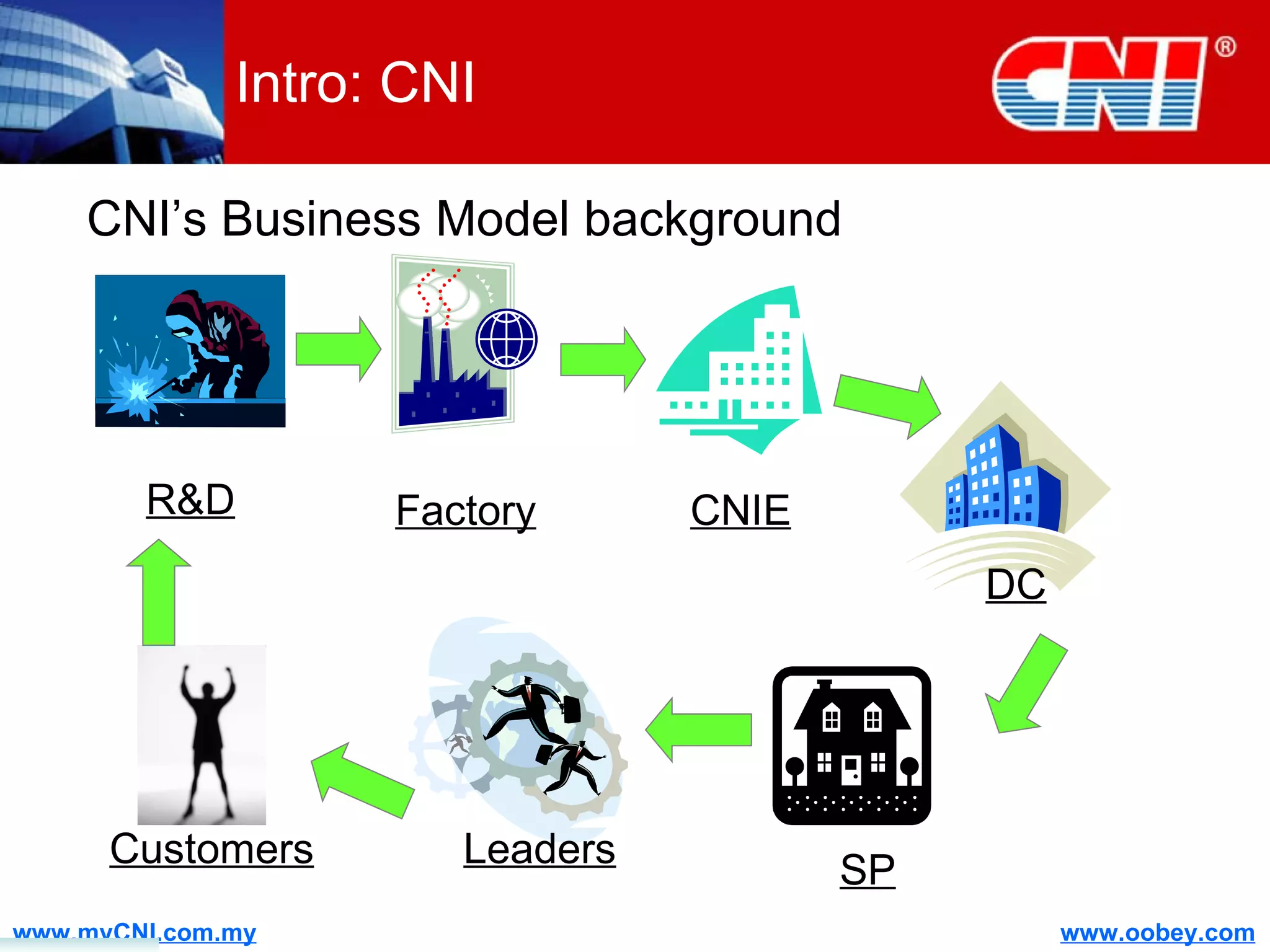
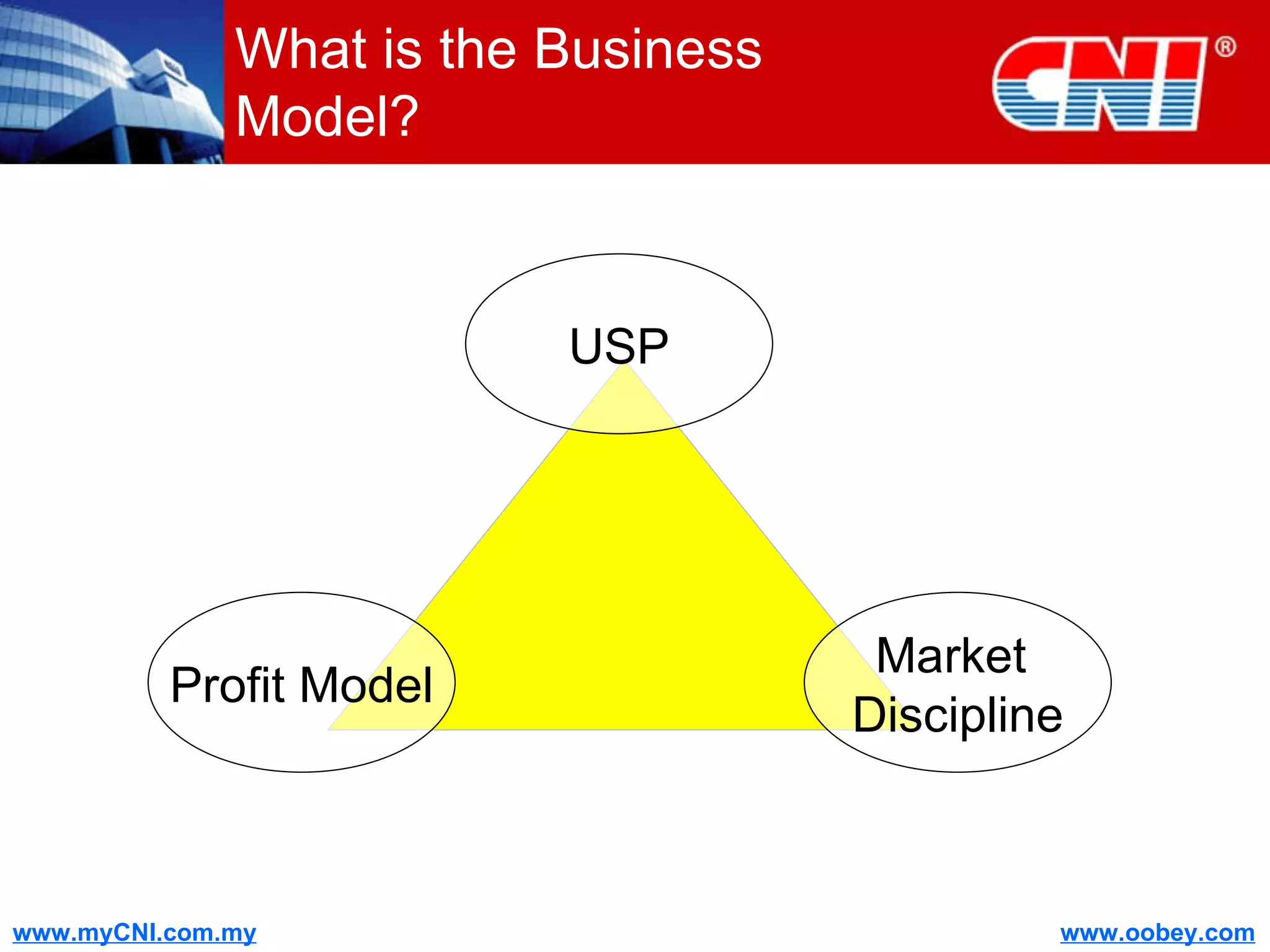
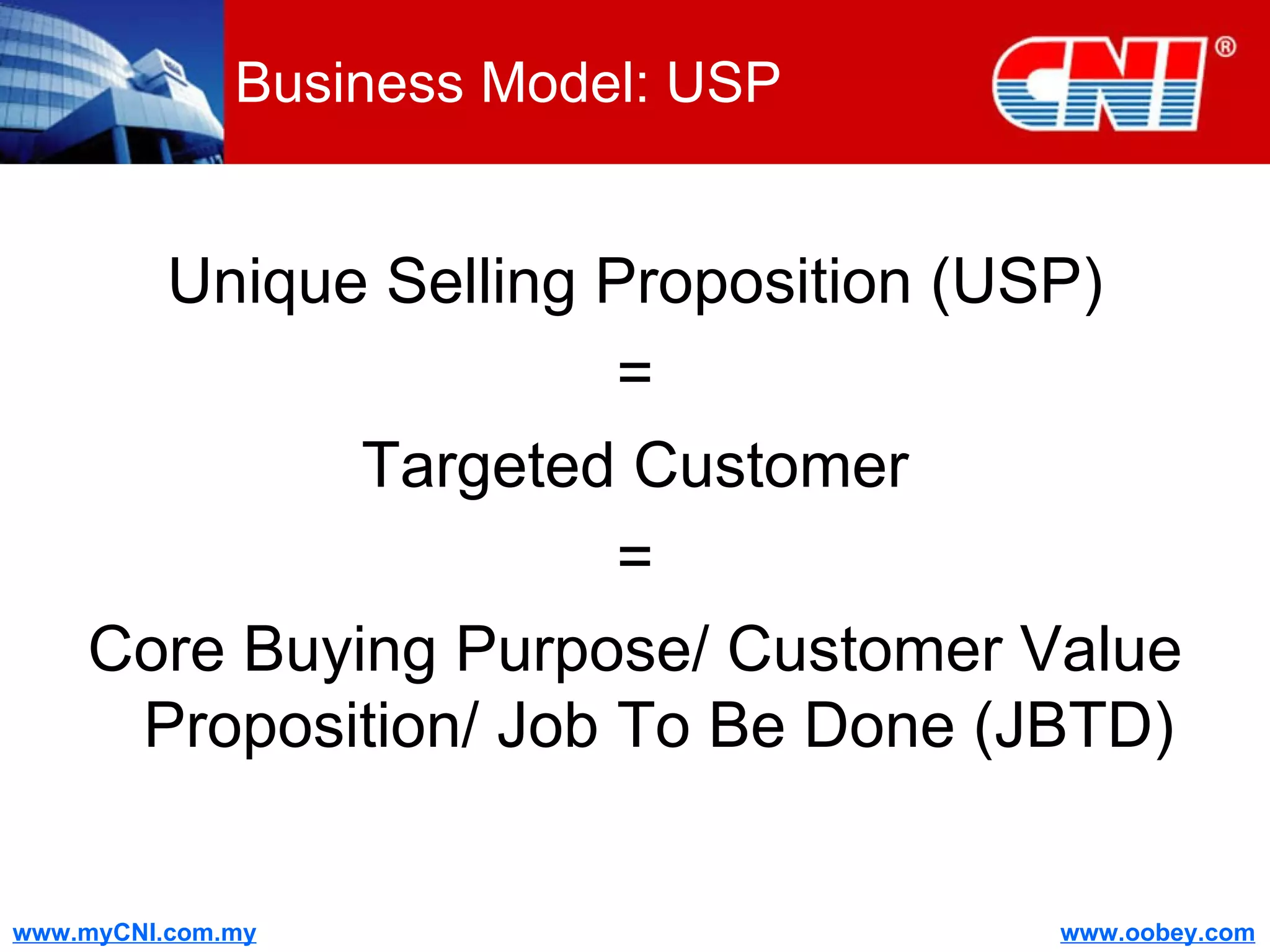
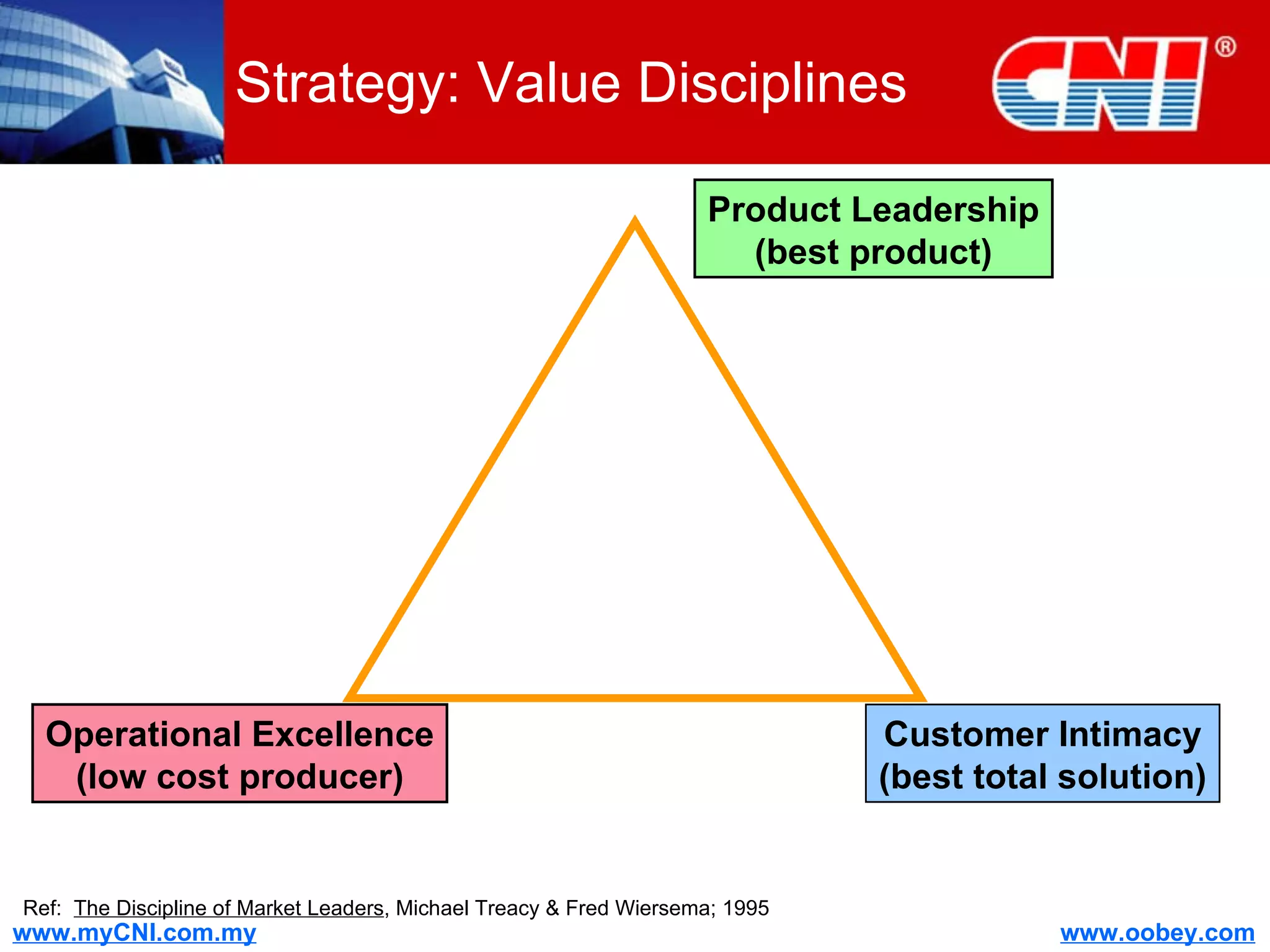
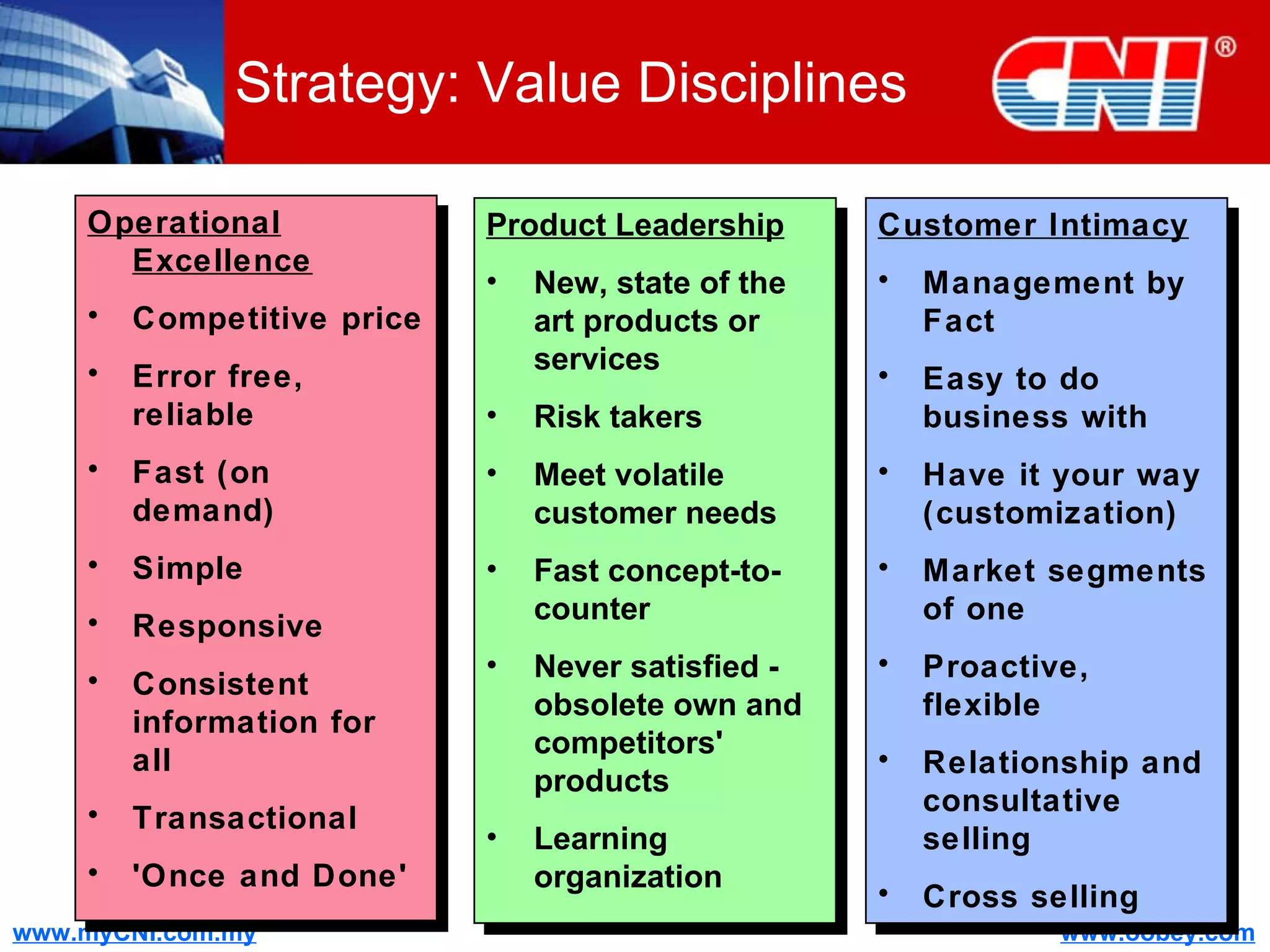
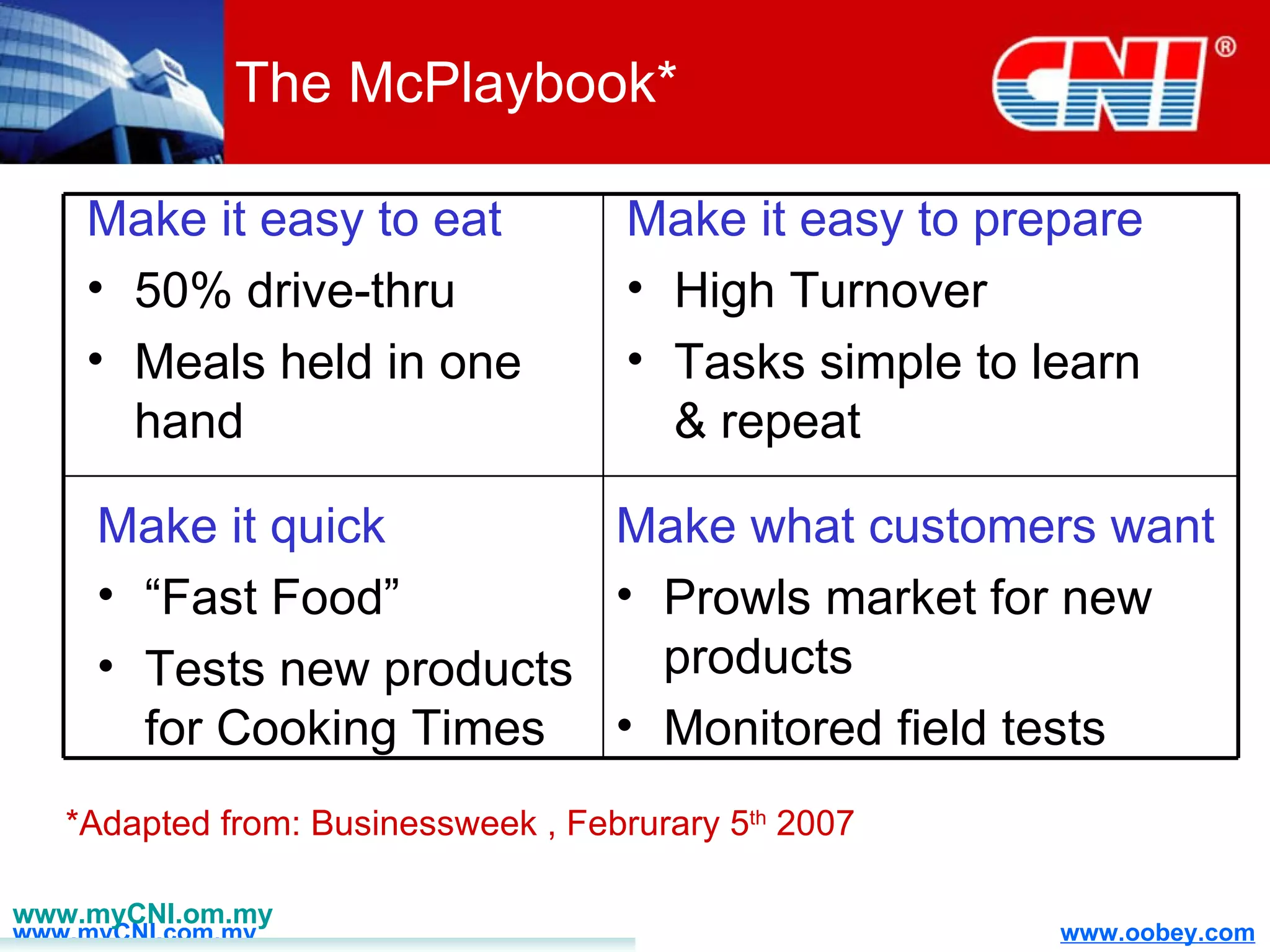
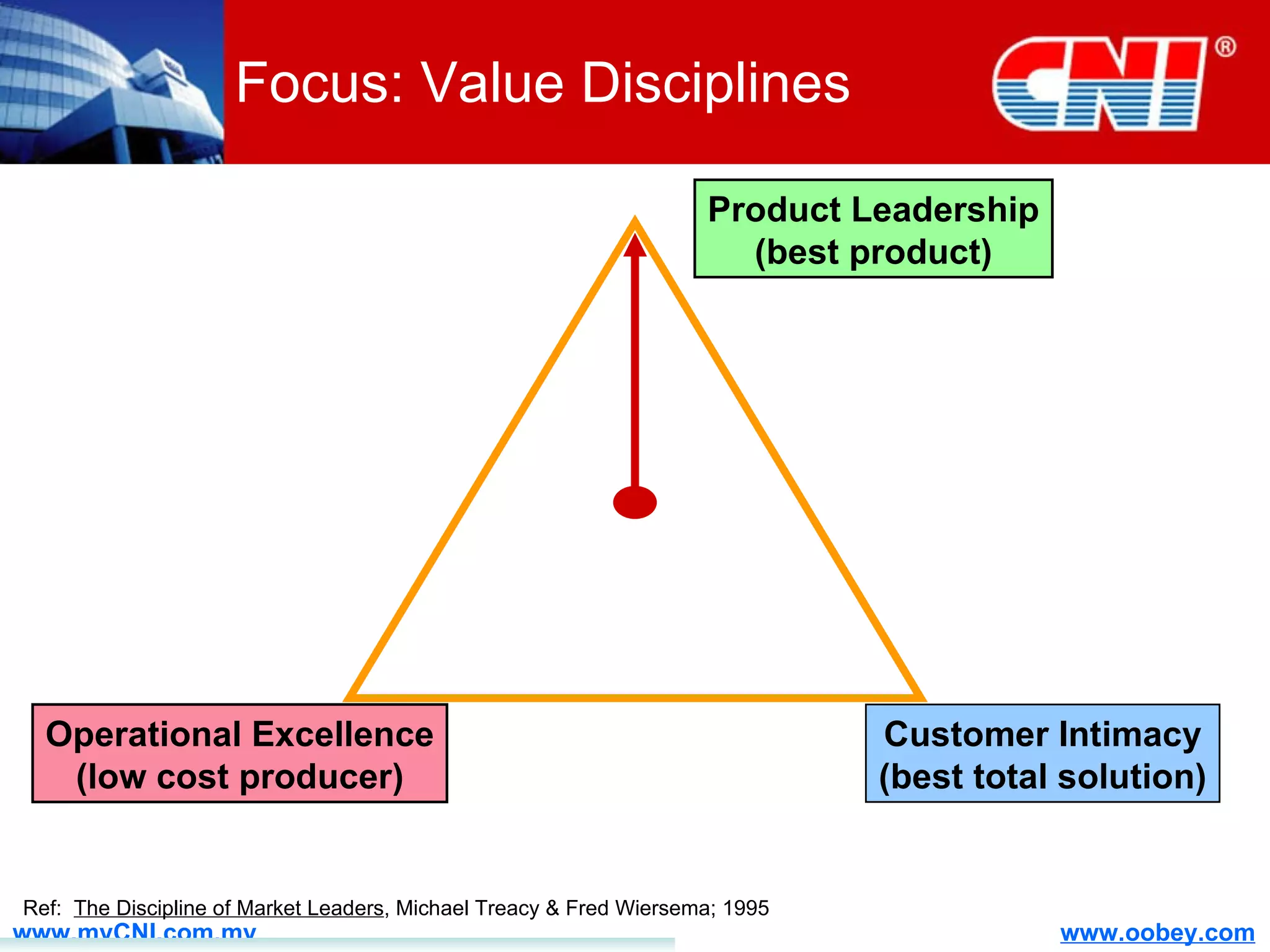
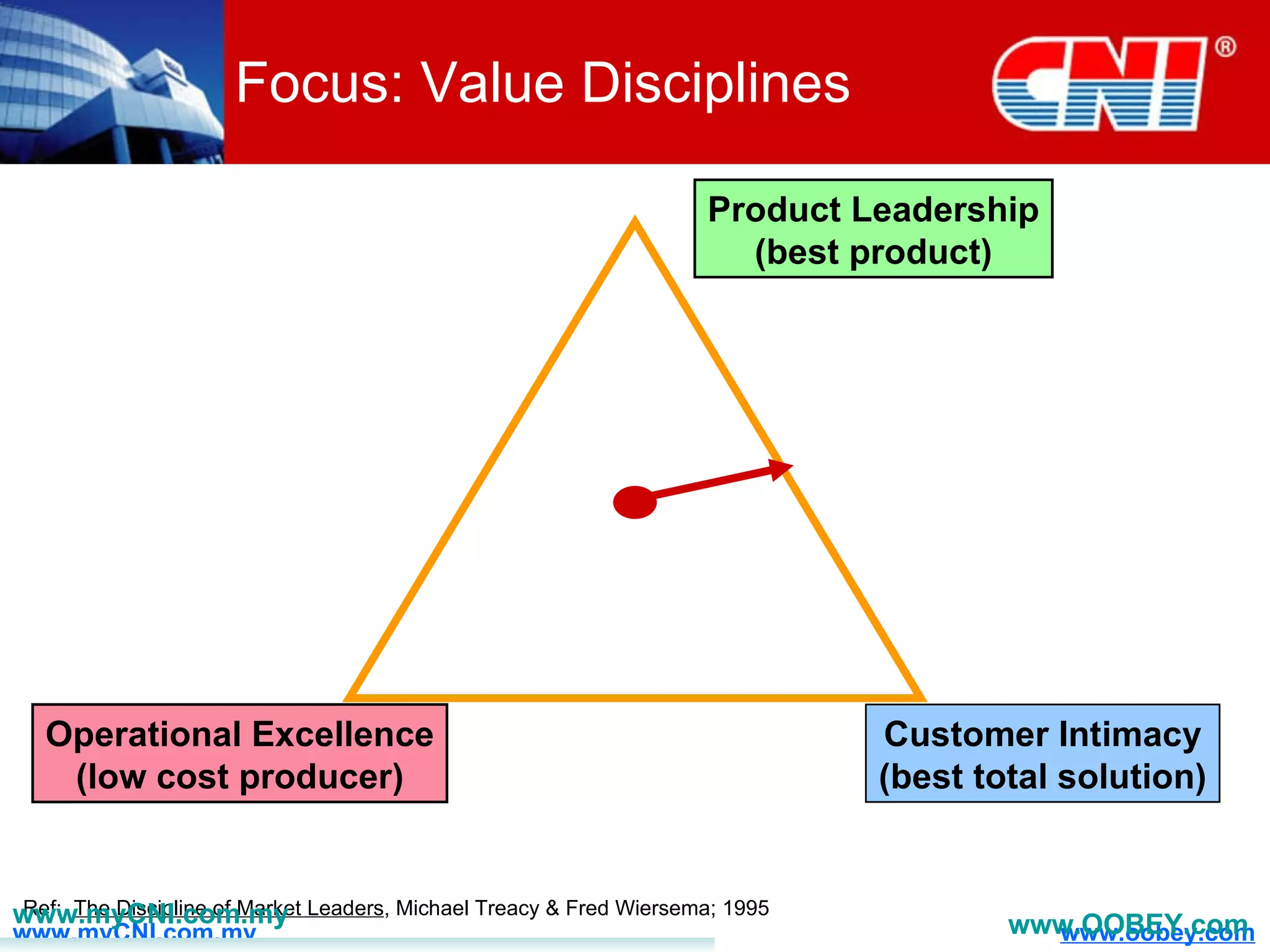
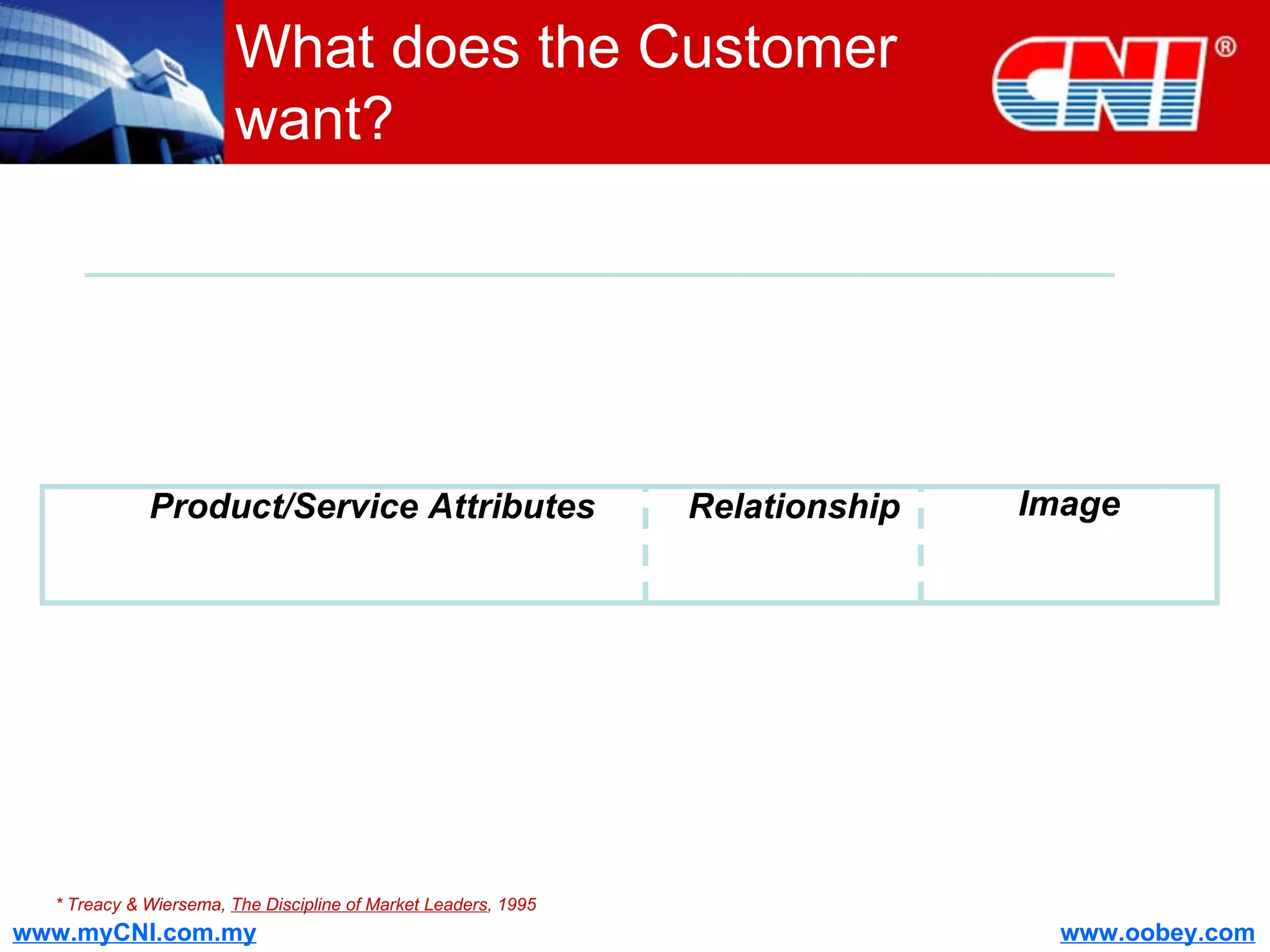
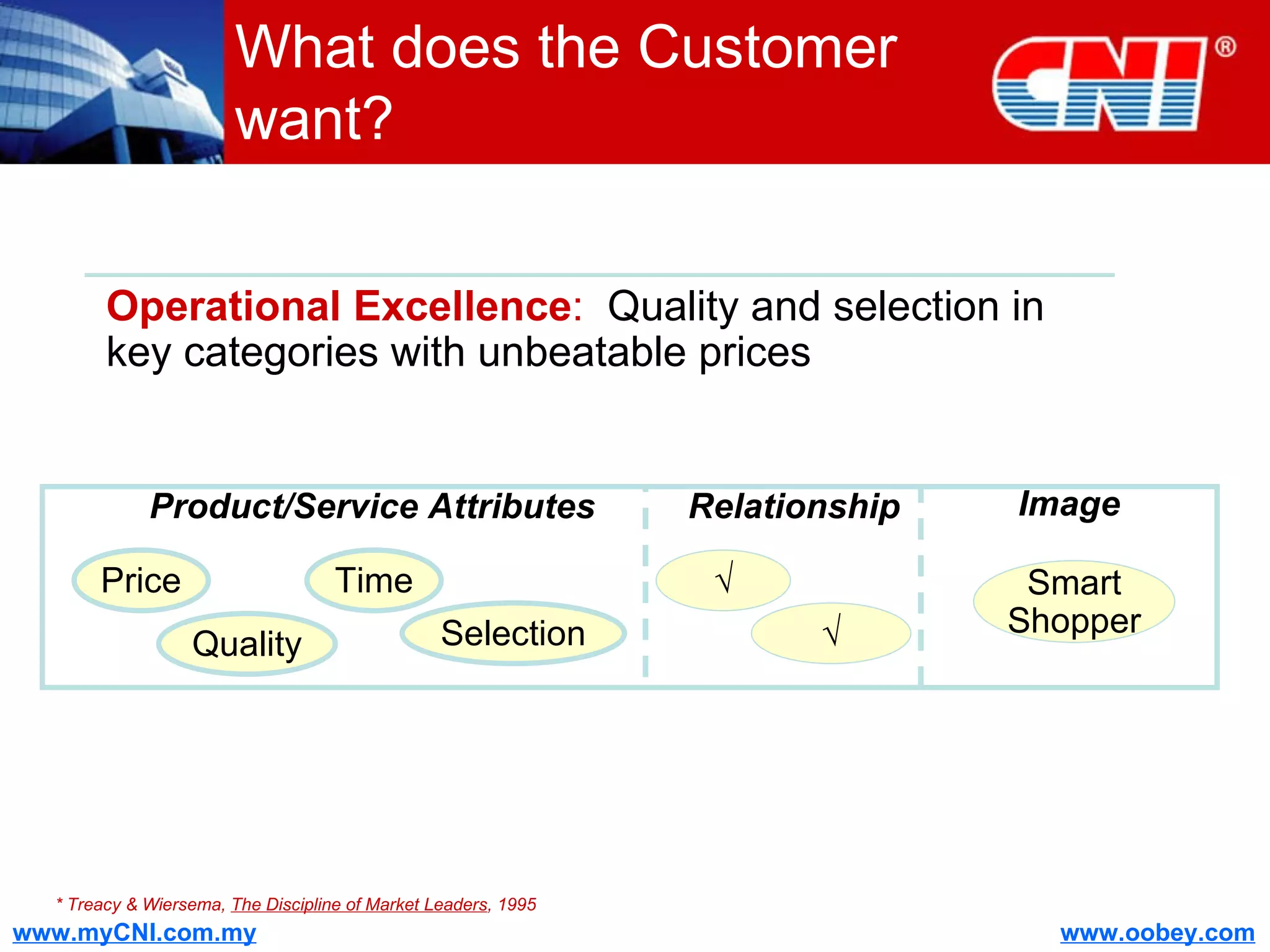
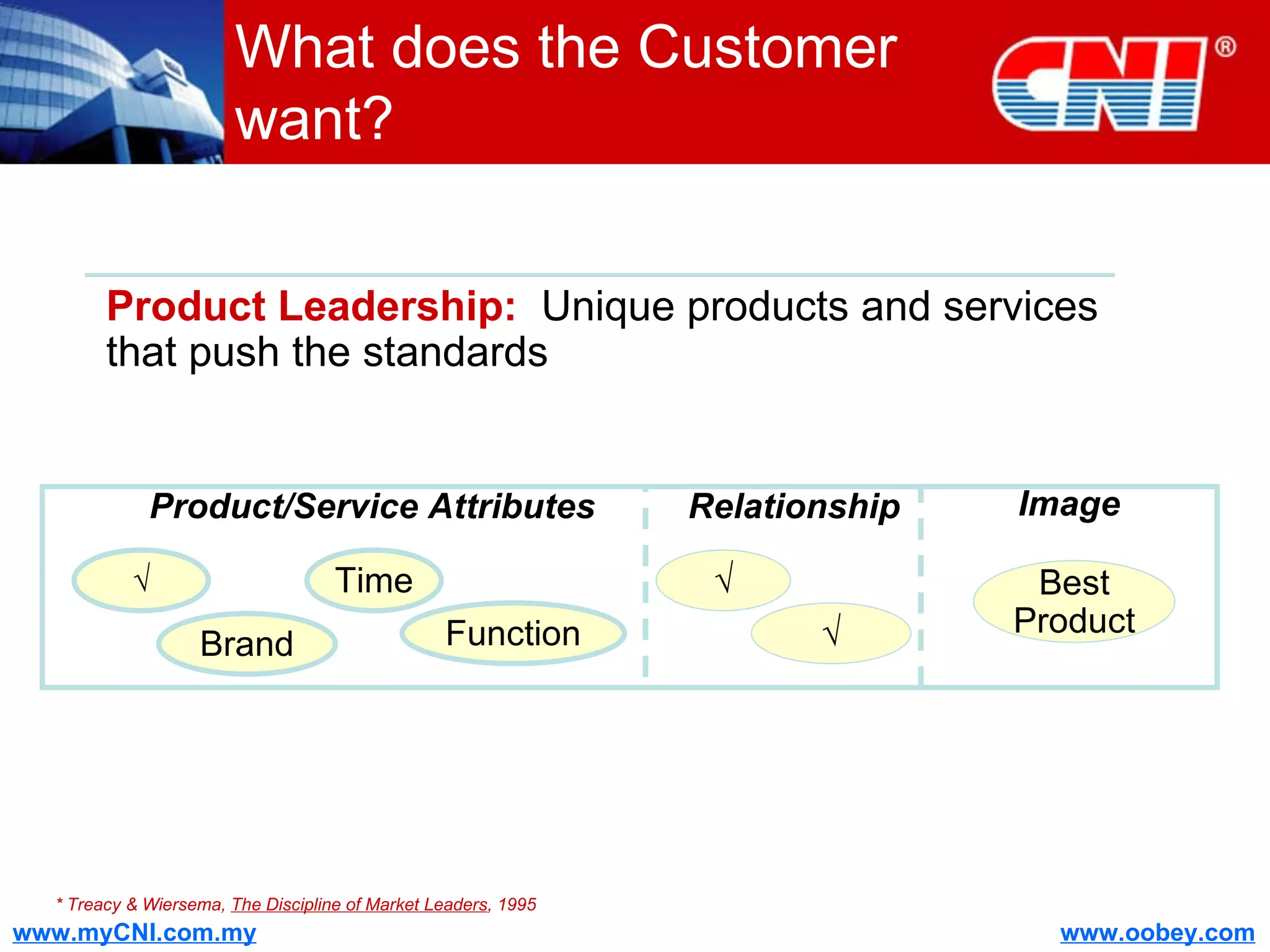
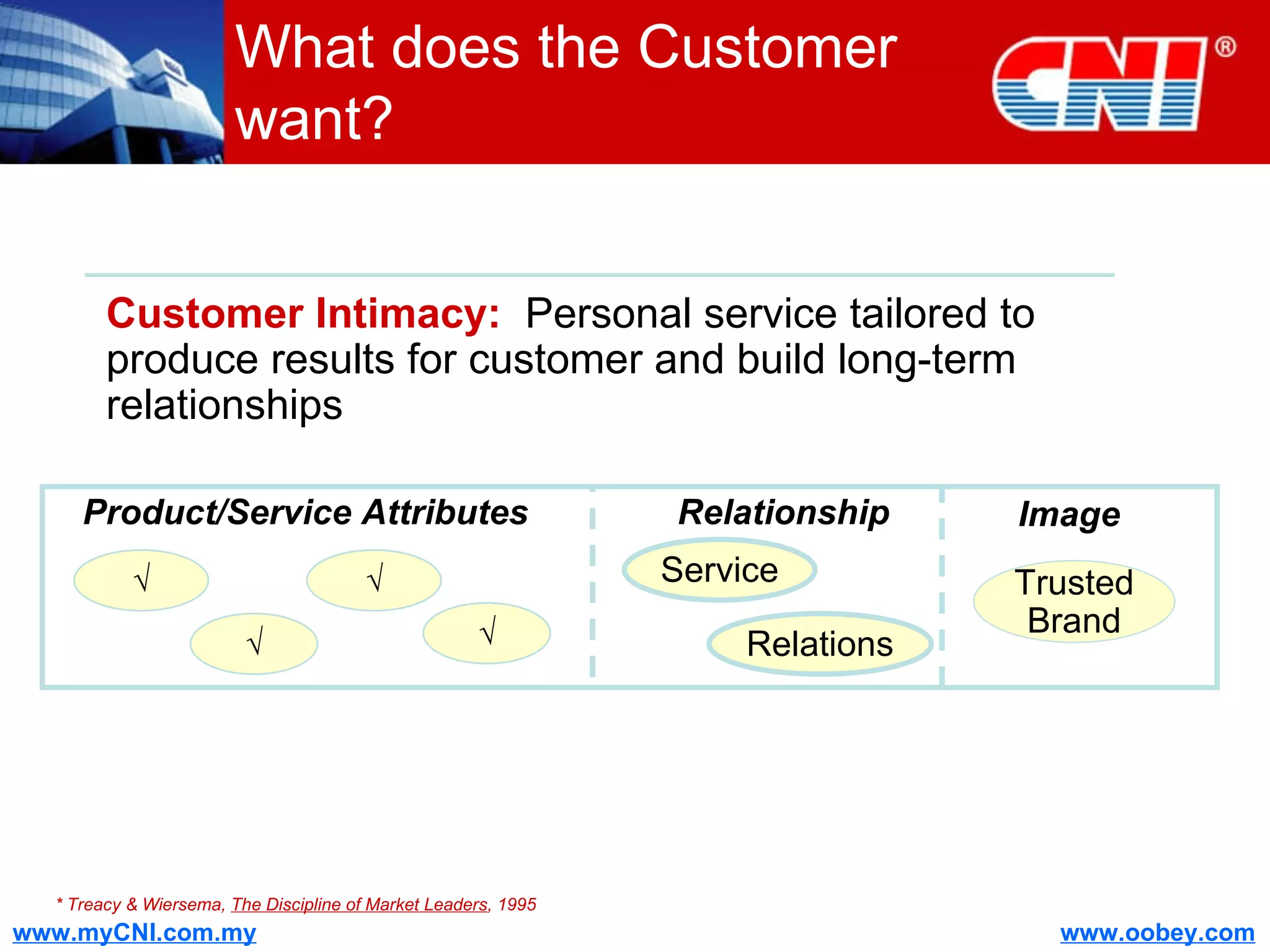
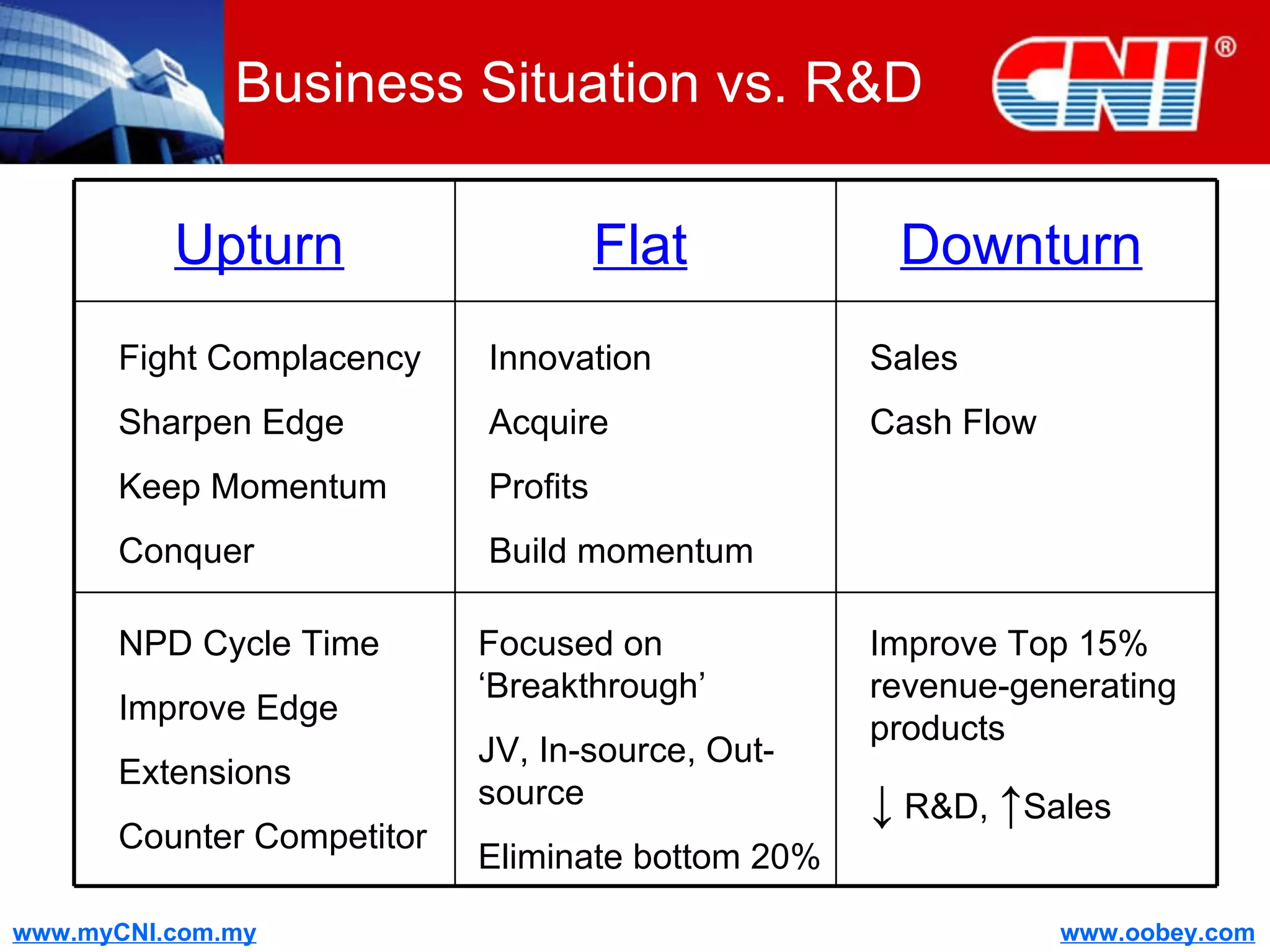
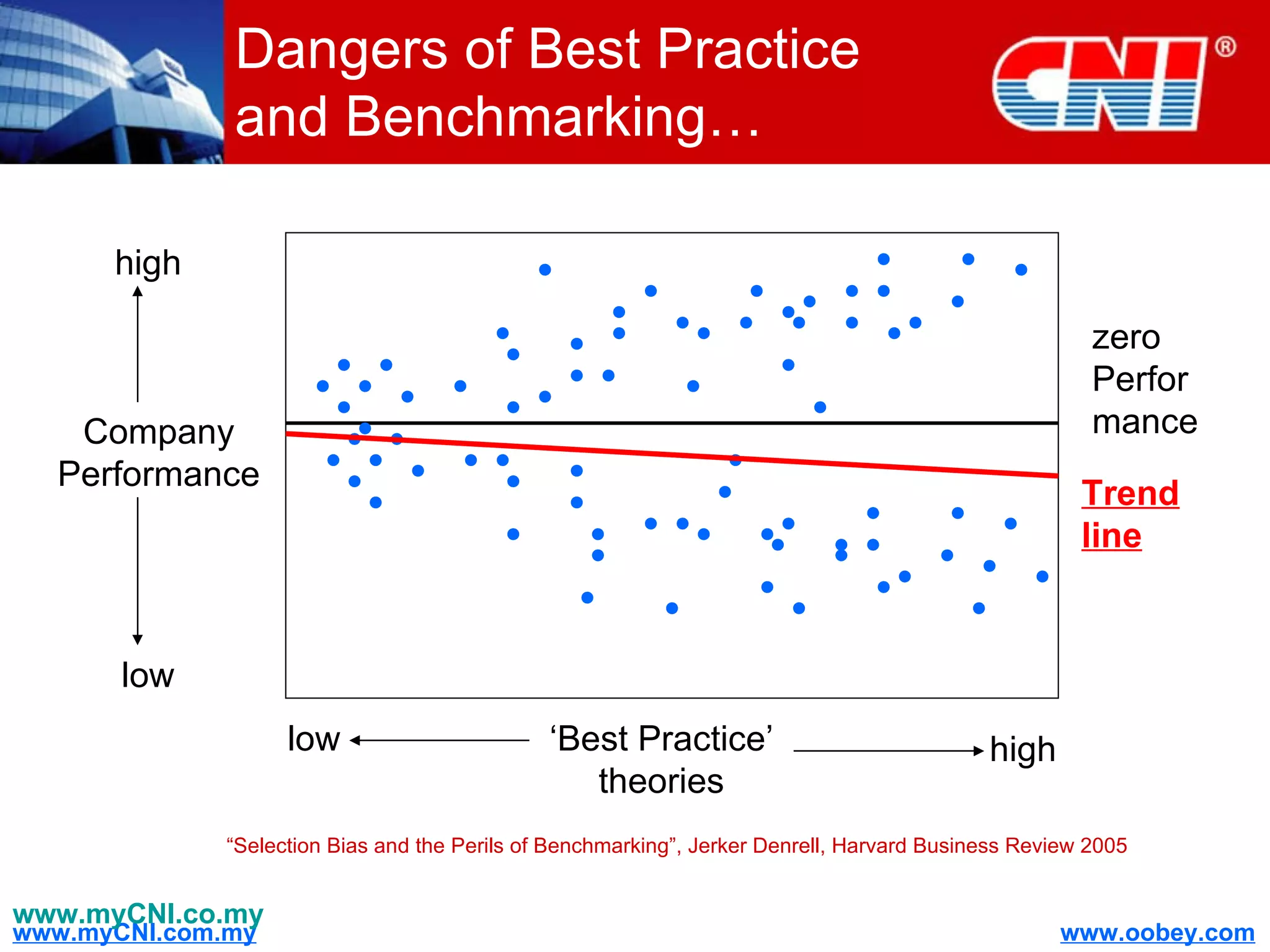
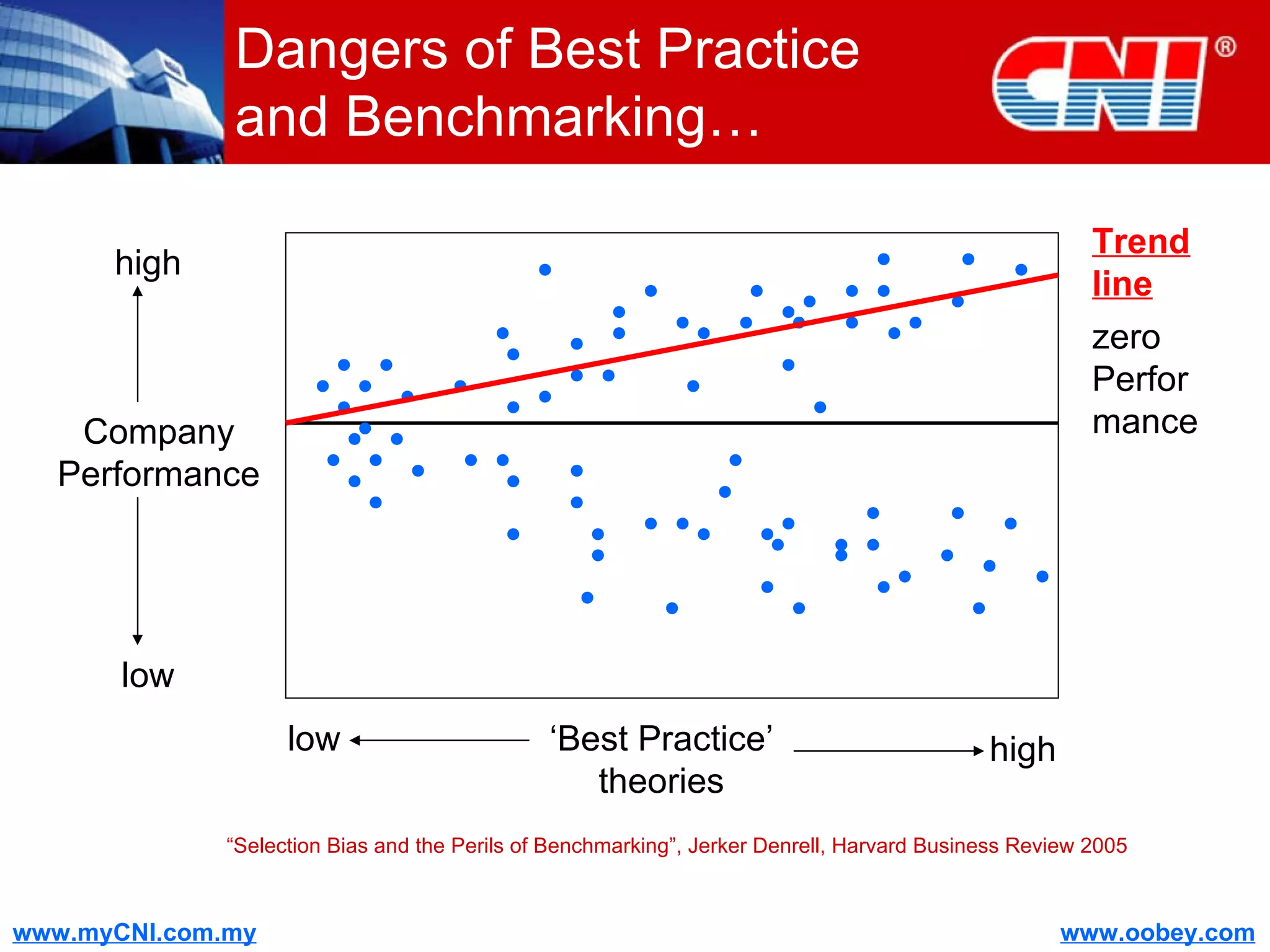
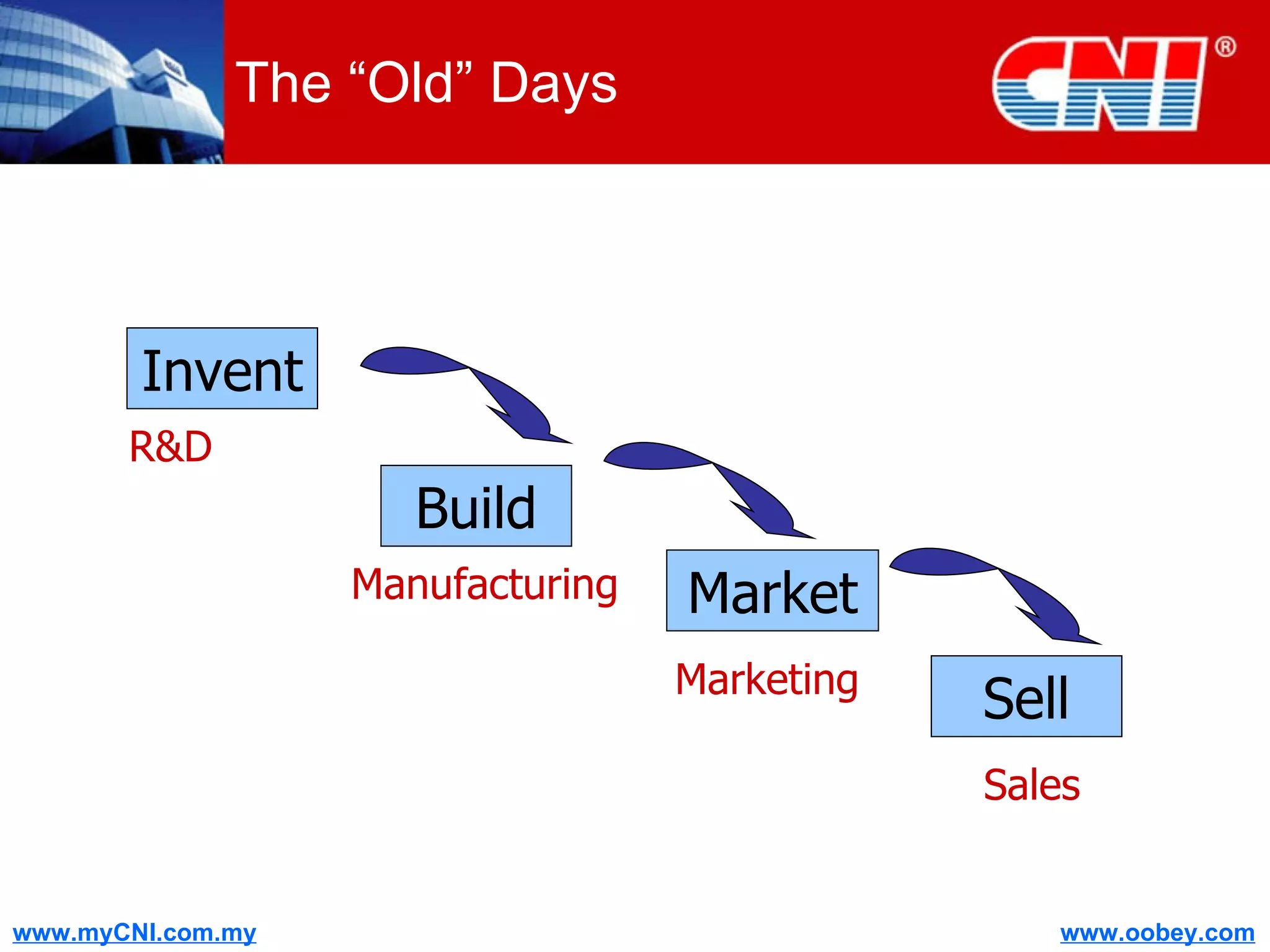
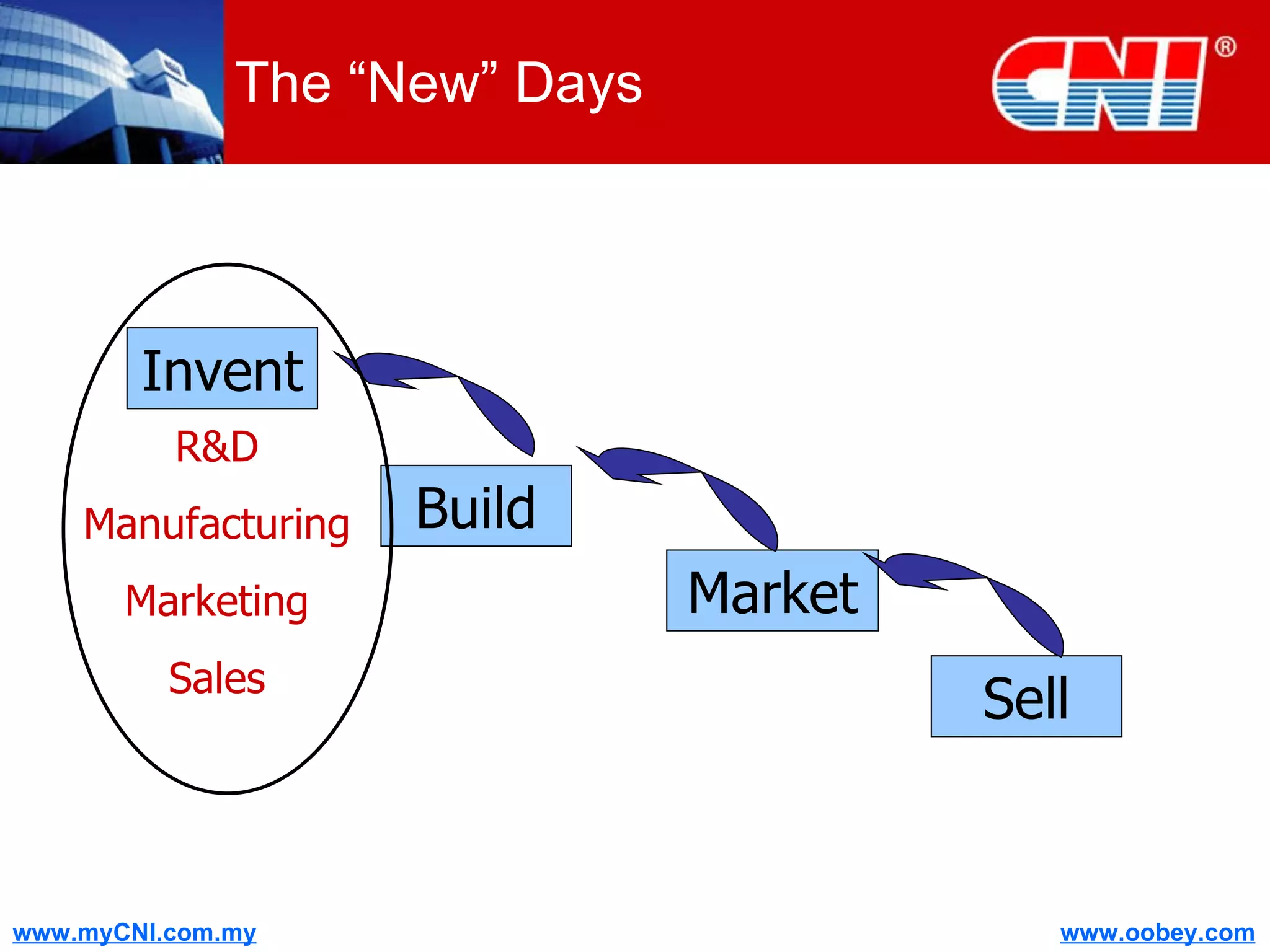
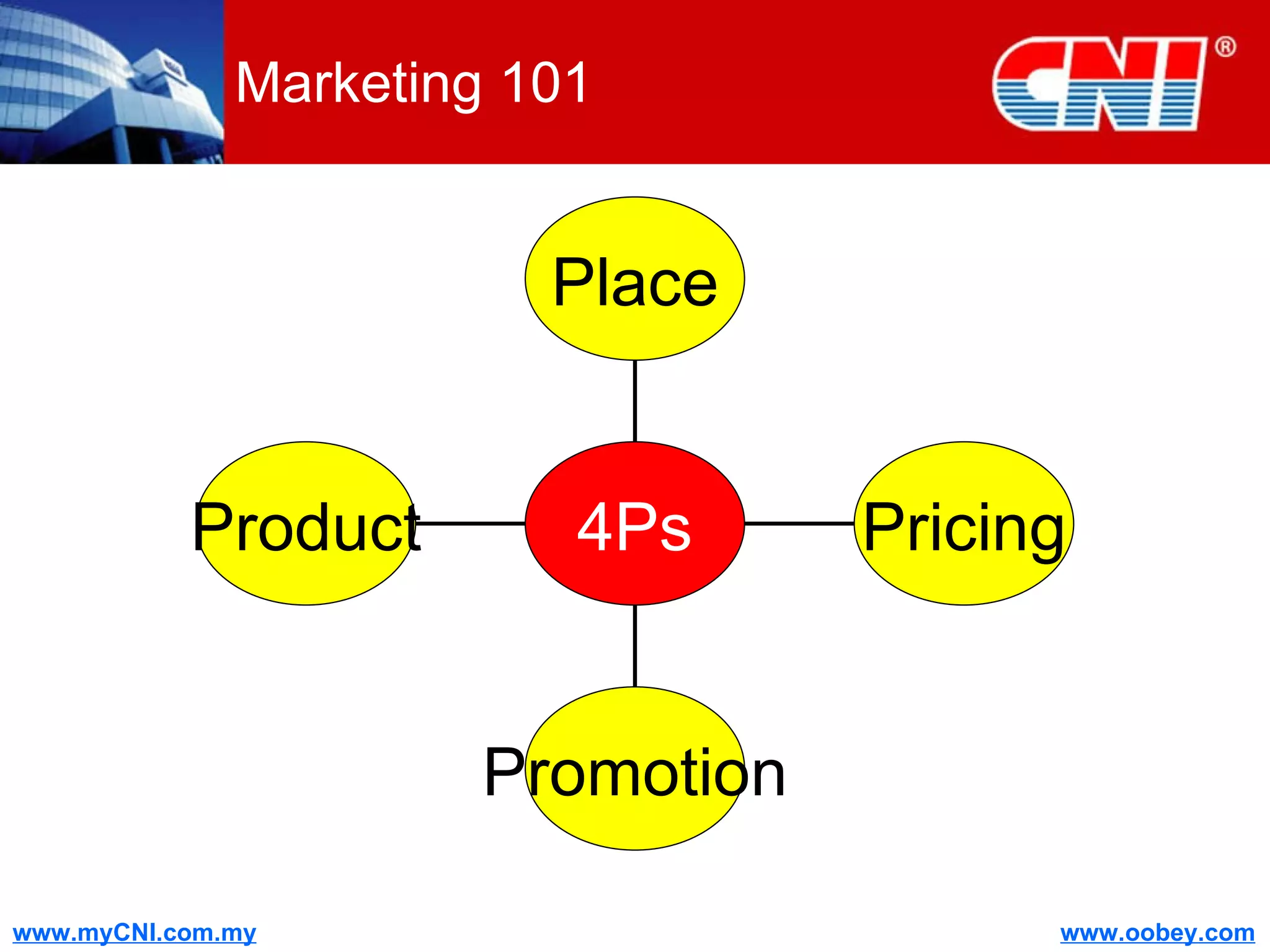
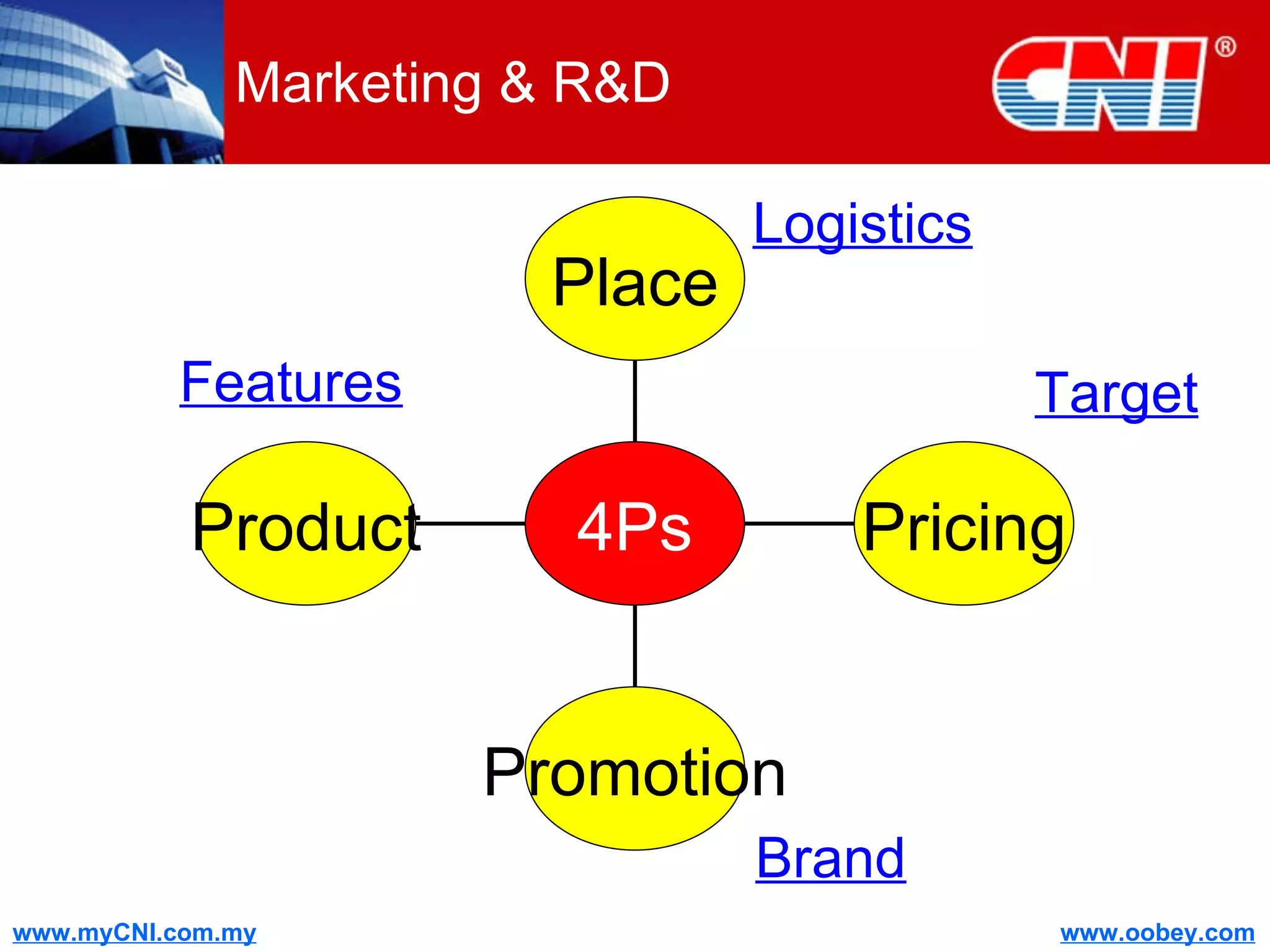
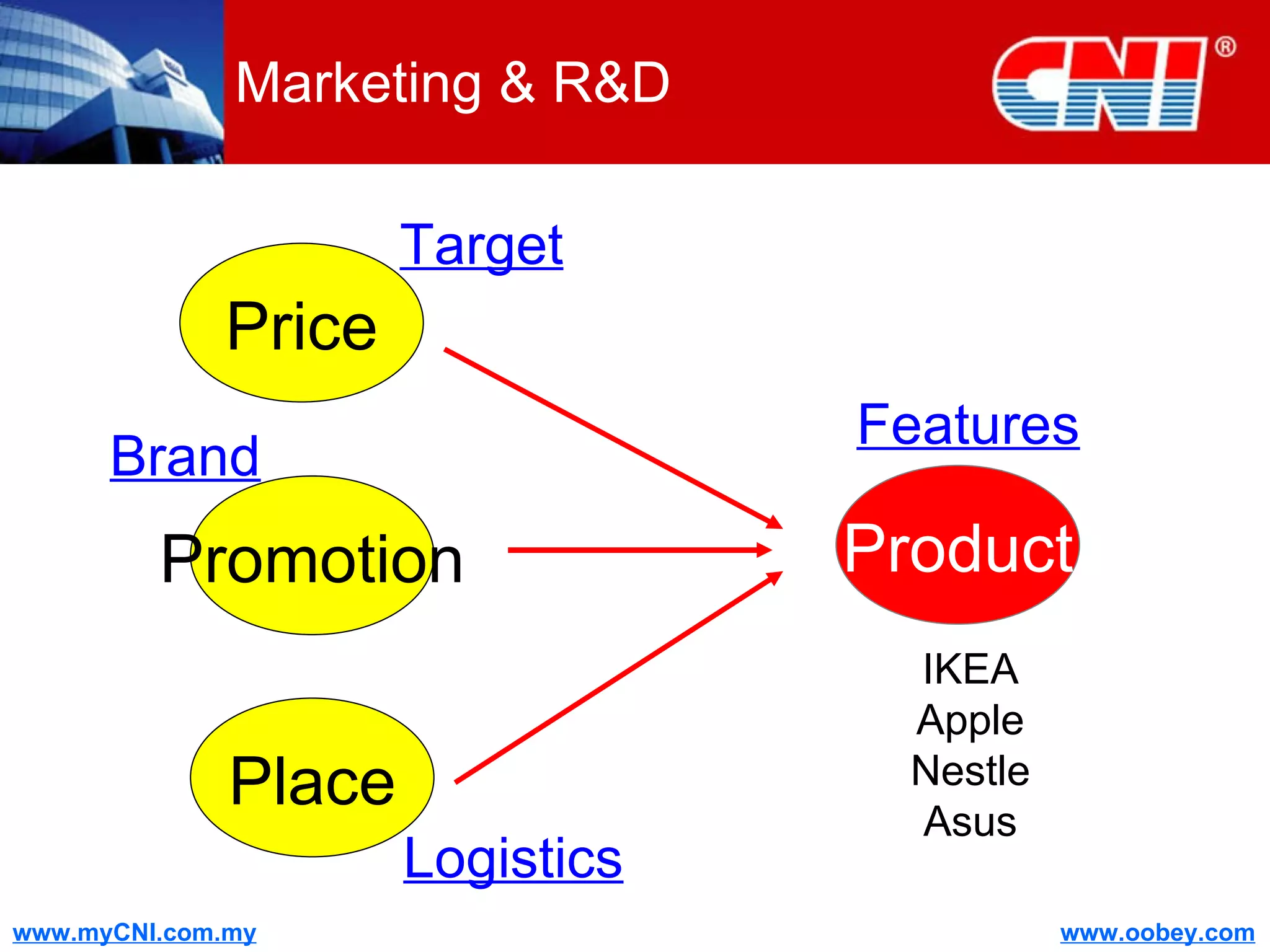
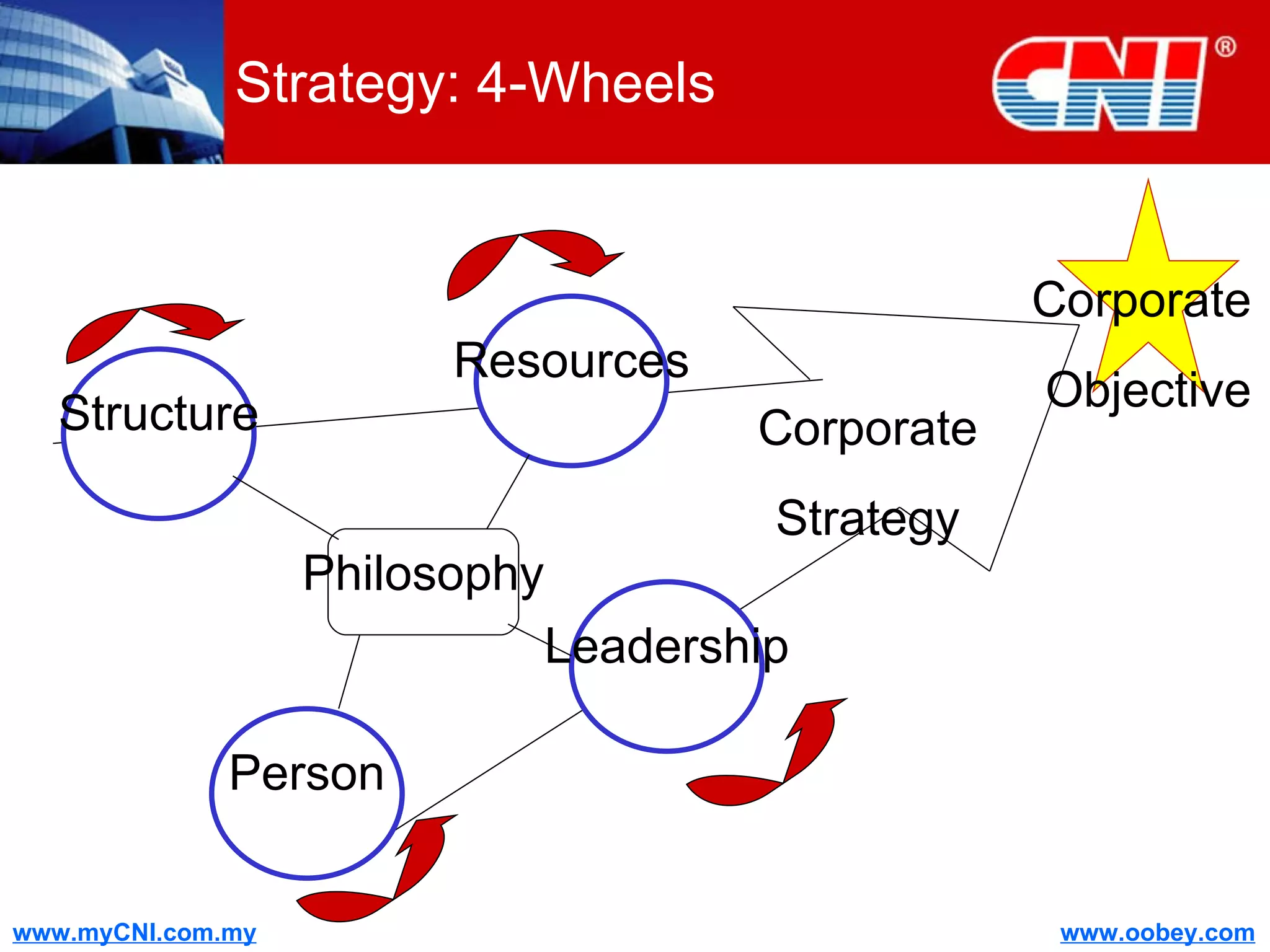
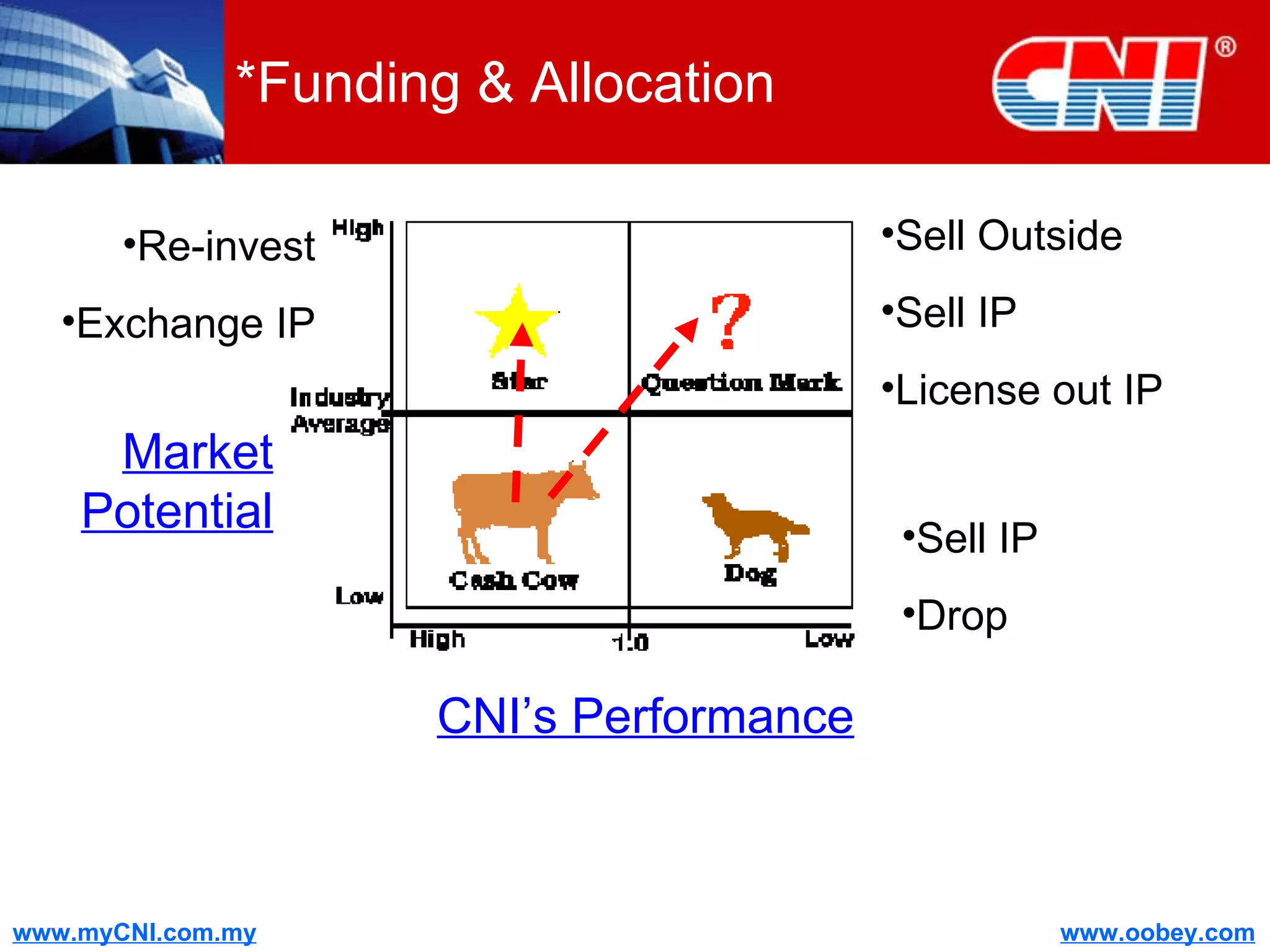
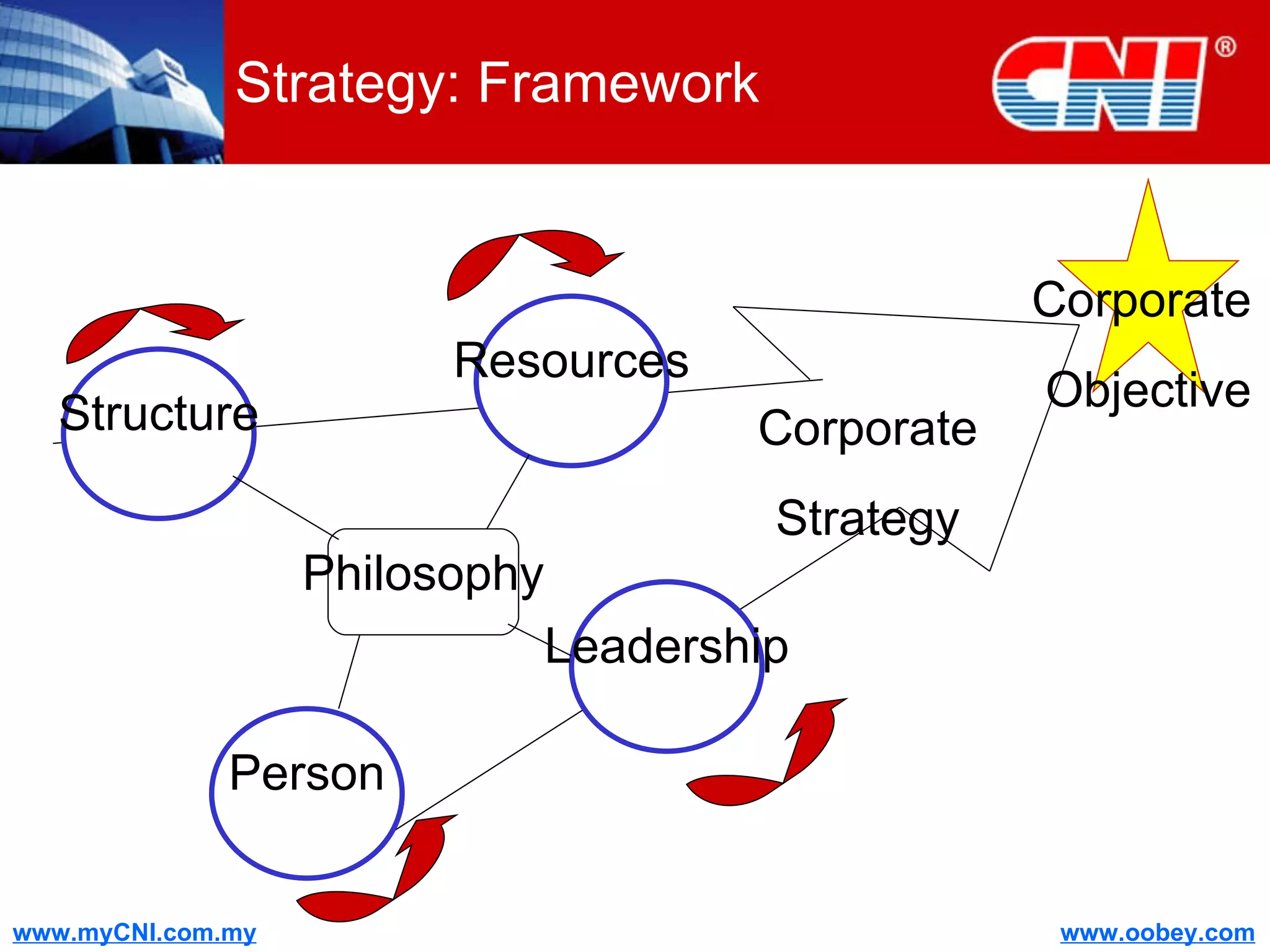
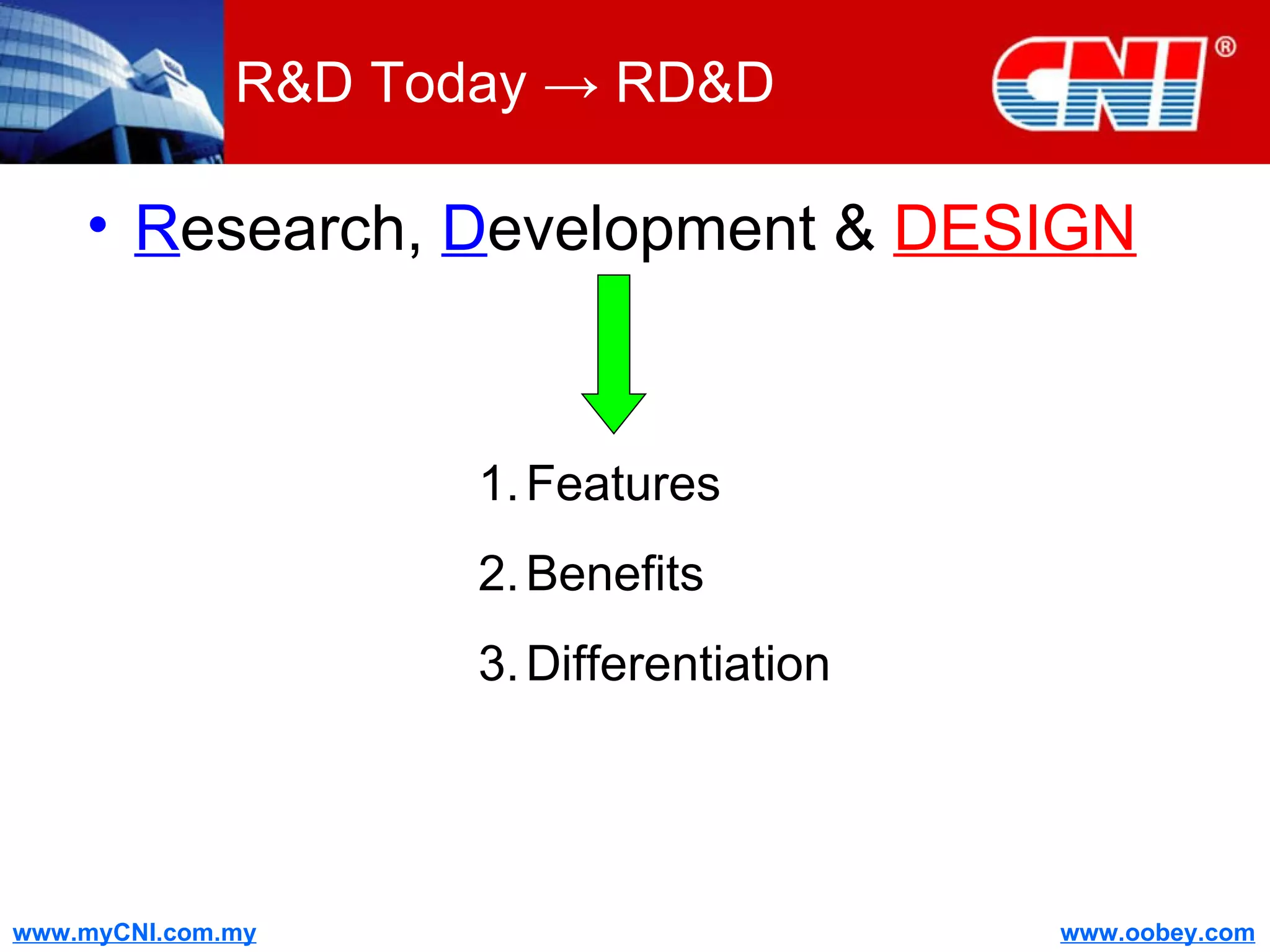
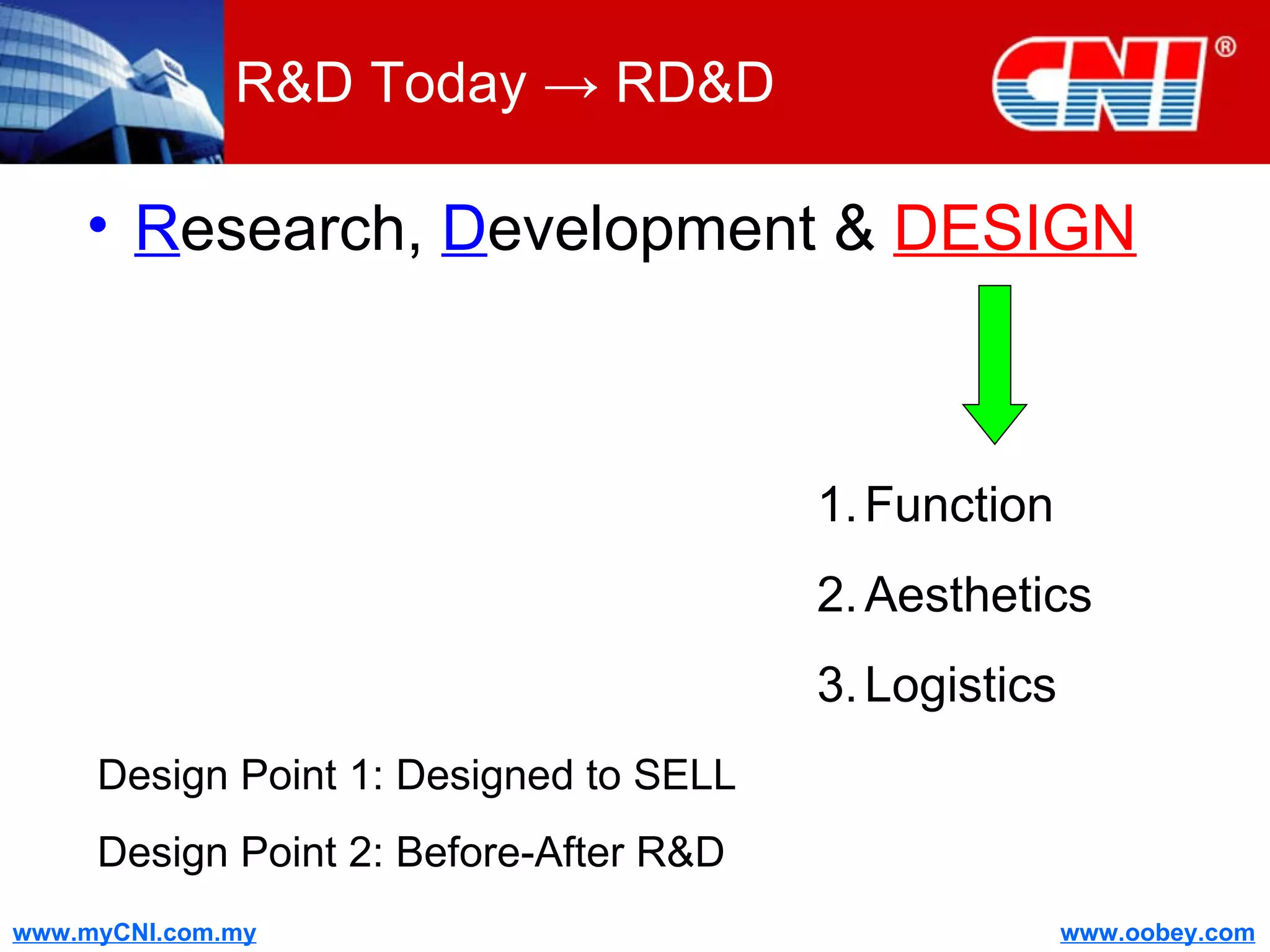
The document discusses strategies to enhance the effectiveness of research and development (R&D) in businesses, identifying common issues such as process problems and alignment challenges. It emphasizes understanding business needs, aligning R&D with marketing, and adopting customer-centric approaches to create value. Additionally, it highlights the importance of overcoming information biases and utilizing reverse marketing to adapt to changing market demands.