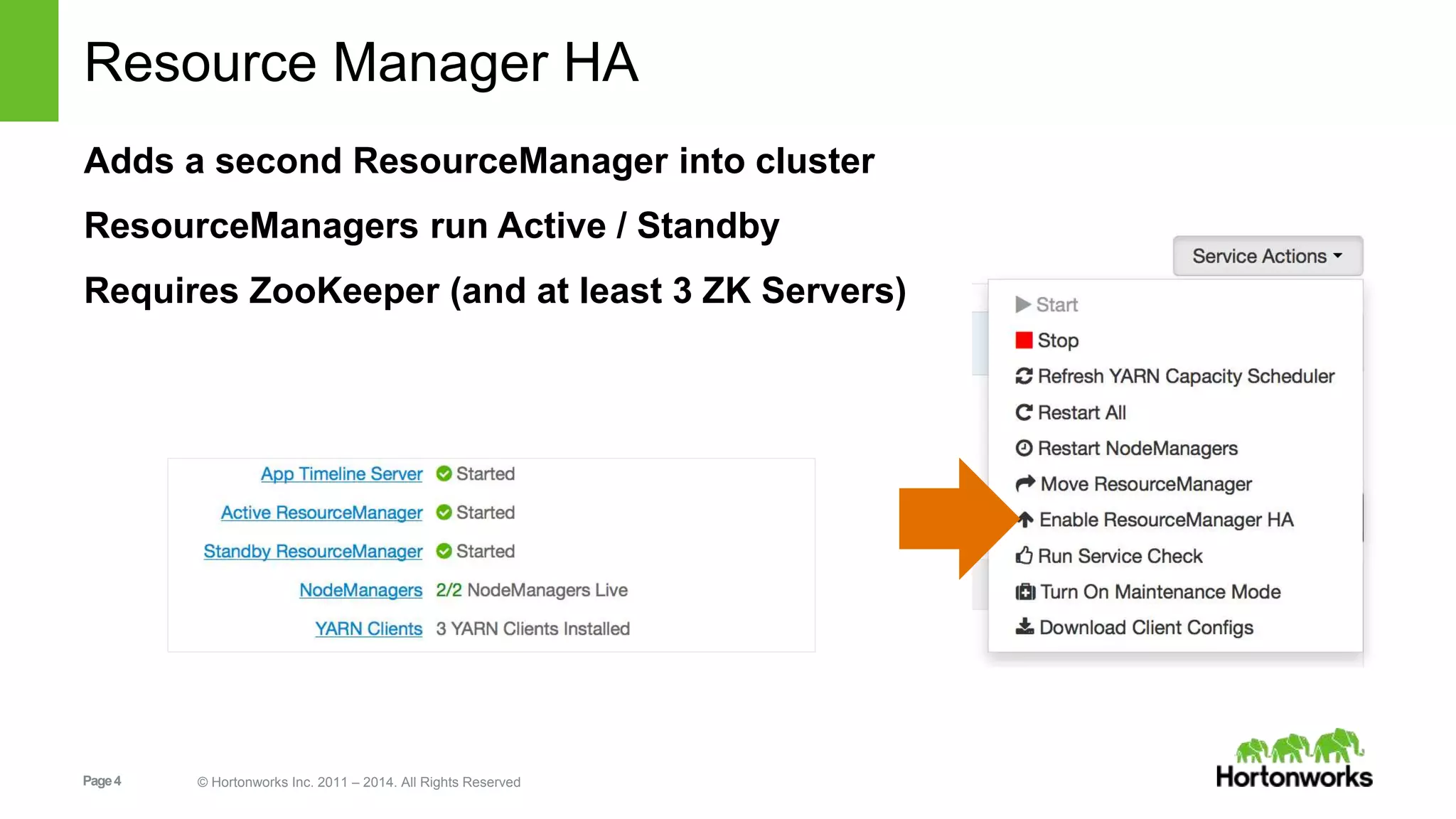
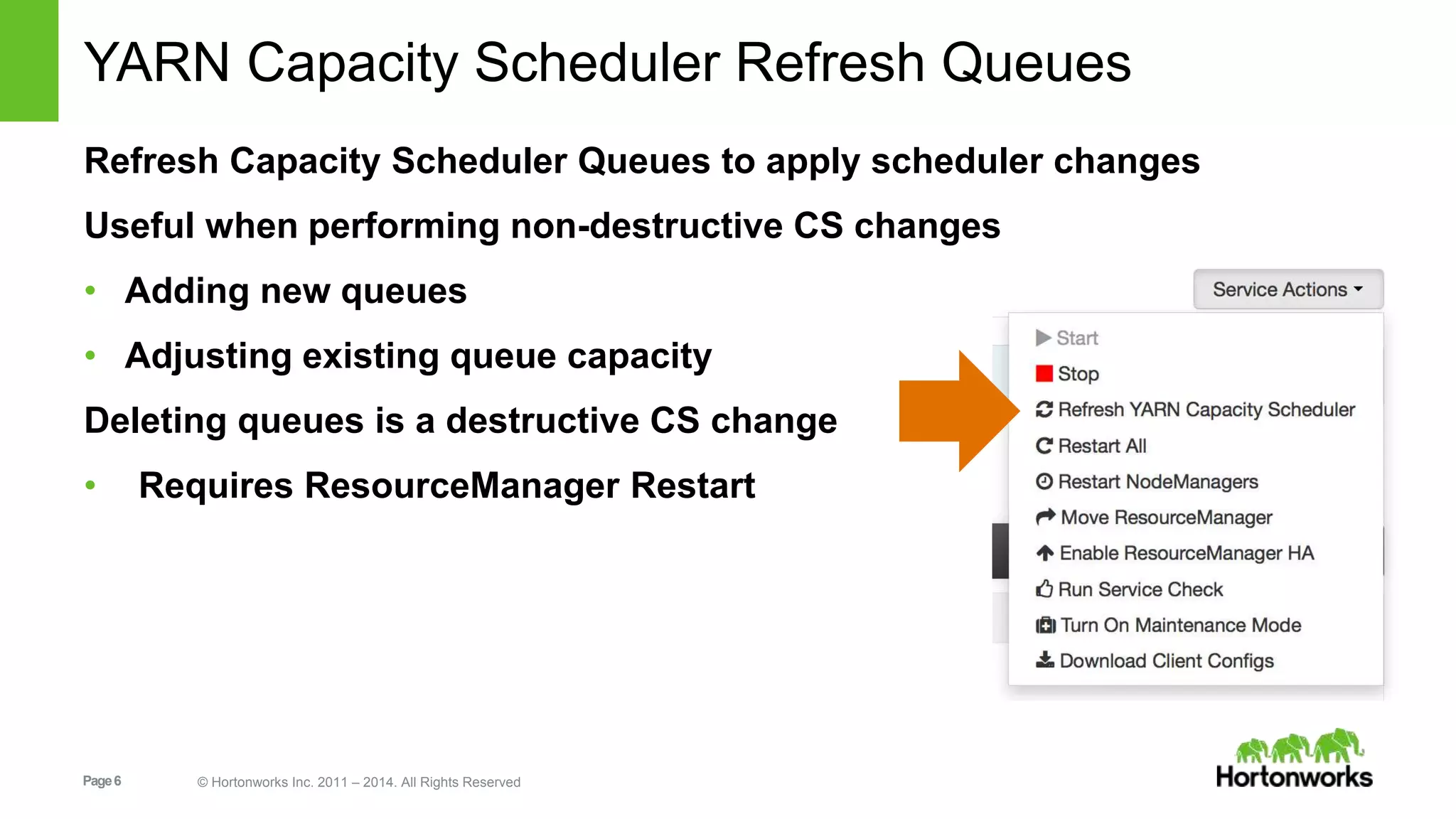
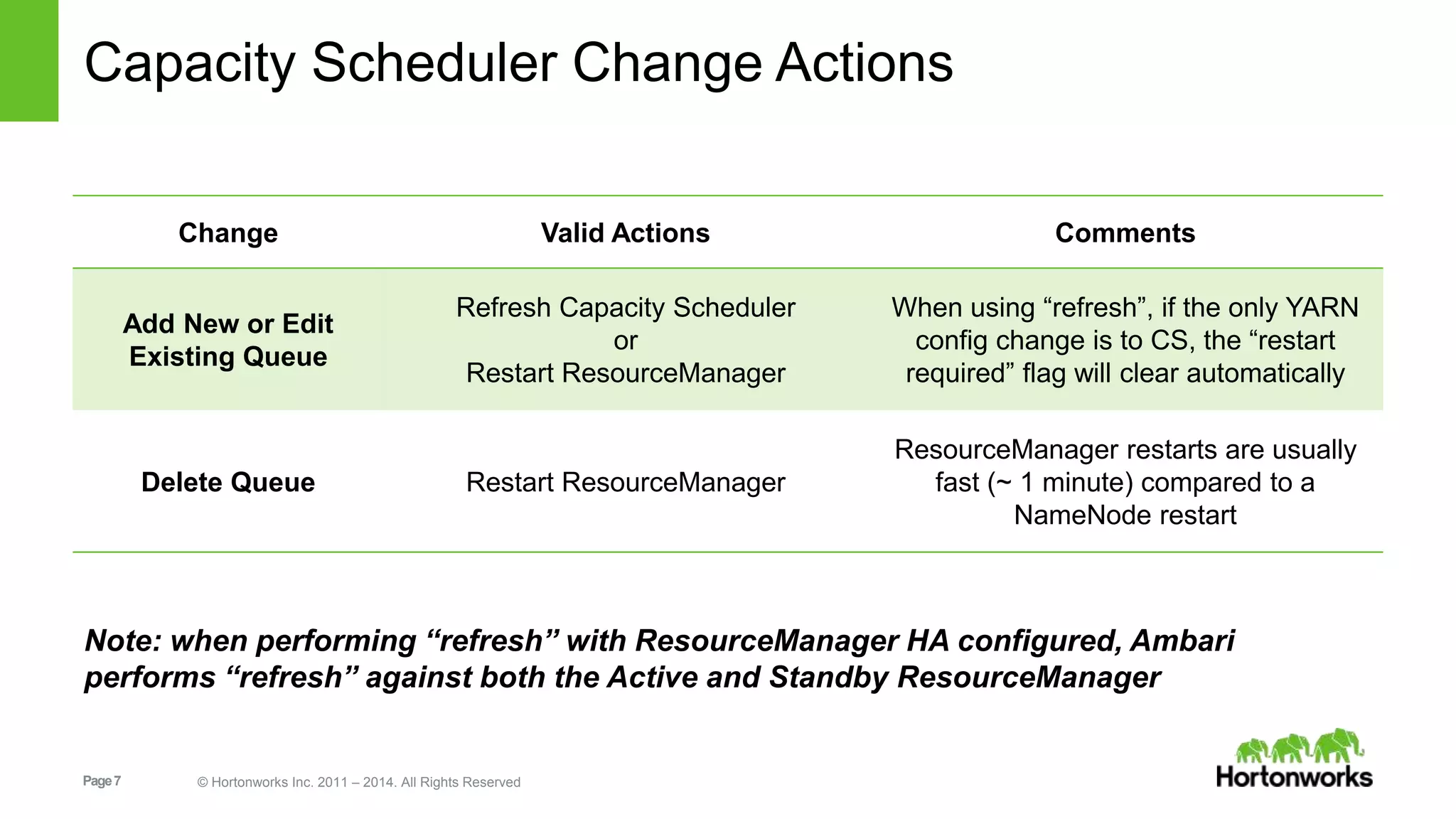
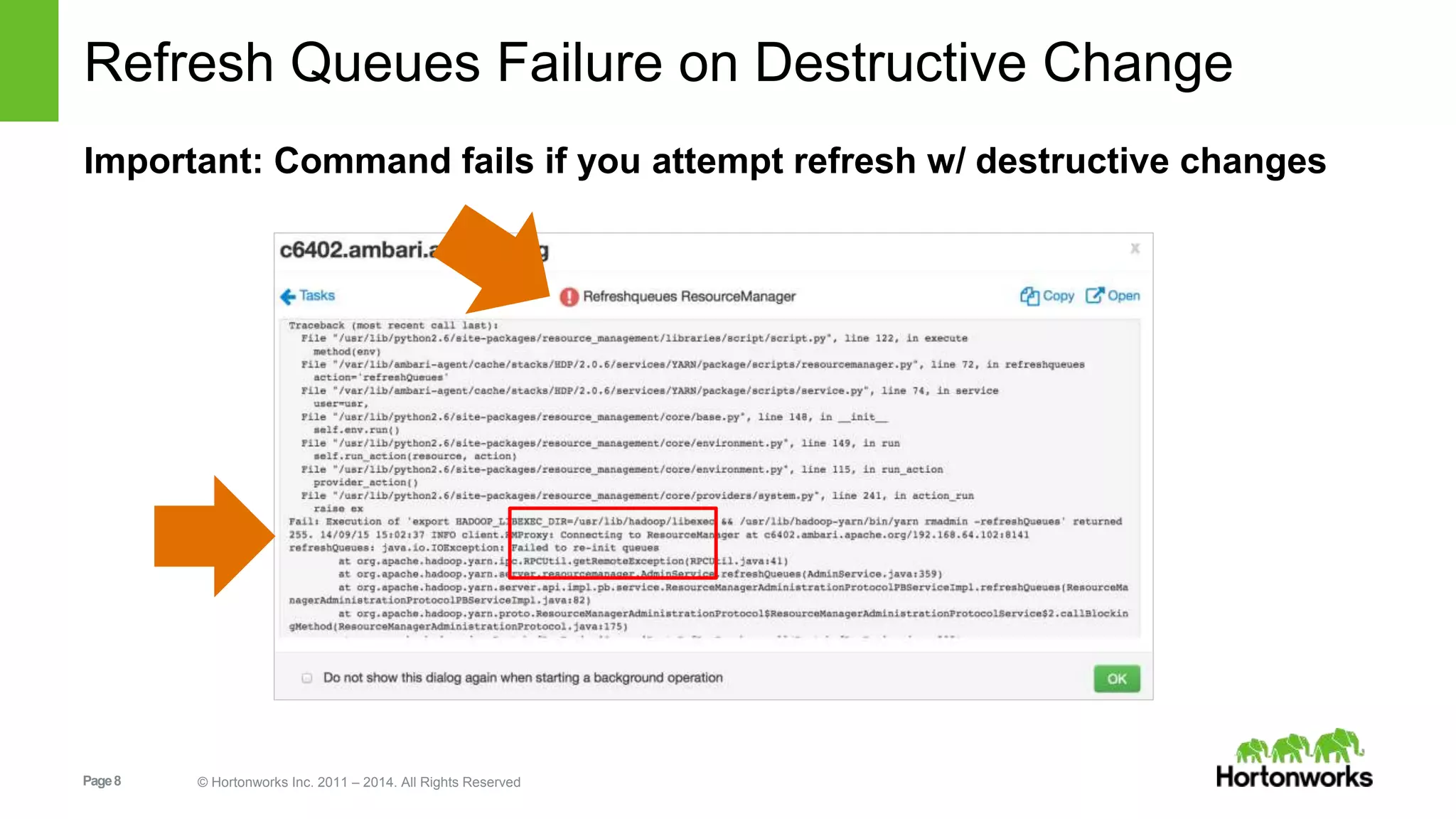
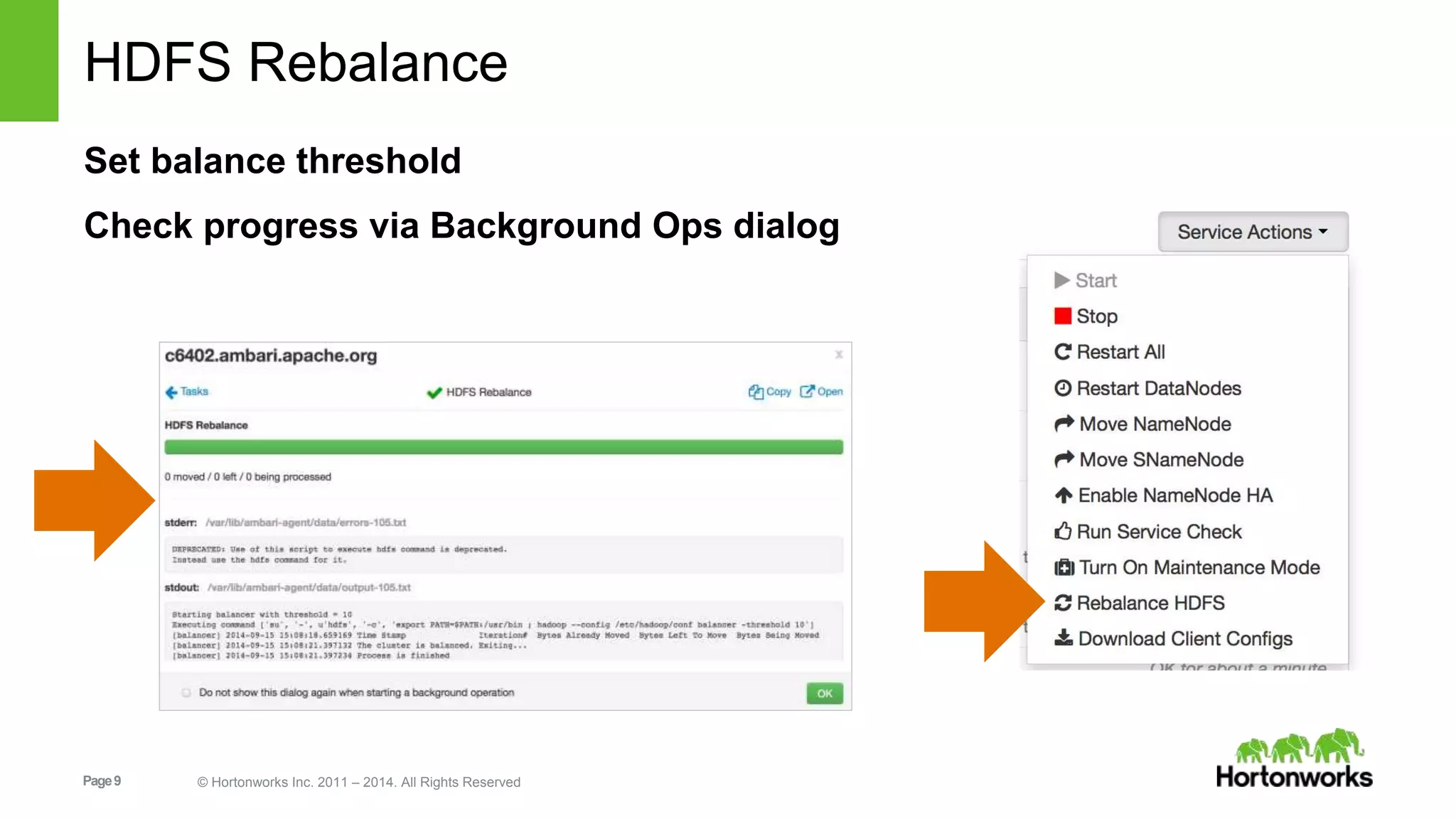
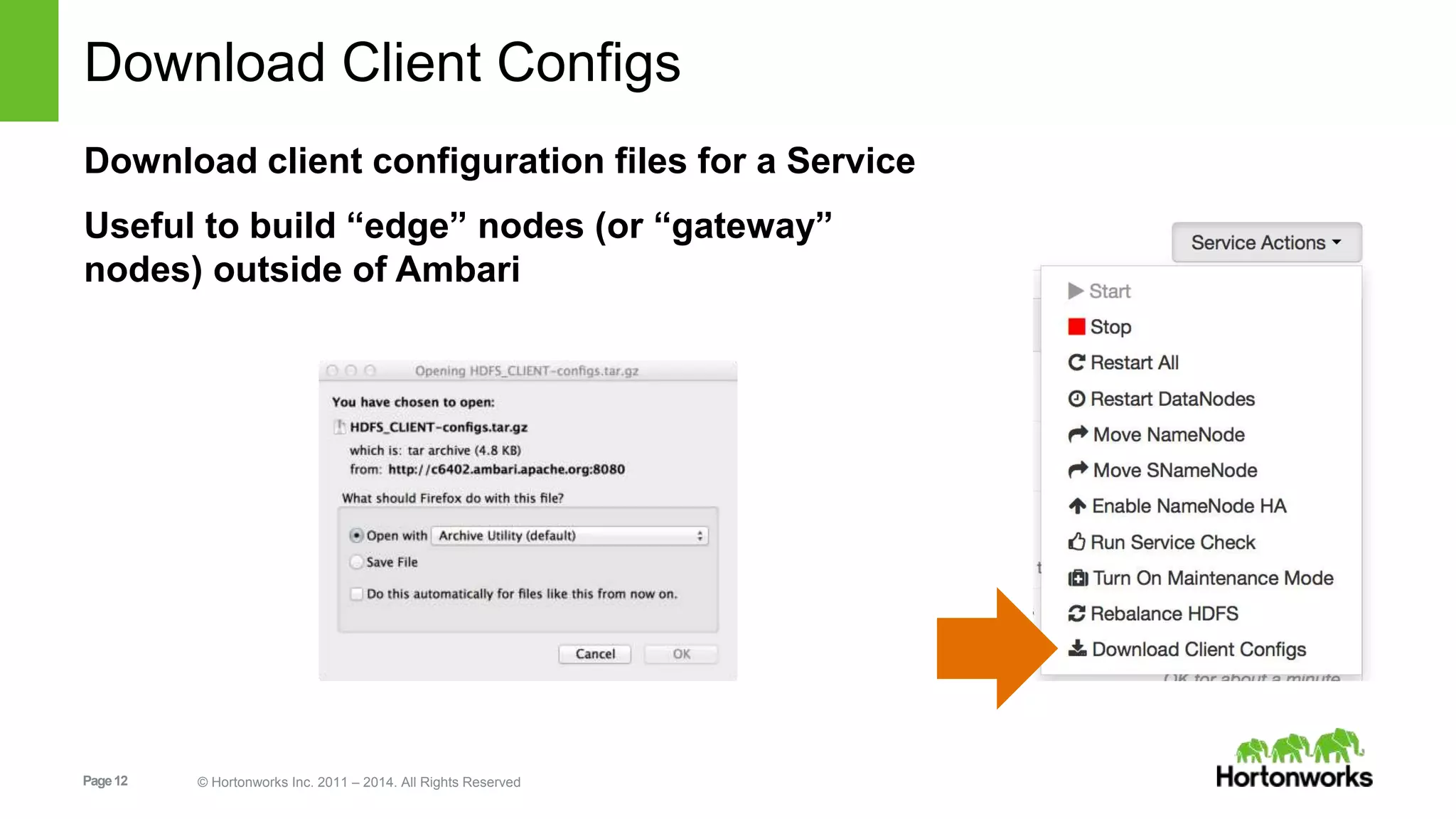
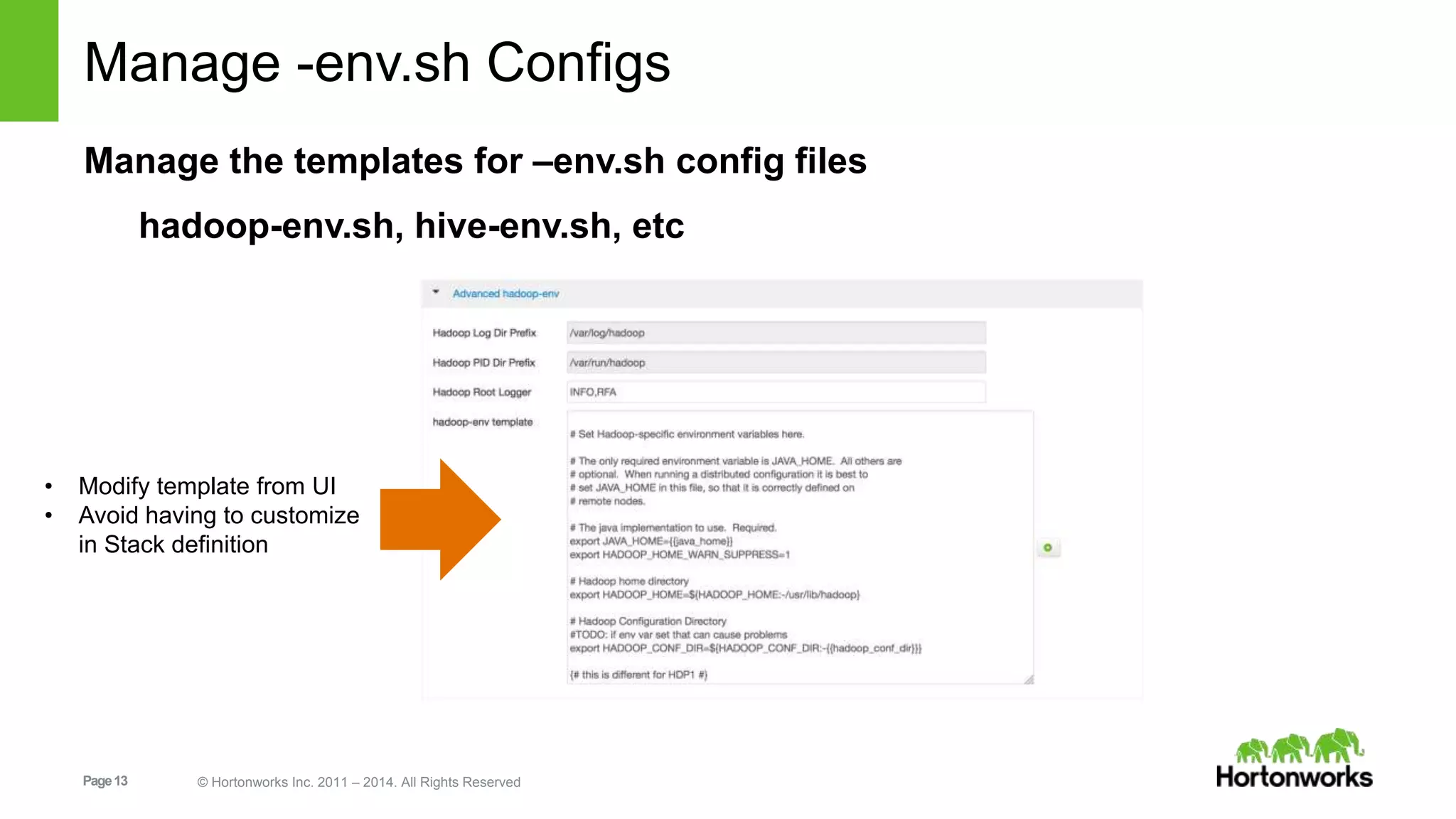
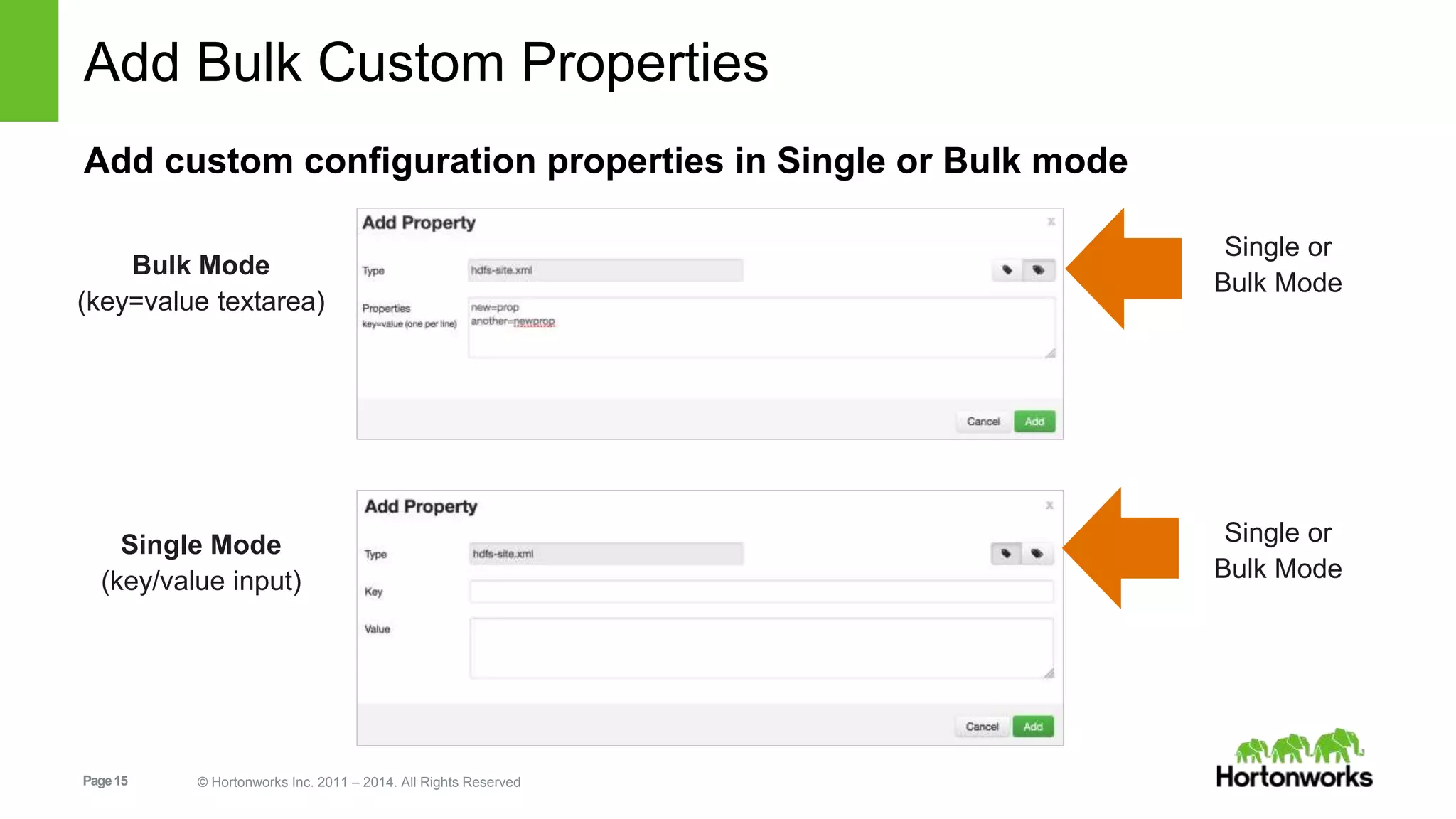
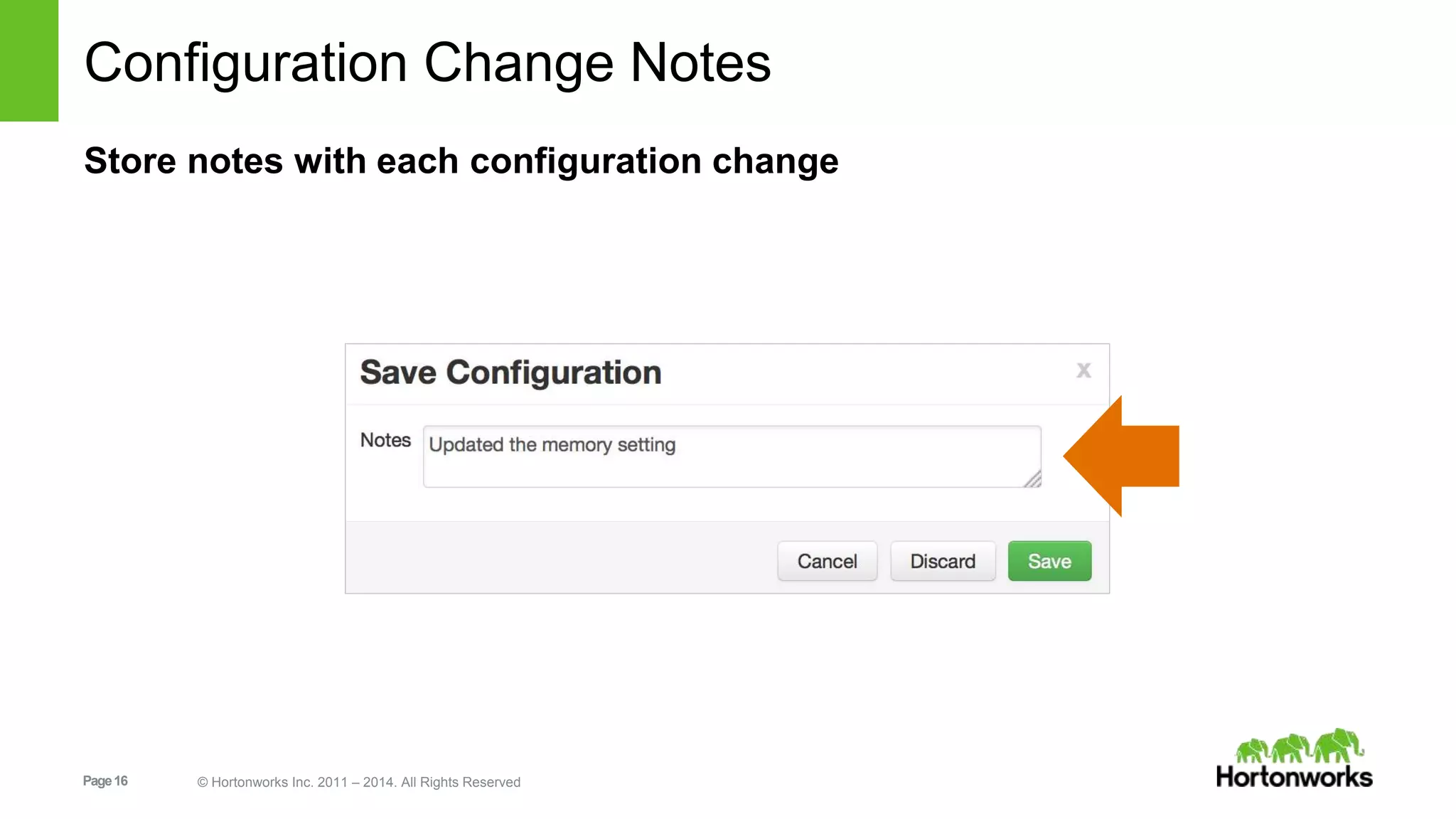
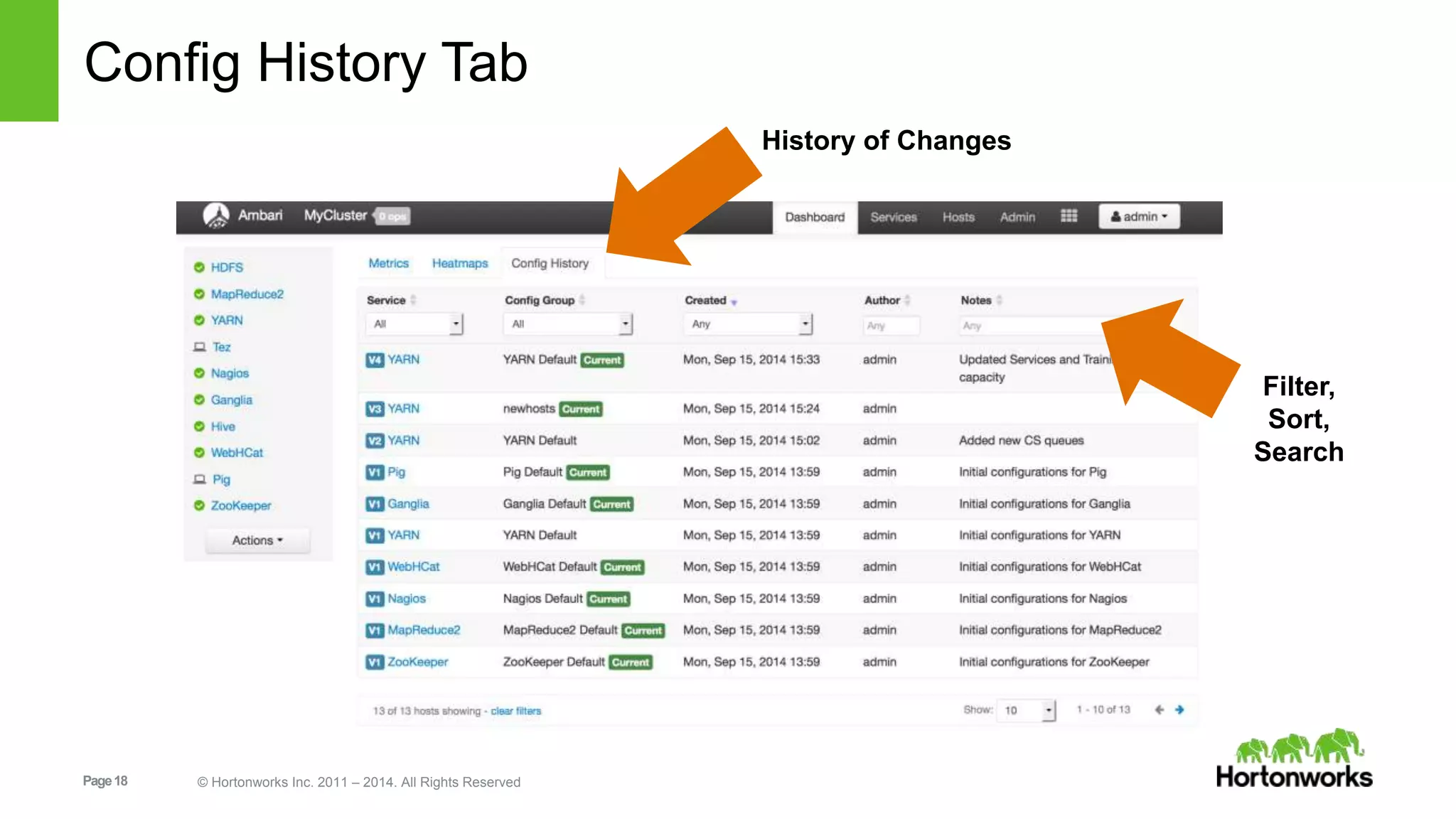
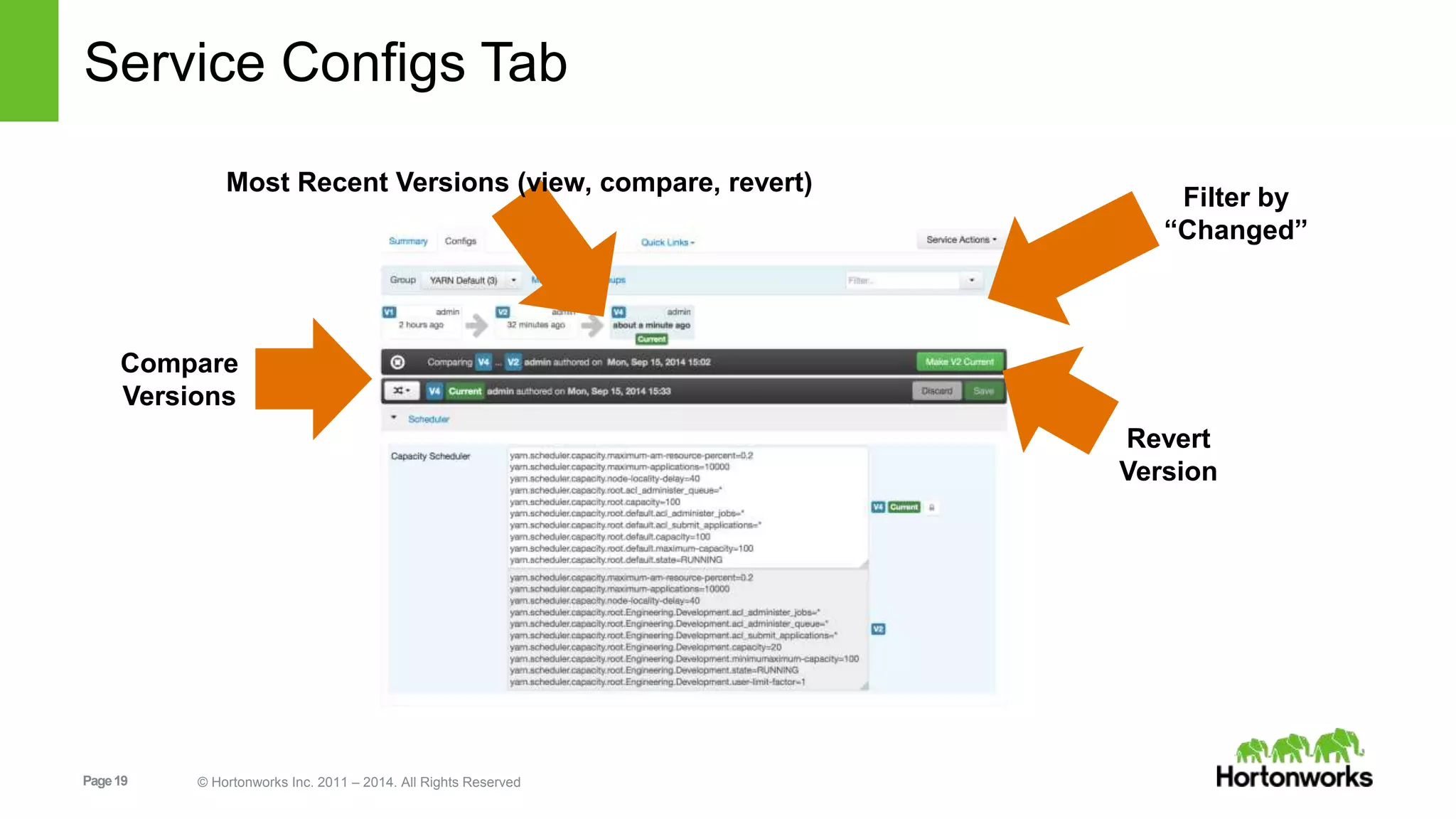
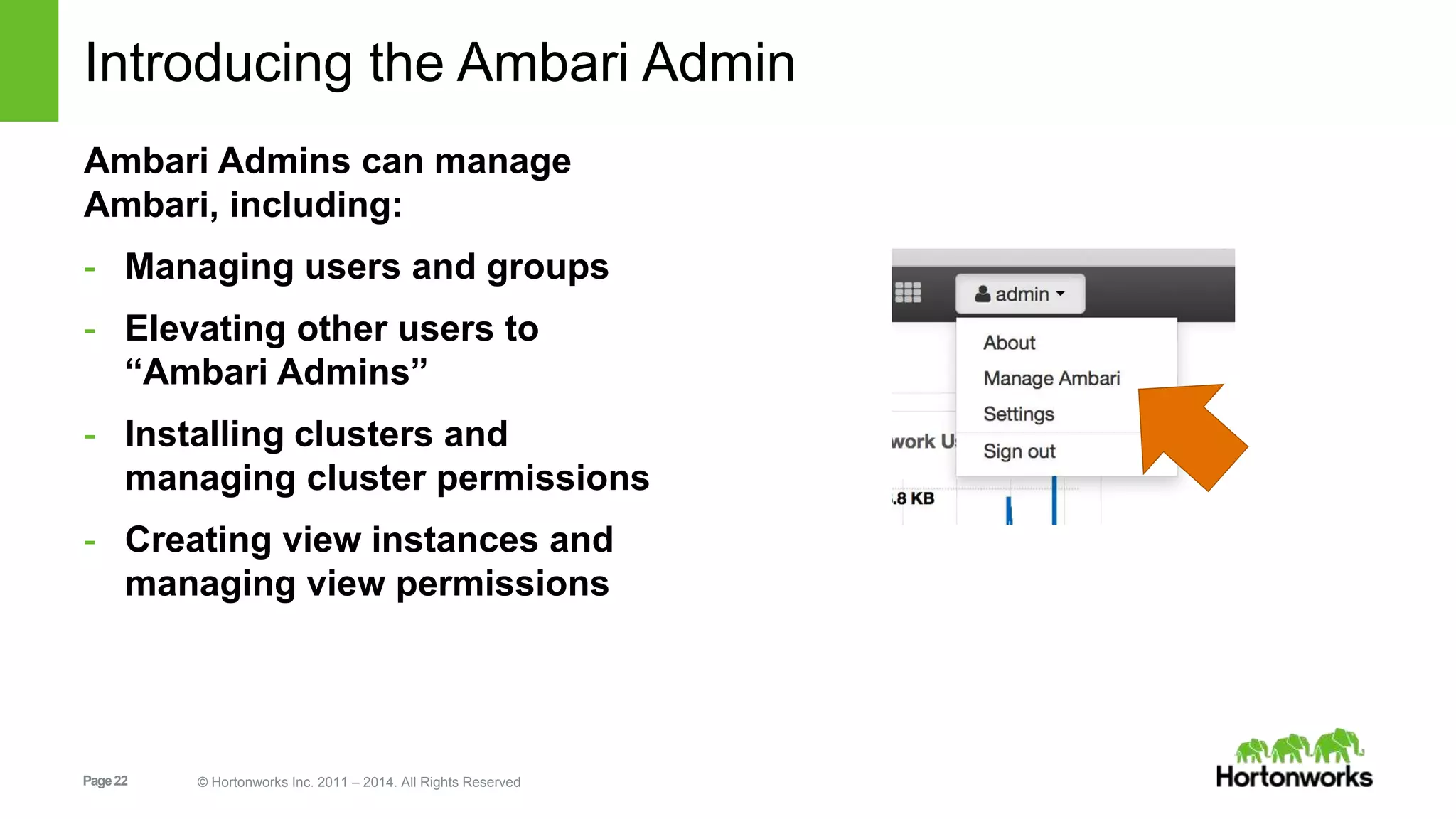
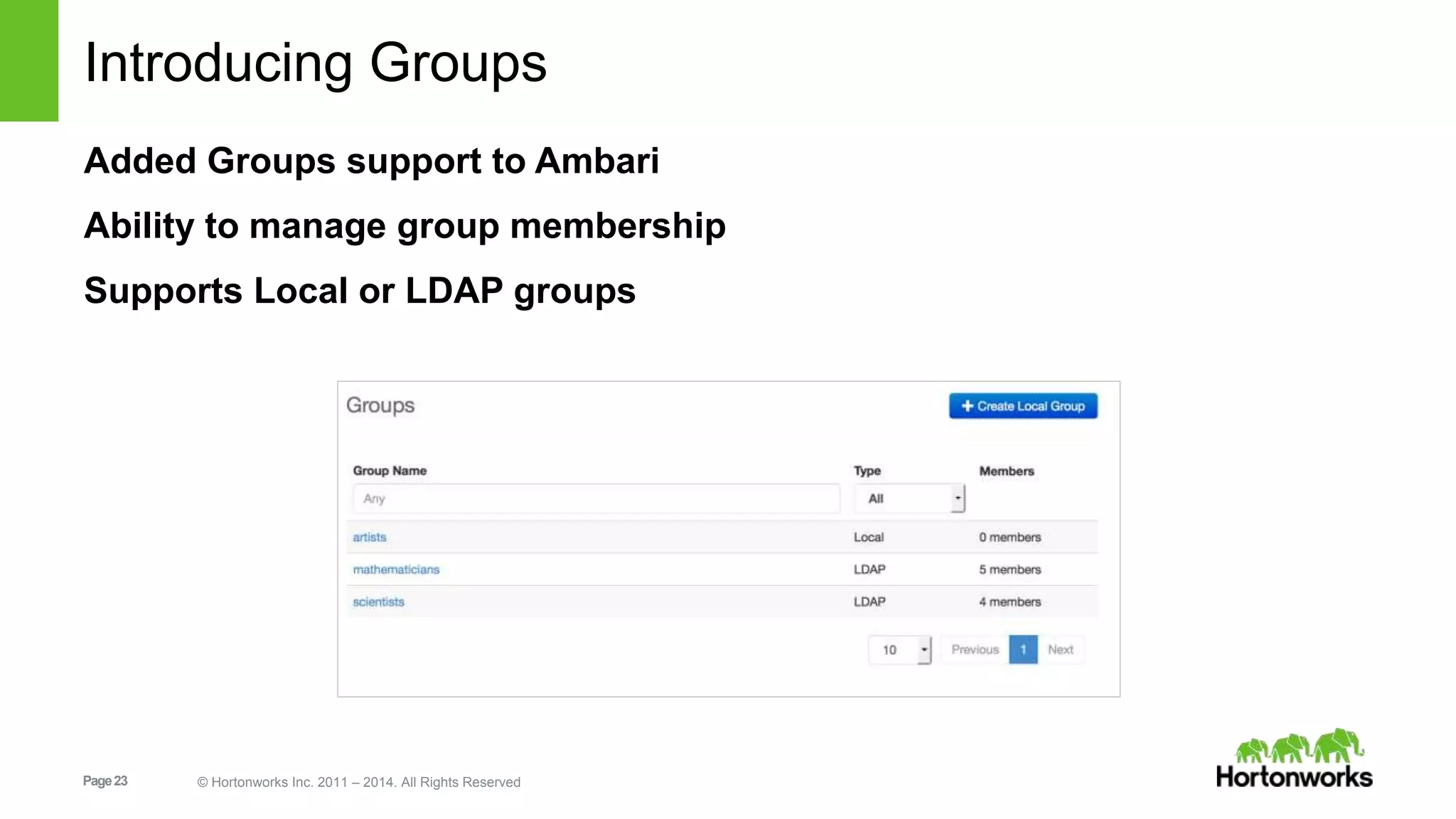
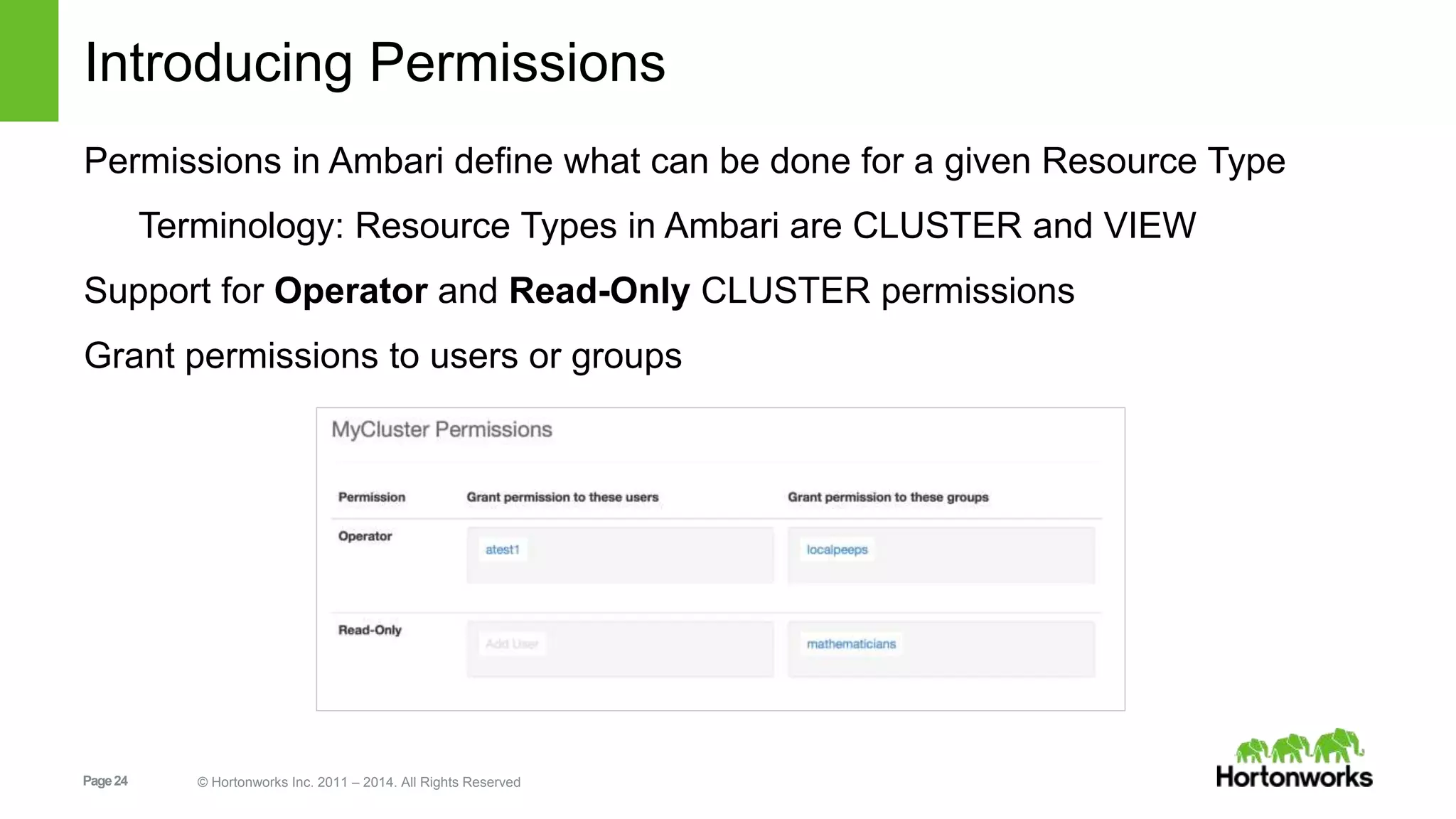
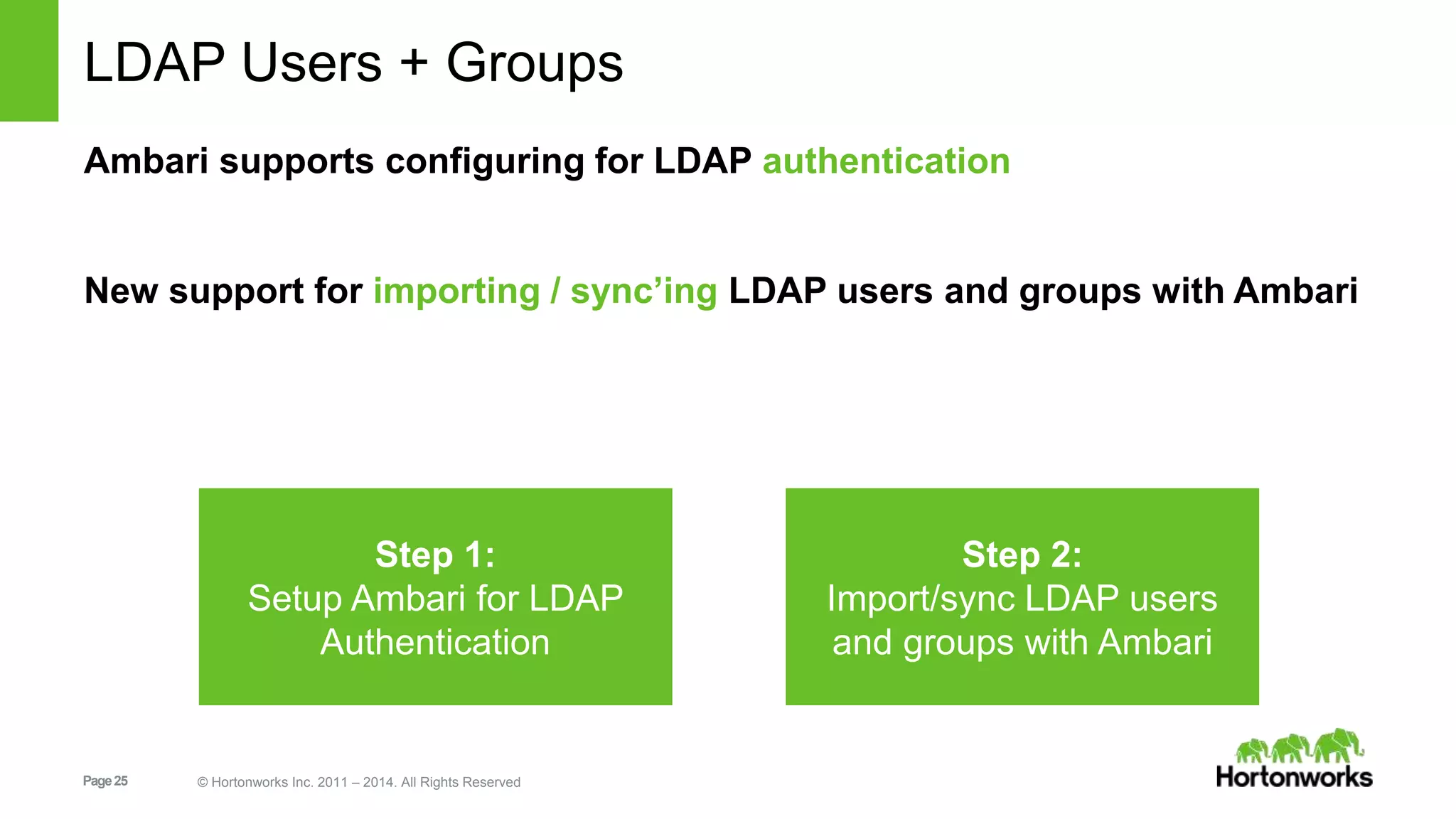
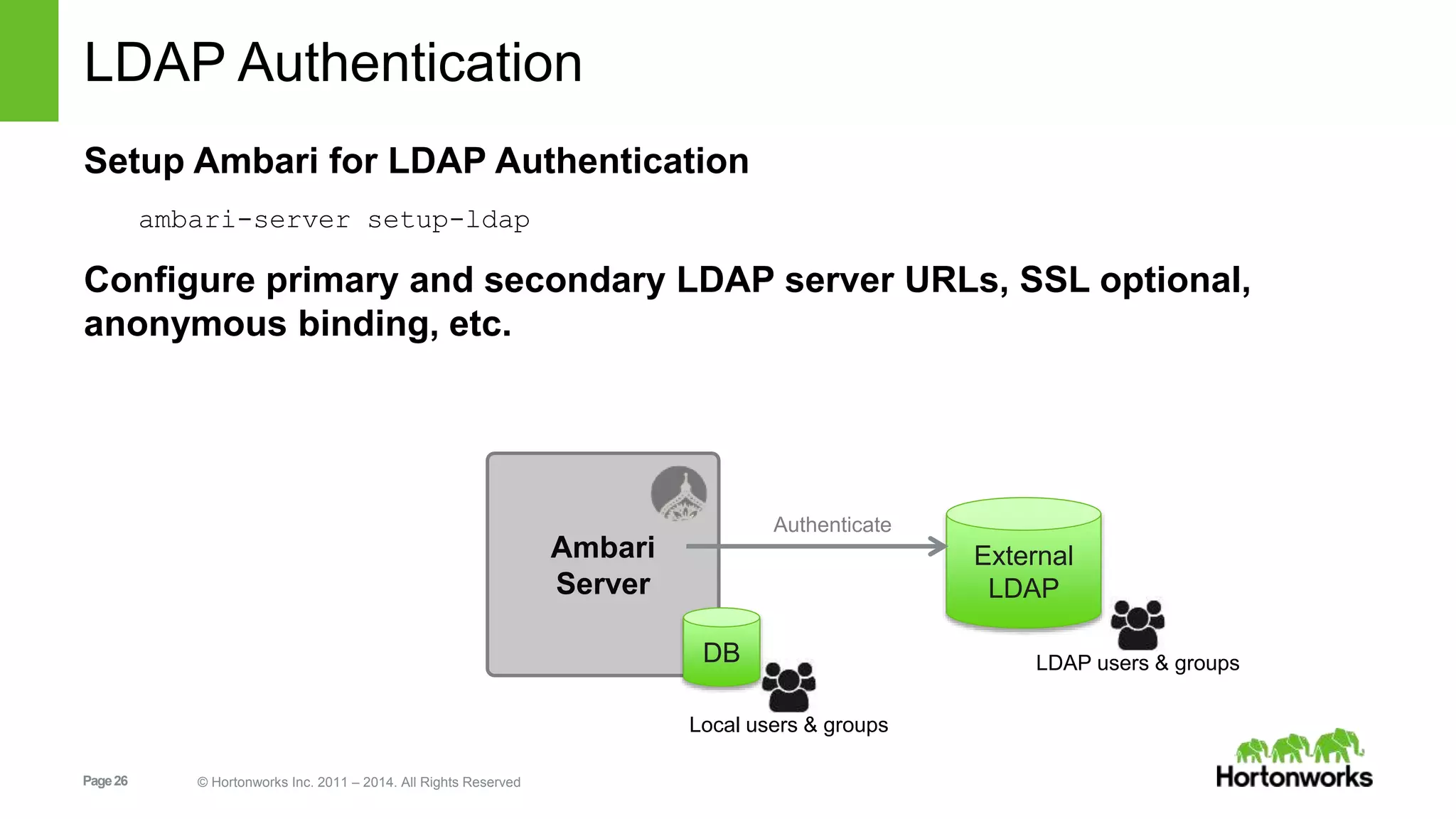
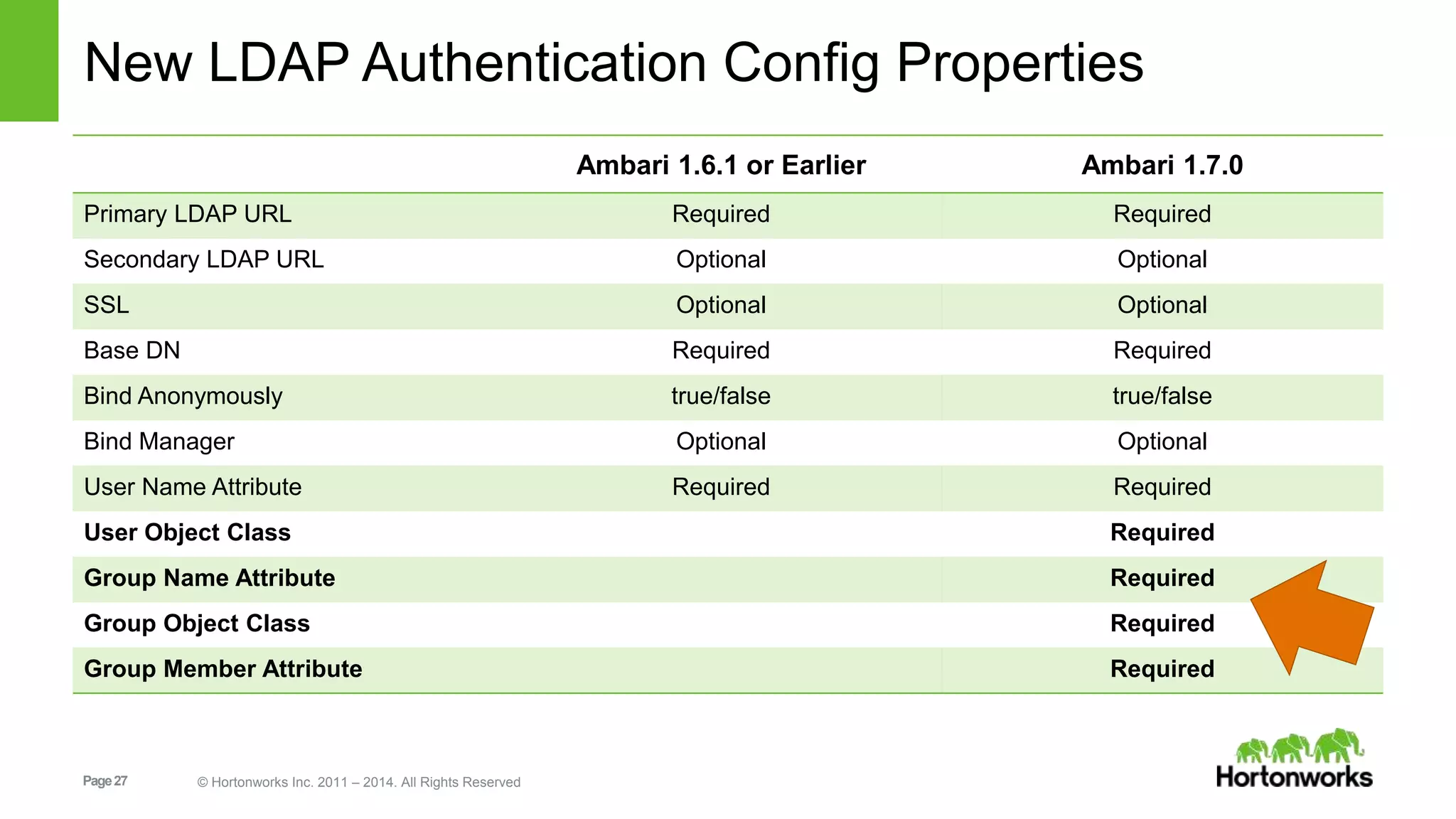
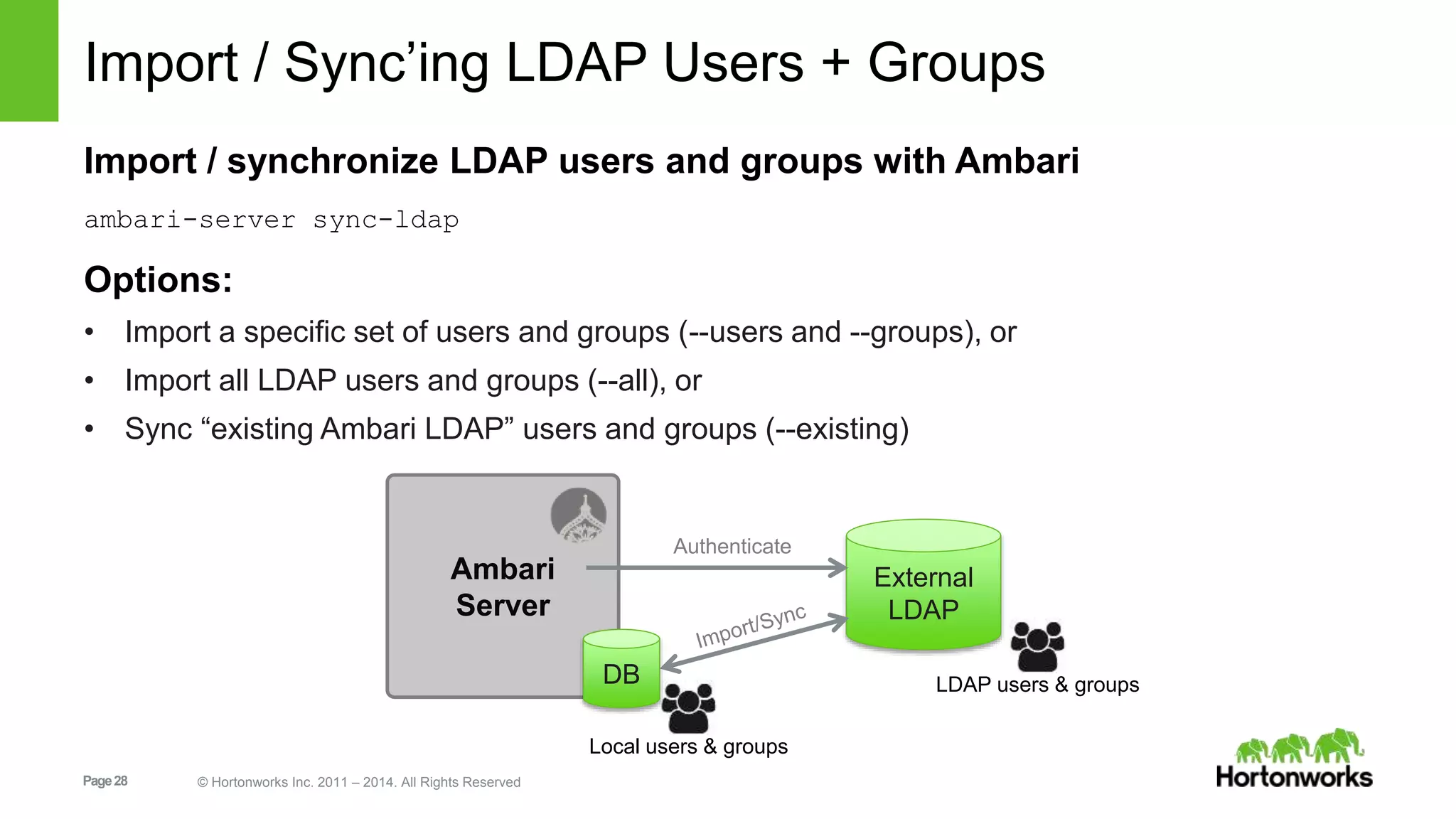
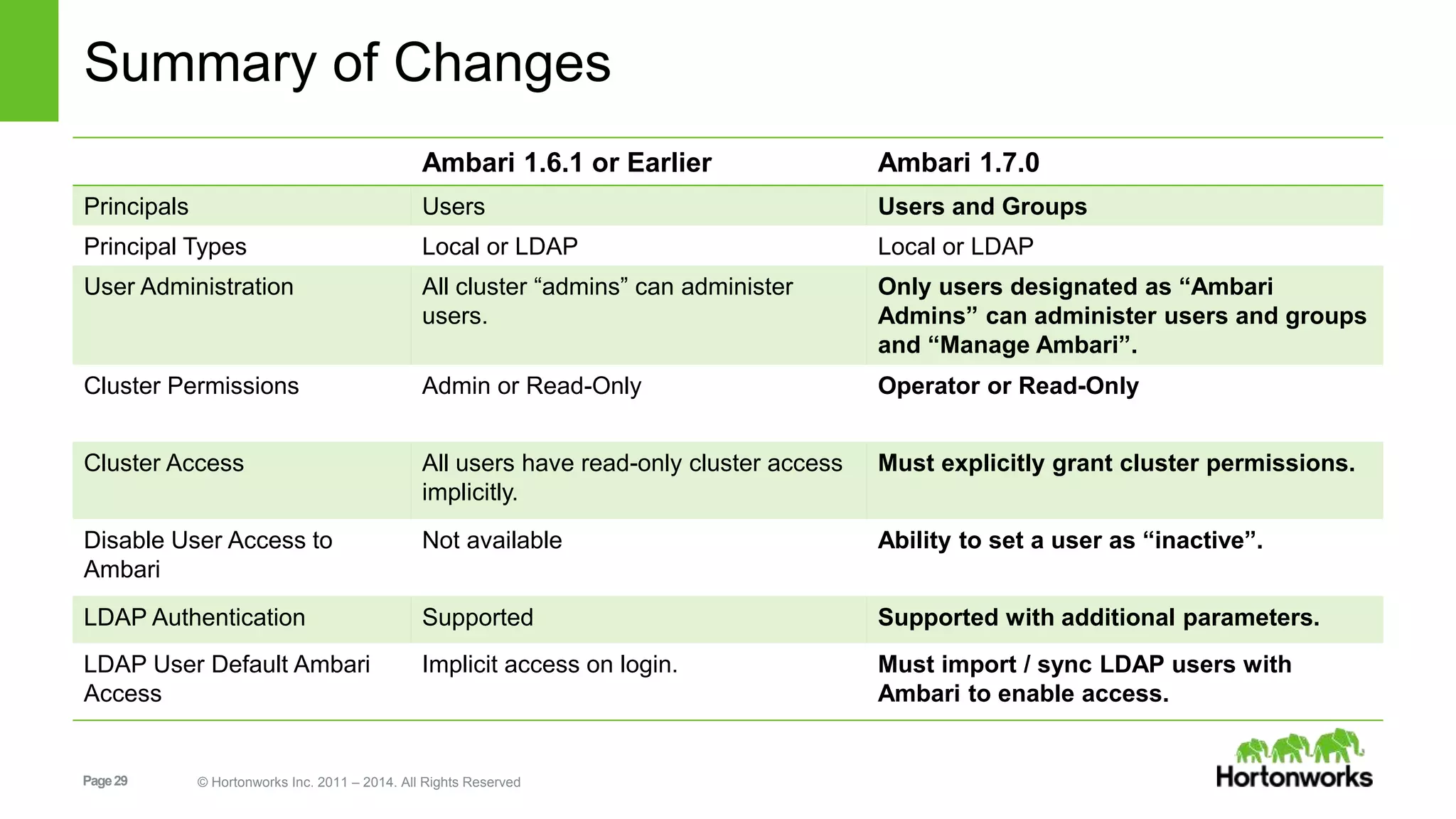
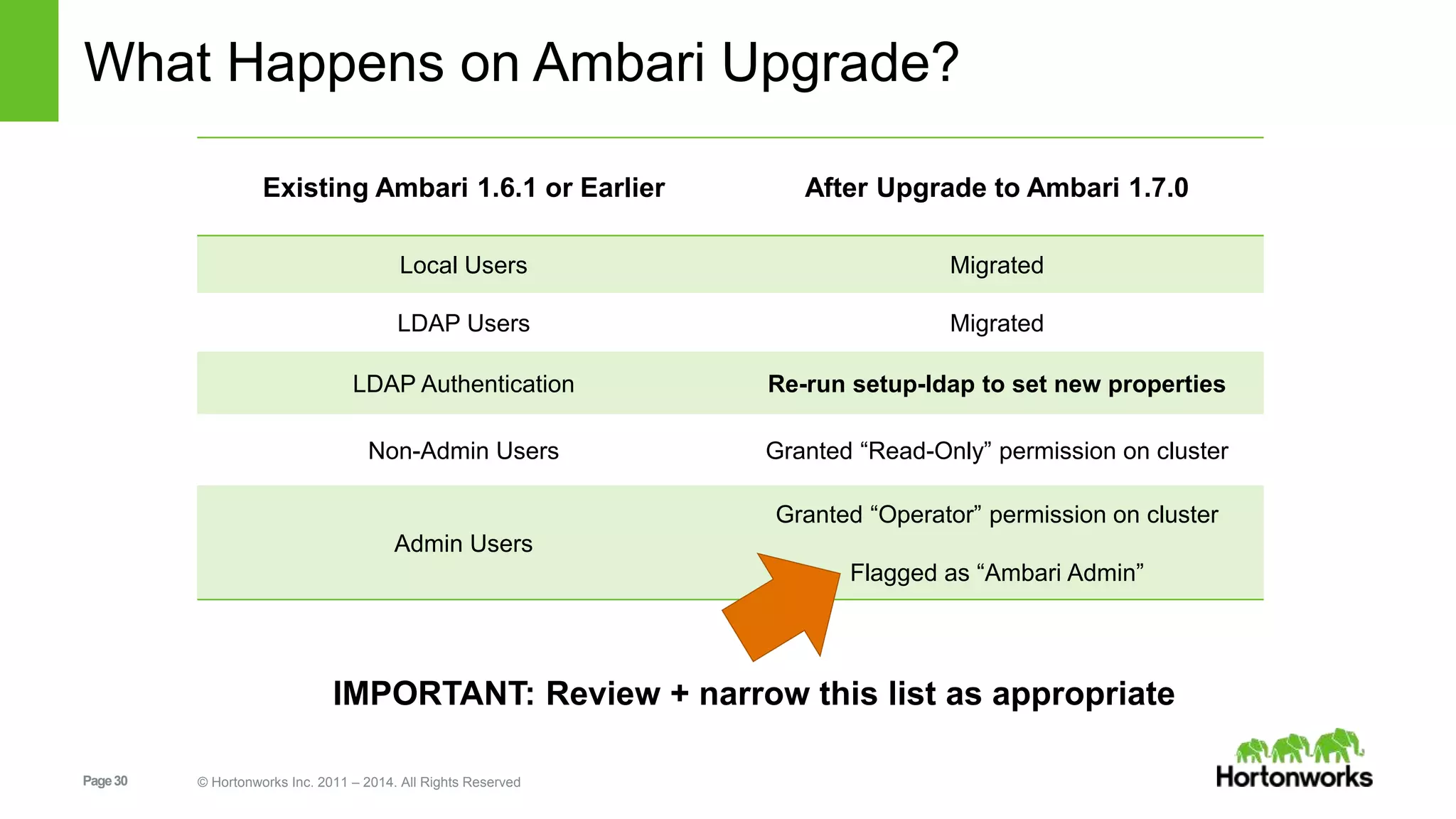
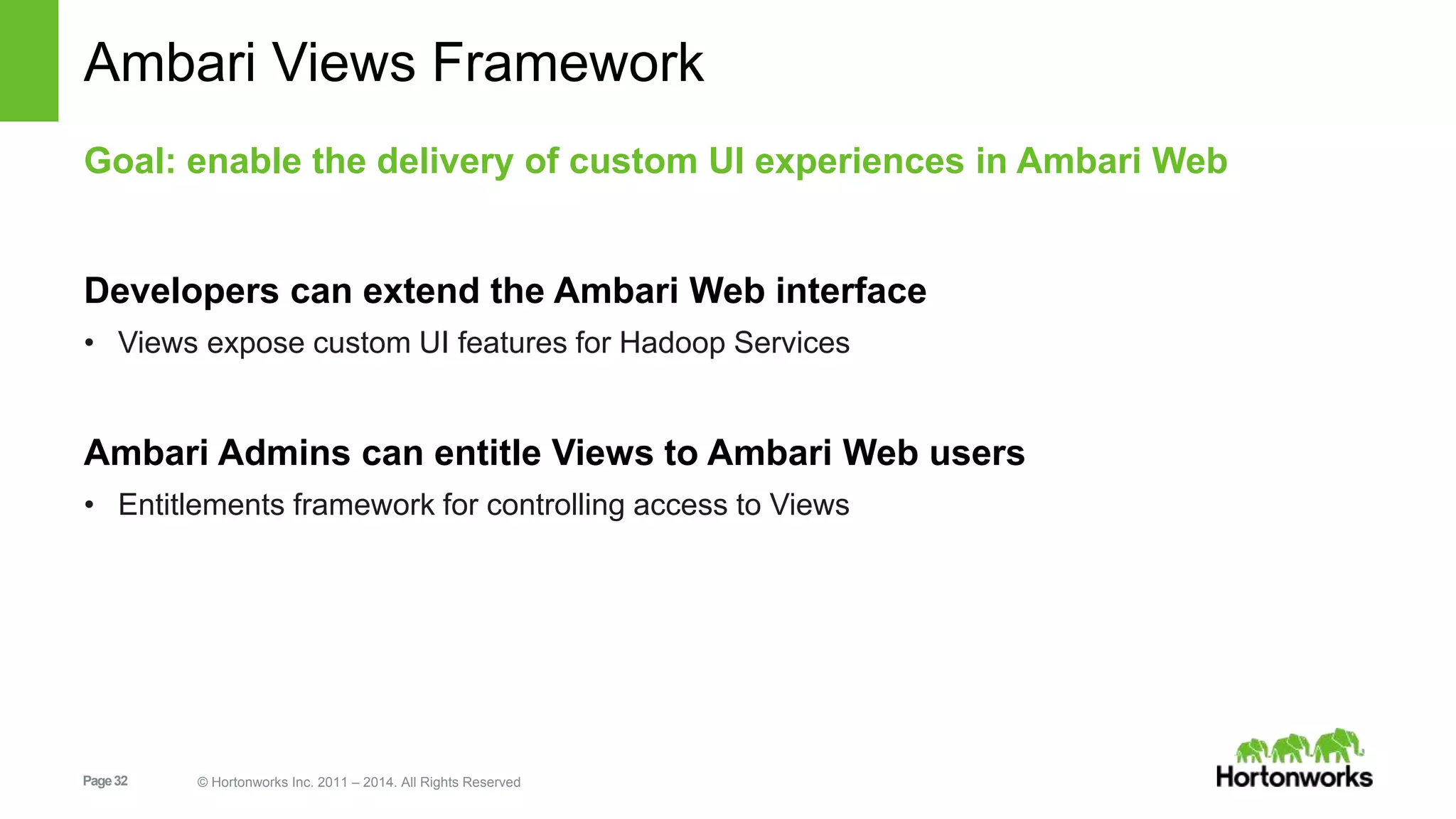
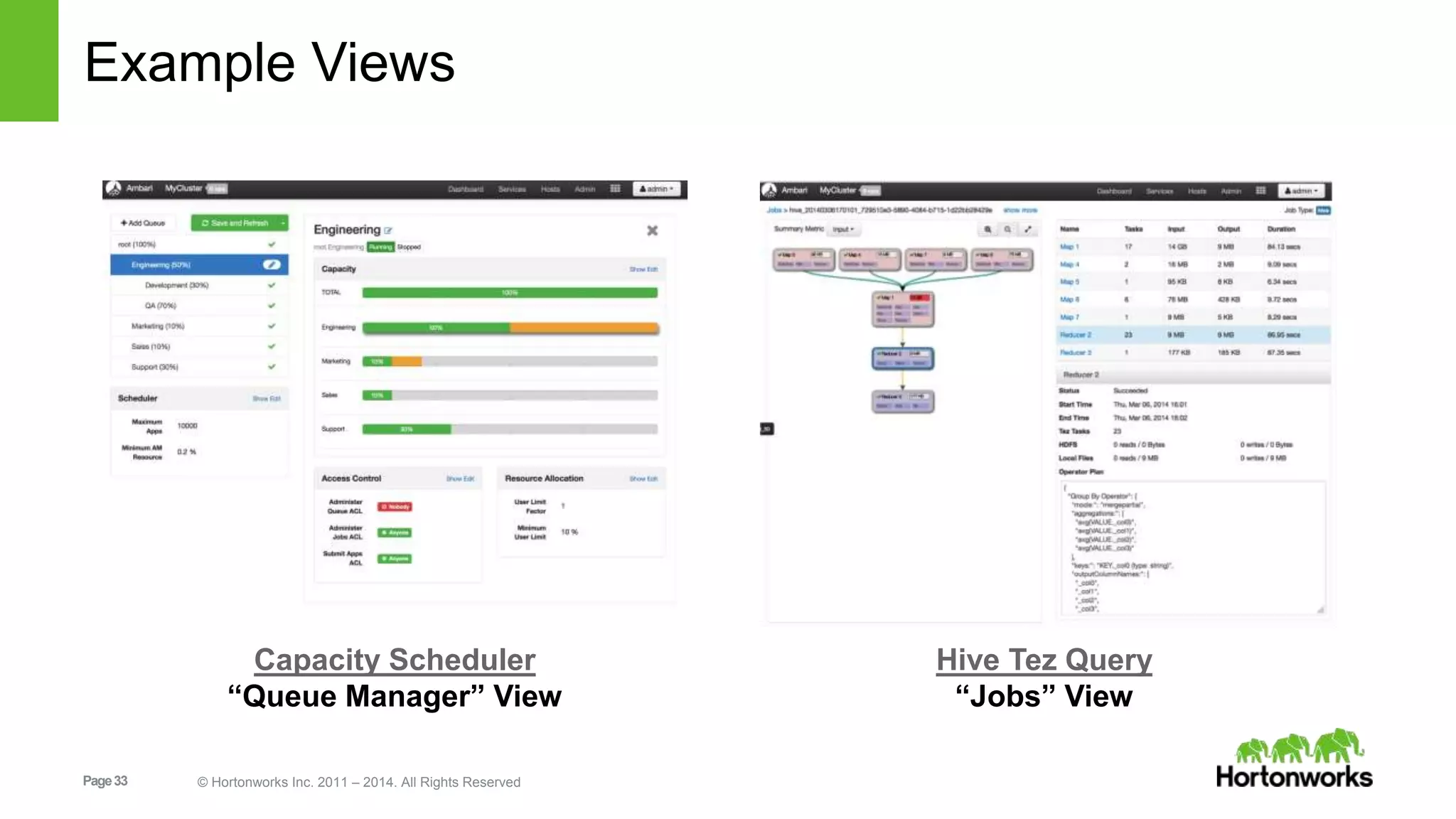
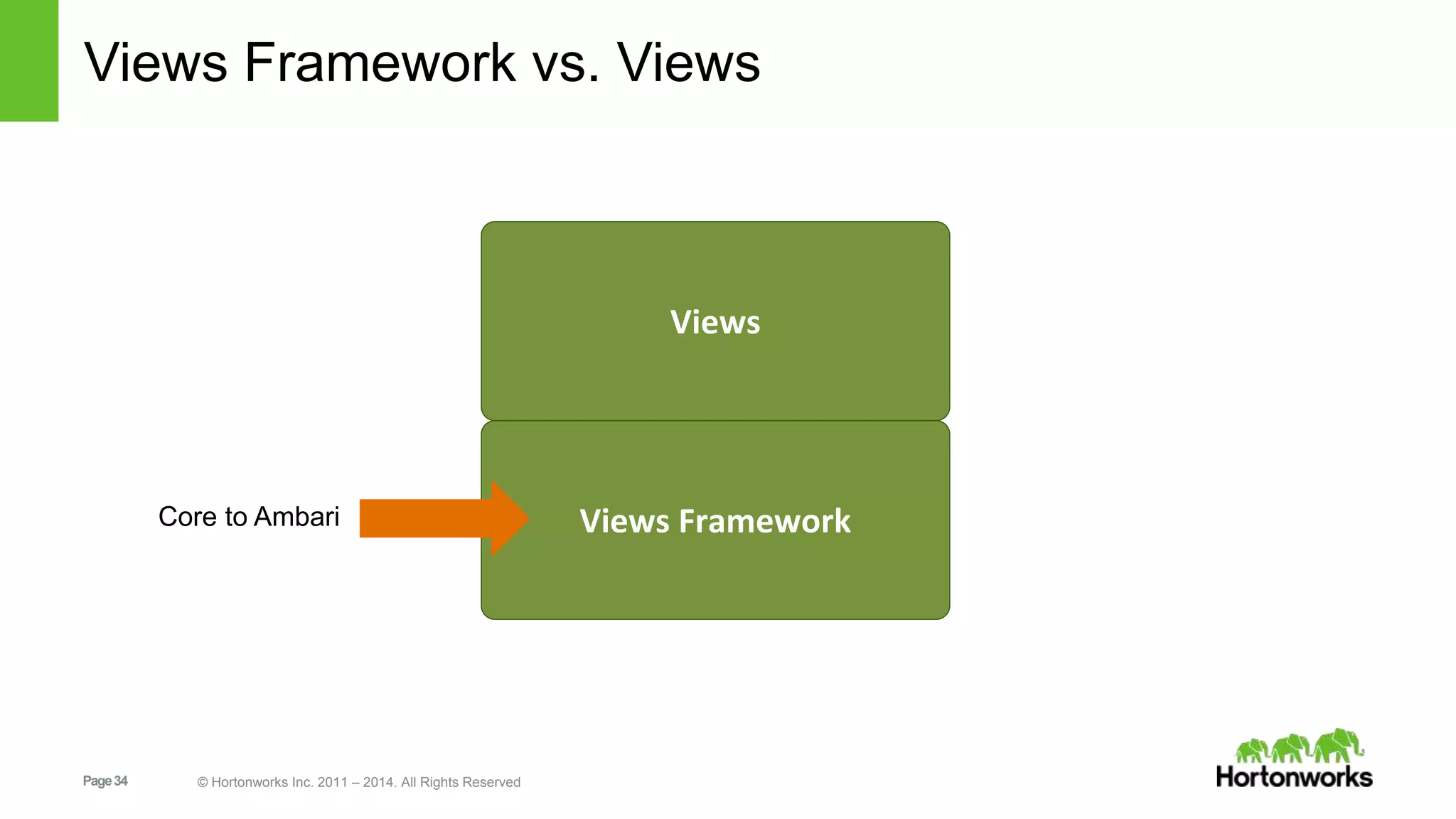
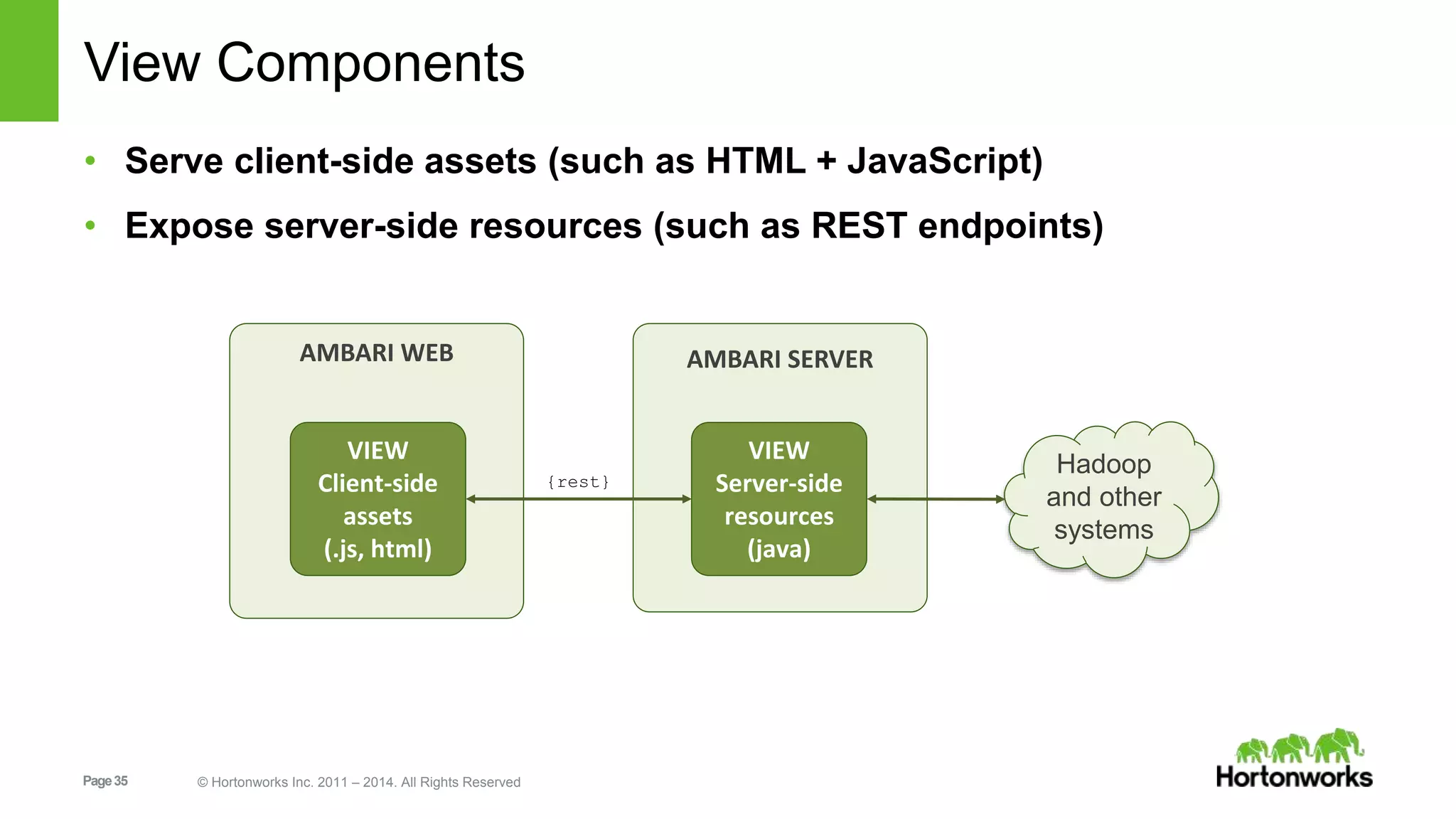
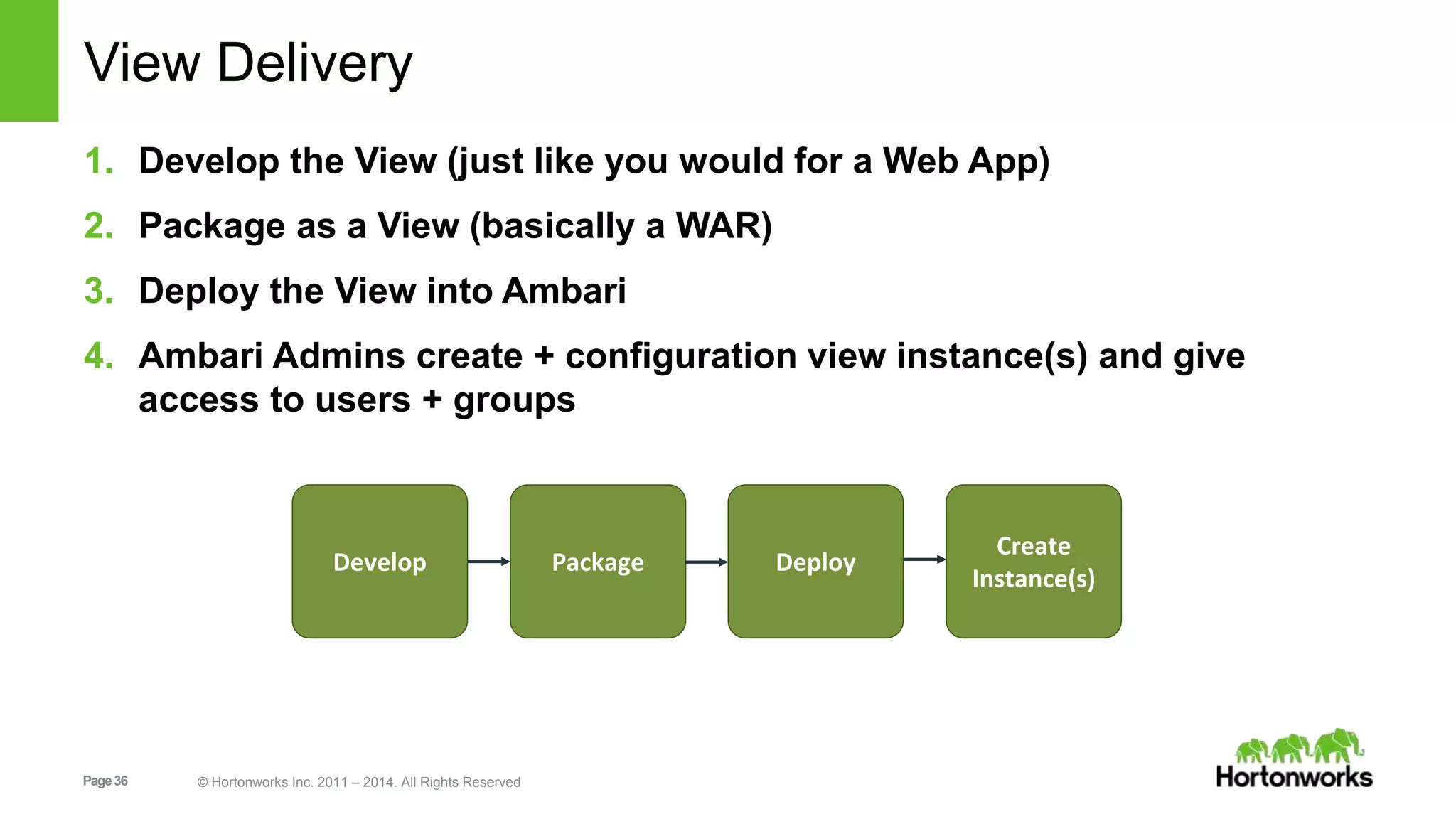
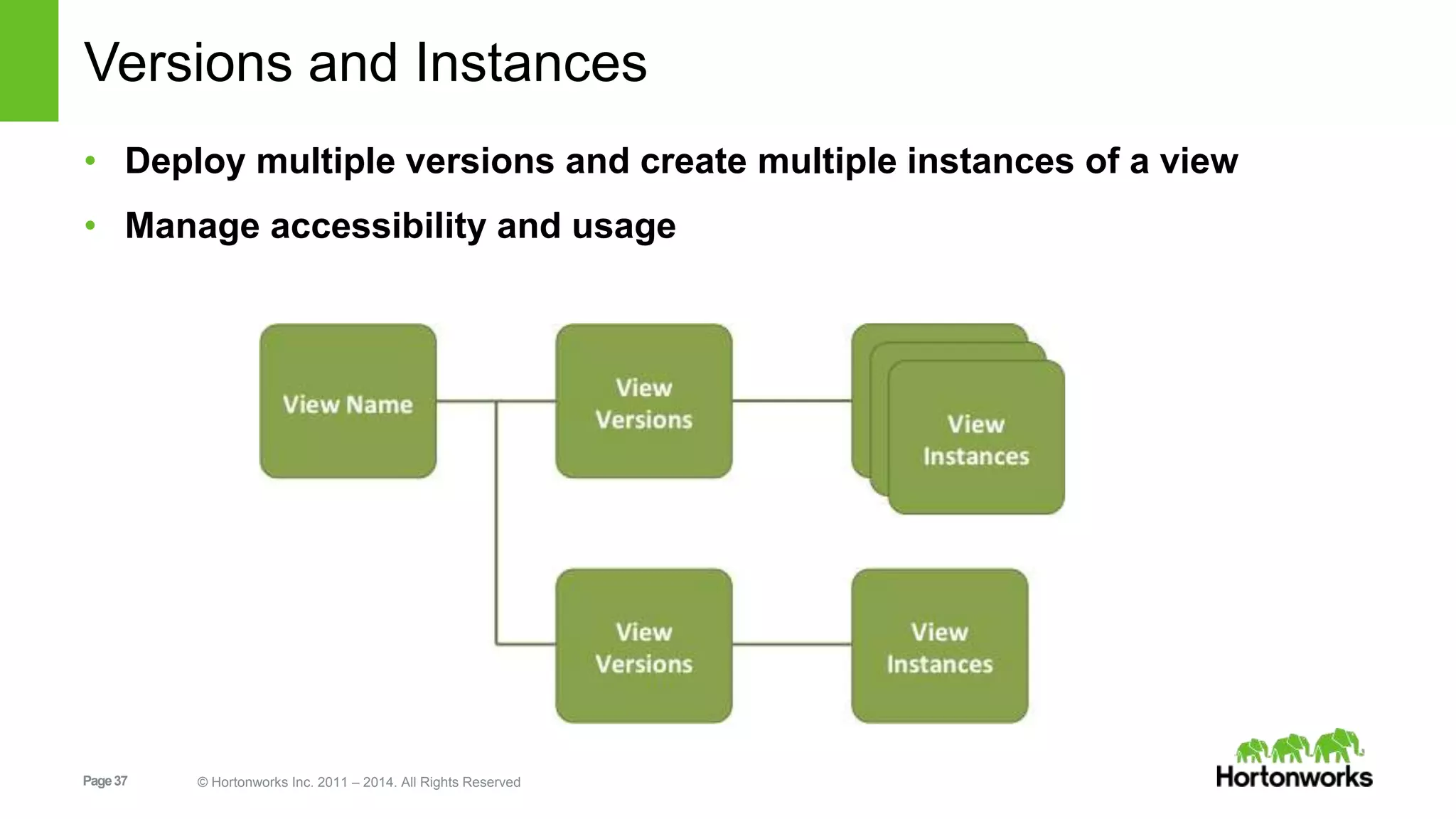
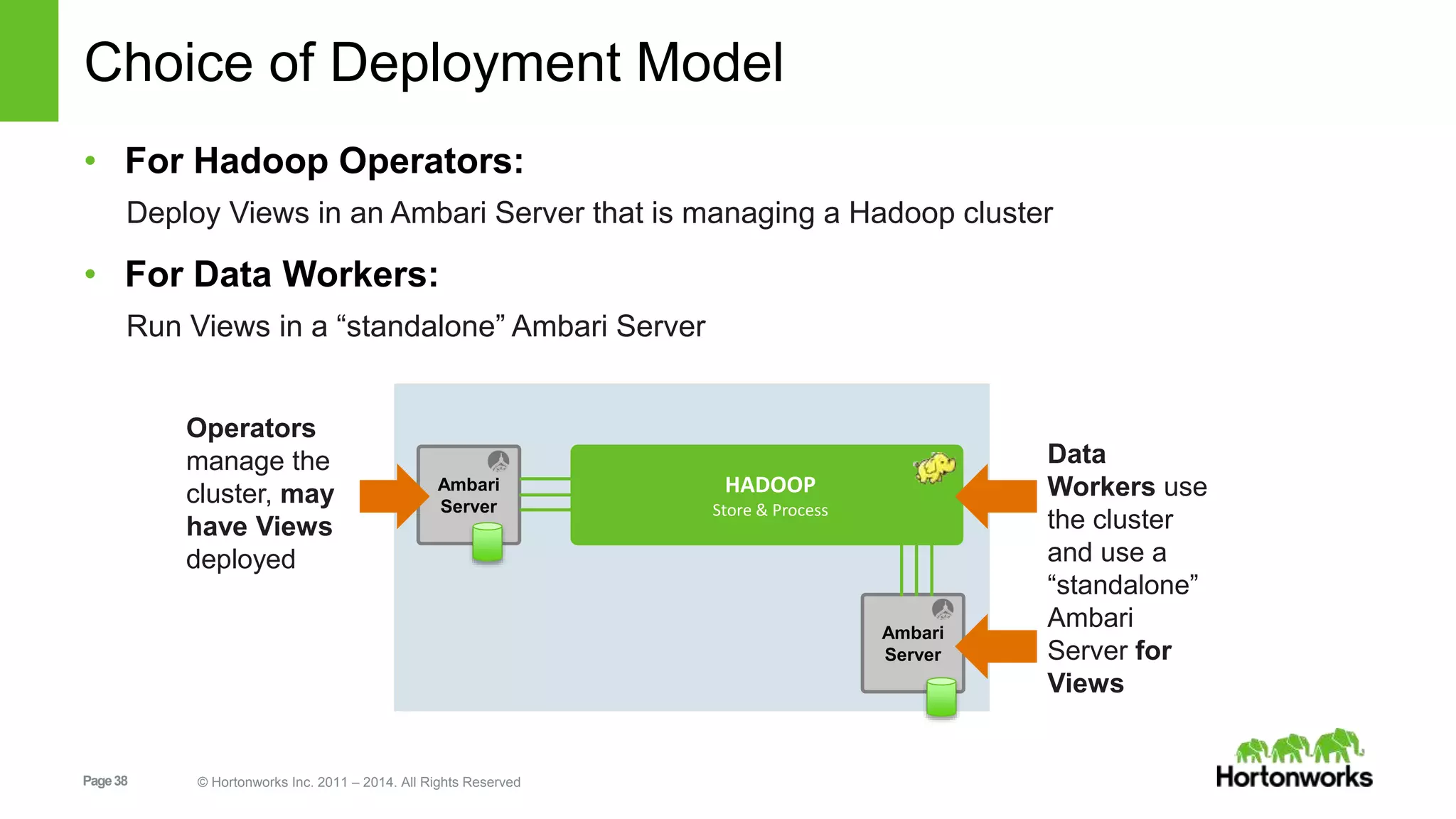
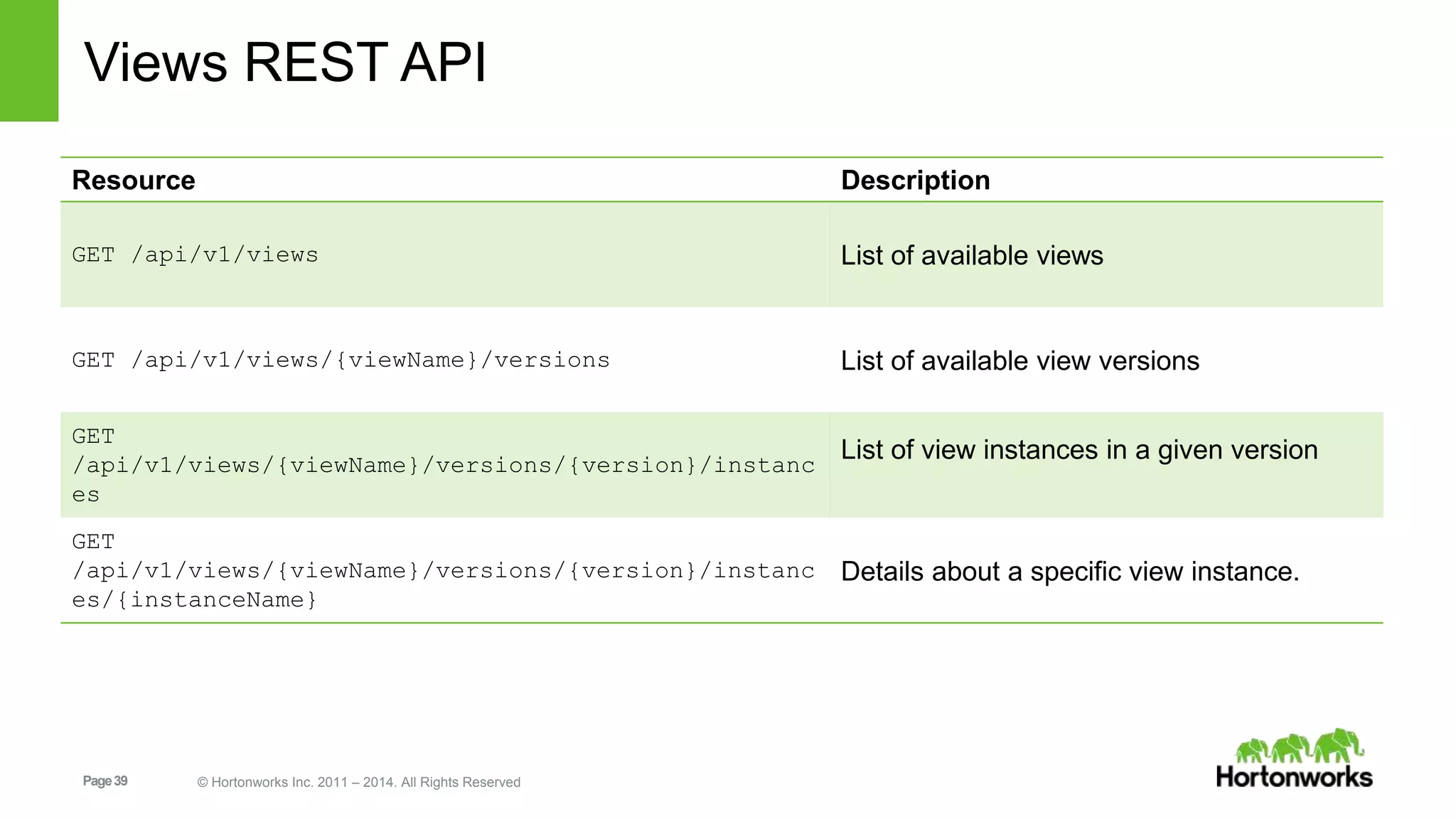
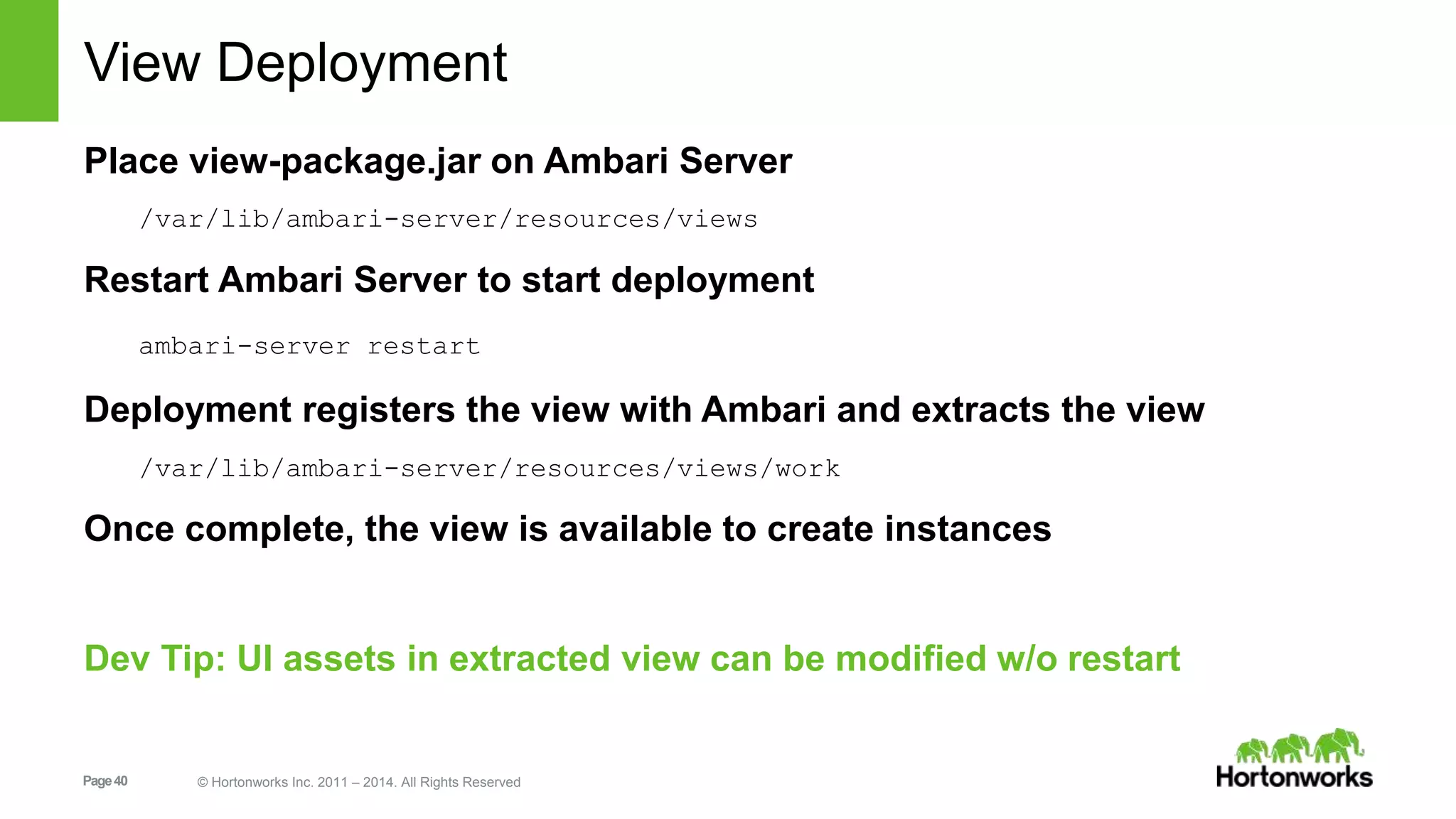
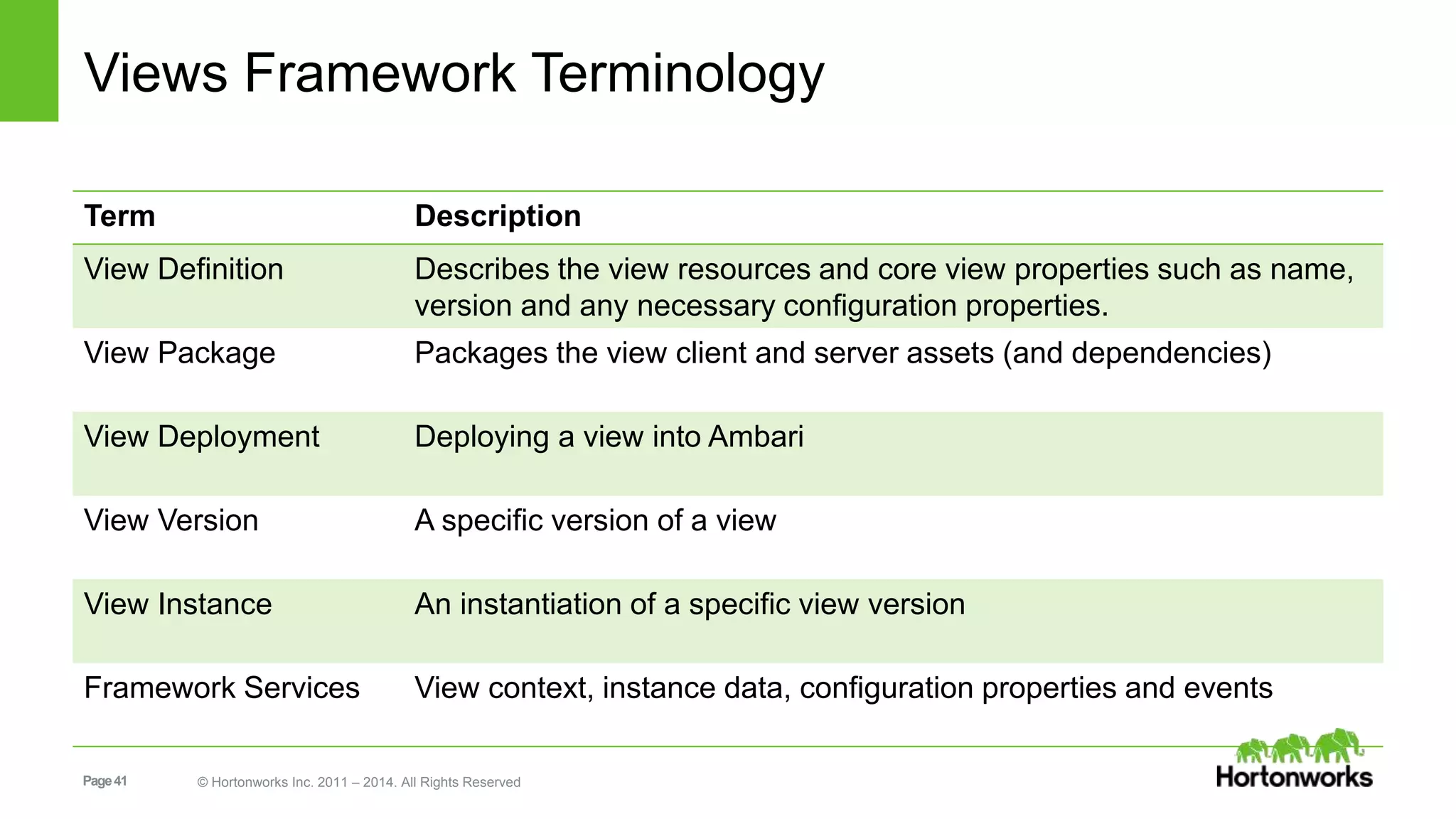
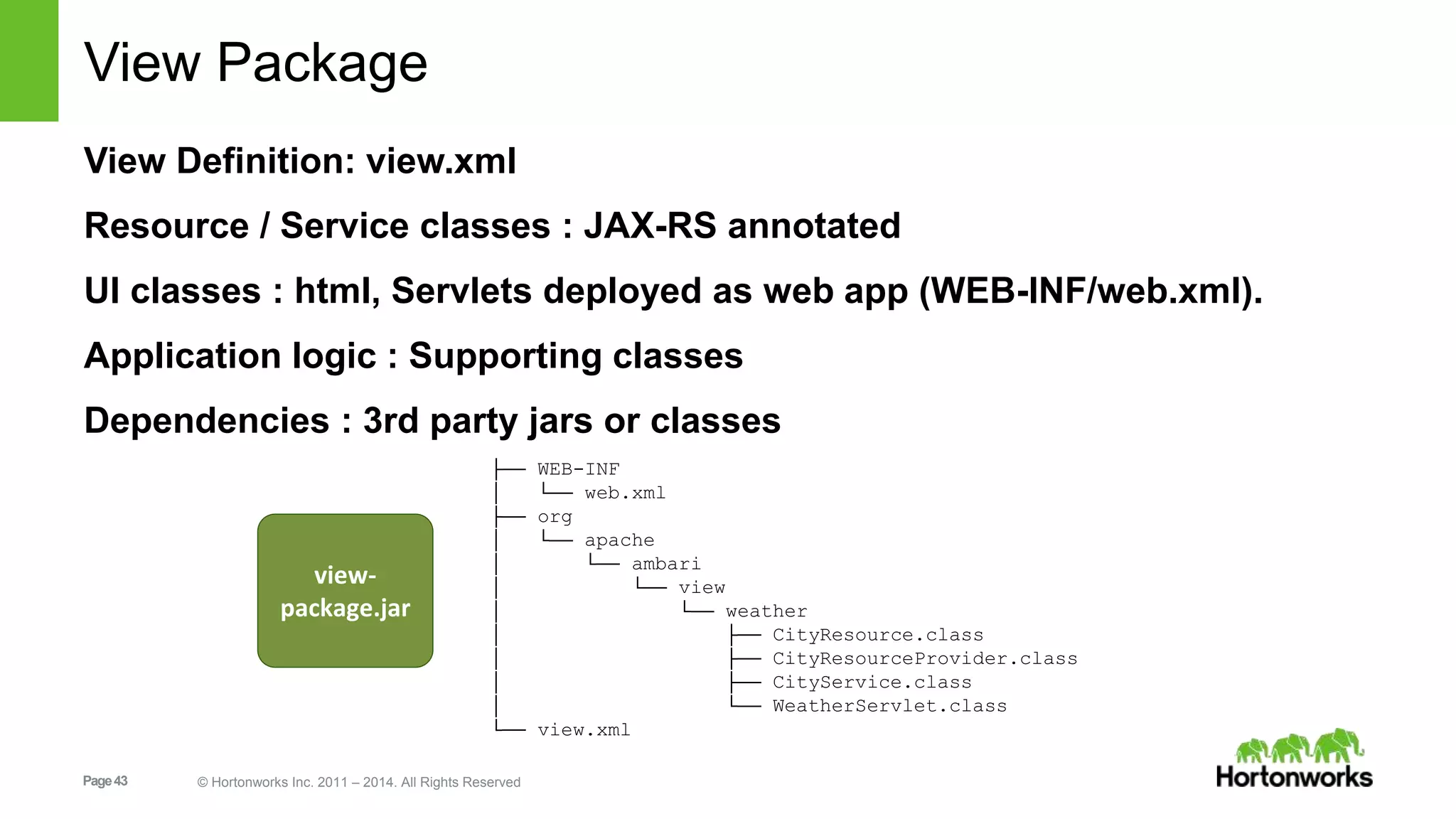
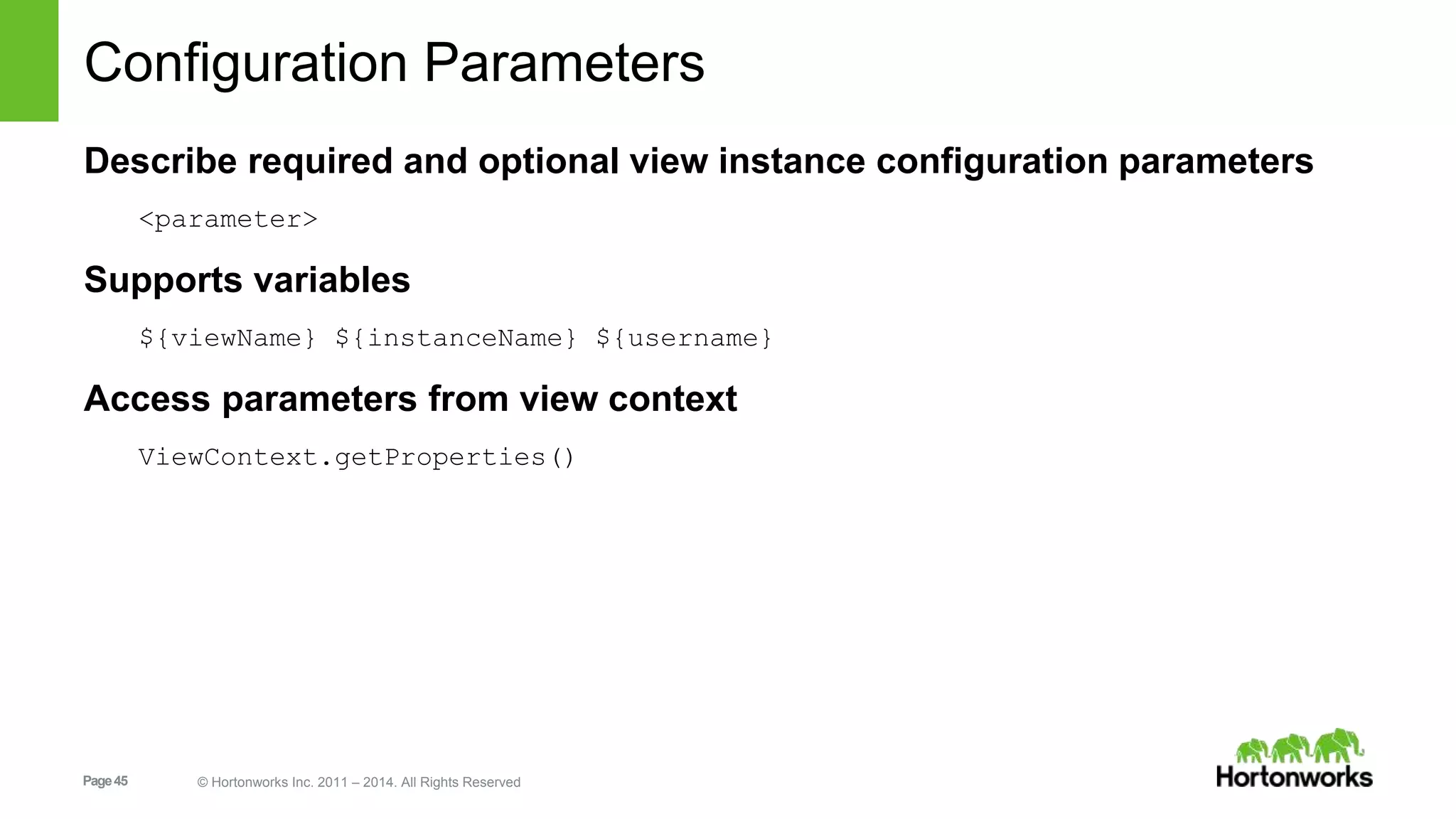
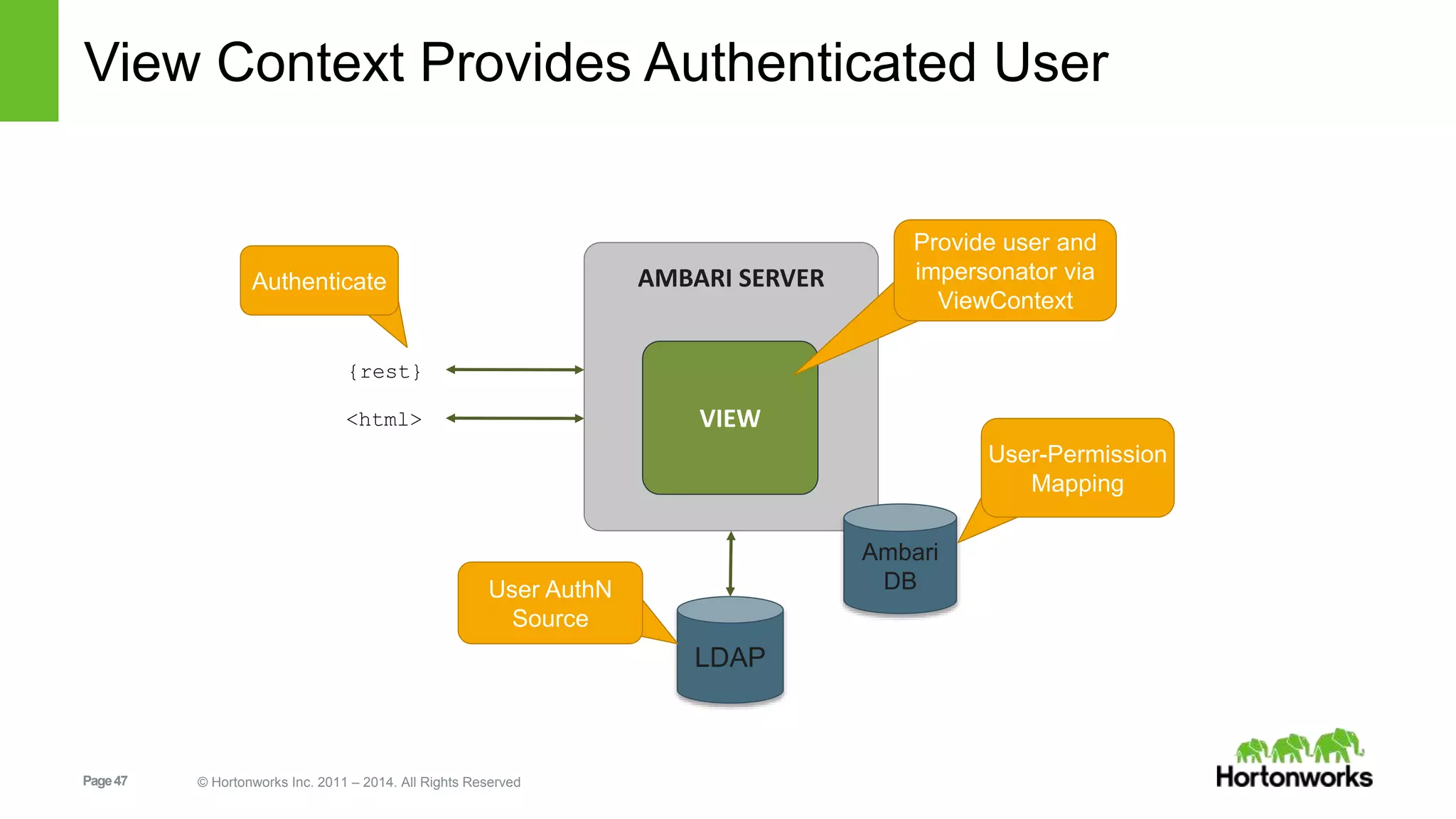
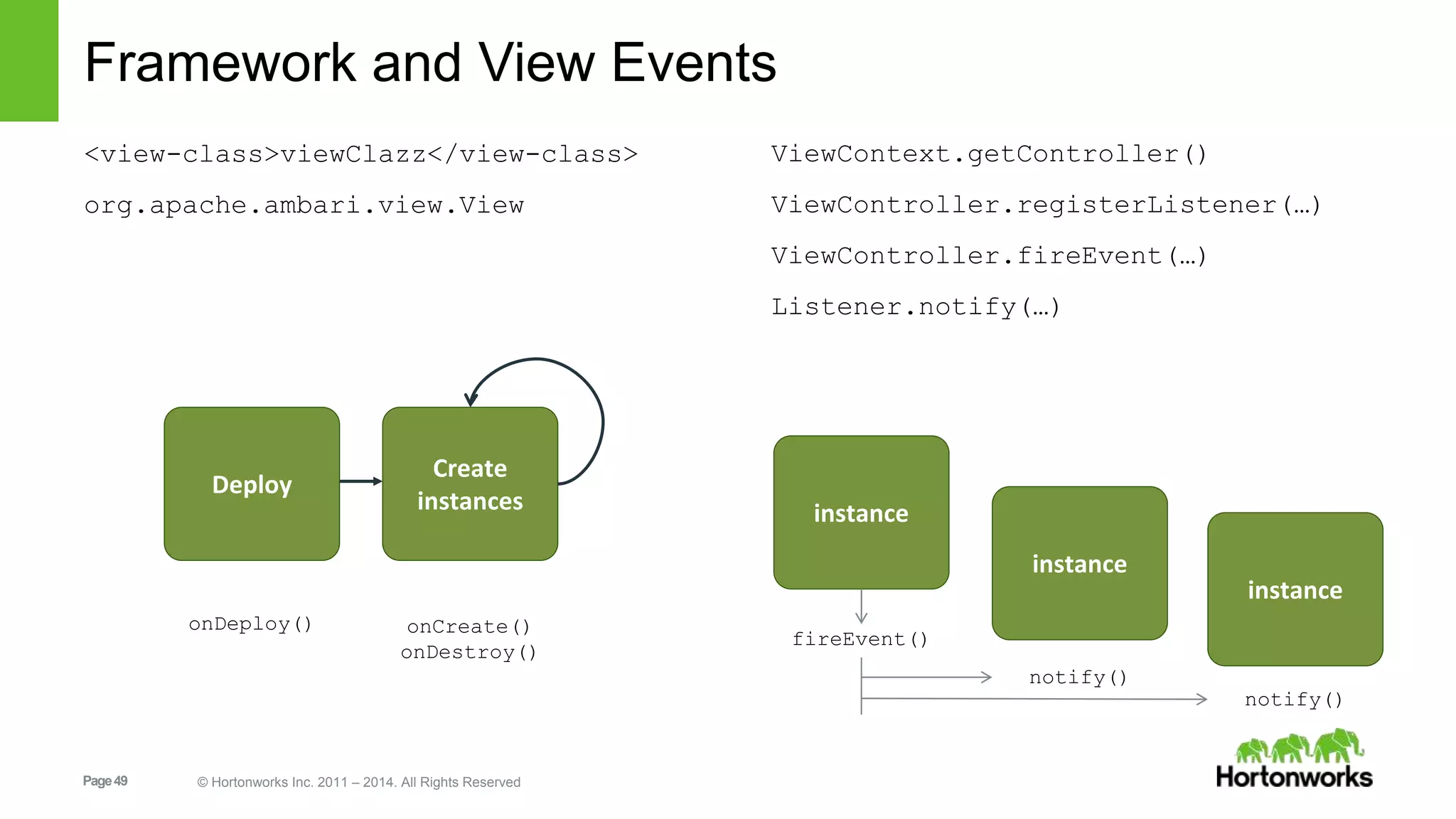
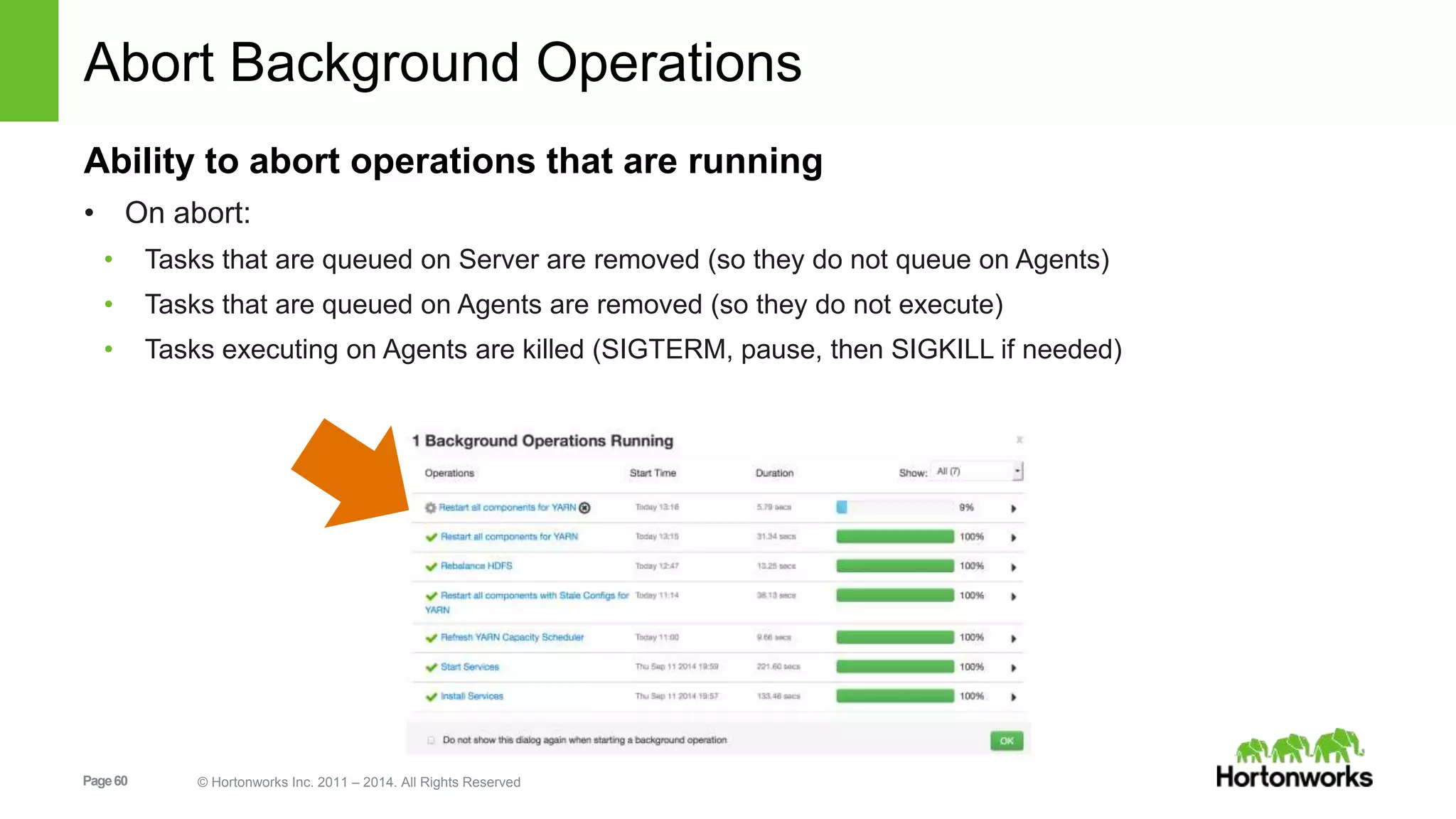
This document provides release notes for Apache Ambari 1.7.0, including new features and enhancements in several areas. Key additions include: ResourceManager HA for YARN; refreshing Capacity Scheduler queues without restarting; HDFS rebalancing; improved configuration management such as downloading client configs and setting final properties; Ambari administration capabilities like user/group management and permissions; a views framework for custom UI extensions; and Ubuntu 12 platform support.